25 years of Runet
Whatever Russian Internet users do, they entered search queries, listened to music, checked email, corresponded on social networks, they do it mostly on Russian sites. Western technology giants like Google and Facebook have to crowd, contrary to the habit that has developed during the global expansion . This makes Runet a phenomenon of the World Wide Web, for which we love him very much.
This year, Runet marks a quarter of a century. This is a good reason to indulge in nostalgia, and at the same time go through the most significant events and see how the Russian-speaking segment of the network has changed.

Dashing nineties
The countdown of the history of Runet was taken from April 7, 1994, when the national domain ru was officially registered.
The audience of the global Internet is less than 6 million users, and most of the population of Russia does not really know about its existence.
In 1995, the eponymous version of Windows was released, in which familiar elements of the interface first appeared - the desktop with icons, the taskbar, and the Start menu.
Together with the launch of the operating system in Russia, Microsoft accepts the Windows-1251 encoding as a standard - from this moment on, Russian-language pages are displayed normally, without any “I <Ø”.
Since 1996, in a package with Windows Internet Explorer starts to go. Supporting Microsoft technologies, it in fact sets the development vector for all web technologies. After all, if the site does not work under IE, the majority of users will not use it.
In Russia, the browser is called a donkey, and all because the abbreviation of the name (IE) resembles the sound “Ia” made by animals.
Watch the historic browser race here .
In 1996, the first Russian search engine was launched - Rambler , which a year later publishes the first ranking of the most visited sites.
Soon, Rambler has a serious rival - Yandex , which understands user requests, regardless of the cases and conjugations of words.
Communicating with each other users Runet chat Crib , which was divided into communities of interest.
Since 1998, you can get a free mailbox on Mail.ru. The service is rapidly becoming the leader in the number of users.
The Webmoney service is the first in RuNet to make electronic payments.
In the same year, the Ozon online store opens. - analogue of American Amazon.com.
Computers still continue to be rare - lucky people come into contact with the latest technology in the offices of their parents, where they play DOOM and Warcraft. The Internet still seems inaccessible.
What did the sites of that time look like?
Just look at the same age as the Runet, which has not changed much - the Maxim Moshkov Library . The bandwidth of the Internet at that time did not allow something cooler than a tabular html-layout with variations of one font. Users turned off in the browser settings download images to save traffic.
Not all major Russian companies had their own websites. Not everyone understood what the Internet is becoming, and did not realize the need to be online.
But those who felt the spirit of the time then, now have become giants - without Rambler, Yandex, Mail. ru, OZON. ru present modern Runet impossible.

Rebel zero
The new millennium begins with the fact that the word “Runet” becomes a full-fledged concept and falls into the spelling dictionary of the Russian Academy of Sciences. At the same time , the Internet penetration rate in the country is low - 20% of Russians do not know what the Internet is; 37.3% heard something about him; and only 3.6% of the population regularly network.
The latter have the opportunity to make their own site and place it for free on the hosting service. The leader quickly becomes Narod.ru . It is on it almost every Internet user considers it his duty to have a hamster (homepage). Usually this page contains a brief biography of the author, a list of his hobbies and some pictures. There are legends about the vigorous design of these pages. However, if you breed wavy parrots, then everything is not so scary .
Bad taste is present not only in the visual design, but also in speech - the slang of padonkaff (olbansky yezig) is gaining great popularity, the essence of which is in the deliberately wrong spelling of words. Remember "hello" and "LOL"? However, many words that we use every day have been left since those times - “kamenty”, “tin”, etc.
In 2001, the Russian “Wikipedia” appeared - just four months later than the “Wikipedia” in English. The lag of the Runet from the global web is rapidly declining.
