CRM-systems: protection or threat?
March 31 is the international day of backup, and the week before is always full of security related stories. On Monday, we already learned about the compromised Asus and the "three unnamed manufacturers." Particularly superstitious companies sit on pins and needles all week long, make backups. And everything comes from the fact that we are all a bit careless in terms of security: someone forgets to fasten the belt in the back seat, someone ignores the shelf life of the products, someone stores the username and password under the keyboard, and even better records all the passwords in a notebook. Individuals manage to disable antiviruses, "so as not to slow down the computer" and not use the separation of access rights in corporate systems (what secrets in a company of 50 people!). Probably, humanity just has not yet developed the cyber-preservation instinct, which, in principle, can become a new basic instinct.
Not developed such instincts and business. A simple question: Is a CRM system a threat to information security or a security tool? It is unlikely that someone just like that immediately answer. Here we need to start, as we were taught in English classes: it depends ... It depends on the settings, the form of delivery of CRM, vendor habits and beliefs, the degree of disregard for the staff, the proficiency of the attackers. In the end, you can hack everything. So how to live?

Protect data on commercial and operating activities and securely store the customer base is one of the main tasks of a CRM system, and in this it is more important than all the other application software in the company.
')
Surely you began to read this article and in the depths of your heart grinned, saying, who needs your information. If so, then you probably have not dealt with sales and do not know how much demand for "live" and high-quality customer databases and information about how to work with this database. The content of a CRM system is interesting not only for the company's management, but also for:

Such is information security in small and medium business.
If someone fits into your CRM, he will get access to your operating activities, that is, to the array of data with which you make the most of the profits. And from the moment the malicious access to the CRM-system is received, the profit begins to smile at who is in the hands of the client base. Well, or its partners and customers (read - new employers).
A good, reliable CRM system is able to close these risks and give a bunch of nice security bonuses.
(we tell on the example of RegionSoft CRM , since we cannot be responsible for others)
 Clickable
Clickable
This is the implementation of security on the example of a single system, each vendor has its own policies. However, the CRM-system really protects your information: you can see who and what time shot this or that report, who viewed what data, who did the upload and much more. Even if you find out about the vulnerability after the fact, you will not leave the act unpunished and easily calculate the employee who has abused the trust and loyalty of the company.
Relaxed? Early! This very protection with negligence and disregard for data protection issues may play against you.
If your company has at least one PC, this is already a source of cyber threats. Accordingly, the degree of threat multiplies with the increase in the number of workstations (and employees) and with the variety of installed and used software. And with the CRM-systems, the situation is not easy - after all, this is a program designed to store and process the most important and expensive asset: the customer base and commercial information, and we are talking about its security here. In fact, not everything is so gloomy near, and with the right treatment, you will not get anything from the CRM system, except for use and security.
Let's start with a little excursion to the basics. CRM are cloud and desktop. Cloud are those whose DBMS (database) is located not in your company, but in a private or public cloud in some data center (for example, you are sitting in Chelyabinsk, and your base is spinning in a super cool data center in Moscow, because the vendor of the CRM decided so and he has an agreement with this provider). Desktop (they are also on-premise, server-side - which is not so true) base their DBMS on your own servers (no, no, don't draw yourself a huge server with expensive racks, most often in a small and medium business it’s a single server or even PC modern configuration), that is, physically in your office.
You can get unauthorized access to CRM of both types, but the speed and ease of access are different, especially if we are talking about an SMB that doesn’t care much about information security.
The reason for the higher likelihood of problems with data in the cloud system is the relationship connected by several links: you (CRM tenant) are a vendor provider (there is a longer version: you are a vendor IT vendor outsource provider). 3-4 levels of relationship have more risks than 1-2: a problem can occur on the vendor’s side (contract change, non-payment of the provider’s services), on the provider’s side (force majeure, hacking, technical problems), on the outsourcer’s side (manager change or engineer), etc. Of course, large vendors are trying to have backup data centers, manage risks and keep their DevOps department, but this does not eliminate problems.
