Creating a farm of Android devices using Open STF
The share of mobile traffic is increasing every year. A modern person is mobile and it is easier for him to get information from the screen of his own smartphone. Therefore, in the development of mobile applications. When developing and testing, it is important to have access to a variety of devices so that the application works correctly on all kinds of smartphones. Consider the various options for accessing devices.
One way is mobile cloud farms :
SAMSUNG Developres: Remote Test Lab
Firebase test lab
BrowserStack
AWS Device Farm
App Center
Sauce Labs
Some of them are free - with a limited number of devices, others - paid, with a large fleet of devices. Through them, you can get remote access to real devices and track the bugs that occur on devices, but not reproduced on emulators.
')
Another way is to create your own Android smartphone farm, thanks to which employees from different cities and countries can connect to office devices. Consider how you can make your own farm of Android devices through the project Open STF
Update apt-get:
Install dependencies for OpenSTF (Node.js, NPM, GraphicsMagick, ZeroMQ, Protocol Buffers, yasm, pkg-config, adb).
Download the deb package RethinkDB (the package is not available for Ubuntu 18.04 via apt):
Install OpenSTF:
If errors occur during installation, that npm cannot access / usr / local / lib or / usr / local / bin, provide access to them:
And restart
Install homebrew:
Download and install all dependencies:
If you get the following error when installing protobuf:
Then you need to create the / usr / local / Frameworks folder and give permission to write to it:
Install OpenSTF:
Possible through Cygwin, but not officially supported by developers.
For OpenSTF to work, you must first run RethinkDB.
Next run openstf itself
By default, OpenSTF independently detects and connects the device without rebooting when connecting mobile devices to the machine.
But in Ubuntu problems are possible:
If a mobile device is not visible in openstf and the following openstf message is displayed:
and the adb devices command produces the following output:
You will have to add the device manually:
To do this, run
and find a device that could not decide.
For example,
The USB device ID consists of two parts — the manufacturer ID (the first part is ID to ':', 2e04, as in the example above) and the device model ID (c026).
Next, run the commands where the ATTR {idVendor} and ATTR {idProduct} parameters are filled in with the ID of the incorrectly found device:
It is worth considering that the device is recommended to connect via a separate USB hub with separate power supply (for example, like this ).
One of the features of the farm is that due to constant charging, the battery life of mobile devices will be limited to 2-3 years, so if the device has a removable battery, it makes sense to purchase it in advance. On devices, you can turn off the mode in which the device screen is always on when charging (just leave the setting, which turns off the screen automatically after 30 seconds of inactivity), because OpenSTF is able to turn on the screen when it is needed - this will increase the use of the device. It is important to say that OpenSTF should not be accessible from outside the corporate network, except through a VPN, since there is no normal authorization for it.
