How does the received power from the wireless charging, depending on the location of the phone

In this part I want to answer some questions that were asked in the first article. Below there is information about various improvements in wireless charging and some information about the received power, depending on the location of the phone in charge.
Modifications
There are various "chips" for wireless charging:
')
1. Reversible charging. There were a lot of comments about it, there are already comparisons and reviews on the Internet. What is it about? The Samsung S10 and Mate 20 Pro have a reverse wireless charging feature. That is, the phone can take charge and give it to other devices. I have not yet succeeded in measuring the strength of the current being delivered (but if you have such a device and it is interesting to test, write to the messages :), but it’s by indirect signs equal to 3-5W.
To charge another phone is almost not suitable. Suitable in emergency situations. But it is great for recharging gadgets with a smaller battery: wireless headphones, watches or electric toothbrushes. According to rumors, Apple may add this feature to new phones. It will be possible to charge the updated AirPods and maybe a new watch.
For information, the battery capacity of wireless headphones with a case is approximately equal to 200-300 mAh, this will affect the battery of the phone more strongly, approximately 300-500 mAh.
2. Charging the power bank from wireless charging. The function is similar to reverse charging, but only for Power Bank. Some models of wireless external batteries can be charged by wireless charging. The received power is about 5W. Considering the usual amount of batteries, it will take about 5-15 hours to do this charging from wireless charging, which makes it practically useless. But as an additional feature also has a place to be.
