Use of thermal potentials for territory analysis
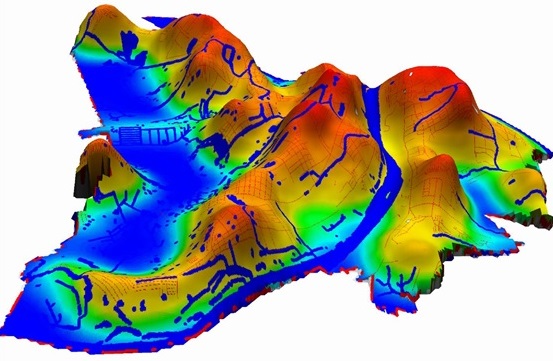
An example of calculating the thermal potential for the street network of Nizhny Novgorod
The territory of the city is a complex, heterogeneous system that is in constant change. It is possible to describe the territory and assess the urban environment with the help of spatial objects (factors). The factors that describe the territory are different in the nature of influence (positive, negative) and geometric configuration (points, lines, polygons).
It is often difficult to determine the degree of influence of each individual object on the level of development of the territory as a whole or some particular aspect of it. Today, the problem of defining and describing such concepts as “culture”, “social sphere”, “social tension”, “good life”, “economic development”, and “public health” is becoming ever more relevant. The ambiguity of these concepts increases if we want to apply them with respect to different social groups, people of different age and gender.
')
Also, it should be noted that the boundaries of the city in the modern concept are rather relative. Daily migration of the population, transport accessibility of remote areas “blur the border” of the city even more. The widely used notion of agglomeration now reflects the boundaries of the city as a whole, but at the same time it makes the concept of the boundary of the city even more vague.
Despite the problems described above, the analysis and assessment of territories today are among the most promising and interesting areas, allowing to solve many pressing problems of the urban environment.
The article proposes to consider the method of territory analysis using the “thermal” model. The basis of this method is the study of the potentials created by objects (factors) of various nature (point, linear and area). Territory analysis using this method makes it possible to move from a set of spatial data (factors) describing a territory to an exact numerical (ball) estimate at each point of the territory.
The potentials studied in the framework of the analysis of the territory have a physical interpretation - the distribution of heat in media of different dimensions (2D, 3D). This phenomenon can be represented in the form of "thermal" images ("thermal" maps of the territory), which give an idea of the degree of development of the territory, depending on the intensity of the color of the image.
Territory factors
Territory analysis involves the search and processing of information on the factors influencing the territory and on their indicators. Influencing factors are objects that affect the surrounding area, have a set of characteristics and spatial coordinates. Examples of influencing factors are shops, industrial sites, roads, forests, water bodies.
The indicators of influence are objects that reflect the influence of objects and also possess a set of characteristics and spatial coordinates. Examples of impact indicators: ATMs, billboards, monuments.
In the following, we will use the notion of factors of influence, combining both terms - factors and indicators of influence.
Below is an example of spatial data that are influencing factors.
One of the important stages of the work on the analysis of territories is the stage of collecting and processing initial information. At present, there is a lot of information about the factors influencing the territory of varying degrees of detail.
Information can be obtained from open sources or sources of limited access. In many cases, open information is sufficient for analysis, although, as a rule, it needs fairly time-consuming processing.
Among open sources, the leader, in our opinion, is the resource - OpenStreetMap (OSM). Information received from this source is updated daily around the world.
Information resource OpenStreetMap (OSM) is presented in the following formats:
- OSM format. The main format with the “.osm” extension is used to describe graphic images XML - nodes, paths, relationships.
- “Polish format”. Text format with the extension “.mp” is used for working with graphics.
- PBF format. Data storage format with the extension ".osm.pbf".
The sources of information can also be used:
- 2GIS
The resource contains high-quality, monthly processed information, with an excellent 3-level classifier for enterprises and organizations.
- KML (Keyhole Markup Language) files
KML (Keyhole Markup Language) files are a file format that is used to display geographic data in Google Earth programs, Google Maps and Google Maps for mobile.
Using KML files, you can:
- set different icons and make signatures to indicate places on the surface of the Earth
- create different angles for selected objects by changing the camera position
- use different overlay images
- define styles to customize the display of the object, use HTML code to create hyperlinks and embedded images
- use folders to hierarchically group items
- dynamically receive and update KML files from remote or local hosts
- receive KML data in accordance with changes in the 3D viewer
- Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography "Rosreestr"
Information on the Rosreestr portal is valuable for its content and relevance, but, unfortunately, it does not provide an opportunity to receive graphics for capital construction objects and land plots free of charge. The Rosreestr portal also contains a large amount of information of limited access.
