Robotic Process Automation - a new look at old technology

If today you come to the MFC on any issue, a lot of time is spent waiting: while the employee enters information from various documents in the required forms, puts some check marks, sends some requests ... And imagine a wonderful future: just come to the MFC, you give a passport, it is scanned, and then the magic happens - the software robot is all parsing, instantly sending requests to different databases, aggregating the answers and after a few minutes gives the result / answer / help / new document, registering it in the annals along the way.
Say unrealistic fantasies? Yes, why unrealizable - suitable technologies are already ready and practically run in. This is RPA (Robotic Process Automation). The term appeared in 2012 thanks to Blue Prism. She became a pioneer in the field of office services management services 17 years ago. True, at that time they did not take this idea seriously and big business considered it rather utopian than real.
')
But everything changed with the advent of artificial intelligence systems. It was they who radically changed the attitude towards RPA.
RPA today
Modern RPA-systems can fully or partially automate the work that previously had to be done manually. Take, for example, the operating office of a large bank: 200 people, more than half of their working time, simply insert customer details into the program and transfer data from one system to another, print all sorts of receipts, invoices, certificates. And all this primitive routine can be automated.
According to GVR (Grand View Research, Inc.), by 2025, companies are expected to spend $ 3.11 billion in RPA technology.
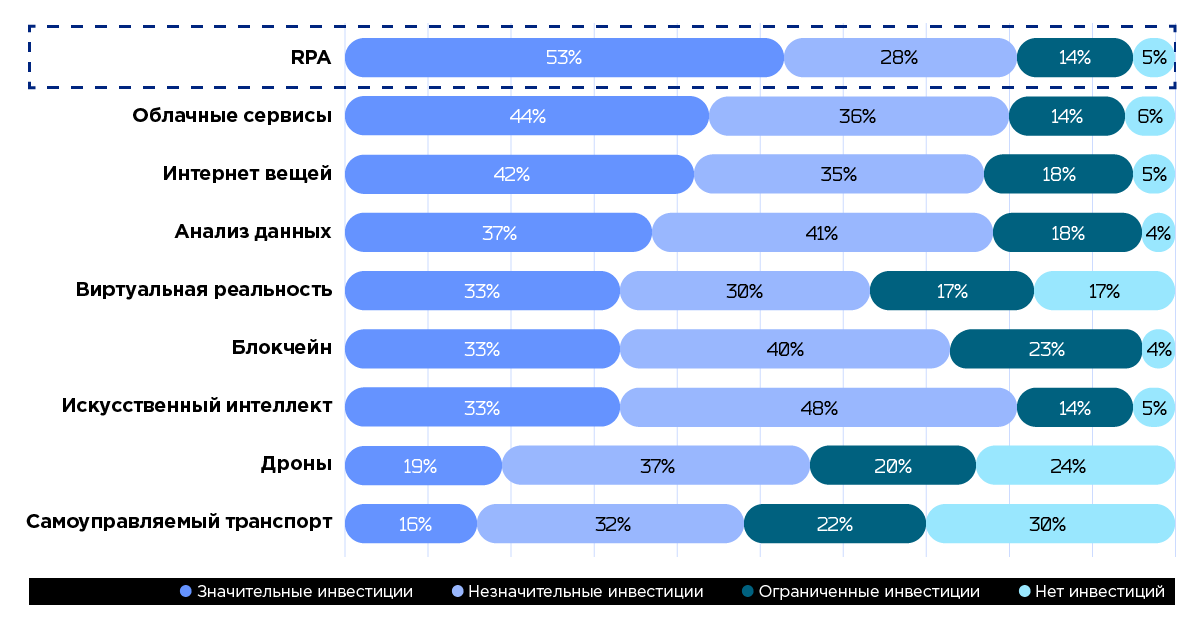
Investment in various industries, Grand View Research
What can a robot do, for example, in retail, financial and insurance services?
- Open and close web-client and email applications and systems (including attachments)
- Move inside applications (ERP, CRM, etc.)
- Create and move files and folders
- Follow links and emulate button presses
- Make automatic transition between applications.
- Fill and copy forms
- Download data from external sources to the program interface and directly to the database
- Compare and verify data, perform math calculations
- Work on complex logic with conditions and cycles
- Recognize Text (PDF / DOC / XLS)
- Perform a multi-level revalidation of data entered by people.
