How to generate hypotheses about the needs of potential consumers of your future product
The vast majority of businesses die because they offer a product that consumers do not need. This is a famous statement by Eric Rees, author of the Lean Startup technique. How not to fall into this trap with your project?
The answer is simple - before you make a product, you need to conduct a study to determine the demand for your future product. Any product exists to solve any problems of consumers. Therefore, the study should start with a set of hypotheses about the needs of consumers. That is, to come up with answers to the question - what problems and difficulties will help solve your future product?
Creating hypotheses is a creative process and it is difficult to conduct it strictly according to a certain algorithm, but it is worth trying. In this article, I describe an algorithm that will help create a set of hypotheses for later verification using problem interviews.
')
My name is Igor Sheludko.
I have been an entrepreneur in software development and sales since 2000. I have a higher technical education. I began my work activity as a programmer, also led small teams, was engaged in both product and custom development.
For 3 years I have been cooperating with the Accelerator of the Southern IT Park (Rostov-on-Don) as a tracker for start-up projects. During this time, over 20 projects passed through my caring hands of an individual tracker, and more than 200 projects passed through Accelerator in general.
In my opinion, it is worth starting with understanding who will be the target audience (CA) of your future product. If you already have an idea for a product, think who might need such a product? It often happens that the idea is not about the product, but about the process or technology. Nevertheless, you may well think of who it might be useful for and for what.
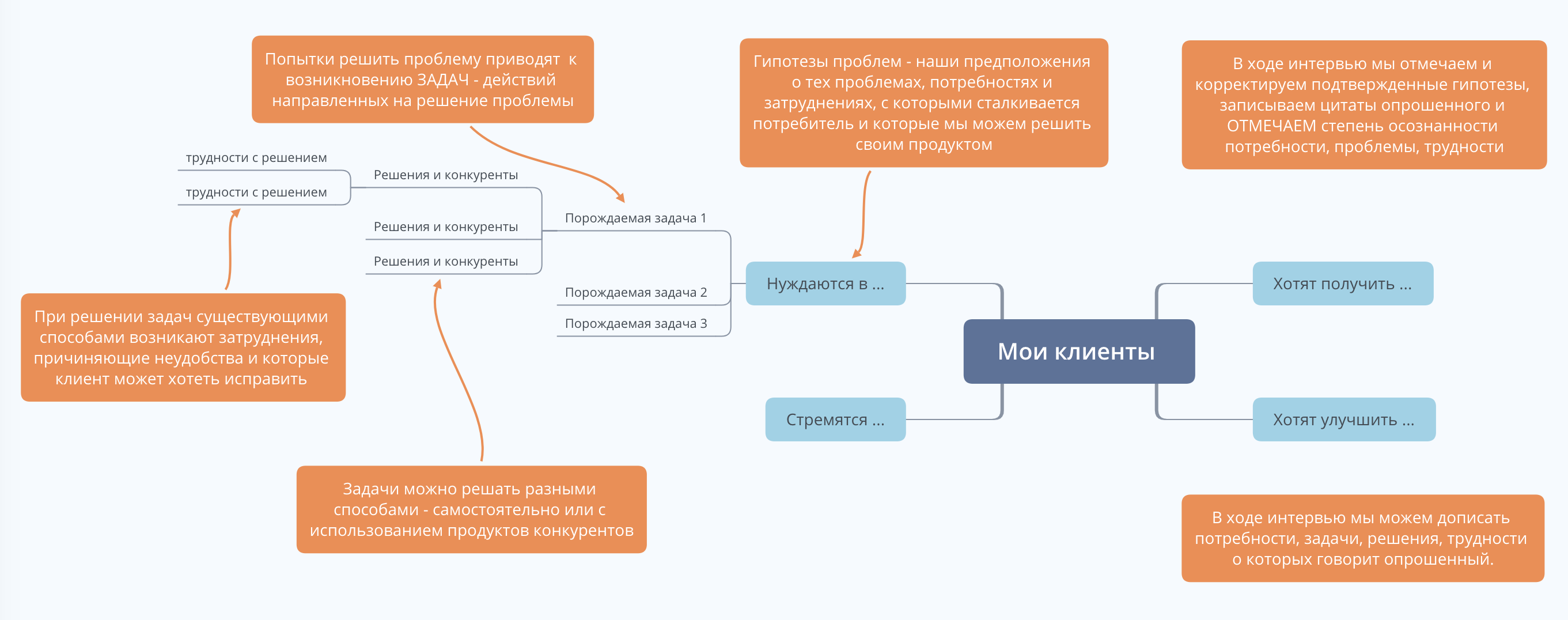
Requirement hypotheses are answers to the question - for what tasks of Central Asia can your product be used? How can he be useful?
I recommend generating hypotheses in the form of a tree or mental map (mind map), adhering to the following algorithm.
At the top level (right from the root), place your assumptions about the basic needs of Central Asia, which you can satisfy with your product. Try to give specificity to these hypotheses, if possible use measurable parameters in the wording.
If you have a very large list of needs hypotheses, then think about priorities. It is unlikely that all needs will be equally important for Central Asia and for you. Mark the most important hypotheses. If it is convenient for you, assign priority ratings to the hypotheses of needs and then work on the most important needs.
Tasks arising from problem solving are a set of consecutive actions that lead a client to the desired result - solving a problem. The tasks form the second level of the tree of hypotheses.
