Ancient Greek hacking: the results of the online stage NeoQUEST-2019

Summing up the online stage NeoQUEST-2019 : we will tell about tasks under the cut, look at the statistics of their passing and praise the winners!
Disclaimer: the product may contain traces of peanuts and spoilers for those who have not completed the task, but are honestly going (and there is such an opportunity - the on-line site of the stage continues to work!). Not recommended for use if you have not shown enough persistence to get all the keys yourself.
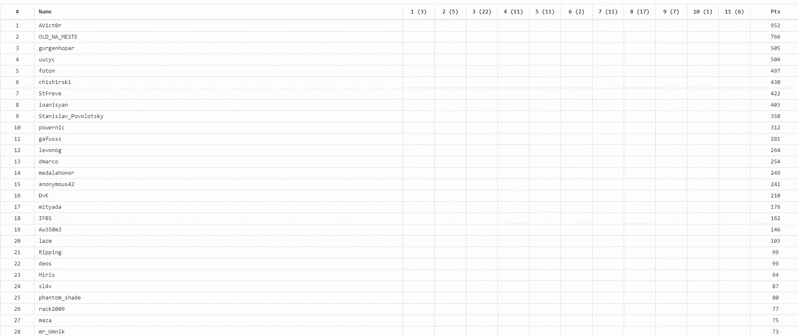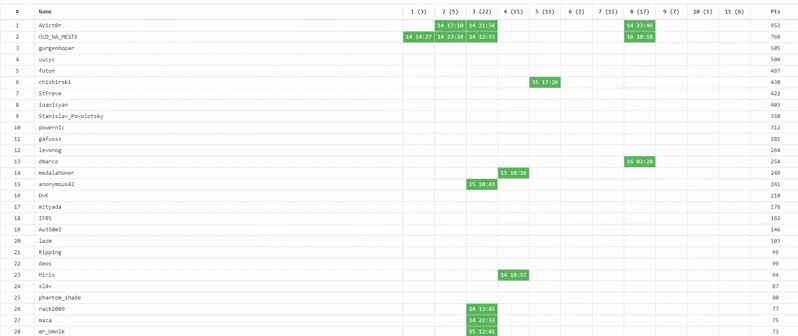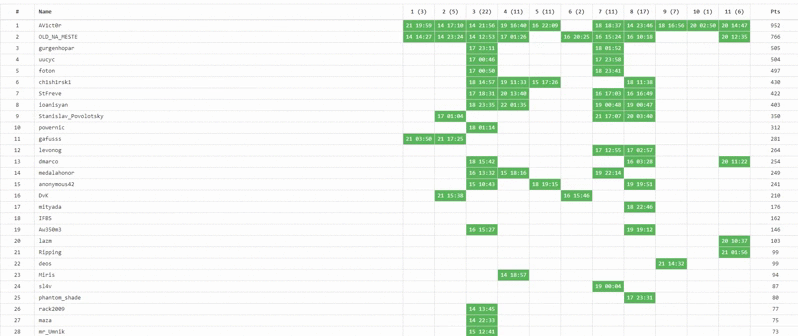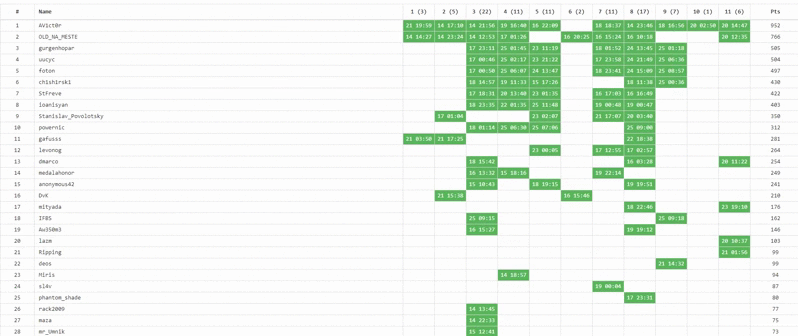
Who is the best?