- Chat with instant messengers with chatbots
- Use predictive analytics to manage decisions based on statistics and data mining.
It sounds beautiful, but what about life examples?
Automating the process of filling out applications for granting loans to legal entities
Prior to the implementation of the RPA system, in the process of applying for a loan for legal entities in one of the large Russian banks, it was necessary to collect and structure data from as many as 9 different systems. Employees simply manually copied and pasted information into Excel-files. And 53 people were engaged in this highly intellectual work. And then another 6 people manually checked the entered information for errors. According to bank statistics, 20% of the employees from the first group made 1-2 mistakes per day. At the same time, at least one of the inspectors also missed one or two errors every day, undetected.
When the RPA was implemented in this department, out of 53 people 30 were transferred to other tasks, and the number of errors in filling out applications decreased by 10–15 times.
Automation of entering information into the help system
For one of our clients, we calculated a pilot project for automating the introduction of data from document scans into the reference system.
The company was engaged in this 5 employees. It took about 5M rubles per year to pay for their labor, equipping workplaces and depreciation of equipment. During the year, taking into account holidays, vacations and sick leave, about 4,000 man-hours were spent on entering information into the system.
The main cost of a robot is the purchase of a license (usually purchased for a year) and services for the development and technical support of the system. We estimated the implementation of the robot at 600,000 rubles and asked the customer for 3 months for everything. Under this task, the UiPath license package, worth approximately 300,000 rubles per year, was perfect. And for further support of the robot, the customer only needs to spend about 30,000 rubles per month. And even at the time of development and implementation of RPA, it was necessary to manually carry out the process to be robotic.
As a result, the total cost of automation was as follows: 600,000 + 300,000 + 270,000 = 1,170,000 rubles. Even if we add to this the mentioned expenses for manual execution of the process, the robot will pay off in just six months. In the first year, the client will save 46.5% (2,070,000 rubles), and in the second year, when you only need to spend money on a license and regular support, the savings will be 85.2% (3,795,000 rubles).
What is behind the abbreviation RPA
Let's talk now what is hidden under the “hood” of popular robotization solutions. As a rule, they are based on software that is easily adapted to your needs, which is connected via API and simulates all the necessary actions of a person. Here you can add chat bots, text recognition system and human voice and other elements.
Each of the modules is an independent product, and all of them are managed by a single platform coordinating the work of the RPA (this is a kind of conductor responsible for the harmonious and precise performance of the work by the orchestra). The platform can launch robots on request or on a schedule, issue visual graphs to the operator for successfully completed or failed operations, as well as generate detailed reports on the operation of the RPA system.
RPA-solution can be built on the basis of Open Source products, as well as using proprietary software for robotization. And you don’t have to rush to conclude that it’s impossible to create anything good based on free software. Here everything is decided by the qualifications and professionalism of the developers.
And for illustration, here's another example.
Free cheese only in a mousetrap?
A large bank asked us to automate the application process in the internal workflow system with a large number of parameters.
The data came from an external Excel file, and after preliminary validation, it was necessary to enter it into the system, fill in all the required fields and track the fact of successful bid generation. All incorrect entries in the file should have been recorded in the electronic journal.
We offered a software package written in Java that contained all the necessary libraries for working with the browser. The package was unpacked on the operator’s working machine, and the whole system was controlled via a web interface.