- Statistical authorities
Statistical data is a legitimate source of information about a territory, but as of today, data from statistical bodies are available only for a certain number of indicators, mainly in reports of statistical bodies and reports of regional authorities.
- Information systems of authorities
Qualitative information is contained in the information systems of the authorities, but only a small part of them is published in the public domain and is available for analysis.
The analysis of the territories does not impose any specific requirements on the composition of the information, in fact, you can use everything that was found, information from open sources as ruled interchangeably. However, it should be noted that even just information obtained from the OSM resource is enough to make an analysis of an unfamiliar territory.
Analysis of the territory using the "thermal" model. Physical interpretation of potentials
As it was said earlier, the analysis of the territory today is a topical issue and a powerful tool for reasoned attraction of investments in the development of infrastructure of various urban environments.
A variety of tasks solved by conducting territory analysis can be combined into several major areas:
- Getting the most interpretable and detailed assessment of the territory at each point.
Solving the task, you can get a set of point estimates at each point of the territory, giving an idea of the level of development of the territory in general, as well as in a certain subject area. This subject area may be, for example, culture, industry, trade, etc.
- Determination of the most profitable places for placing investment objects of a certain type (for example, banks, specialized stores, shopping and entertainment centers, etc.) in a selected area.
- Analysis of the most efficient use of the territory.
This direction allows for a detailed study of the characteristics of the territory, the market situation prevailing in the study area, the identification of popular options.
- Determining the contribution of one factor to the cost model, for example, the emergence of new roads and new routes.
- Analysis of different aspects of one territory and analysis of different territories (comparison of territories).
The originality of the territory analysis method proposed in the article with the use of a “thermal” model consists in using the territory development indicators - potentials presented in numerical terms and reflecting the degree of the object’s influence (factor of influence) on the territory.
To understand the essence of the study, it is necessary to say a few words about the thermal potential itself, to give its physical interpretation.
In physics, there are such concepts as the force field and the force function . The force field has the dimension of energy, the force function is the dimension of force.
For the law of the world, the force field is defined by the formula:
where
k is a constant;
r is the distance between interacting objects.
The strength function ϕ is defined by the expression:
where
ϕ is the potential of the force field;
dϕ, dr - differentials;
r is the distance between interacting objects,
Consequently .
The physical meaning of the potential of the force field ϕ is the work E performed by the force field while passing a certain path. In the case of the law of universal perception when changing the distance to the object from r2 to r1, the force function is determined by the formula
where
E - the work done by the force field when passing a certain path;
r1, r2 - the initial and final position of the object.
For the task of analyzing a territory, the influence of objects (factors) on a territory can be viewed as a force ( power function ), and the level of development of a territory, as a total thermal potential ( force field ) of all objects (factors). In problems of physics, thermal potential is temperature, and in problems of analysis of territories using the “thermal” model, potential represents the total effect of all factors influencing a point of a territory.
Spatial data is points, lines, polygons. For the calculation of potentials, extended spatial data is divided into small fragments. For each fragment, the potential is calculated from a point with a multiplier equal to the size of the object fragment (factor).
Data is divided into semantic groups according to the principle of close similarity. For example, objects of trade are combined by goods. There are groups of forest objects, water objects, settlements, transport stops, etc. Combined within the meaning of the group represent a factor. Having passed through all the objects (factors), we obtain a set of thermal potentials suitable for further processing.
The use of potentials ("heat maps") allows you to move from spatial data to "thermal" images of objects (factors) of influence on the territory (visualization of potentials). Such a transition makes it possible to determine the degree of presence of the factor at each point of the territory and conduct further analysis, i.e. display different directions of development of the city in color. Thus, we obtain a glow of varying intensity for each point of the territory.
Examples of "thermal" images of the territory of Nizhny Novgorod in the context of several factors are presented below.