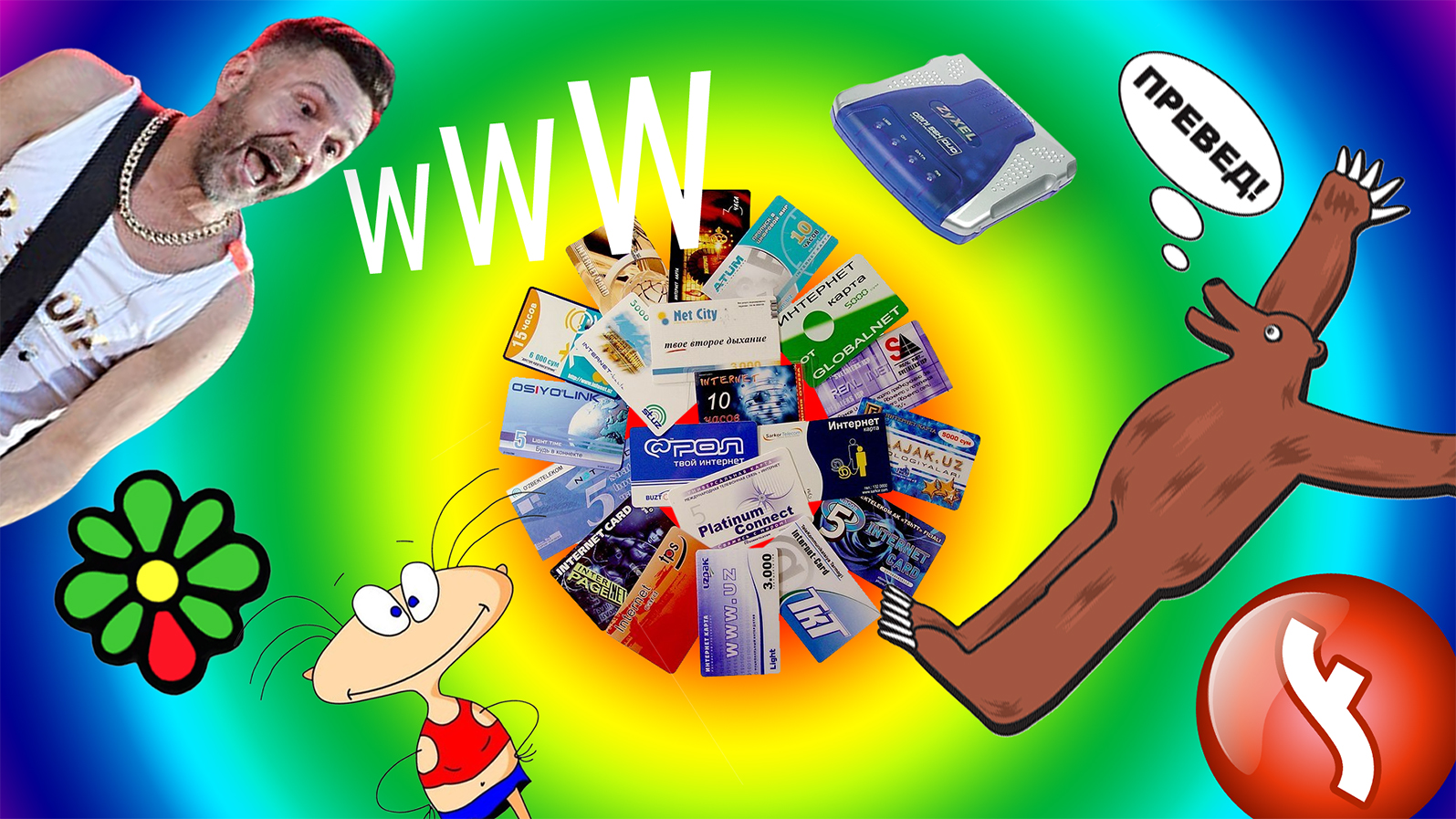
In 2002, with an easy presentation of the Leningrad group, the whole country learns that the address is not only a house and a street, but also a domain on the Internet.
Thanks to flash technology, the Internet is no longer text-only and becomes more alive.
A vivid example is the Internet cartoon “Masyanya” , which, having sharply gained popularity, goes from the Internet to television, where it advertises ZyXel modems.
A new conflict between fathers and children is brewing - households are quarreling because of the busy telephone line, which is needed to access the Internet, and does not allow to use the telephone at this time.
In Soyuzpechat you can buy an internet card and sit on ICQ (ICQ) all night long in order not to annoy the older generation.
These are the golden years of ICQ. Due to the small demands on the speed of the Internet and the power of the computer, communication in the network becomes more accessible.
Business begins to move to the Internet, which contributes to the commercial success of universal content management solutions like Bitrix, NetCat, UMI and others .
The government also looks in the direction of the Internet and in 2003 obliges all state institutions to acquire websites. Their appearance and functionality leaves much to be desired, and it still does not save from bureaucracy and long lines.
Since 2004, the mass distribution of peering services begins. The most popular is RuTracker , from where you can download for free and not quite legally a new blockbuster, which you learned about at the recent Kinopoisk .
Thanks to the development of CSS, graphic design begins to imitate material objects - bulging buttons appear with shadows and highlights, flash animations, and overloading with graphic elements. On the websites of the beginning of zero, there is often background music, a jumble of gif-animations, massive side menus, notifications with recommendations about the IE version and guest books.