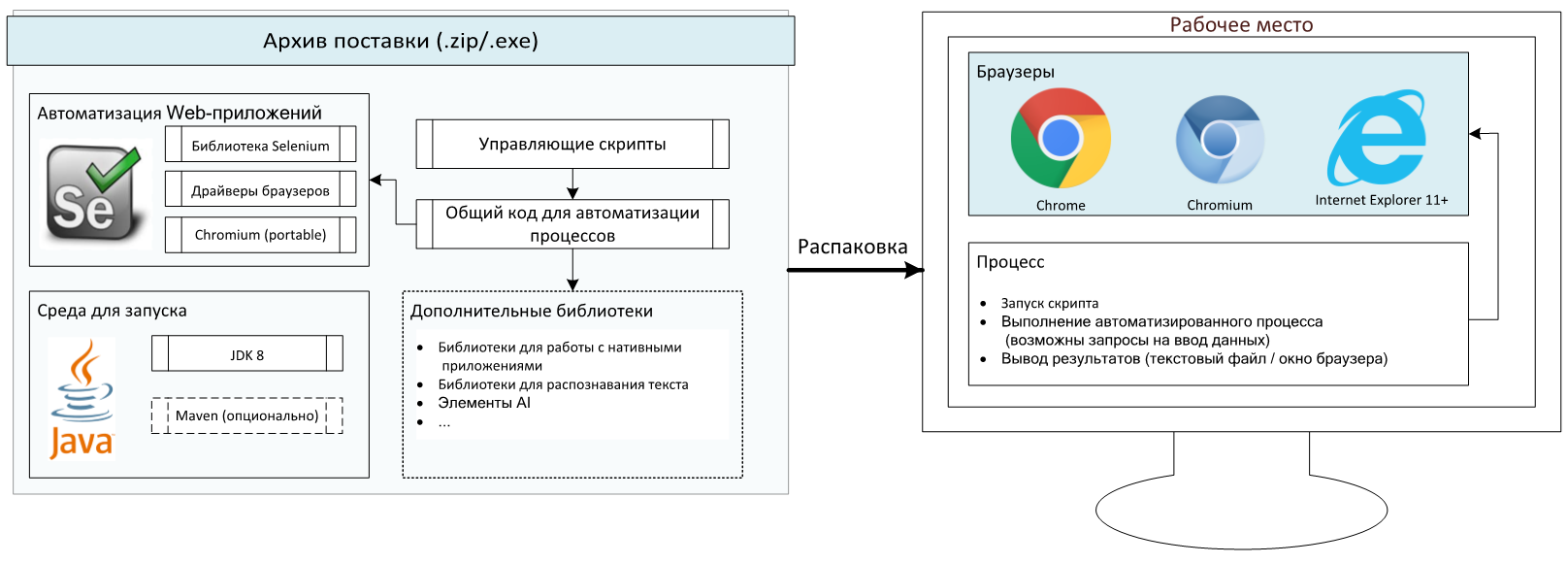
With this simple solution, we were able to speed up the execution of routine operations approximately 8 times. And, most importantly, the influence of the human factor was completely excluded.
The cost of supporting such a solution is approaching zero, since it is an internal workflow system and no changes in it are foreseen in the near future. It would seem that we have automated only one small cog in the huge mechanism of monotonous manual operations, and the benefit turned out to be very tangible.
The shoemaker must not be without shoes
Another example of automation is using an open source solution. And the example is not someone's, but our own.
We needed to free people from the need to fill in cards of new counterparties in the ERP system, so as not to drive in 50–70 fields each time. Each card took about 10 minutes, and it was no wonder somewhere to make a mistake.
We decided to do this: let the employee scan the papers, then the robot will launch the tesseract-ocr utility for data recognition, and then fill in the fields in the web form. By the way, you can improve the recognition quality of this utility with the help of a neural network. The robot will log in to the system itself, open the desired page in the browser and fill in all the fields. This will take him half a minute. And if we receive the initial data not on paper, but in electronic form, then it is possible not to waste time on scanning and checking, the robot will execute it and correct errors.
As a result, our employees were extremely happy: they could only check the correctness of filling out the form and make sure that the robot did not disappoint.
The effect of the introduction of RPA
How to estimate the effectiveness of RPA? This will help statistics. According to the HFS Research survey, many companies that have implemented RPA technologies have gained tangible benefits and competitive advantages.

Source: HFS Research, “INSIGHTS FROM EARLY BPO ADOPTERS OF ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION“ and KPMG.
And according to information from ABBYY, the introduction of their products into RPA has allowed many organizations to significantly reduce overhead costs.

Source - ABBYY official data
What are the advantages of robotization routine processes?
- Increase the speed of work: you can do more without attracting additional staff.
- Fast return on investment: the result is noticeable after the first pilot projects (usually from 4 weeks).
- Easy scaling after the first implementations.
- High accuracy of work: the probability of the manifestation of the human factor is much lower, since a person only checks the operation of the machine.
- Security: managed data access privacy.
- Improving the quality of service.
- Multitasking and configuration flexibility for any IT infrastructure.
- Strategic positioning of the company: a good way to transition to AI-technology.
- Personnel development and staff turnover reduction: training and transfer to more complex tasks (for example, to the newly created RPA Competence Center, which will be engaged in supporting and developing the system).
