Comparison of space communication systems
Friends, as you already know, we are preparing a new geek project - “Server in the clouds 2.0”, or “Cosmic Data Center”. In a nutshell: on April 12, we will launch a self-made servachok on a stratostat to an altitude of about 30 km, transmit data to it via a space communications system, and transmit data to Earth via radio communication from the server.
And today we want to talk about the three space communications systems that we will test in our project - Iridium, Global Star and Gonets. To do this, we will mount the receiving equipment next to our transcendental server.
')
All three described systems were created and deployed at about the same time, in the 1990s. The American Iridium is not only the oldest one (the work started in 1990), but also the most ambitious - initially it was planned to launch 77 satellites, which corresponds to the atomic number of iridium, but today there are 66 satellites in orbit (+ 9 backup). Commercial operation of the system began in 1998. In just one year, the company managed to go broke, and in 2000 its assets were bought out by a company acting in the interests of the US Department of Defense. In 2001, commercial exploitation began again, in 2009 the owner of Iridium changed again. Since then, this satellite network has been living and well.
GlobalStar was also founded in the USA, although corporations from France, England, Germany and South Korea are participating in the project. The deployment of satellite constellation began in 1998, and in 2000, GlobalStar was launched into commercial operation. Here, too, was not without bankruptcy, the network in the early 2000s changed ownership. Today, 48 GlobalStar satellites (+ 4 backup) are in orbit.
The Russian Gonets system is a project not initially private, but a state one. It began to develop in 1989, and the launches of the first satellites began in 1996. It was originally planned that the grouping will consist of 24 satellites, but today there are only 12 in operation. In the coming years, a couple of dozen more satellites are planned to be launched, including for the replacement of obsolete ones.
Iridium has the largest coverage with the highest data transfer rates. Its satellites rotate around the Earth at an altitude of 780 km in orbits with an inclination of 86.5 o , and cover the entire surface of the planet, fromear to ear poles to poles, with a bond.
Now the data transfer rate ideally reaches 352 Kbps with Iridium, and by the end of the year they plan to bring up to 704/352 Kbps (receive and transmit). But the real values, of course, are lower. When communicating with voice, the sound quality is not too good, there are distortions.

Iridium maintains direct communication between satellites, so the system can formally do without numerous gateway stations in different countries for transmitting data to the Internet and the land telephone network, unlike Global Star, and instead transmit all traffic via satellite network to the main gateway station in USA. However, probably, for reliable communications, the gateway stations are still being built, though not so much.
Phones for Iridium are among the most expensive on the market, although they are distinguished by a rich bundle and capabilities. Both cellular modems and cellular devices are available for text communication (much cheaper than voice communication). To transfer data via Iridium, in addition to the phone itself, you need a computer on which you install the proprietary Iridium Data Kit software. Communication services for this satellite network are higher than those of competitors. For example, an annual voucher for 250 minutes inside the Russian Federation is 28,700 rubles, a two-month voucher for 150 minutes worldwide — 17,400 rubles. In postpaid tariffs, one minute of conversation starts from 58 rubles, SMS - 22 rubles, + subscription fee from 12,000 rubles (less than six months) and from 3,100 rubles. (more than half a year). And besides, the company still does not enter into roaming agreements with anyone, so SIM-cards of GSM operators in Iridium devices cannot be used, only “native”.
GlobalStar satellites fly at an altitude of 1400 km and have an orbit inclination of 52 o . The satellites do not exchange data with each other, therefore the network also includes a network of gateway stations, which are a link between the repeater satellites, the Internet, and the land telephone network.
Iridium satellites are shown in red, GlobalStar in blue:
Coverage with GlobalStar is more modest - up to 70 o north and south latitude, that is, the circumpolar regions are not covered by this network. However, according to reviews, coverage at other latitudes is unstable. Although if the satellite is in direct line of sight, then you will not have problems with communication. The data transfer rate of GlobalStar is lower than that of Iridium, but the sound quality of voice communication is comparable to a conversation on a cell phone.

Formally, the network supports CDMA and GSM standards, but in practice not all gateway stations work with GSM, although this is not relevant for our country. In most countries, you can insert SIM cards of “regular” mobile operators into phones compatible with GlobalStar. Devices for GlobalStar are noticeably cheaper than for Iridium. On sale there are phones of different degrees of advancement, a gadget for text communication with a mechanical keyboard, hot spots, trackers for installation on vehicles or personal wear, and much more. The subscription fee is absent, and communication services cost less than Iridium: for example, a package for calls in the Russian Federation for half a year and 250 minutes - 9,800 rubles, in postpaid tariffs a minute from 44 rubles, SMS - 4 rubles, internet access - from 13 rub.
The satellites of this system rotate around the planet at an altitude of 1500 km in orbits with an inclination of 82.5 o . As a result, the surface coverage of the Earth is complete, but not at the same time.
On the territory of Russia, 3 gateway stations were built (and one is planned), which connect the satellite constellation with the Internet.