So, this year our winners are:
1st place - AV1ct0r, 952 points;
2nd place - OLD_NA_MESTE, 766 points;
3rd place - gurgenhopar, 505 points.
Guys honor and respect! It should be noted that the winners of the 1-2 places were determined from the very first day of the competition, and did not give up their positions to anyone (except for changing places with each other). But the fight for third place was hot: sometimes the “bronze” participant changed several times a day!
Three leaders are waiting for well-deserved gifts, and all those who have completed at least one task completely - memorable souvenirs from the NeoQUEST team! (yes, by the way: if you have decided at least one task, but have not yet informed us how you would like to receive a gift, now is the time to do this by writing to support@neoquest.ru )
Reveal secrets
For the participants, we have prepared 10 tasks, different in complexity and subject. We will tell about some in detail, and the rest will soon be published on Habré in the form of separate articles!
Task number 1 - "Nemean Echo"
In this task, the participants were provided with a so-called echo server, to which you can connect to a specific port and send data. In response, the server sends the same as sent to it. The flag lies on the server, and you need to get it, having only an IP address and port.
Task number 2 - "Soft and silky"
The story is commonplace - very important information flows into the network. Participants are given two files: the binary file itself, which generated the leaked traffic, and the pcap-dump of this traffic itself. The flag is in pcap-dump, but in encrypted form, and you need to reverse the binary file in order to decrypt the data and get the flag.
Analysis of tasks number 1 and number 2 will be released separate Habrastayami!
Task number 3 - "Communication with the heavens"
Almost all participants managed to establish celestial connections, the task became the leader in terrain. Baseline - reference to the telegram-bot.
The first step was to add a bot and read its description. It says that the bot “freezes” in its favorite social network and nowhere else. For all attempts to somehow talk to him, the bot waves him off and asks him to write to him at Olympia. We go to the address specified by the bot and get to the page with authorization in the "divine" (no) social network.
When communicating with a bot, you can get the following message: “I do not click on unfamiliar links!”, Which may give us the idea that a bot may follow a familiar link.
When you try to go somewhere other than the login page (to the index page, for example), we redirect in an interesting way (in fact, this is done on many sites, but they normally filter the next parameter):
login? next = index
The first thing that comes to mind: “Isn't there an OpenRedirect here?”. It is, but it works only for the authorized user in the social network, which is the God of ridicule and slander My , because constantly sitting in it. Yeah, let's raise your site, as a parameter next, give it a link and see if the bot follows the link? Quickly we lift any site on a free hosting. We send bot:
http://213.170.100.214?next=https://your.freeapp.kek/
The bot did not reach the page, the redirect did not work. The whole thing is in the filter, pseudo-developers are checking whether the “next” parameter contains http or https substrings, hoping to redirect the user only within their own domain. Naive. We ship:
http://213.170.100.214?next=//your.freeapp.kek/
Iiii ... bot goes to our site! But nothing else happens. The bot came in, looked, and left (on the first day it wasn’t because there was a bug in the bot: we threw cookies with the session after the redirect to the attacker's site, which made the task a little easier, on the second day the loophole was closed).
However, if you make a copy of the authorization page, the bot will think that it has been logged out and logged in on your page. Copy resources from the social network authorization page and make a phishing page. On the server, we write to the logs all entered logins and passwords. We send the link to the bot, and he inadvertently logs in on the fake page.
We take the login and password and log in to the social network, we get the key. Success!
On this task, write-up wrote one of our participants - mr_umnik , read here .
Task number 4 - "Kripota Crypto"
The fourth task of "Kripota Cryptovaya" is dedicated, strangely enough, to cryptography! And this is not about the traditional for CTF RSA, but about the ciphers of the Ancient World, when the art of cryptography was only in its infancy.
So, given an archive with three files. The contents of the first file include readable text and an encrypted string:
Use the wisdom the goddess has bestowed upon you.