Someone will say, "it was smooth on paper, but they forgot about the ravines." Fair remark. Like any technology, RPA is not omnipotent and carries with it certain risks.
Risks and limitations of RPA solutions
The robots need technical support to reconfigure the work of the RPA in case of changes in the system interface or business processes. And this is an additional cost.
RPA requires well-documented algorithms for the operation of the system and business processes. Robot chaos is impossible, so you have to start with the initial audit of business processes and their formalization.
Fortunately (or unfortunately), robots cannot yet replace humans completely. In any case, the responsibility for the work of automation are people. Therefore, when introducing RPA, always have “Plan B” ready : how to manually support the work of a business in case of a refusal or forced completion of a robotic process.
Trusting the robots completely and completely is not worth it - constantly monitor the entire process of robotization. And it is best to appoint a specially trained person who will be the first to respond to possible problems in the work of the RPA. So that he immediately analyzed the reasons and made decisions to minimize financial and reputational losses.
Information security is our everything. Robots must operate in a closed software loop to avoid the influence of malware. For example, a fraudster can change the code of a robot so that it starts transferring money using other requisites. Or so that the robot deliberately made mistakes in credit applications - sales will stand up, and the company's reputation will turn into scraps. So, trust the robots only to proven experts and organizations who can ensure the security of your business processes after the implementation of the RPA.
Any technology that replaces a person becomes an object of Luddism. Therefore, be prepared for the fact that at first many of your employees and colleagues will oppose the ideas of automation, and even sabotage them. On the one hand, for them, automation is an opportunity to find a new position for themselves, to climb the career ladder. However, progress does not stand still, and some professions really die with time. It can be assumed that in the foreseeable future there will be no database operators, financial operators, operators on the phone, wage specialists, financial controllers-operators, secretaries for registering visitors, first-line technical support specialists, etc.
Finally, if (or when) you begin to robotize processes in an organization, you will need to create your own RPA competency center.
How to approach the implementation of RPA?
Finally, we want to give some tips that we haven’t, have not suffered, but nevertheless brought out, in our own experience and the experience of our clients, who implemented the RPA on their own.
Stages of implementation
First of all, even before the initial audit, count the money - how much will you save on robotization? Choose the right technical solution, calculate ROI, draw beautiful graphics. And only after that come to the business with specific numbers. And do not forget to paint all the buns that RPA will bring to the company. Usually such a plan works smoothly and the business agrees.
Then you need to understand which processes will most effectively be automated. Do not hesitate to involve other companies for analysis and consultation: an outside view will be broader and more objective. Such companies have extensive experience in the implementation of such systems, and most have a set of ready-made solutions - perhaps something will do with minimal modifications. For example, from ready-made solutions it will be possible to “assemble” the system you need. And it will be much cheaper than designing from scratch.
Having decided on the tools, do not immediately rush to automate everything. Start with one or two pilot projects, then draw conclusions on the results and adjust future plans. Try to automate not the entire process, but each of its operations. This will make it easier to support the solution and implement it in other company processes.
IB and Ubiquitous Testing
Do not neglect information security! Any robotic process should be isolated from external influence as much as possible and taxed on controls and controls. Appoint a person responsible for the work of the RPA and start to pick up like-minded people in his team.
Test any solution for robotization very meticulously. You can even arrange acceptance testing by teams of other vendors, not those who developed your RPA solution.
How to live with RPA?
Again, do not forget about people who can - and most likely will - perceive robots as competitors in the food chain. Tell the employees of the departments in which you are implementing RPA about the features of the system, discuss the further professional development of the staff whose work the robot will now do. Deliver a thought: the main goal of the robot is to perform work faster and more accurately, and not to fire people. If a person from 9 to 18 was engaged in a boring routine, then now he has a chance to do more interesting and intellectual tasks, to become an expert in the new field.
If you think that robotization will take root in the company, then invest in training your own specialists in support and development of the system. Perhaps, at first glance, this is not obvious, but in the future it will be cheaper and much more efficient than hiring outside professionals.
And the last piece of advice is to take up the robotization, keep your nose in the wind of global trends. And then you can solve all the more complex tasks.
Alexander Sadykov, Deputy Head of the Jet Infosystem Testing Department
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/447398/
All Articles