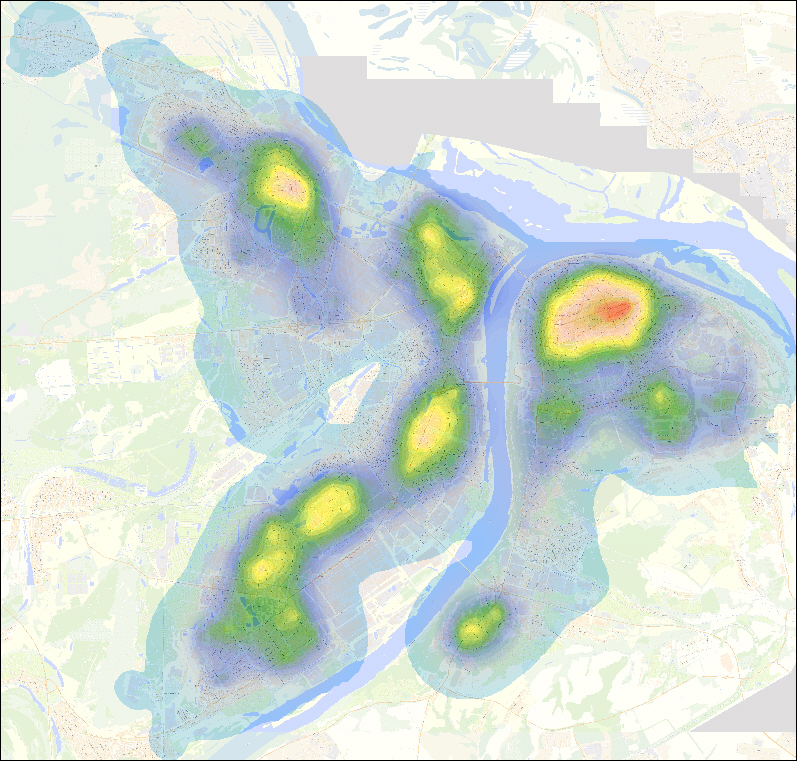
"Heat" map of N.Novgorod, reflecting the factor "Pharmacy chain"
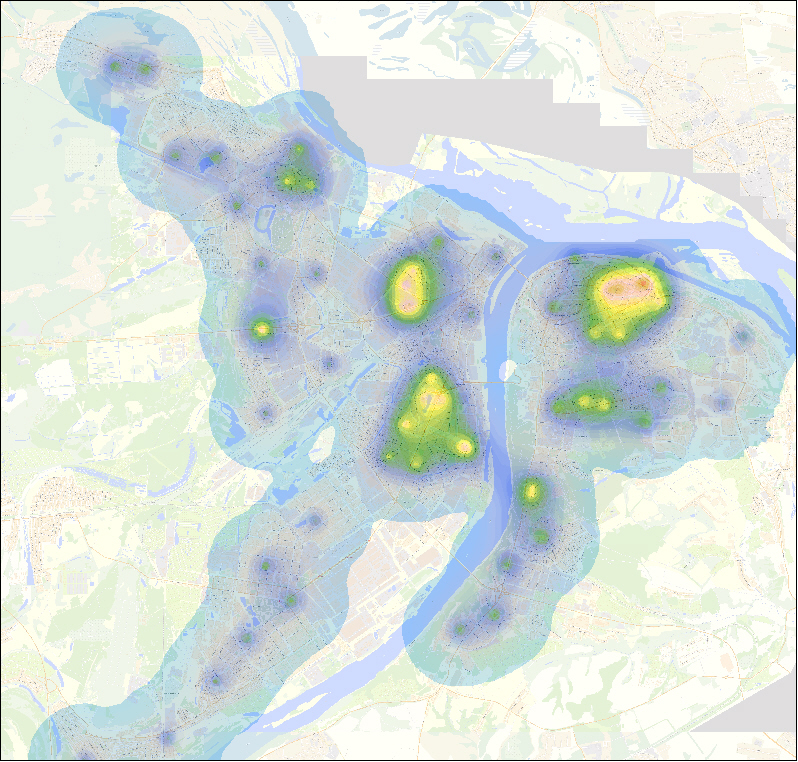
"Heat" map of N.Novgorod, reflecting the factor "Polyclinics for adults"
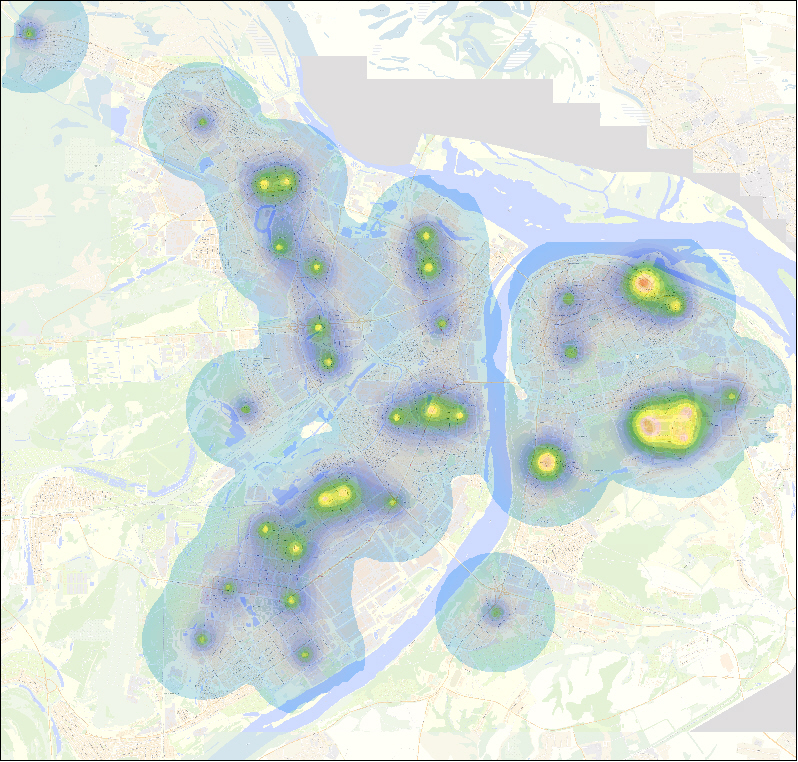
"Heat" map of N.Novgorod, reflecting the factor "Children's clinics"
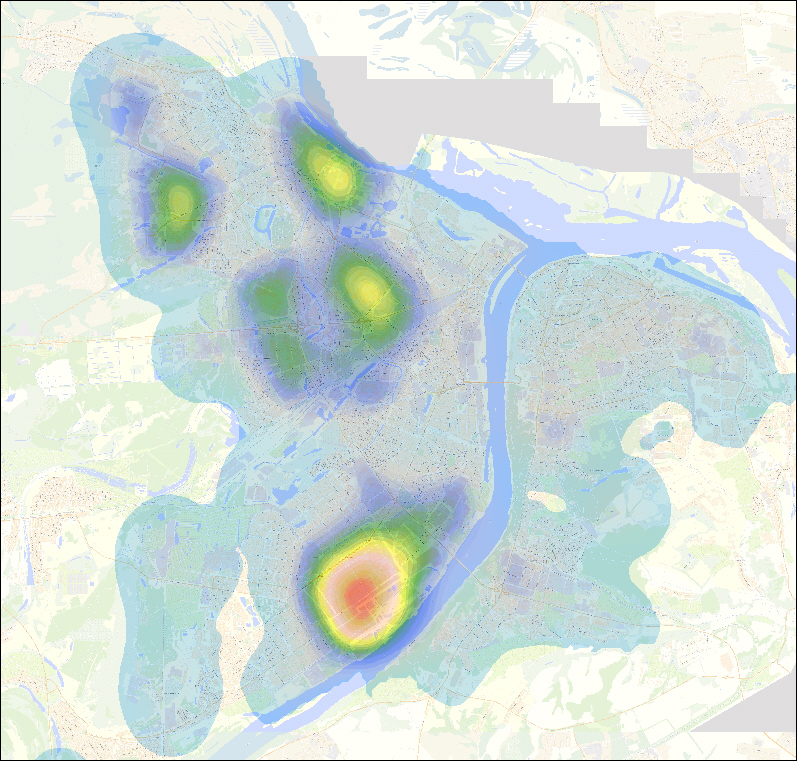
"Heat" map of N.Novgorod, reflecting the factor "Industrial zones"
“Thermal” images of the territory allow determining the concentration of potentials from various objects of influence. Next, it is necessary to combine the obtained potentials into an integral characteristic, which makes it possible to assess the territory by a large number of factors. This requires a method that allows you to analyze a large amount of information, to recognize objects, and also to reduce the dimension of the data, losing the least amount of information. One of such methods is the principal component analysis method (Principle component analysis, PCA). More information about this method can be found in Wikipedia .