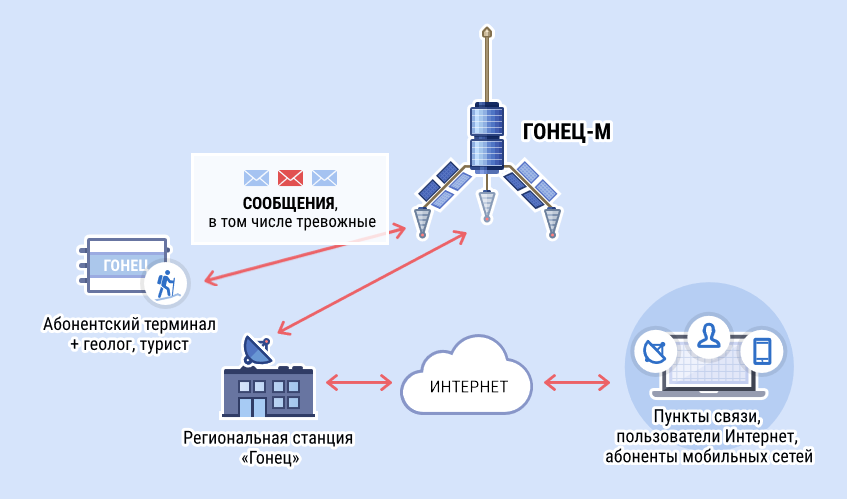
It is curious that "Messenger" does not compete with other systems in the field of voice communications. Instead, the Russian project specializes in text messaging. To do this, you need to purchase a subscriber device and an antenna, and connect a smartphone, laptop or desktop computer to them. In short, the introvert's dream is all chat only in chatty and no unexpected calls to you.
Also "Gonets" offers M2M communication services for automatic monitoring of the state and removal of telemetry of various objects, stationary and mobile.
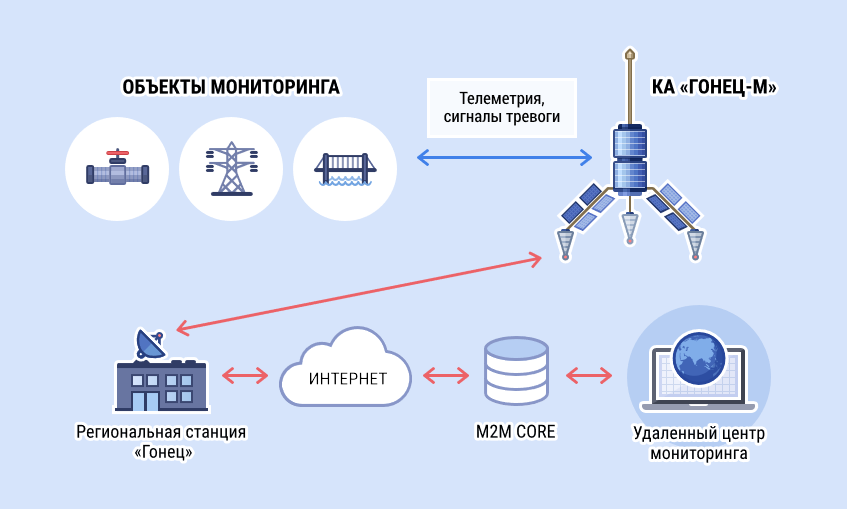
And plus additional services such as relaying geo-coordinates of transport and sending alerts.
Communication services in the network are paid on the basis of subscription fees - in fact, they are prepaid monthly packets of kilobytes of traffic. For example, at a zero monthly fee take on 26 rubles. for each kilobyte of transmitted data, and there are a number of packages from 470 rubles. (30 Kb) up to 8,650 rubles. (2 000 Kb). Plus 10 rubles for each outgoing message on the cellular networks of the Russian Federation. Each kilobyte above the limit is paid separately, from 11 to 26 rubles.
Our wishes are: equip the "transcendental" server with a tracker to track the location, and a module for exchanging data via satellite. Theoretically, these features can offer all three networks. We have already purchased Iridium and GlobalStar modems, and the device from the “Gonta” is going to us. We will tell you more about our communication system in a future publication.

In the meantime, we invite you to take part in our experiment, guess the probe landing point and win the main prize - a trip to Baikonur.
Do not disconnect!

And today we want to talk about the three space communications systems that we will test in our project - Iridium, Global Star and Gonets. To do this, we will mount the receiving equipment next to our transcendental server.