5fw909zcmxsc7sxn1m6m86wxs2xrhrx78r72333mms8rlkg1u41o4dm82n632n2c2s8r17nwx3673c6hnh8n8x3mn7dwrrdswmxm1nc3wc681d16rmdc8cx
The question arises, what goddess are we talking about? Turn to the legend. The only reference is the mention of a certain wise woman in a helmet with a spear in her hands, depicted on a Cerberus medallion. Such a vestment corresponds to the goddess of wisdom Athena, which immediately suggests the use of a consonant affine cipher . Good old brute force allowed to decrypt the secret message:
modulus 9b6598564ebfb1fd6576cac681c87000bb51
Ciphertext 2b174f07479751ce84d60f809fa4a14160b482dcc25db6be490d9f1e2efcb29196
So what to do with this next? Maybe the second file will give more information? So, its contents:
What other antique cipher comes to mind? Let's start with a simple ...
35ub2b9slmkjonnqtsokomumqnphkinmrqlqoyz4aayvr4tzv4ax8vv19xrcvb9ayv6fayrx58vr4ayv58v3r4uayvtyz4v9v68v9v4avuayvtyz4v9vayv58vv4z
The first cipher that comes to mind is Caesar's cipher . Fortunately, it can be easily decrypted! We get:
modulus b45327669cb7375d596803165a9497
hint the pythagorean theorem
Aha Here is a hint! Moreover, suggesting the Chinese theorem on residues . This theorem asserts that a certain integer can be reconstructed from the set of its residuals by dividing by numbers from a set of pairwise coprime numbers.
So, so, so, we have 2 modules, as well as a certain Ciphertext. Maybe this Ciphertext is the same recovered integer? Then, to find the residuals, it is sufficient to simply bring Ciphertext over the two modules we know. We get:
Balance 1: C1 = Ciphertext mod (modulus 1) = 8b53bd874ebfb1fd6576cac681c86ffc36e7
Balance 2: C2 = Ciphertext mod (modulus 2) = 14327669cb7348d59680c6595418
What to do next? Pay attention to the third file:
We had two mutually simple modules, one mysterious ciphertext, a tip on some Chinese technology and ... the seal of Ancient Sparta.
Not that it was the necessary supply for solving the riddle, but since I started collecting hints, it is difficult to stop ... Maybe it's time to start a solution?