The essence of the method is to find a linear combination of initial parameters, the most strongly changing in the field of analysis. For spatial data, it is the most varying by territory.
The method of principal components identifies objects (factors) that most strongly vary over a territory. As a result of the work of the method, new variables appear - the main components, which are more informative in comparison with the original data, with the help of which it is easier to analyze, describe and visualize the territory, on which it is easier to build models.
The main components are analytical expressions - the sum of the potentials of the original factors with some coefficients. However, if a factor has a significant impact on the territory, but does not change over the analyzed territory, the method of principal components will not include this factor in the composition of the principal components.
The main components are ordered by decreasing information - i.e. spread over the territory. The first main components carry much more information than individual factors and describe the territory well. As a rule, when using about a hundred factors, the first main component carries about 50% of all information (dispersion) over a territory. The main components do not correlate with each other and can be used for models as characteristics of the territory at each point.
The main component, as some abstractly calculated territory indicator, does not have a clear name and classification. However, a combination of factors strongly correlated with the main component allows the main components to be interpreted. As a rule, the following factors correlate with the main components:
- the level of infrastructure development;
- transport component of the territory;
- climatic zones;
- the level of development of agriculture;
- economic potential of the territory.
Further analysis, including clustering, comes with several first significant major components.
In the figures you can see a graphic display of the first major components in several cities of the Russian Federation.
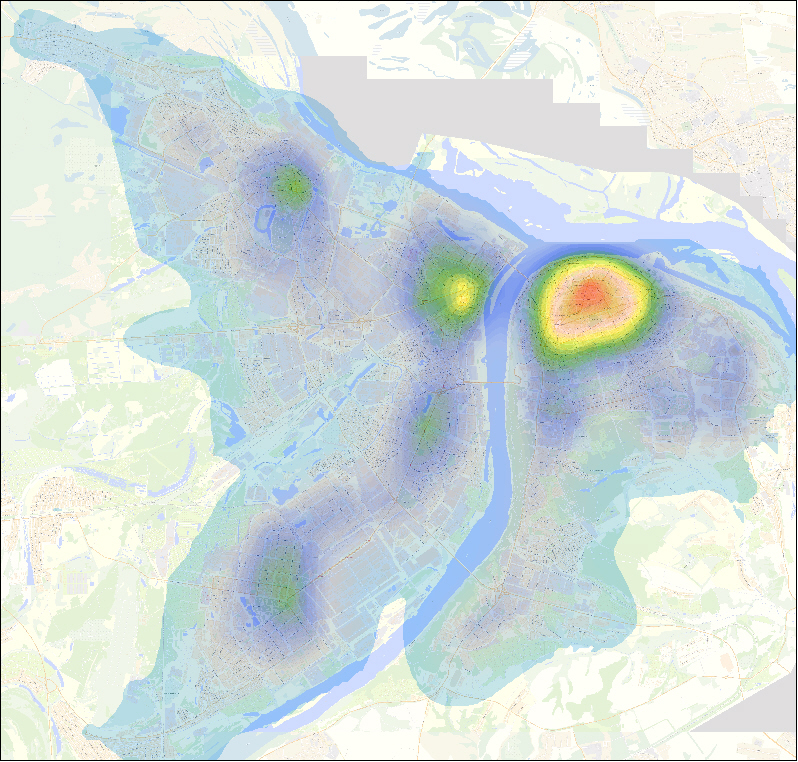
The first main component characterizing the level of development of urban infrastructure in the city of N. Novgorod
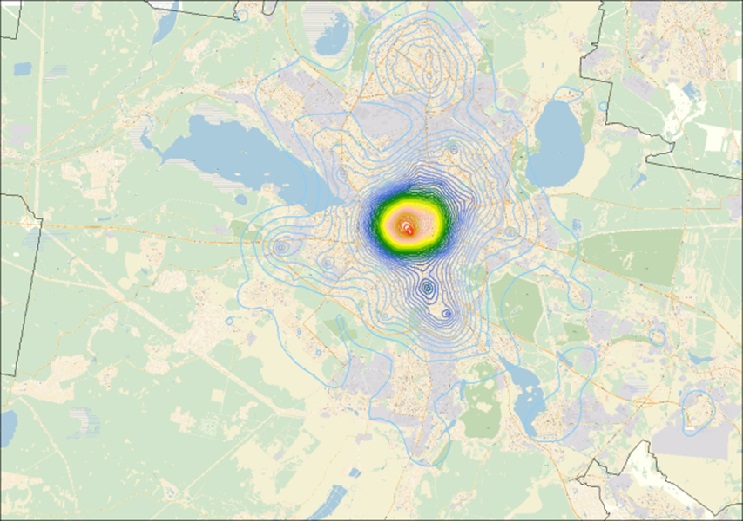
The first main component characterizing the level of development of the urban infrastructure of Yekaterinburg
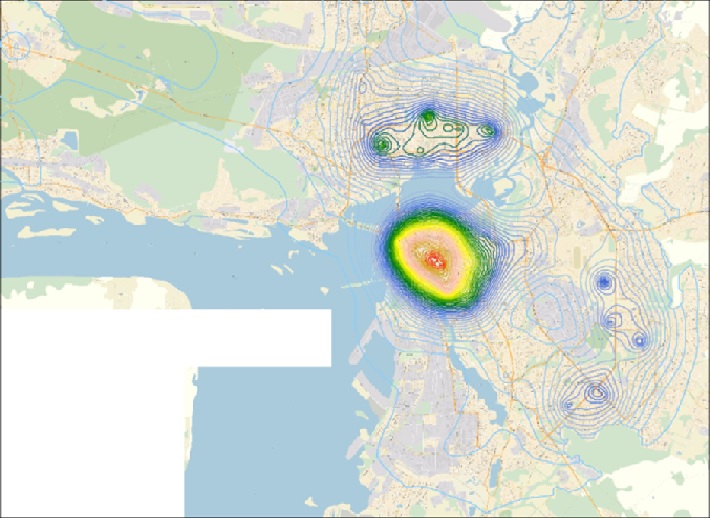
The first main component characterizing the level of development of the urban infrastructure of Kazan
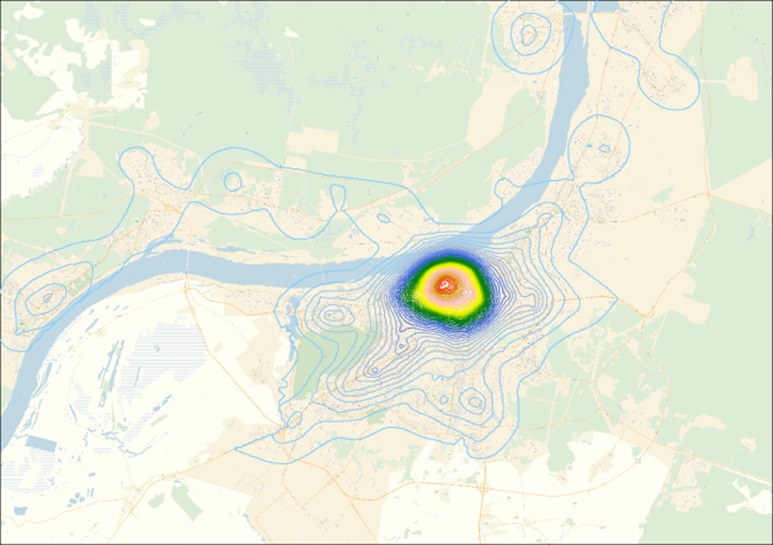
The first main component characterizing the level of development of the urban infrastructure of Perm
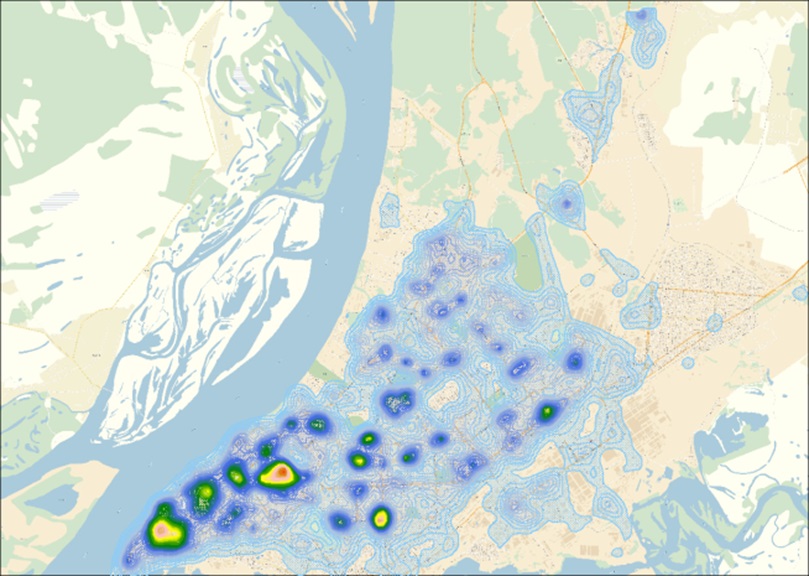
The first main component characterizing the level of development of urban infrastructure of the city of Samara
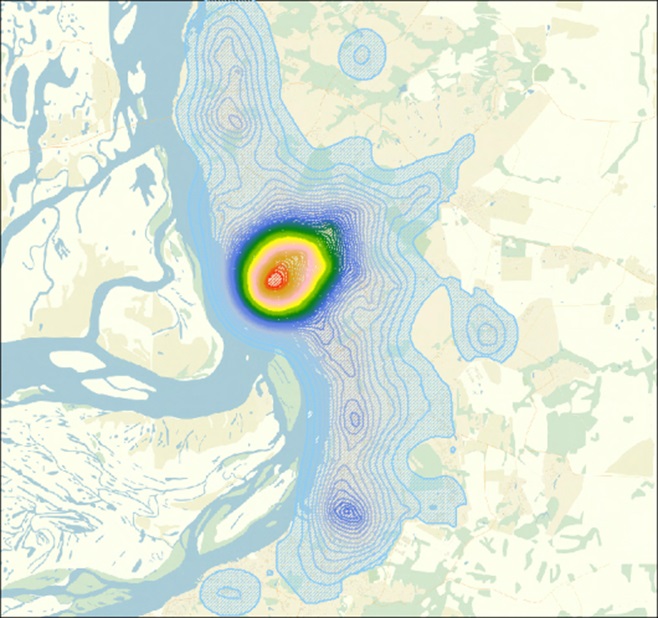
The first main component characterizing the level of development of the urban infrastructure of Khabarovsk
Integral characteristics: clustering
The next stage of work on the analysis of territories is a search for urban areas of uniform quality. This search is based on the analysis of the values of the main components at each point of the territory. The task of searching for these homogeneous zones can be solved using clustering - the process of grouping territories according to the principle of proximity of a set of characteristics.
The clustering of the territory has two goals:
- creating a better perceived visualization of the territory;
- selection of areas for the compilation of individual models.