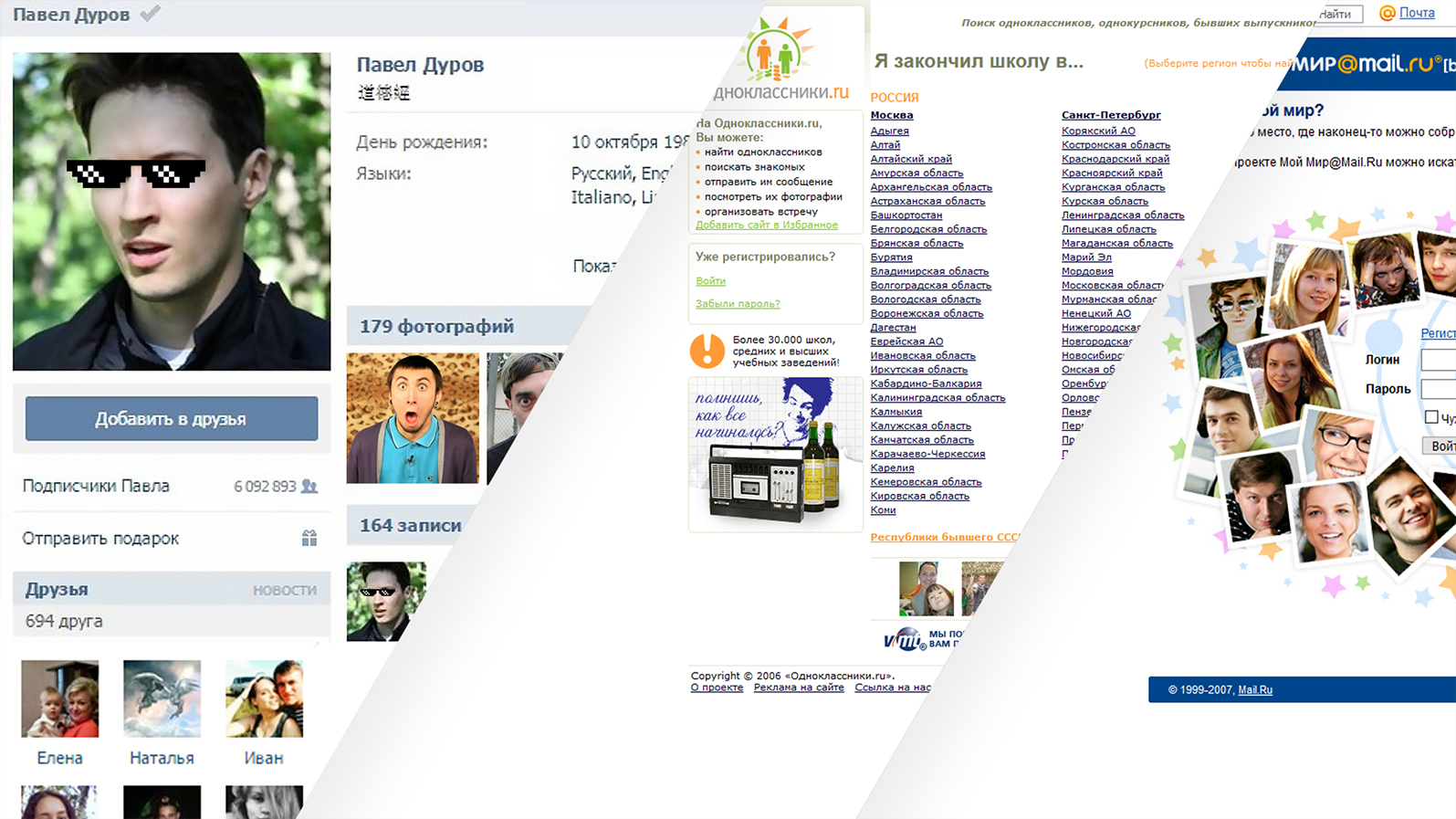
The second half of the decade passes under the banner of social networks: Odnoklassniki and Vkontakte appear with a difference of six months. The latter is quickly becoming not just the most popular social network in Russia, but also the most frequently visited site of the Runet. By the end of the decade, the audience will grow to 60 million users.
From this point on, the short-lived era of home pages goes into decline, and with it sites like Narod. Instant communication is now also conducted in social networks, which contribute to the departure of users from ICQ. A broadband connection is gradually replacing remote access, so from instant messengers they want not only instant messaging, but also video chats.
By the middle of the decade, the Internet connection bandwidth increases - you no longer need to save traffic, sites are beginning to actively use graphic elements and sliders, carousels with large photos.