It seems that everything is in place ... except for the print of Ancient Sparta. What is she here for? Maybe there is such a cipher? And indeed, the cipher of Ancient Sparta is also called the Scytal cipher .
Let's try to decrypt the resulting balances. As a result, select those fragments of which coincide with the flag pieces shown in the legend. As a result, received:
M1 = 88b78fb7161c54fcc33eda86bb6c6edf56f7
M2 = 19d64c553b9927657384640168c8
Then the final flag takes the form:
NQ2019 88b78fb7161c54fcc33eda86bb6c6edf56f719d64c553b9927657384640168c8
Task number 5 - "Apple Letter"
According to legend, we have the following data: a picture from a webcam on which there is an inscription “Robert B. GmbH”. And yet - a file with some strange content. To get the key, you must fill in the following fields of the mold:
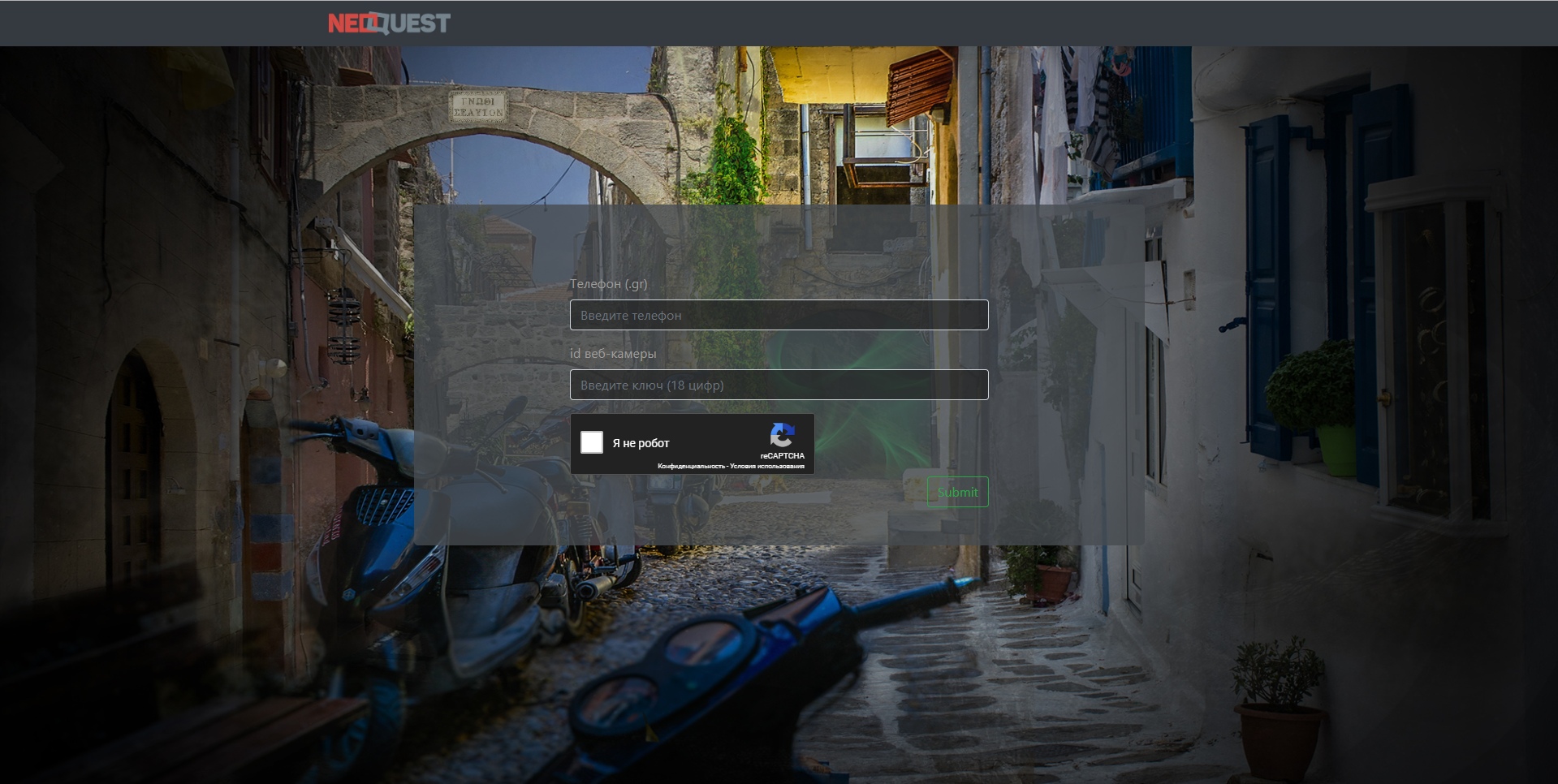
And the hero of the legend hints that the picture is a hint to the phone number, and the file should somehow lead us to the camera id.
We will understand first with the picture. Finding it on the Internet does not lead to anything. But the inscription “Robert B. GmbH” after the first request on Google tells us that the manufacturer of this camera is the German company Bosch, the founder of which is Robert Bosch. And then it's time to remember that in the web form near the "Phone" field there was a mark "(.gr)". Well, the action takes place in Greece, it is logical. Therefore, after some deliberation, go to the Greek site Bosch . And the phone number listed there ( +30 210 5701360 ) is just what we need!
Go to the second file. It has the following type of entry:
... c6d1eb6f29d739176bdbe79c3d3b504c9d64fe ... olympic_shot.png
It was necessary to guess that in front of us is a magnet link in its simplest format, in which there is a hash used in the most popular BitTorrent network! It remains to correctly restore the format of magnet links.