Territories are clustered according to selected factors for analysis. These factors may be factors affecting pricing or factors describing some aspect of the development of a territory, for example, the social sphere.
There are two common classical clustering methods: the K-means method and the dendrogram method. When working with the territories, the K-means method has proved itself well, the peculiarity of which is to “grow” the cluster by attaching new objects to the growth points. The advantages of the K-means method are in the similarity of its work to the natural process of the formation of territories: the integration of similar ones, and not the separation of dissimilar ones.
The K-means method was used to calculate Nizhny Novgorod (figure below).
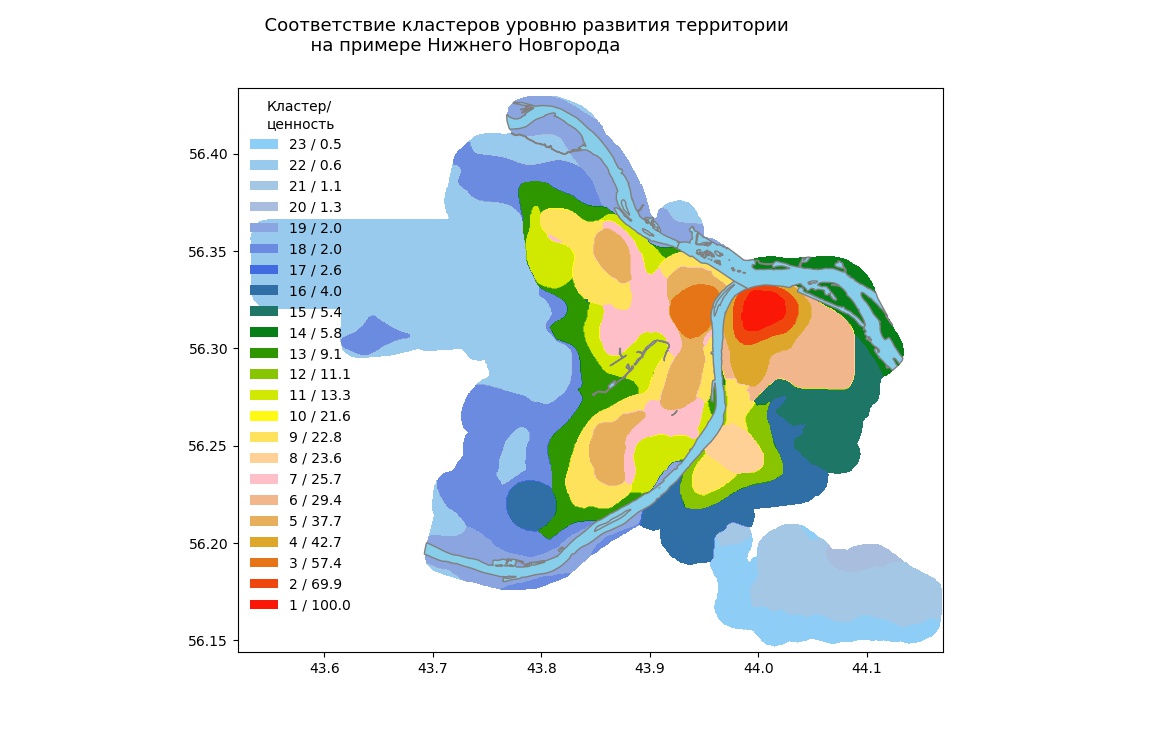
Correspondence of clusters to the level of development of the territory on the example of N.Novgorod
With the proposed approach, you can get an idea of the territory on various topics. Topics of interest to us can be, for example, the level of development of urban infrastructure, the level of “elitism” of a territory, the level of cultural development, the social component of a territory’s development. These topics are poorly defined integral concepts, and consist of many interrelated factors.
With a certain algorithm for the selection of parameters for analysis (including with the involvement of experts), we will receive thematic maps that give an idea of one aspect of the development of a territory.
The integral characteristics are understood as the first main components, first of all the most informative first main component, and the territory clustering according to the selected parameters.
Thematic maps of the first major components in various aspects of development are presented in the figures below.
