Cancer, autism and diabetes: what will AI help treat in 2019
The market for AI in medicine in 2019, according to Frost & Sullivan, will reach $ 1.7 billion. By 2021, it will grow another three times - to 6.6 billion. For information on which diseases will be treated with the help of artificial intelligence and which companies plan to capitalize on this, see the Binary District review.
A neural network that knows everything about cancer
“Watson, is there such a difficult case for me that you can advise?” - probably, the doctors could have invented an artificial intelligence invented by IBM. The IBM Watson supercomputer was created in 2011 and named after IBM’s first president, Thomas Watson. In 2014, the company invested a billion dollars in the development of this project. Now one of its modules, Watson for Oncology , is used to diagnose and treat cancer.
The main task of Watson (computer, not the president) is to understand what he is told and to look for the necessary information in natural language in the databases. In the case of Watson for Oncology, this database includes more than 600 thousand medical reports and diagnoses, as well as two million pages of texts from medical journals and clinical trials in the field of oncology.
')
On the basis of these data, the AI and the medical card of a particular patient makes a diagnosis and tells doctors how best to treat cancer in specific cases. Information about the patient enters the computer in a depersonalized form.
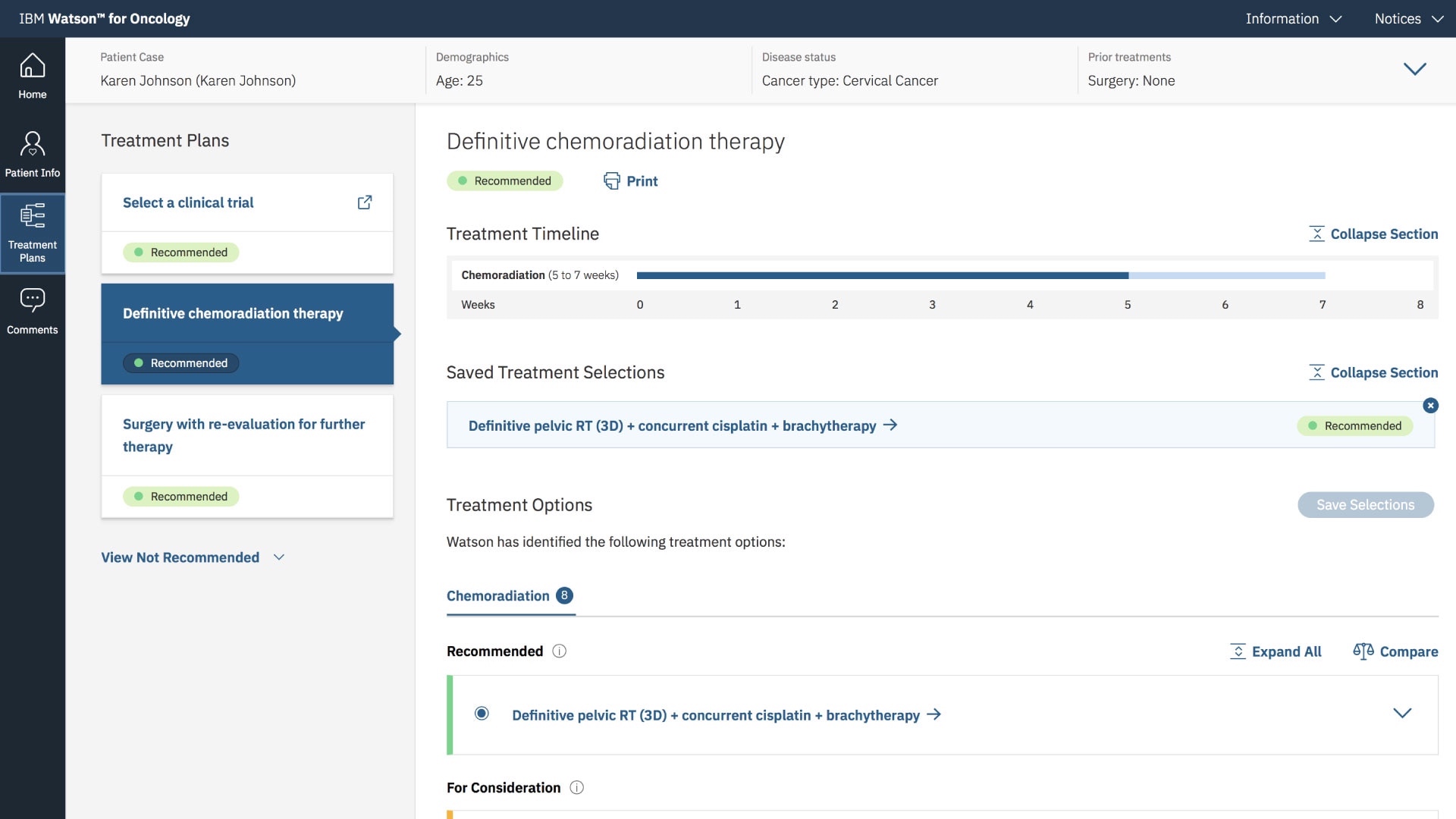
The neural network can offer several treatment options, the doctor will have to choose the best one.
The attending physician can add information to the system. For example, to write: “the patient has blood in the sputum during expectoration” - the computer will understand what was said and after 30 seconds will issue a refined diagnosis and an updated course of treatment.
In 2016, the AI identified a rare form of leukemia in a 60-year-old patient who was initially diagnosed incorrectly. To do this, the system for ten minutes studied 20 million scientific articles about cancer.
Starting in 2019, IBM Watson for Oncology will be used to treat cancer of veterans of the US Army. Other Watson modules are used to diagnose other diseases. By 2021, according to Frost & Sullivan, IBM will occupy 45% of the market for AI in medicine, which by then will amount to $ 6.6 billion.
Last May, it was reported that Sberbank would use IBM Watson in its insurance system. Then, Sberbank Life Insurance (a subsidiary of Sberbank) concluded Russia's first contract with IBM on the use of the Watson for Oncology system.

