WebAuthn standard officially completed
The W3C and FIDO Alliance have announced the completion of the development of the WebAuthn password-free authentication standard , which has been in progress since 2015. Read more about it below.

/ Flickr / Mark Burnett / CC BY (photo changed)
The most common cause of data leaks in companies remain weak passwords. They are responsible for the majority of attacks - 81% of cases, according to Verizon. Those organizations that actually work on password policy spend a lot of resources on this. The Ponemon Institute argues that the total procedures for resetting and updating authentication data cost companies $ 5.2 million annually.
')
If we talk about the general situation in the field of authentication, we can refer to the data of specialists from the University of Cambridge. Back in 2010, they analyzed the security policies of 150 major sites and found that 57% of them do not use TLS. At the same time, 84% of sites allow infinitely select authentication data.
Nine years later, the situation with the spread of encryption has improved, but still causes some concerns - according to WatchGuard statistics for the third quarter of 2018, almost 21% of the 100,000 Alexa sites do not use HTTPS.
This is where the standard passwordless authentication WebAuthn comes to the rescue. He must solve the above problems. Instead of password phrases, its developers suggest using biometric data: fingerprint, retina and face.
Three entities participate in the authentication process. The first is the WebAuthn Relying Party . It is the site that the user wants to access.
The second entity is the WebAuth API . It is based on two basic methods responsible for registering and logging into the system: navigator.credentials.create () and navigator.credentials.get () . One creates access details when registering a new account and associates a pair of keys with an existing one. Another - uses known data for authorization on the site. Both methods use a secure connection to transfer information (for example, HTTPS).
The third entity is the authenticator . It manages user identities and is responsible for generating public keys of accounts.
In general, the authorization procedure on the site might look like this:
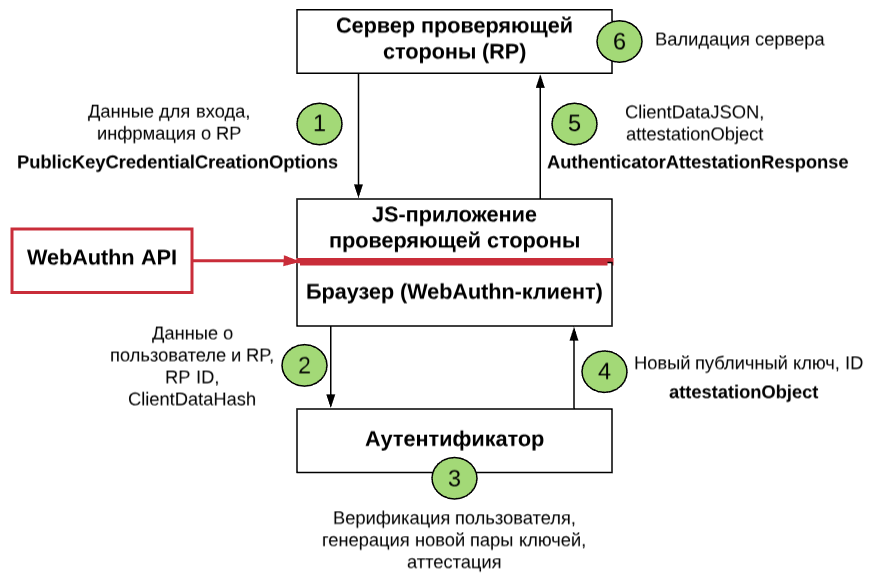
To protect against phishing, the standard uses special transactions that are tied to a specific session. If the server notices that the identifier has changed, then it understands that the request comes from fraudsters and will not confirm authorization.
According to the creators of WebAuthn, the implementation of the new standard will help get rid of passwords, and hence the vulnerabilities associated with them. FIDO Alliance senior certification engineer Yuri Ackermann says that password-free login will protect users from phishing, simplify interaction with sites and make biometric technologies more accessible.
In our blog, we published an interview with Yuri , in which we talked about web security and password-free solutions.
A number of security experts, however, are concerned about the fact that WebAuthn uses the asymmetric encryption scheme ECDAA. It is needed to create digital signatures. Paragon engineers believe that using elliptic curve based cryptography (which involves ECDAA) is not safe due to a number of potential vulnerabilities.
In Paragon also criticized the creators of the standard. Allegedly, they did not consult with leading cryptographers of the IT industry and conducted the development "covertly" without providing a standard for conducting large-scale cryptographic tests.
But despite all the above, representatives of the Paragon Initiative still believe in the prospect of password-free authentication and advocate for the massive introduction of WebAuthn.
WebAuthn is already supported in the most popular browsers and OS. Completion of work on the standard was only the first step towards the distribution of passwordless systems.