If you had many needs hypotheses at the previous step, then work through the tasks for the most important hypotheses. Less important - leave it undeveloped for now. They should be checked in the course of problem interviews, but now you shouldn’t give them much time and energy.
At the third level, products and services emerge - our possible competitors.
Each of the decisions can cause difficulties and inconveniences for the consumer - this is the fourth level of the tree of hypotheses. At this level, there are functions and distinctive features - "features" of products.
As a result, you will have a map (tree) of hypotheses, which will serve as a good basis for developing a plan for conducting problem interviews. During the interview, you will need to touch on all the important points that are present in the hypothesis map.
The answer is simple - before you make a product, you need to conduct a study to determine the demand for your future product. Any product exists to solve any problems of consumers. Therefore, the study should start with a set of hypotheses about the needs of consumers. That is, to come up with answers to the question - what problems and difficulties will help solve your future product?
Creating hypotheses is a creative process and it is difficult to conduct it strictly according to a certain algorithm, but it is worth trying. In this article, I describe an algorithm that will help create a set of hypotheses for later verification using problem interviews.
')

About myself
My name is Igor Sheludko.
I have been an entrepreneur in software development and sales since 2000. I have a higher technical education. I began my work activity as a programmer, also led small teams, was engaged in both product and custom development.
For 3 years I have been cooperating with the Accelerator of the Southern IT Park (Rostov-on-Don) as a tracker for start-up projects. During this time, over 20 projects passed through my caring hands of an individual tracker, and more than 200 projects passed through Accelerator in general.
Where to begin?
In my opinion, it is worth starting with understanding who will be the target audience (CA) of your future product. If you already have an idea for a product, think who might need such a product? It often happens that the idea is not about the product, but about the process or technology. Nevertheless, you may well think of who it might be useful for and for what.
How to generate needs hypotheses?
Requirement hypotheses are answers to the question - for what tasks of Central Asia can your product be used? How can he be useful?
I recommend generating hypotheses in the form of a tree or mental map (mind map), adhering to the following algorithm.
At the top level (right from the root), place your assumptions about the basic needs of Central Asia, which you can satisfy with your product. Try to give specificity to these hypotheses, if possible use measurable parameters in the wording.
If you have a very large list of needs hypotheses, then think about priorities. It is unlikely that all needs will be equally important for Central Asia and for you. Mark the most important hypotheses. If it is convenient for you, assign priority ratings to the hypotheses of needs and then work on the most important needs.
Example:Further assume that Central Asia really has such a need and think about what tasks need to be solved in order to satisfy this need. Tasks can not immediately get specific and it's not scary. A task is the answer to the question “what needs to be done to solve a problem?” It’s not the desired result, not a process, but an action.
Situation - a young man wants to buy his first car.
Central Asia - motorists who buy their first passenger car.
Need # 1 hypothesis: The client wants to buy a used / used car no older than 7 years with automatic transmission and a budget of no more than XXX tr.
Tasks arising from problem solving are a set of consecutive actions that lead a client to the desired result - solving a problem. The tasks form the second level of the tree of hypotheses.
If you had many needs hypotheses at the previous step, then work through the tasks for the most important hypotheses. Less important - leave it undeveloped for now. They should be checked in the course of problem interviews, but now you shouldn’t give them much time and energy.
ExampleTo solve each of these problems, different methods and tools can be applied.
To buy a used car you need:
- To determine the model (not just “model” and not “model choice”)
- See the model "live", try
- To decide on a complete set and color (not just "color")
- Find multiple instances to compare.
- Verify the accuracy of the information about each instance (not “break through the traffic police database”, because this is far from the only check)
- To assess the technical condition, to estimate the costs to bring in good condition (not just “go to the service”)
- Select a specific instance
- Sign a sales contract
- Get insurance
- Put on the account, register the sale
At the third level, products and services emerge - our possible competitors.
ExampleIn the latter case, an interesting situation arises - such a consultant will still solve the above tasks. In spite of the fact that we can delegate a number of tasks to one solution, one executor, tasks still remain. In this case, the target audience will change and decisions may change, but the challenges remain. So during the study of one consumer segment, we came to the hypothesis of the existence of another consumer segment.
To determine the model of car, you can:
- Go to avito, set criteria - price range, auto age and other parameters, view ads and select several options for auto model
- To ask more experienced friends - what will they recommend?
- Call on several car dealers selling used cars - so we can immediately solve the following task (see live, try on ourselves), but we may not see all the interesting options - this is already a difficulty, we will deal with them further
- Hire a professional consultant for this and the following tasks - to delegate several tasks at once.
Each of the decisions can cause difficulties and inconveniences for the consumer - this is the fourth level of the tree of hypotheses. At this level, there are functions and distinctive features - "features" of products.
Examples:
- For avito, the issue in the avito application is inconvenient, since we wanted to see the options for the models, and specific ads show us.
- It is inconvenient to call in salons, as they are not in our area and need to go to the outskirts of the city.
- Our friends do not have experience with cars in this price category.
- There is no confidence in the consultant; suddenly he will offer only those options for which he will receive an additional bonus from sellers.
The hypotheses of difficulties can not be worked out in detail at the initial stage of hypothesis formation, but you should definitely ask about the difficulties when conducting problem interviews.
What do you get in the end?
As a result, you will have a map (tree) of hypotheses, which will serve as a good basis for developing a plan for conducting problem interviews. During the interview, you will need to touch on all the important points that are present in the hypothesis map.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/446436/
All Articles