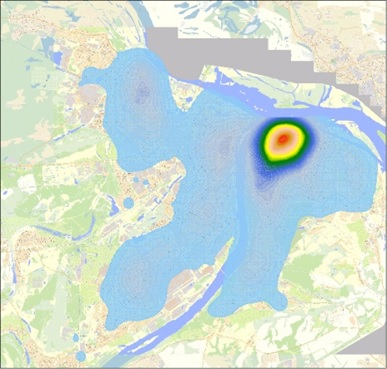
Thematic map "Objects of Culture" on the example of N.Novgorod
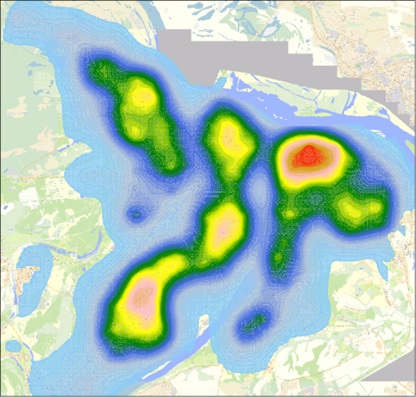
Thematic map "Social sphere" on the example of the city of Nizhny Novgorod
Integral characteristics make it possible to understand the characteristics of the territory, operating with many factors with minimal loss of information.
In conclusion, it is worth noting once again that today the analysis of territories is an extremely important stage in solving the problems of developing the urban environment, choosing places to invest in construction, finding the most advantageous location of new objects and other tasks.
The proposed method for analyzing a territory using a “thermal” model from factors of a different nature is not critical to a set of factors, that is, it does not impose restrictions and requirements on the initial information.
The diversity and redundancy of the source information, as well as the ability to use open data, provides unlimited prospects for the analysis of any territories of the world.
In the following publications, devoted to the problems of territory analysis, we plan to reveal the features of modeling with the use of main components and methods for their implementation for such tasks as:
- selection of the best place when placing a new object;
- building a price surface for a certain category of objects using market value;
-evaluation of the profitability of a certain type of activity depending on the location of objects.
We also plan to present methods for the reverse transition from the main components to the factors, which in turn allows us to obtain a model from the factors for a given territory.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/446222/
All Articles