And now to the main point:
How does the received power change depending on the location on the charge?
For testing was taken 3 different wireless charging: X, Y, Z.
X, Y - wireless charging at 5 / 10W from different manufacturers.
Z - Wireless Power Bank with 5W output.
Prerequisites: the same Quick Charger 3.0 charging unit and USB to Micro USB cable were used. Also used the same beer coasters as plates (from the personal collection), which were enclosed under the meter. The meter itself also has a 1mm protective plate from the coil, which I also added to all values. The thickness of the top cover above the coil is not considered. To measure the range of the received charge, I recorded the maximum values that the meter caught. To measure the charging zone, I recorded what the meter shows at a given point (I took measurements first along and then across. Since the coil is round in all charges, the values were almost the same).
Charges in the test had one coil.
At first, I measured the received power depending on the height (thickness of the phone case).
The result was the following chart for charging power at 5W:
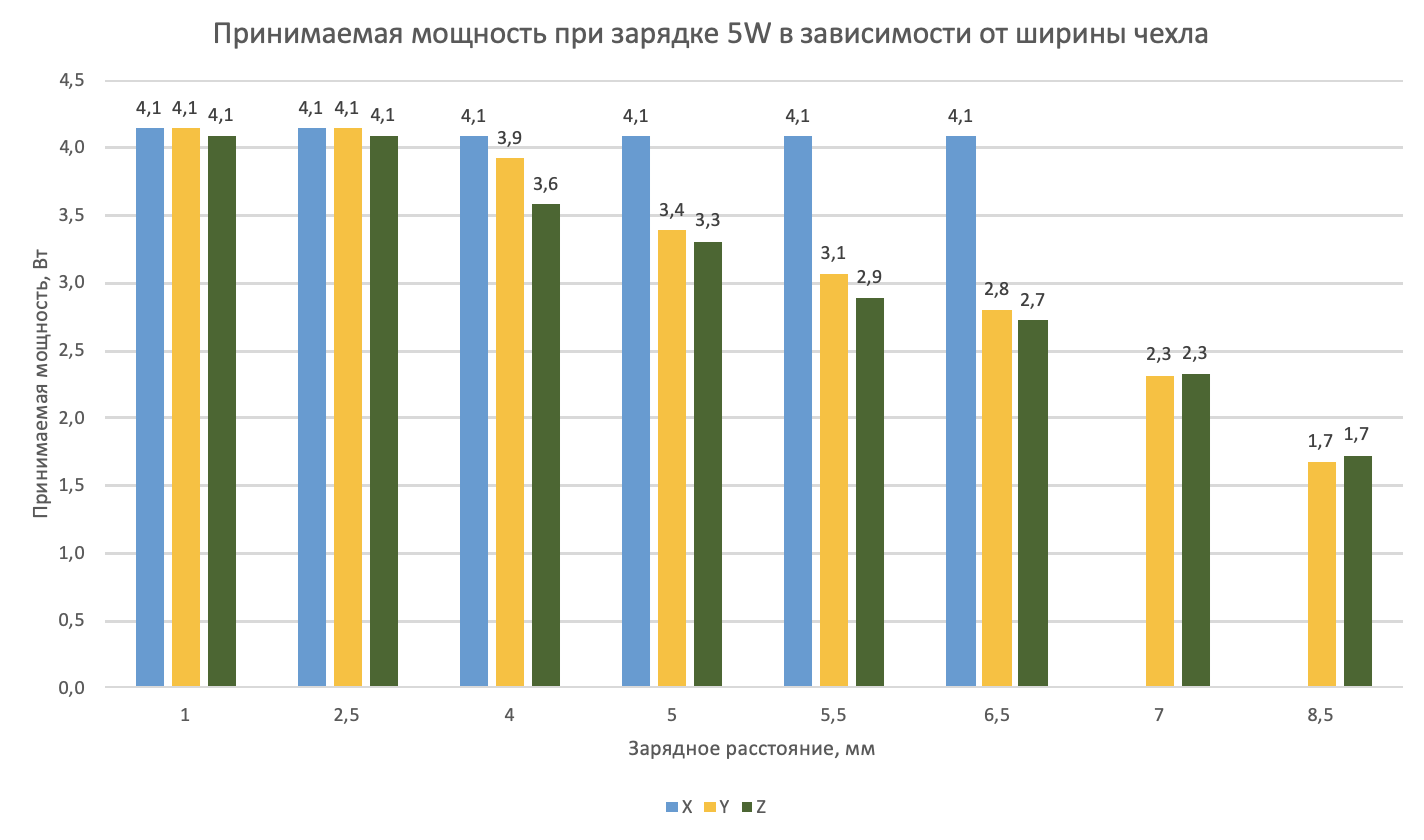
Usually in the description of the wireless charge they write about the width of the cover up to 6 mm, which is approximately what happens for all the charges of the test. Further 6mm charging or is already turned off (which seems to me more correct) or gives very little power.
Then he began testing the power of 10W for charging X, Y. Charging Y did not hold this mode for more than a second. It immediately restarted (perhaps with phones it works more stably). And charging X gave a stable power up to a height of 5mm.

After that, I began to measure how the received power varies depending on the position of the phone in charge. For this, I printed the lined paper in a cage and measured the data for every 2.5 mm.