An example of a more traditional type of AI in medicine is QTrobot: a robot for treating children with autism spectrum disorders. It is difficult for such children to communicate with other people: they poorly recognize other people's emotions and express their own. With age, this problem is exacerbated. If you do not pay attention to her already in the first years of the child’s life, later it will be much more difficult for him to cope with this.
QTrobot is designed for children from the age of four. He communicates with them with words, gestures and facial expressions. Before using it, you can easily program it yourself - according to the founder, even a parent without technical skills can do it in less than 20 minutes. How to do this is shown in two short videos on the project website. With the help of a robot, you can teach your child to understand someone else's mood, to communicate and perform simple tasks - like, for example, in this video .
The startup LuxAI, which developed the robot, was created by researchers from the University of Luxembourg in 2016. The final prototype of the robot was presented a year later, and the first QTrobot test was conducted in 2018: scientists compared a therapeutic session of fifteen boys with autism between the ages of four to 14 years with a robot and a doctor. It turned out that the children pay more attention to the robot: on average, they looked at it twice as long.
The only disadvantage of QTrobot, like many other robots of this type, is its price: in 2017, the developers said that it would be 5,500 euros. While the robot, however, did not go on sale: according to the scientific portal IEEE Spectrum, it passes the test tests in medical centers in Luxembourg, France, Belgium and Germany.

JARVIS (Just Another Very Intelligent System) is a Diabnext AI diabetic diabetes platform. Named after the Iron Man's butler, Tony Stark, it serves as a complement to the CLIPSULIN system developed by the company. The system includes “smart” trackers that are mounted on an insulin pen and on a glucometer (a device for measuring blood sugar), a mobile application and a computer program for storing and analyzing records. In 2017, CLIPSULIN won the 2017 CES Innovation Award in the biotechnology category.
The system helps a diabetic keep a daily diary of his condition: fix insulin doses, eaten meals and other parameters. Diary need diabetics to control blood sugar levels. Usually, entries in it are made manually - in special notebooks or in mobile applications. After each meal, the diabetic records the approximate amount of carbohydrates it contains and the insulin dose set for them. CLIPSULIN trackers allow you to do this automatically.
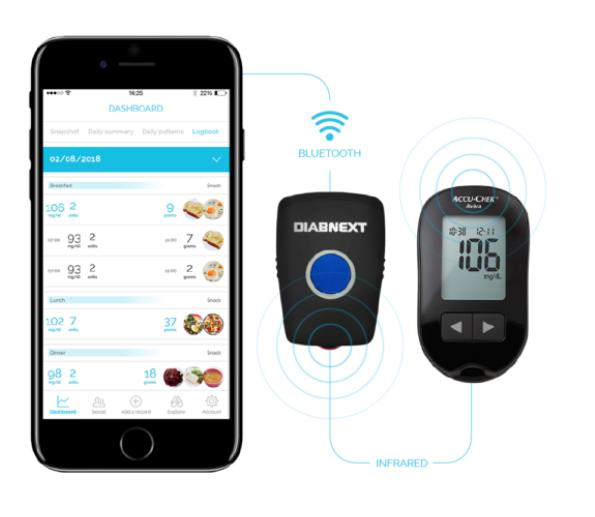
The principle of operation of the device is described in the video presented in the company's blog: a diabetic takes pictures of breakfast, and the image recognition system built into the tracker determines how much carbohydrates it contains. After that, the patient puts a dose on his insulin pen: the number of units is fixed immediately.
Another tracker connects to the meter: it can transfer data about each measurement of sugar to a mobile application and to a computer. Other parameters can also be entered into the system: standard test results, glycated hemoglobin level, weight data, exercise, and so on.
“Jarvis” at the same time can answer the user's questions and, like any neural network, it learns in the process of data collection. As the developers explain , if a person, for example, periodically eats a lot of pizza, the AI will analyze how this type of food affects the blood glucose level, and will help to calculate the insulin dose more accurately. A physician with a diabetic who is constantly observed can also access Diabnext if desired by the patient.