Desktop CRM is basically not rented, but purchased by the company, and accordingly the relationship looks more simple and transparent: the vendor adjusts the necessary security levels during the implementation (from the distinction between access rights and a physical USB key to placing the server on a concrete wall, etc.) and transfers control to the CRM company that can increase protection, hire a system administrator, or contact your software vendor as needed. Problems come down to working with employees, protecting the network and physically protecting information. In the case of desktop CRM, even a complete shutdown of the Internet will not stop work, since the base is located in the "native" office.
About cloud technology tells one of our employees, who worked in the company-developer of integrated cloud office systems, including CRM. “At one of my jobs, the company created something very similar to basic CRM, and all this was related to online documents, etc. Once in GA, we saw anomalous activity from one of the customer subscribers. What a surprise it was for us, the analysts, when we, not being developers, but having a high level of access, could simply click on the link to open the interface that the client used, to see what kind of a tablet he had. By the way, it seems the client would not want someone to see this commercial data. Yes, it was a bug, and it was not eliminated for several years - in my opinion, it’s still there. Since then, I am an adept of the desktop and do not really trust the clouds, although, of course, we use them in work and in personal life, where funny packs happened too. ”
From our survey on Habré, and these are employees of advanced companies
Loss of data from a cloud-based CRM system may be due to data loss due to server failure, server inaccessibility, force majeure, vendor activity termination, and so on. The cloud is a permanent, uninterrupted access to the Internet, and protection must be unprecedented: at the level of code, access rights, additional measures of cybersecurity (for example, two-factor authentication).
It is not even a single sign, but a group of signs related to the vendor and its policies. Let us list some important examples that we and our employees had to meet.
Typically, these problems are associated with small or young vendors, however, the large ones have repeatedly found themselves in unpleasant stories (google it). Therefore, you should always have ways of protecting information on your side + discuss security issues with a selected CRM system provider in advance. Even the very fact of your interest in the problem will already force the supplier to take implementation as responsibly as possible (it is especially important to do so if you are dealing not with the vendor’s office, but with its partner, which is important to conclude an agreement and receive a commission, and not your two-factor ones ... well did you understand).
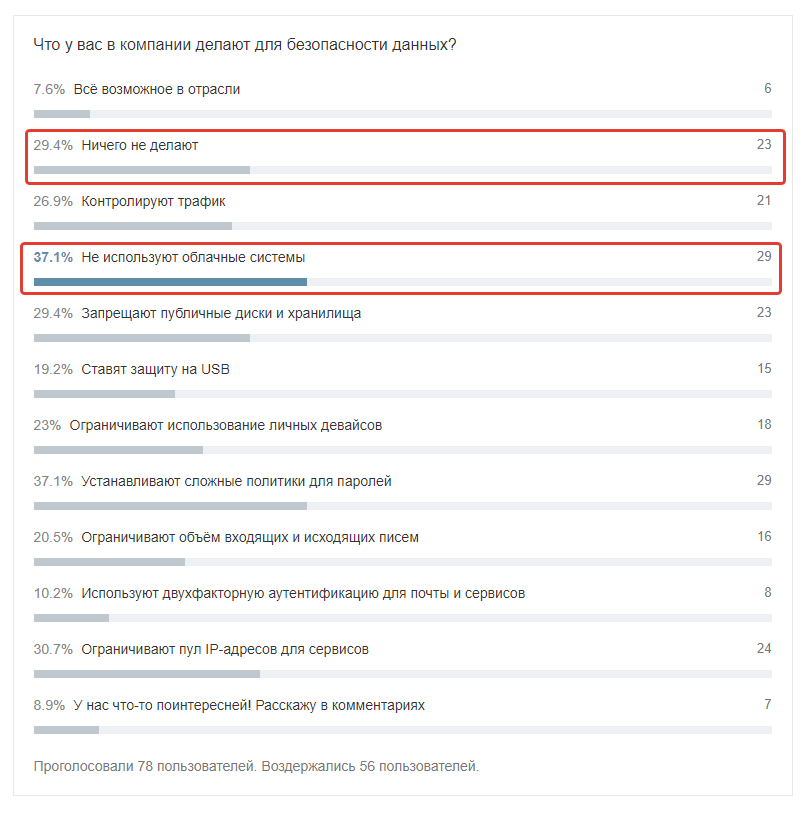
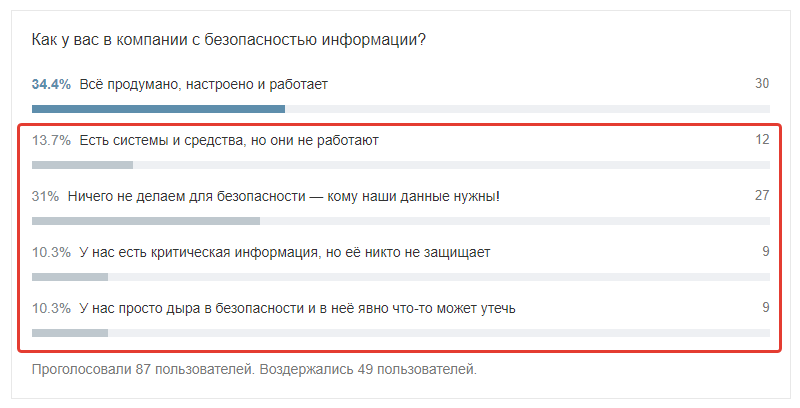
Organization of work with security in your company. A year ago, we traditionally wrote about security in Habré and conducted a survey. The sample was not very large, but the answers are indicative:
At the end of the article we will give links to our publications, where we analyzed in detail the relations in the “company-employee-security” system, and here we give a list of questions that you should find answers within your company (even if you don’t need CRM).