')
Short story
All three described systems were created and deployed at about the same time, in the 1990s. The American Iridium is not only the oldest one (the work started in 1990), but also the most ambitious - initially it was planned to launch 77 satellites, which corresponds to the atomic number of iridium, but today there are 66 satellites in orbit (+ 9 backup). Commercial operation of the system began in 1998. In just one year, the company managed to go broke, and in 2000 its assets were bought out by a company acting in the interests of the US Department of Defense. In 2001, commercial exploitation began again, in 2009 the owner of Iridium changed again. Since then, this satellite network has been living and well.
GlobalStar was also founded in the USA, although corporations from France, England, Germany and South Korea are participating in the project. The deployment of satellite constellation began in 1998, and in 2000, GlobalStar was launched into commercial operation. Here, too, was not without bankruptcy, the network in the early 2000s changed ownership. Today, 48 GlobalStar satellites (+ 4 backup) are in orbit.
The Russian Gonets system is a project not initially private, but a state one. It began to develop in 1989, and the launches of the first satellites began in 1996. It was originally planned that the grouping will consist of 24 satellites, but today there are only 12 in operation. In the coming years, a couple of dozen more satellites are planned to be launched, including for the replacement of obsolete ones.
Features and Features
Iridium
Iridium has the largest coverage with the highest data transfer rates. Its satellites rotate around the Earth at an altitude of 780 km in orbits with an inclination of 86.5 o , and cover the entire surface of the planet, from
Now the data transfer rate ideally reaches 352 Kbps with Iridium, and by the end of the year they plan to bring up to 704/352 Kbps (receive and transmit). But the real values, of course, are lower. When communicating with voice, the sound quality is not too good, there are distortions.

Iridium maintains direct communication between satellites, so the system can formally do without numerous gateway stations in different countries for transmitting data to the Internet and the land telephone network, unlike Global Star, and instead transmit all traffic via satellite network to the main gateway station in USA. However, probably, for reliable communications, the gateway stations are still being built, though not so much.
Phones for Iridium are among the most expensive on the market, although they are distinguished by a rich bundle and capabilities. Both cellular modems and cellular devices are available for text communication (much cheaper than voice communication). To transfer data via Iridium, in addition to the phone itself, you need a computer on which you install the proprietary Iridium Data Kit software. Communication services for this satellite network are higher than those of competitors. For example, an annual voucher for 250 minutes inside the Russian Federation is 28,700 rubles, a two-month voucher for 150 minutes worldwide — 17,400 rubles. In postpaid tariffs, one minute of conversation starts from 58 rubles, SMS - 22 rubles, + subscription fee from 12,000 rubles (less than six months) and from 3,100 rubles. (more than half a year). And besides, the company still does not enter into roaming agreements with anyone, so SIM-cards of GSM operators in Iridium devices cannot be used, only “native”.
Globalstar
GlobalStar satellites fly at an altitude of 1400 km and have an orbit inclination of 52 o . The satellites do not exchange data with each other, therefore the network also includes a network of gateway stations, which are a link between the repeater satellites, the Internet, and the land telephone network.
Iridium satellites are shown in red, GlobalStar in blue:
Coverage with GlobalStar is more modest - up to 70 o north and south latitude, that is, the circumpolar regions are not covered by this network. However, according to reviews, coverage at other latitudes is unstable. Although if the satellite is in direct line of sight, then you will not have problems with communication. The data transfer rate of GlobalStar is lower than that of Iridium, but the sound quality of voice communication is comparable to a conversation on a cell phone.

Formally, the network supports CDMA and GSM standards, but in practice not all gateway stations work with GSM, although this is not relevant for our country. In most countries, you can insert SIM cards of “regular” mobile operators into phones compatible with GlobalStar. Devices for GlobalStar are noticeably cheaper than for Iridium. On sale there are phones of different degrees of advancement, a gadget for text communication with a mechanical keyboard, hot spots, trackers for installation on vehicles or personal wear, and much more. The subscription fee is absent, and communication services cost less than Iridium: for example, a package for calls in the Russian Federation for half a year and 250 minutes - 9,800 rubles, in postpaid tariffs a minute from 44 rubles, SMS - 4 rubles, internet access - from 13 rub.
"Messenger"
The satellites of this system rotate around the planet at an altitude of 1500 km in orbits with an inclination of 82.5 o . As a result, the surface coverage of the Earth is complete, but not at the same time.
On the territory of Russia, 3 gateway stations were built (and one is planned), which connect the satellite constellation with the Internet.

It is curious that "Messenger" does not compete with other systems in the field of voice communications. Instead, the Russian project specializes in text messaging. To do this, you need to purchase a subscriber device and an antenna, and connect a smartphone, laptop or desktop computer to them. In short, the introvert's dream is all chat only in chatty and no unexpected calls to you.

Also "Gonets" offers M2M communication services for automatic monitoring of the state and removal of telemetry of various objects, stationary and mobile.

And plus additional services such as relaying geo-coordinates of transport and sending alerts.
Communication services in the network are paid on the basis of subscription fees - in fact, they are prepaid monthly packets of kilobytes of traffic. For example, at a zero monthly fee take on 26 rubles. for each kilobyte of transmitted data, and there are a number of packages from 470 rubles. (30 Kb) up to 8,650 rubles. (2 000 Kb). Plus 10 rubles for each outgoing message on the cellular networks of the Russian Federation. Each kilobyte above the limit is paid separately, from 11 to 26 rubles.
What should we choose?
Our wishes are: equip the "transcendental" server with a tracker to track the location, and a module for exchanging data via satellite. Theoretically, these features can offer all three networks. We have already purchased Iridium and GlobalStar modems, and the device from the “Gonta” is going to us. We will tell you more about our communication system in a future publication.

In the meantime, we invite you to take part in our experiment, guess the probe landing point and win the main prize - a trip to Baikonur.
Do not disconnect!

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/446708/
All Articles