A neural network that knows everything about cancer
“Watson, is there such a difficult case for me that you can advise?” - probably, the doctors could have invented an artificial intelligence invented by IBM. The IBM Watson supercomputer was created in 2011 and named after IBM’s first president, Thomas Watson. In 2014, the company invested a billion dollars in the development of this project. Now one of its modules, Watson for Oncology , is used to diagnose and treat cancer.
The main task of Watson (computer, not the president) is to understand what he is told and to look for the necessary information in natural language in the databases. In the case of Watson for Oncology, this database includes more than 600 thousand medical reports and diagnoses, as well as two million pages of texts from medical journals and clinical trials in the field of oncology.
')
On the basis of these data, the AI and the medical card of a particular patient makes a diagnosis and tells doctors how best to treat cancer in specific cases. Information about the patient enters the computer in a depersonalized form.

The neural network can offer several treatment options, the doctor will have to choose the best one.
The attending physician can add information to the system. For example, to write: “the patient has blood in the sputum during expectoration” - the computer will understand what was said and after 30 seconds will issue a refined diagnosis and an updated course of treatment.
In 2016, the AI identified a rare form of leukemia in a 60-year-old patient who was initially diagnosed incorrectly. To do this, the system for ten minutes studied 20 million scientific articles about cancer.
Starting in 2019, IBM Watson for Oncology will be used to treat cancer of veterans of the US Army. Other Watson modules are used to diagnose other diseases. By 2021, according to Frost & Sullivan, IBM will occupy 45% of the market for AI in medicine, which by then will amount to $ 6.6 billion.
Last May, it was reported that Sberbank would use IBM Watson in its insurance system. Then, Sberbank Life Insurance (a subsidiary of Sberbank) concluded Russia's first contract with IBM on the use of the Watson for Oncology system.
A robot that teaches children with autism to smile

An example of a more traditional type of AI in medicine is QTrobot: a robot for treating children with autism spectrum disorders. It is difficult for such children to communicate with other people: they poorly recognize other people's emotions and express their own. With age, this problem is exacerbated. If you do not pay attention to her already in the first years of the child’s life, later it will be much more difficult for him to cope with this.
QTrobot is designed for children from the age of four. He communicates with them with words, gestures and facial expressions. Before using it, you can easily program it yourself - according to the founder, even a parent without technical skills can do it in less than 20 minutes. How to do this is shown in two short videos on the project website. With the help of a robot, you can teach your child to understand someone else's mood, to communicate and perform simple tasks - like, for example, in this video .
The startup LuxAI, which developed the robot, was created by researchers from the University of Luxembourg in 2016. The final prototype of the robot was presented a year later, and the first QTrobot test was conducted in 2018: scientists compared a therapeutic session of fifteen boys with autism between the ages of four to 14 years with a robot and a doctor. It turned out that the children pay more attention to the robot: on average, they looked at it twice as long.
The only disadvantage of QTrobot, like many other robots of this type, is its price: in 2017, the developers said that it would be 5,500 euros. While the robot, however, did not go on sale: according to the scientific portal IEEE Spectrum, it passes the test tests in medical centers in Luxembourg, France, Belgium and Germany.
"Jarvis" for "iron people" -diabetics

JARVIS (Just Another Very Intelligent System) is a Diabnext AI diabetic diabetes platform. Named after the Iron Man's butler, Tony Stark, it serves as a complement to the CLIPSULIN system developed by the company. The system includes “smart” trackers that are mounted on an insulin pen and on a glucometer (a device for measuring blood sugar), a mobile application and a computer program for storing and analyzing records. In 2017, CLIPSULIN won the 2017 CES Innovation Award in the biotechnology category.
The system helps a diabetic keep a daily diary of his condition: fix insulin doses, eaten meals and other parameters. Diary need diabetics to control blood sugar levels. Usually, entries in it are made manually - in special notebooks or in mobile applications. After each meal, the diabetic records the approximate amount of carbohydrates it contains and the insulin dose set for them. CLIPSULIN trackers allow you to do this automatically.

The principle of operation of the device is described in the video presented in the company's blog: a diabetic takes pictures of breakfast, and the image recognition system built into the tracker determines how much carbohydrates it contains. After that, the patient puts a dose on his insulin pen: the number of units is fixed immediately.
Another tracker connects to the meter: it can transfer data about each measurement of sugar to a mobile application and to a computer. Other parameters can also be entered into the system: standard test results, glycated hemoglobin level, weight data, exercise, and so on.
“Jarvis” at the same time can answer the user's questions and, like any neural network, it learns in the process of data collection. As the developers explain , if a person, for example, periodically eats a lot of pizza, the AI will analyze how this type of food affects the blood glucose level, and will help to calculate the insulin dose more accurately. A physician with a diabetic who is constantly observed can also access Diabnext if desired by the patient.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/445176/
All Articles