Intel Gen11 GPU architecture and Intel discrete graphics card
Discrete entry-level graphics card Intel Graphics Xe, the official announcement took place on March 20 at the GDC 2019 gaming conference
Intel has published documentation on Gen11 graphics processors describing how they will differ from the previous generation. It is expected that the architecture of Intel Gen11 will become the basis for the future architecture of the discrete Xe video card, so the technologies described here can be considered as a preview of at least some of the functions implemented in these video cards. So far, Intel did not tell anything about future graphics cards, it only showed a few photos (or renders).

Intel Core processor architecture, system on chip (SoC) and ring interconnect (Ring Interconnect)
Historically, Intel's mid-level GT2 graphics processors for desktops and some mobile chips were inferior in performance to those from AMD. In such comparisons, Intel has historically taken advantage of a more powerful processor than c APUs derived from the AMD Bulldozer microarchitecture. Now the situation has changed. Ryzen has a much more efficient processor core, and AMD Ryzen mobile processors are much more competitive with Intel. Therefore, the latter must do something, including to solve the problem with the performance of the GPU.
')

Gen11 block diagram
According to the technical documentation it is difficult to judge the performance of Gen11. But some experts believe that Intel will be able to more effectively compete with AMD. At least more efficient than ever before.
The new Intel GT2 architecture provides 64 instruction execution units (EU, execution unit) compared to 24 units in Skylake class processors. This significant expansion of on-chip resources should improve overall performance over the previous generation. The table below shows the comparative characteristics of the graphic subsystems Gen9 and Gen11.
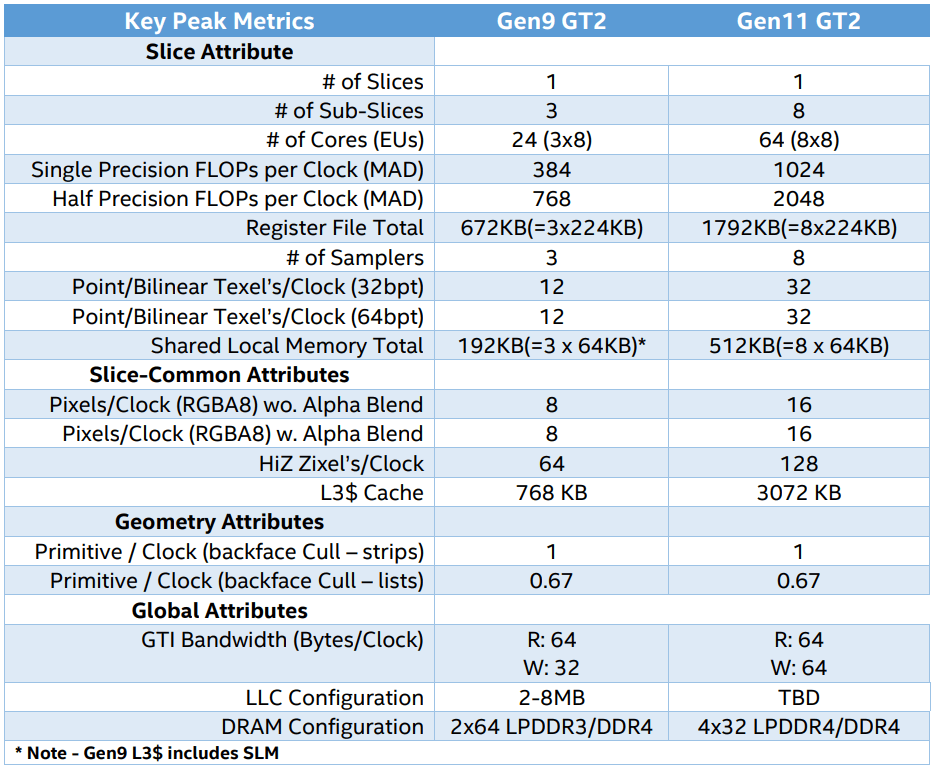
