5. Check Point Getting Started R80.20. Gaia & CLI

Welcome to the 5th lesson! Last time we completed the installation and initialization of the server management, as well as the gateway. Therefore, today we are “digging a little” in their insides, or rather, in the settings of the Gaia operating system. Gaia settings can be divided into two broad categories:
- System settings (IP addresses, Routing, NTP, DNS, DHCP, SNMP, backups, system updates, etc.). These parameters are configured via WebUI or CLI;
- Security settings (All that concerns Access Lists, IPS, Anti-Virus, Anti-Spam, Anti-Bot, Application Control, etc. Ie all security features). To do this, use the SmartConsole or API.
In this lesson we will discuss the first paragraph, i.e. System settings.
As I said, these settings can be edited either through the web interface, or through the command line. Let's start with the web interface.
')
Gaia Portal
It is called Gaia Portal, in Check Point terminology. And you can access it using a browser, “knocking” on https to the device ip-address. It supports browsers Chrome, Firefox, Safari and IE. Even Edge works, although it is not on the list of officially supported ones. The portal looks like this:
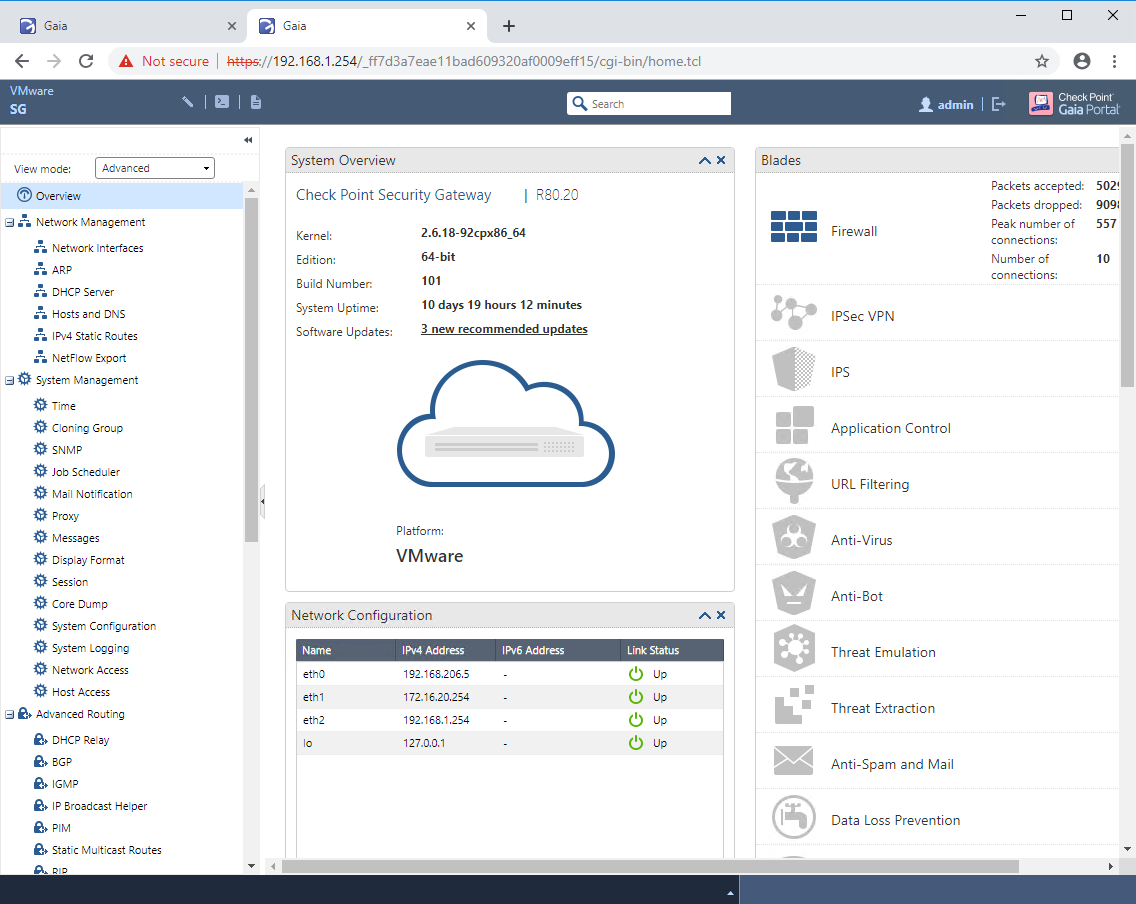
You can find a more detailed description of the portal, as well as setting up interfaces and the default route in the video tutorial below.
Now let's take a look at the command line.
Check Point CLI
Until now, there is a perception that Check Point cannot be controlled from the command line. This is not true. Almost all system settings can be changed in the CLI (In fact, you can change the security settings using the Check Point API). There are several ways to get into the CLI:
- Connect to the device on the console port.
- Connect via SSH (Putty, SecureCRT, etc).
- Go to CLI from SmartConsole.
- Or from the web interface by clicking on the “Open Terminal” icon in the top panel.
The symbol > means that you are in the default Shell, called Clish . This is a limited mode in which a limited number of commands and settings is available. For full access to all teams you need to enter Expert mode. This can be compared to the Cisco CLI, where there is a user mode (user mode) and a privileged mode (privileged mode), which requires the enable command to enter. In Gaia, to enter expert mode, enter the expert command.
The CLI syntax itself is quite simple: Operation feature parameter
In this case, the four main operators that you will use most often: show, set, add, delete . Finding documentation on CLI commands is quite simple, just google “ Check Point CLI ”. There are also some sets of useful commands that you will definitely need in your daily work with checkpoint. There is no need to memorize them, there are good guides for these commands, plus there are very useful cheat sheets. I will put a link to one neither of them under the video. I recommend to pay attention to two of our articles:
- Useful Checkpoint R80.10 CLI Console Commands
- Check Point R80.10 API. Management through CLI, scripts and not only
We will cover working with Check Point CLI in the video tutorial below.
Video lesson
Check Point CLI Cheat Sheet
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/446394/
All Articles