OpenSTF launch:
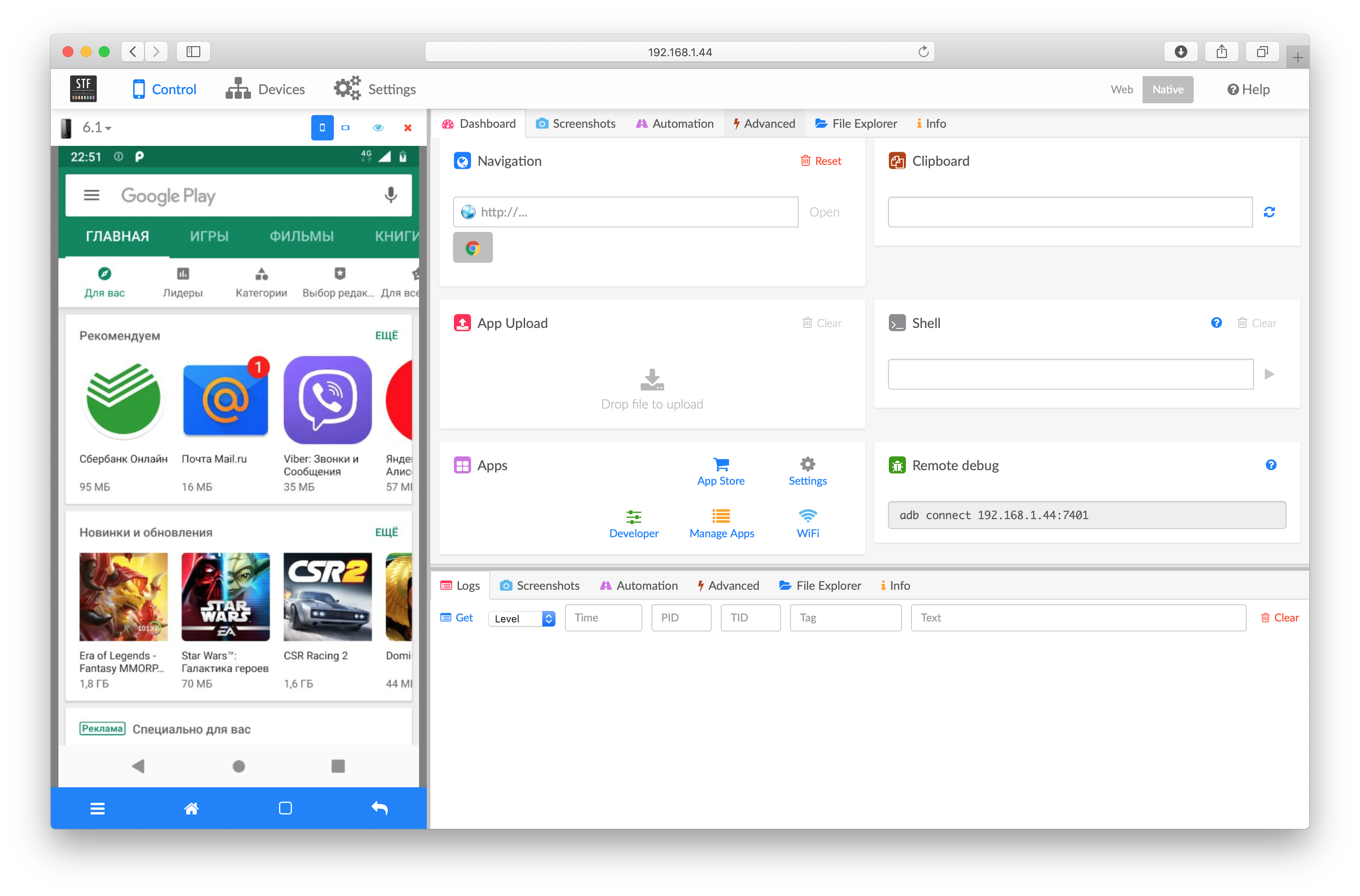
Running the Google Play application in OpenSTF
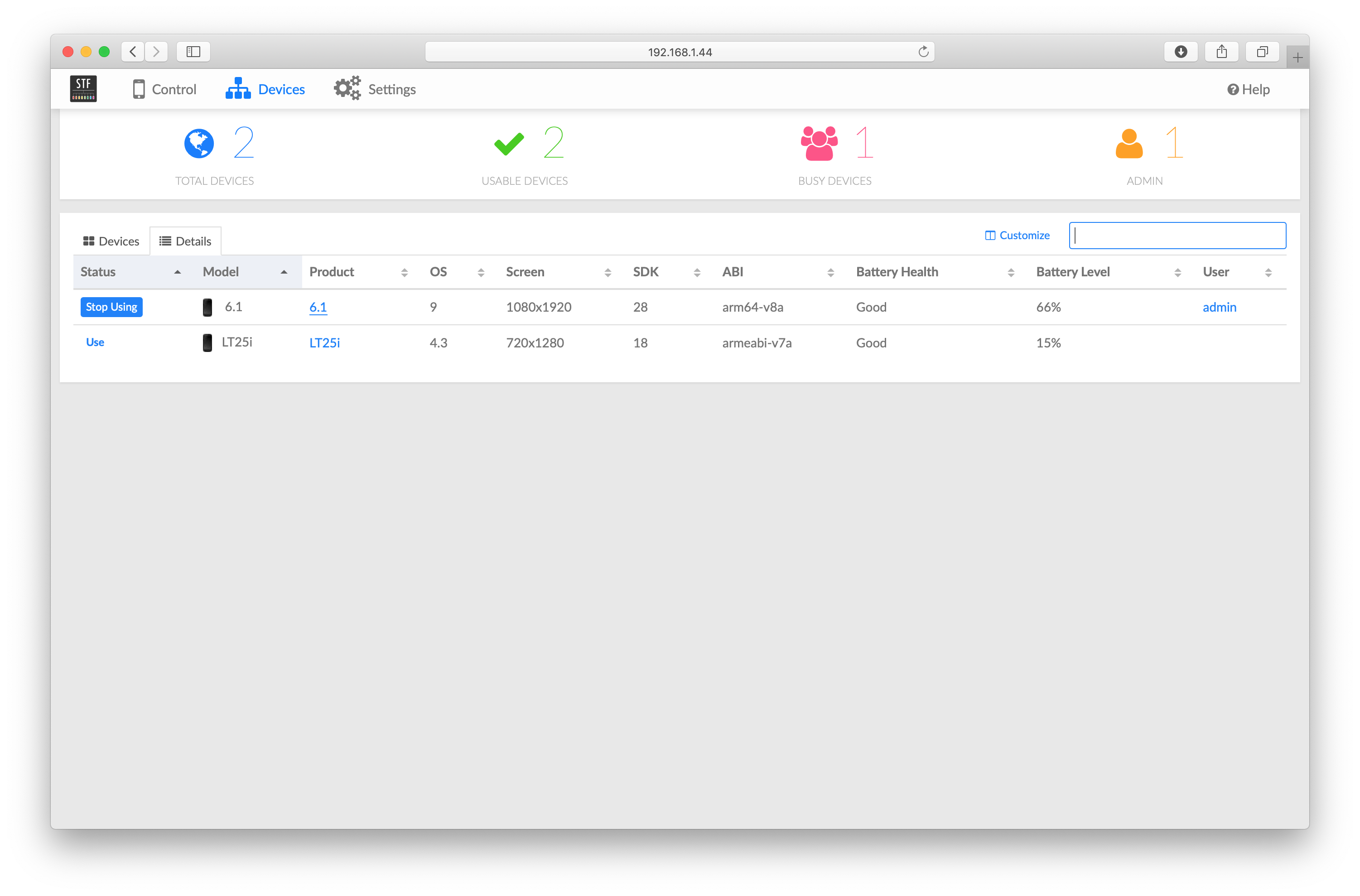
List of connected devices in OpenSTF
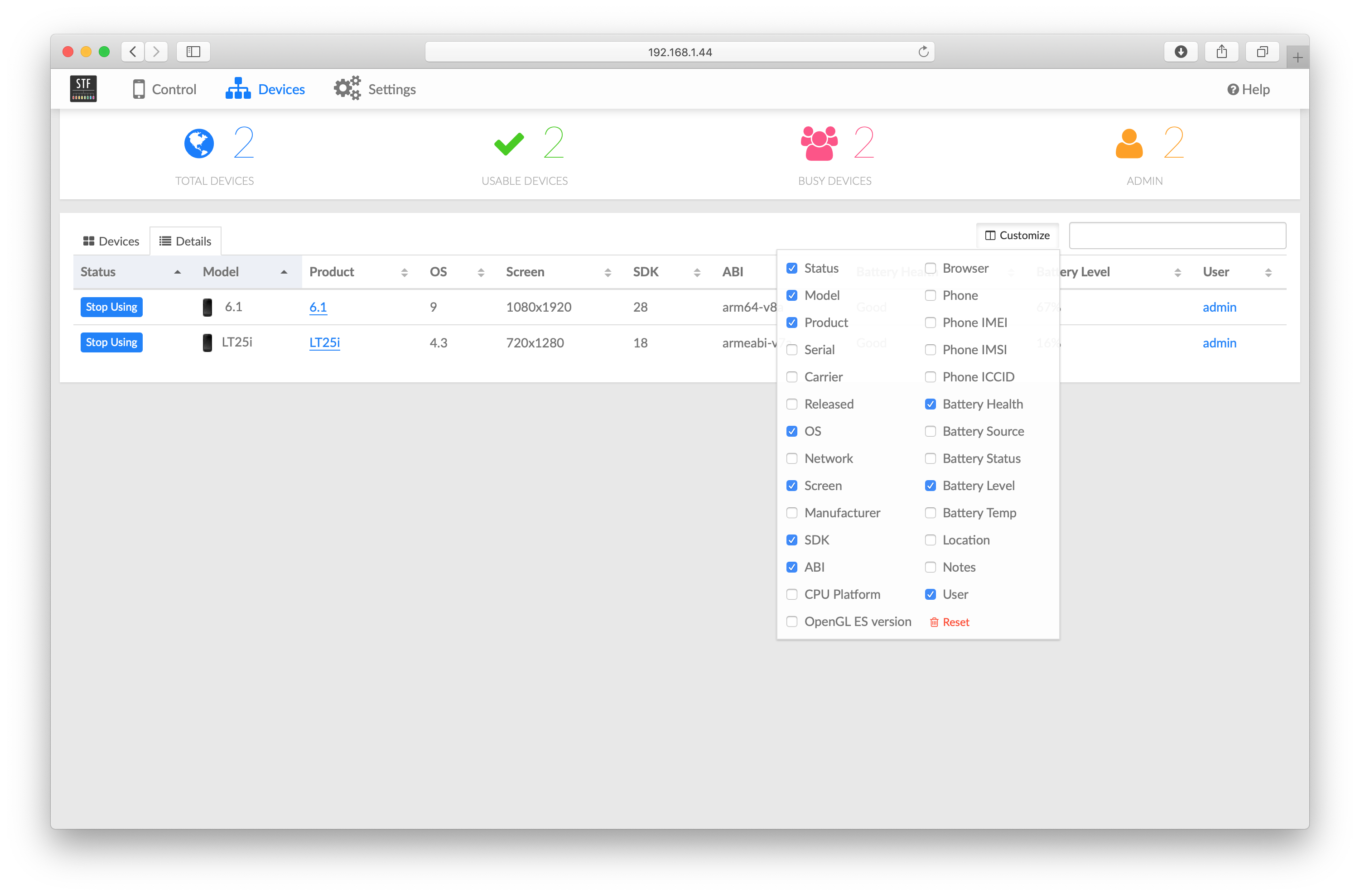
Configuring device information in OpenSTF
Thus, its own farm of Android devices helps to configure access to office devices for remote employees, thereby improving the quality of developed applications. It has its pros and cons, which is worth considering.
One way is mobile cloud farms :
SAMSUNG Developres: Remote Test Lab
Firebase test lab
BrowserStack
AWS Device Farm
App Center
Sauce Labs
Some of them are free - with a limited number of devices, others - paid, with a large fleet of devices. Through them, you can get remote access to real devices and track the bugs that occur on devices, but not reproduced on emulators.