These are the results for charging:
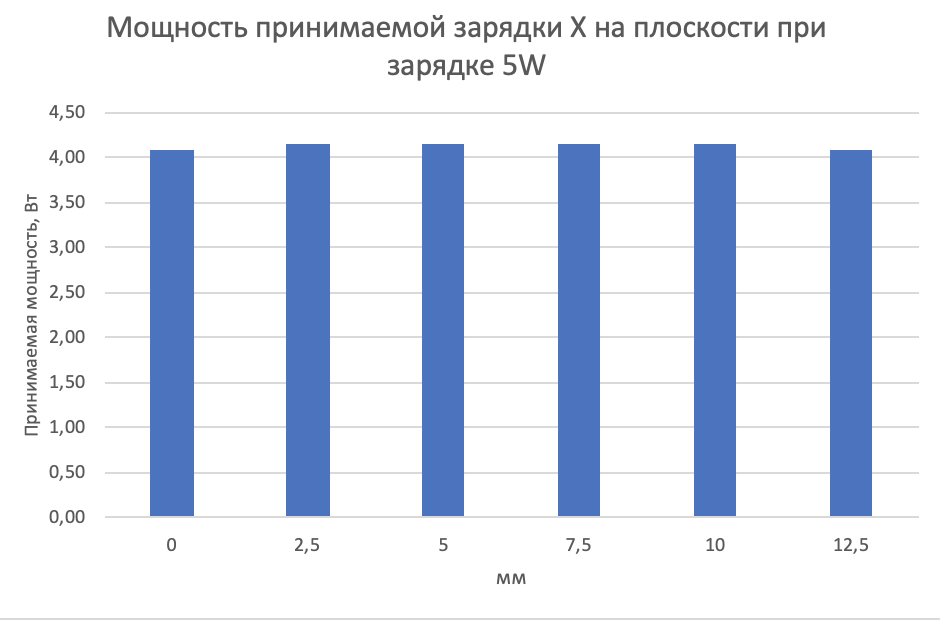
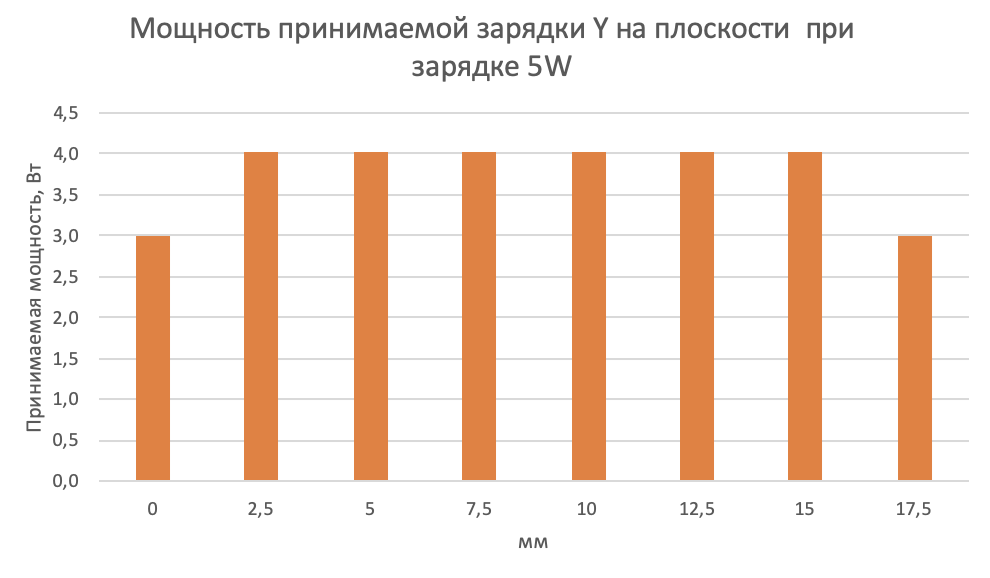

The conclusion of them is logical - the phone must be placed in the center of the charger. It is possible to change plus or minus 1 cm from the center of charge, which will not be very critical impact on charging. It works for all devices.
Then I wanted to make some advice on how to get to the center of the charging zone. But this is too individual and depends on the width of the phone and the model of wireless charging. Therefore, the only advice is to place the phone in the charging center by eye, this is enough for a normal charging speed.
Must make an important caveat that this may not work for some charge! I came across charges that could charge the phone only when they hit 1 in 1. When vibrating from 2-3 sms, the phone has already moved from the charging zone and stopped charging. Therefore, the graphs above are just an approximate measurement of three charges.
About heating charge, charge with several coils and new developments the following articles will be written. If someone from the owners of the Samsung S10 and Mate 20 Pro also has a thermometer or multimeter with temperature measurement, please write :)
For those who want to help with measurements
Or if you are an expert who will help me with writing an article, then also welcome. I wrote in the first article that I have my own store charge. I relate to charging mainly from the side of user characteristics, I measure everything and compare it in order to offer customers what works. But I’m not quite savvy in technical details: boards, transistors, characteristics of coils, and so on. Therefore, if you can help in writing articles, developing new products, improving, then write!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/446728/
All Articles