In fact, these are basic questions - in the comments they will certainly add hardcore, but this is a base, the basics of which even an individual entrepreneur with two employees should know.
Of course, using a cloud system, you can achieve a sufficient level of security: use dedicated servers, configure routers and separate traffic at the application and database levels, use private subnets, introduce strict security rules for administrators, ensure uninterrupted backup by backing up as much as possible. and completeness, to carry out round-the-clock monitoring of the network ... If you think about it, it’s not that difficult, rather expensive. But, as practice shows, such measures are taken only by some companies, mostly large ones. Therefore, do not hesitate to say it again: the cloud and the desktop should not live by themselves, protect your data.
These are trifles, but they perfectly complete the big picture. And, in fact, there are no safety details.
By implementing a CRM system, you ensure the security of your data - but only if the implementation is carried out correctly, and information security issues are not overshadowed. Agree, it is foolish to buy a car and not check the brakes, ABS, airbags, seat belts, EDS. After all, the most important thing is not just to drive, but to drive safely and get there safe and sound. The business is the same.
And remember: if safety rules are written in blood, business cybersecurity rules are written in money.
On the topic of cybersecurity and the place of the CRM system in it you can read our detailed articles:
 Our channel in Telegram , in which without advertising we write not quite formal things about CRM and business.
Our channel in Telegram , in which without advertising we write not quite formal things about CRM and business.
Not developed such instincts and business. A simple question: Is a CRM system a threat to information security or a security tool? It is unlikely that someone just like that immediately answer. Here we need to start, as we were taught in English classes: it depends ... It depends on the settings, the form of delivery of CRM, vendor habits and beliefs, the degree of disregard for the staff, the proficiency of the attackers. In the end, you can hack everything. So how to live?

CRM-system as protection
Protect data on commercial and operating activities and securely store the customer base is one of the main tasks of a CRM system, and in this it is more important than all the other application software in the company.
')
Surely you began to read this article and in the depths of your heart grinned, saying, who needs your information. If so, then you probably have not dealt with sales and do not know how much demand for "live" and high-quality customer databases and information about how to work with this database. The content of a CRM system is interesting not only for the company's management, but also for:
- Attackers (less often) - they have a goal related specifically to your company, and will use all the resources to get data: bribing employees, hacking, buying your data from managers, interviewing managers and so on.
- Employees (more often) who can act as insiders for your competitors. They are just ready to take with them or sell the customer base for their own profit.
- Hackers-lovers (quite rarely) - you can get under the hacking of the cloud, where your data is located or hacking the network, or maybe someone will want to “pull out” your data for fun (for example, data on wholesalers of pharmacy or alcohol - just interesting to see ).

Such is information security in small and medium business.