magnet:? xt = urn: btih: c6d1eb6f29d739176bdbe79c3d3b504c9d64fecb & dn = olympic_shot.png
This link is added to the torrent client, download the picture:
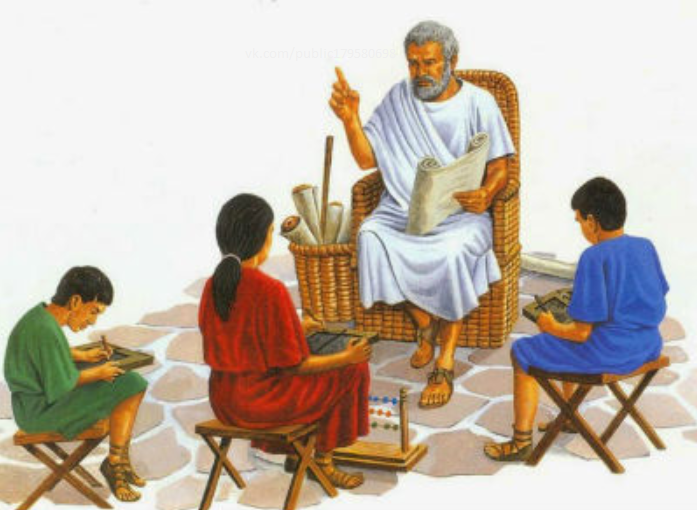

At first glance, there is nothing special in it, but if you look closely, you can see that the teacher in the ancient Greek school does not point the finger at emptiness, but rather a valid reference to the VKontakte group .
In the group we find the post with the next part of the task. It is necessary to download a file written in C from documents and find syntax and semantic errors in it. In the file itself, one can observe a peculiar interpretation of ancient Greek myths.
#include "AncientGreece.h" void eat (int who, int *whom) { *whom = 0; } int BirthOfAthena() { int Zeus = 10000; int Metis = 1000; int Athena = Zeus + Metis; eat(Zeus, &Metis); Athena = 0; bool headache = TRUE; int kick = -1000; do { kick++; if (kick = Athena) { Athena = 1000; headache = FALSE; } } while (headache); return Athena; } int ApplesOfTheHesperides() { int labour = 0; int Heracles = 100; int heaven = 100000; int Atlas = 1000; int golden_apples = 8222; /*why?*/ bool trick = TRUE; while(!Heracles_is_here) { Atlas = Atlas + heaven; if (labour == 10) break; labour++; } Heracles_is_here = TRUE; Atlas = Atlas - heaven; Heracles = Heracles + heaven; Atlas = Atlas + golden_apples; trick = TRUE; Atlas = Atlas - golden_apples; Heracles = Heracles - heaven; Atlas = Atlas + heaven; return Heracles + golden_apples } void BirthOfZeus() { int Cronus = 1000; int newborn_gods[] = {1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000}; int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 6; i++) { eat(Cronus, &newborn_gods[i]); } int Zeus = newborn_gods[6] + 10000; bool battle = TRUE; bool peace = FALSE; int Thetis = newborn_gods[0] + 1000; int Hera = newborn_gods[2] + 1000; int Hades = newborn_gods[3] + 1000; int Demeter = newborn_gods[1] + 1000; int Poseidon = newborn_gods[4] + 1000; Cronus = 0; battle = FALSE; peace = TRUE; } void main() { BirthOfZeus(); BirthOfAthena(); ApplesOfTheHesperides(); } We find the main () function and understand that functions must be considered in the order of their calls to main (). The numbers in this task have their meaning: the unborn / dead person / god is indicated by 0, the person is 100, all gods and titans are 1000 and Zeus the Thunderer - 10,000.
Go to the function BirthOfZeus (). It is logical to assume that this feature tells about the birth of Zeus, as well as about his struggle for power. So, after reading the myth of the birth of Zeus, we look at the code, and we see that the cycle from 0 to 6 in this case is a semantic error - Kronos ate not five of his children, but only five. It remains to understand how to make a key out of this: the key is made up by line numbers with errors. The first part of the key, the line number, is 60. Go ahead.
The next error is waiting for us in the line with number 64 - everything is simple, going beyond the array.
The next error is on line 67. The fact is that Thetis, namely the goddess Thetis, was not the daughter of Kronos and sister of Zeus. Instead, there should be the goddess Hestia.
In the BirthOfAthena () function, an error is waiting for us to be very attentive: the condition on line 20 contains one equal sign, and according to the C standard, you need two equal signs to compare.