/ Flickr / Mark Burnett / CC BY (photo changed)
Why do you need a standard
The most common cause of data leaks in companies remain weak passwords. They are responsible for the majority of attacks - 81% of cases, according to Verizon. Those organizations that actually work on password policy spend a lot of resources on this. The Ponemon Institute argues that the total procedures for resetting and updating authentication data cost companies $ 5.2 million annually.
')
If we talk about the general situation in the field of authentication, we can refer to the data of specialists from the University of Cambridge. Back in 2010, they analyzed the security policies of 150 major sites and found that 57% of them do not use TLS. At the same time, 84% of sites allow infinitely select authentication data.
Nine years later, the situation with the spread of encryption has improved, but still causes some concerns - according to WatchGuard statistics for the third quarter of 2018, almost 21% of the 100,000 Alexa sites do not use HTTPS.
This is where the standard passwordless authentication WebAuthn comes to the rescue. He must solve the above problems. Instead of password phrases, its developers suggest using biometric data: fingerprint, retina and face.
How it works
Three entities participate in the authentication process. The first is the WebAuthn Relying Party . It is the site that the user wants to access.
The second entity is the WebAuth API . It is based on two basic methods responsible for registering and logging into the system: navigator.credentials.create () and navigator.credentials.get () . One creates access details when registering a new account and associates a pair of keys with an existing one. Another - uses known data for authorization on the site. Both methods use a secure connection to transfer information (for example, HTTPS).
The third entity is the authenticator . It manages user identities and is responsible for generating public keys of accounts.
In general, the authorization procedure on the site might look like this:
- The user enters the site and selects the passwordless authentication option (for example, using the phone).
- The site sends a corresponding JavaScript request to the WebAuthn client (browser).
- The browser requests the authenticator (smartphone) to generate keys and send them to the verifier.
- The server verifies login information.
- If everything is in order, the user is authorized on the site.

To protect against phishing, the standard uses special transactions that are tied to a specific session. If the server notices that the identifier has changed, then it understands that the request comes from fraudsters and will not confirm authorization.
Potential and disadvantages
According to the creators of WebAuthn, the implementation of the new standard will help get rid of passwords, and hence the vulnerabilities associated with them. FIDO Alliance senior certification engineer Yuri Ackermann says that password-free login will protect users from phishing, simplify interaction with sites and make biometric technologies more accessible.
In our blog, we published an interview with Yuri , in which we talked about web security and password-free solutions.
“WebAuthn can change the way we interact with Internet resources,” said Sergey Belkin, head of development at IaaS-provider 1cloud.ru . - Users do not have to invent and memorize passwords. However, until this point, the standard should begin to be used by website owners and application developers. It is already being implemented by Google, Dropbox, Bank of America. But before besparolnaya authentication gets widespread, it will take some time. "
A number of security experts, however, are concerned about the fact that WebAuthn uses the asymmetric encryption scheme ECDAA. It is needed to create digital signatures. Paragon engineers believe that using elliptic curve based cryptography (which involves ECDAA) is not safe due to a number of potential vulnerabilities.
In Paragon also criticized the creators of the standard. Allegedly, they did not consult with leading cryptographers of the IT industry and conducted the development "covertly" without providing a standard for conducting large-scale cryptographic tests.
But despite all the above, representatives of the Paragon Initiative still believe in the prospect of password-free authentication and advocate for the massive introduction of WebAuthn.
WebAuthn is already supported in the most popular browsers and OS. Completion of work on the standard was only the first step towards the distribution of passwordless systems.
What we write about in the corporate blog:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/445534/
All Articles