If someone fits into your CRM, he will get access to your operating activities, that is, to the array of data with which you make the most of the profits. And from the moment the malicious access to the CRM-system is received, the profit begins to smile at who is in the hands of the client base. Well, or its partners and customers (read - new employers).
A good, reliable CRM system is able to close these risks and give a bunch of nice security bonuses.
So what can a CRM system do in terms of security?
(we tell on the example of RegionSoft CRM , since we cannot be responsible for others)
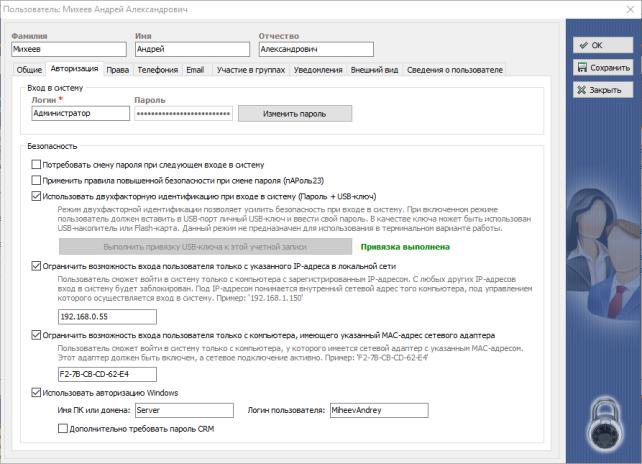
- Two-factor authentication with a USB key and password. RegionSoft CRM supports two-factor user authentication mode at login. In this case, when entering the system, in addition to entering the password, it is necessary to insert a USB key that was previously initialized into the USB port of the computer. Two-factor authentication mode helps to hedge against theft or disclosure of the password.

- Run from trusted IPs and MAC addresses. For enhanced security, you can restrict users from logging on to their registered IP addresses and MAC addresses only. As IP-addresses can be used as internal IP-addresses in the local network, and external addresses, if the user connects remotely (via the Internet).
- Domain authorization (Windows authorization). System startup can be configured so that when you log in, you do not need to enter a user password. In this case, Windows authorization occurs, which identifies the user using WinAPI. The system will be started under the user under whose profile the computer is running at the time the system is started.
- Another mechanism is private clients . Private clients are clients that only their curator can see. In the lists of other users, these clients will not be displayed, even if other users have a full set of permissions, including administrator rights. In this way, you can protect, for example, a pool of critical clients or a group on another basis, which will be entrusted to a trusted manager.
- The mechanism of separation of access rights is a standard and primary measure of protection in CRM. To simplify the process of administering user rights, in RegionSoft CRM, rights are assigned not to specific users, but to templates. And the user is assigned to one or another template with a certain set of rights. This allows each employee - from a novice and intern to a director - to assign powers and access rights that will allow / not allow them to access confidential data and important commercial information.
- Automatic data backup system (backups) , customizable using the RegionSoft Application Server script server .
This is the implementation of security on the example of a single system, each vendor has its own policies. However, the CRM-system really protects your information: you can see who and what time shot this or that report, who viewed what data, who did the upload and much more. Even if you find out about the vulnerability after the fact, you will not leave the act unpunished and easily calculate the employee who has abused the trust and loyalty of the company.
Relaxed? Early! This very protection with negligence and disregard for data protection issues may play against you.
CRM system as a threat
If your company has at least one PC, this is already a source of cyber threats. Accordingly, the degree of threat multiplies with the increase in the number of workstations (and employees) and with the variety of installed and used software. And with the CRM-systems, the situation is not easy - after all, this is a program designed to store and process the most important and expensive asset: the customer base and commercial information, and we are talking about its security here. In fact, not everything is so gloomy near, and with the right treatment, you will not get anything from the CRM system, except for use and security.
What are the signs of a dangerous CRM system?
Let's start with a little excursion to the basics. CRM are cloud and desktop. Cloud are those whose DBMS (database) is located not in your company, but in a private or public cloud in some data center (for example, you are sitting in Chelyabinsk, and your base is spinning in a super cool data center in Moscow, because the vendor of the CRM decided so and he has an agreement with this provider). Desktop (they are also on-premise, server-side - which is not so true) base their DBMS on your own servers (no, no, don't draw yourself a huge server with expensive racks, most often in a small and medium business it’s a single server or even PC modern configuration), that is, physically in your office.