With the advent of social networks, sites appear sharing buttons, links to corporate profiles and blocks with subscribers from social networks.
Convenience for users, tools for creating and publishing content is put in the foreground. The era of Web 2.0 comes when users themselves improve projects and services: blogs, wikis, social networks.
Patriarchal tenths
Only in this decade, the state seriously takes on the Internet, in which it sees both a threat and a source of profit.
Since 2010, many public services are provided in electronic form. Now you can send all documents for registration of a passport in a matter of minutes , without leaving the house.
At the same time, control by the authorities is increasing - first, Roskomnadzor creates a unified register of prohibited sites, then anti-piracy law is adopted, which makes some popular resources no longer available, such as Rutreker, who was blocked for distributing Darya Dontsova’s books.

In 2014, the government is trying to equate bloggers to media.
Against this background, there is a curious situation with “Ribbon. ru ”- the former employees of the Internet edition transfer the official page in“ Vkontakte ”not to the new edition, but to the community of subscribers. Thus, separating it from the media and turning it into an independent media project.
In 2015, the law on the transfer of personal data of Russians to the territory of the Russian Federation comes into force, which is why LinkedIn is soon blocked.
After another three years, the state will attempt to completely block Telegram because of the refusal to provide the FSB with keys for decrypting user correspondence.
However, the successes of Roskomnadzor are controversial. The law on bloggers is powerless in the new reality, when 3000 pupils can recruit 3000 subscribers. Telegram audience after blocking continues to grow . And only the number of users of RuTracker has really decreased , but it would be wrong to link this directly with the blocking - in a few years, how users consume media content has changed radically.
Despite the fact that with the help of phones you can surf the Internet for a long time, it is with the advent of the iPhone and the spread of LTE that user activity in the network changes dramatically - there is a turn towards mobile applications that save traffic and are easy to use.
The media business refuses the advertising model of monetization in favor of subscriptions - it is easier for users to pay once a month to stream music and movies in any format convenient for them - in transport from the phone or at home from the TV, bringing money to online cinemas like ivi and okko.
Communication goes into mobile messengers - Whatsapp, Viber, Telegram, which quickly become the main digital communication tool.
Navigation systems and maps are combined in mobile applications, which allows you to build new business models for different target audiences. Uber-fever begins - in all areas they are trying to invent their on-demand service.
There is a two-way process of online merging with offline: players in the real sector of the economy are increasing their presence on the Internet, and established Internet companies open stores in shopping centers. By 2018, the share of ecommerce is 2.5% of GDP , and Wildberries become a unicorn company with an estimate above $ 1 billion.
Russian Internet companies are diversifying their business and expanding into large ecosystems consisting of many services - today we go to Yandex.Taxi, order Yandex.Ed, listen to Yandex.Music, buy tickets to Yandex.Fish.
In RuNet, attempts to repeat the success of foreign Amazon and Alibaba continue; new marketplaces are launched, for example, “I take” created by “Yandex” together with “Sberbank”.
')
As we see, mobile devices are becoming a symbolic phenomenon of this period. The involvement of Russians in the Internet is coming to an end - the growth of users reaches the limit, to get into the network is no longer a problem even in the rural hinterland.
The resolution of monitors grows, the number of possible screens and resolutions increases. The site is ashamed not to have an adaptive layout.
Popularity is gained by intuitive designers who do not require programming skills. Dragging the blocks, you can create a site from scratch to your liking. Such sites begin to win at various awards — for example, at the Golden Site 2015 ceremony, the statuette was picked up by a site made at Tilda.
Graphic design quickly flashes and diminishes trends, for example, the parallax effect, which lasted only a few years.
User experience is becoming an important factor in web development. Designers now think about what the end user will feel. There is a set of techniques and techniques that contribute to immersion - animations, transitions, interactive narratives - we do not fill in boring checkboxes, but communicate with chatbots in order to fill in information about ourselves faster.
Over 25 years of existence, the Runet has matured. The Internet ceases to be exclusive, the low threshold of entry leads to the fact that the Runet is gradually deprived of rebellious spirit - this is manifested both in a more restrained graphic design and in user habits.
The business seeks to automate processes and optimize costs as much as possible, as well as learning to use big data to personalize sales.
The power of individual companies is increasing, there are “oligarchs” in Runet - for example, Yandex, according to its own creators , is today comparable to the entire Silicon Valley, and not a single search engine.
A tour of the past clearly shows that the Runet is constantly changing and sensitively reacting to any changes taking place in the real world. Under such conditions, it is difficult to make predictions about his future, but one thing can be said - in another ten years he will not be recognized again.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/447046/
All Articles