The most intricate was the function ApplesOfTheHesperides (). Literally immediately there is a branch from the direct problem. Why int golden_apples = 8222? While it is not clear.
In the post VKontakte, too, there are several tips for this task:
1) Where to find the answer? In the discovery that happened on the first of March.
By briefly viewing the events of the first of March (and you can immediately find the necessary, remembering the post and the mention of alchemy) is the opening of the Periodic System of DI Mendeleev. Ok, move on!
2) What to use when making part of the key? (must take into account the location of the riddle in the text)
• What does the following three words have in common: Mnemosyne, Ocean, Huygens?
• Who gave fire to people?
We google and find the answer: TITAN PROMETHEUS. As stated in the assignment, it will help in the preparation of the key. It remains to understand why 8222. It is not for nothing that we were looking for information about the periodic table: it is obvious that the answer must be sought there. Remembering the chemistry, we find the serial number of gold = 79.
And what about the apple? Probably, chemistry is also useful here. We find out that in the apple most of all potassium. His serial number is 19. We approach the great secret: why is 8222, not 7919? Well, of course, the good old Caesar cipher. Shift by 3 each element to the right, we get our value 8222.
There was a trifle: to encrypt TITAN PROMETHEUS on the periodic table. Both of these elements are in the table, we get: 2564. Remarkably, we proceed to further finding errors in the code.
In the same function, we expect an uninitialized variable in line 38, a semantic error in line 41 (this was the 12th feat of Hercules!) And the absence of a semicolon in line 52. Phew, we managed. The resulting code = 606467202564384152. This is the id of our camera. Strange, but in ancient Greece that just does not happen.
We enter these two values into the form, we prove to the whole world that we are not a robot, and we get the coveted key!
Task number 6 - "Goes, goby, swinging"
Task number 6 this year was very difficult, but interesting. We will analyze it in detail in a separate Habrastier, but for now, briefly, let's say: you had to play with the Minotaur, using an application in which something is missing.
Task number 7 - “you more quick? No, hurry! ”
In this task (which will also be a separate write-up!), Participants were asked to sort out an application that encrypts the entered data using the device accelerometer parameter values taken while pressing the buttons on the keyboard. To complete the task, it was necessary to enter various data into the application, and carefully analyze the resulting offsets.
Task number 8 - "Divine Interpreter"
Our regular participants may have learned this task - it has remained since last year. Then the second part was not passed by anyone, and we decided to give him a second chance. On the first part of the task there is our Write-up on Habré, it tells mainly about the search for vulnerabilities. This year, the focus of the task was not focused on the search, but on the exploitation of vulnerabilities - and under this we, again, will single out a separate Habrastuju.
The bottom line is that a command interpreter program rotates on the server’s network port. Binary program attached to the task. The server is running Windows Server 2016, and among other things, the CFG security mechanism is enabled there. All that is known about the key is that it consists of 70 characters and lies in the key.txt file next to the executable file on the server.
Assignment number 9 - "The game in the box"
In this task, we have two servers. RAR archives can be sent to server # 1, which are unpacked there, and can help to get the key hidden on server # 2.
Task number 10 - "Do not hit, Odyssey"
This task was one of the most difficult - only one participant mastered it. The source data is an archive with the network infrastructure, all the necessary files in which were found to be encrypted. And once encrypted, the only way is to decrypt!
Analysis of tasks number 9 and number 10 will also be released separate Habrastayami!
British scientists have established
This year's small statistics:
- The number of registered participants - 1014 people.
- Number of completed tasks - 10/10
- The number of participants who completed at least one task completely - 33 people.
The number of correct keys to each task

The number of correct keys on each day of the competition

Over the entire period of the online-stage NeoQUEST-2019, 94 keys were received.
What's next?
And then - "confrontation" on June 26, in St. Petersburg, where the final of our competition will be held! We are waiting for all the best hackers to live to make sure that you are really the best! And about those who do not come, we will think like this ...

Follow the news on the website of the summer event!
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/446286/
All Articles