You can get unauthorized access to CRM of both types, but the speed and ease of access are different, especially if we are talking about an SMB that doesn’t care much about information security.
Hazard Sign # 1
The reason for the higher likelihood of problems with data in the cloud system is the relationship connected by several links: you (CRM tenant) are a vendor provider (there is a longer version: you are a vendor IT vendor outsource provider). 3-4 levels of relationship have more risks than 1-2: a problem can occur on the vendor’s side (contract change, non-payment of the provider’s services), on the provider’s side (force majeure, hacking, technical problems), on the outsourcer’s side (manager change or engineer), etc. Of course, large vendors are trying to have backup data centers, manage risks and keep their DevOps department, but this does not eliminate problems.
Desktop CRM is basically not rented, but purchased by the company, and accordingly the relationship looks more simple and transparent: the vendor adjusts the necessary security levels during the implementation (from the distinction between access rights and a physical USB key to placing the server on a concrete wall, etc.) and transfers control to the CRM company that can increase protection, hire a system administrator, or contact your software vendor as needed. Problems come down to working with employees, protecting the network and physically protecting information. In the case of desktop CRM, even a complete shutdown of the Internet will not stop work, since the base is located in the "native" office.
About cloud technology tells one of our employees, who worked in the company-developer of integrated cloud office systems, including CRM. “At one of my jobs, the company created something very similar to basic CRM, and all this was related to online documents, etc. Once in GA, we saw anomalous activity from one of the customer subscribers. What a surprise it was for us, the analysts, when we, not being developers, but having a high level of access, could simply click on the link to open the interface that the client used, to see what kind of a tablet he had. By the way, it seems the client would not want someone to see this commercial data. Yes, it was a bug, and it was not eliminated for several years - in my opinion, it’s still there. Since then, I am an adept of the desktop and do not really trust the clouds, although, of course, we use them in work and in personal life, where funny packs happened too. ”

From our survey on Habré, and these are employees of advanced companies
Loss of data from a cloud-based CRM system may be due to data loss due to server failure, server inaccessibility, force majeure, vendor activity termination, and so on. The cloud is a permanent, uninterrupted access to the Internet, and protection must be unprecedented: at the level of code, access rights, additional measures of cybersecurity (for example, two-factor authentication).
Sign of danger number 2
It is not even a single sign, but a group of signs related to the vendor and its policies. Let us list some important examples that we and our employees had to meet.
- A vendor can choose an insufficiently reliable data center, where customers' databases will “spin”. It will save, will not control SLA, will not calculate the load, and the result will be fatal for you.
- The vendor may deny the right to transfer the service to your chosen data center. This is a fairly common limitation for SaaS.
- A vendor may have a legal or economic conflict with the cloud provider, and then during the “clashes” backup operations or, for example, speed, may be limited.
- The backup service can be provided for a separate price. A common practice, which a CRM system client can learn about only at the moment when a backup is needed, that is, at the most critical and vulnerable moment.
- Employees of the vendor may have easy access to customer data.
- Data leakage of any nature (human factor, fraud, hackers, etc.) can occur.
Typically, these problems are associated with small or young vendors, however, the large ones have repeatedly found themselves in unpleasant stories (google it). Therefore, you should always have ways of protecting information on your side + discuss security issues with a selected CRM system provider in advance. Even the very fact of your interest in the problem will already force the supplier to take implementation as responsibly as possible (it is especially important to do so if you are dealing not with the vendor’s office, but with its partner, which is important to conclude an agreement and receive a commission, and not your two-factor ones ... well did you understand).
Sign of danger number 3
Organization of work with security in your company. A year ago, we traditionally wrote about security in Habré and conducted a survey. The sample was not very large, but the answers are indicative:

At the end of the article we will give links to our publications, where we analyzed in detail the relations in the “company-employee-security” system, and here we give a list of questions that you should find answers within your company (even if you don’t need CRM).
- Where do employees store passwords?