')
Another way is to create your own Android smartphone farm, thanks to which employees from different cities and countries can connect to office devices. Consider how you can make your own farm of Android devices through the project Open STF
Installation on Ubuntu 18.04:
Update apt-get:
sudo apt-get update Install dependencies for OpenSTF (Node.js, NPM, GraphicsMagick, ZeroMQ, Protocol Buffers, yasm, pkg-config, adb).
sudo apt-get install nodejs npm graphicsmagick libzmq3-dev protobuf-compiler libprotobuf-dev yasm pkg-config android-tools-adb Download the deb package RethinkDB (the package is not available for Ubuntu 18.04 via apt):
wget https://github.com/srh/rethinkdb/releases/download/v2.3.6.srh.1/rethinkdb_2.3.6.srh.1.0bionic_amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i rethinkdb_2.3.6.srh.1.0bionic_amd64.deb Install OpenSTF:
npm install -g stf If errors occur during installation, that npm cannot access / usr / local / lib or / usr / local / bin, provide access to them:
sudo chown -R $USER /usr/local/lib sudo chown -R $USER /usr/local/bin And restart
npm install -g stf Installation on MacOS X:
Install homebrew:
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)" Download and install all dependencies:
brew install node rethinkdb graphicsmagick zeromq protobuf yasm pkg-config homebrew/cask/android-platform-tools If you get the following error when installing protobuf:
Error: An unexpected error occurred during the `brew link` step The formula built, but is not symlinked into /usr/local Permission denied @ dir_s_mkdir - /usr/local/Frameworks Error: Permission denied @ dir_s_mkdir - /usr/local/Frameworks Then you need to create the / usr / local / Frameworks folder and give permission to write to it:
sudo mkdir /usr/local/Frameworks sudo chown $USER /usr/local/Frameworks Install OpenSTF:
npm install -g stf Installing on Windows:
Possible through Cygwin, but not officially supported by developers.
Launch
For OpenSTF to work, you must first run RethinkDB.
rethinkdb Next run openstf itself
stf local --public-ip <ip- > Connecting devices:
By default, OpenSTF independently detects and connects the device without rebooting when connecting mobile devices to the machine.
But in Ubuntu problems are possible:
If a mobile device is not visible in openstf and the following openstf message is displayed:
Unhandled rejection Error: Illegal value for Message.Field .DeviceIntroductionMessage.status of type enum: undefined (not a valid enum value) and the adb devices command produces the following output:
List of devices attached ??????? no permissions (verify udev rules); see [http://developer.android.com/tools/device.html] You will have to add the device manually:
To do this, run
lsusb and find a device that could not decide.
For example,
Bus 001 Device 010: ID 2e04:c026 Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub The USB device ID consists of two parts — the manufacturer ID (the first part is ID to ':', 2e04, as in the example above) and the device model ID (c026).
Next, run the commands where the ATTR {idVendor} and ATTR {idProduct} parameters are filled in with the ID of the incorrectly found device:
echo 'ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ENV{DEVTYPE}=="usb_device", ATTR{idVendor}=="2e04", ATTR{idProduct}=="c026", MODE="0666"' | sudo tee /etc/udev/rules.d/99-android.rules sudo udevadm control --reload-rules sudo udevadm trigger --verbose --action=add --subsystem-match=usb It is worth considering that the device is recommended to connect via a separate USB hub with separate power supply (for example, like this ).
One of the features of the farm is that due to constant charging, the battery life of mobile devices will be limited to 2-3 years, so if the device has a removable battery, it makes sense to purchase it in advance. On devices, you can turn off the mode in which the device screen is always on when charging (just leave the setting, which turns off the screen automatically after 30 seconds of inactivity), because OpenSTF is able to turn on the screen when it is needed - this will increase the use of the device. It is important to say that OpenSTF should not be accessible from outside the corporate network, except through a VPN, since there is no normal authorization for it.
Screenshots of the running program
OpenSTF launch:

Running the Google Play application in OpenSTF

List of connected devices in OpenSTF

Configuring device information in OpenSTF

Thus, its own farm of Android devices helps to configure access to office devices for remote employees, thereby improving the quality of developed applications. It has its pros and cons, which is worth considering.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/447236/
All Articles