- How is the access to the storages organized on the company's servers?
- How is software protected with commercial and operational information protected?
- Do all employees have active antiviruses?
- How many employees have access to customer data, what level is this access?
- How many new recruits do you have and how many employees are in the process of being laid off?
- How long have you communicated with key employees and listened to their requests and complaints?
- Are printers controlled?
- How is the policy of connecting your own gadgets to a PC, as well as using Wi-Fi workers, organized?
In fact, these are basic questions - in the comments they will certainly add hardcore, but this is a base, the basics of which even an individual entrepreneur with two employees should know.
So how to protect yourself?
- Backups are the most important thing, which is often either forgotten or not taken care of. If you have a desktop system, set up a backup system with a given frequency (for example, for RegionSoft CRM this can be accomplished using the RegionSoft Application Server ) and organize proper storage of copies. If you have a cloud-based CRM, be sure to know how to work with backups before entering into a contract: you need information about the depth and frequency, storage location, cost of backup (only backups of the latest data for a period are often free, and full-featured backup security copying is carried out as a paid service). In general, there is definitely no place for economy or neglect. And yes, do not forget to check what is being restored from backups.
- Separation of access rights at the level of functions and data.
- Security at the network level - you need to allow the use of CRM only inside the office subnet, restrict access for mobile devices, prohibit working with the CRM system from home or, even worse, from public networks (coworking, cafes, client offices, etc.). Especially be careful with the mobile version - let it be only a very truncated version for work.
- Antivirus with real-time scanning is needed anyway, but in the case of security of corporate data - especially. Forbid at the politician level to disable it yourself.
- Training employees in the hygiene of cyberspace is not a waste of time, but an urgent need. It is necessary to convey to all colleagues that it is important for them not only to warn, but also to react correctly to the incoming threat. Prohibiting the use of the Internet or your mail in the office is the last century and the cause of a sharp negative, so you have to work with prevention.
Of course, using a cloud system, you can achieve a sufficient level of security: use dedicated servers, configure routers and separate traffic at the application and database levels, use private subnets, introduce strict security rules for administrators, ensure uninterrupted backup by backing up as much as possible. and completeness, to carry out round-the-clock monitoring of the network ... If you think about it, it’s not that difficult, rather expensive. But, as practice shows, such measures are taken only by some companies, mostly large ones. Therefore, do not hesitate to say it again: the cloud and the desktop should not live by themselves, protect your data.
A few small but important tips for all cases of implementing a CRM system
- Check the vendor for vulnerabilities - look for information on the combinations of the words “vulnerability Vendor Name”, “hacked into Vendor Name”, “data leakage Vendor Name”. This should not be the only parameter to search for a new CRM system, but it is just necessary to tick off the subcortex, and it is especially important to understand the causes of the incidents that occurred.
- Ask the vendor about the data center: availability, how many, how failover is organized.
- Configure security tokens in CRM, track activity inside the system and unusual surges.
- Disable the export of reports, access through the API for non-core employees - that is, those who do not need these functions for continuous activity.
- Ensure that your CRM system is configured to log processes and logging user actions.
These are trifles, but they perfectly complete the big picture. And, in fact, there are no safety details.
By implementing a CRM system, you ensure the security of your data - but only if the implementation is carried out correctly, and information security issues are not overshadowed. Agree, it is foolish to buy a car and not check the brakes, ABS, airbags, seat belts, EDS. After all, the most important thing is not just to drive, but to drive safely and get there safe and sound. The business is the same.
And remember: if safety rules are written in blood, business cybersecurity rules are written in money.
On the topic of cybersecurity and the place of the CRM system in it you can read our detailed articles:
- The main business instinct: the facets of corporate security is an overview of possible threats to security in the corporate sphere and an approximate detection scheme.
- Whether it is necessary to protect data from employees - a detailed analysis of how employees can harm your business and how they do it in the commercial sphere.
If you are looking for a CRM system, then on RegionSoft CRM until March 31, a 15% discount . If you need CRM or ERP - carefully study our products and match their capabilities with their goals and objectives. There will be questions and difficulties - write, call us, we will organize for you an individual presentation online - without ratings and puzomerok.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/445582/
All Articles