Key Gen9 and Gen11 Metrics
Based on the technical characteristics, the computing performance in Gen11 will increase by about 2.67 times, as well as the throughput for texture sampling. The bandwidth of raster operations (ROP) units has doubled, as has the number of high-Z tests per cycle.
The L3 cache has quadrupled, and the recording bandwidth of the GPU has doubled to 64 bytes per clock. Memory bandwidth when using DDR4 should remain the same, but support for LPDDR4 theoretically allows for higher clock speeds.
The last level cache is shared by the GPU and the CPU to reduce traffic as data is moved. Video decoder blocks are improved to reduce bitrate. They allow simultaneous decoding of multiple 4K and 8K streams. Added support for adaptive sync and improved HD video decoding.
Now the GPU has shared local memory that does not block access to the L3 cache when reading. Intel claims that it reduces latency and increases the efficiency of "atomic operations."
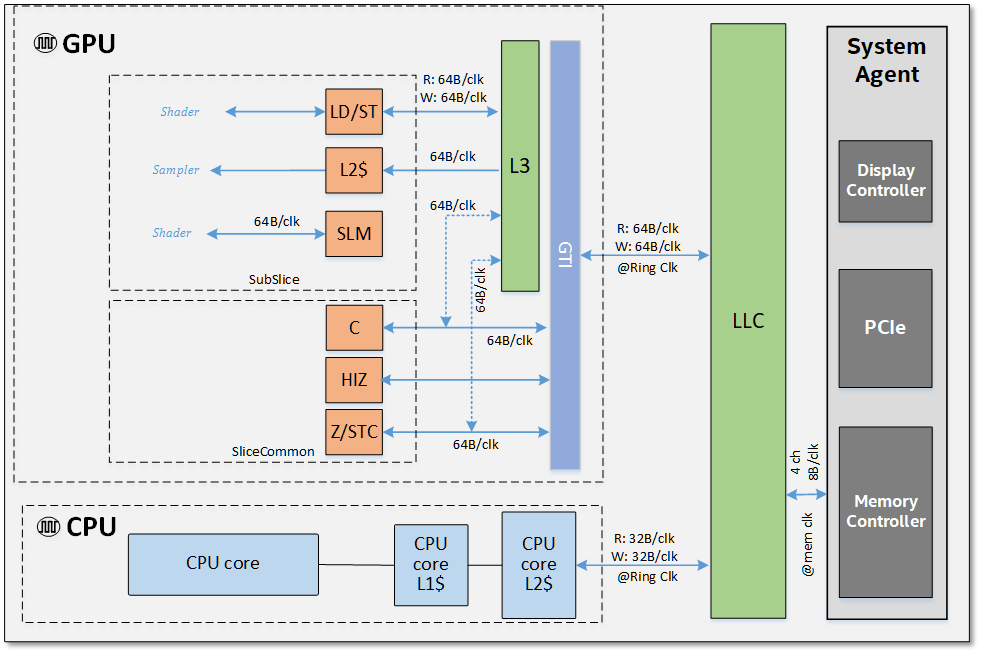
The memory hierarchy at the level of the SoC chip and its maximum theoretical bandwidth
Intel claims to significantly improve Gen11's overall memory bandwidth.
The documentation describes two new technologies that Intel has implemented in a graphics accelerator:
- coarse pixel shading (Coarse Pixel Shading, CPS);
- position shading (Position Only Shading, POSH).
Rough shading of pixels reduces the load on the GPU, reducing the number of color samples that are used to render the image. The screenshot illustrates that CPS has virtually no effect on rendering quality.
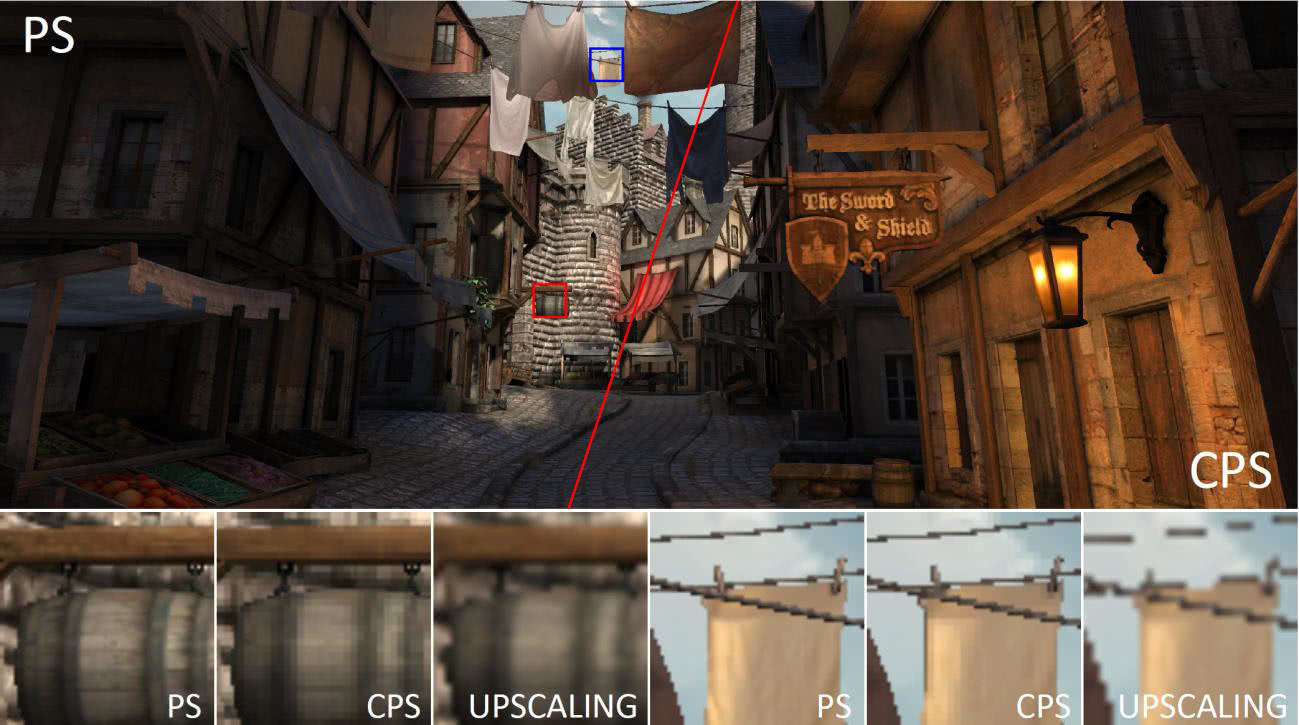

A frame from the game Citadel 1 in the resolution of 2560 × 1440 (on the left pixel rate 1 × 1, and on the right 2 × 2). Although coarse pixel shading reduces the number of shader calls, there is almost no noticeable difference on a display with a high pixel density. For comparison, it also shows a scaled image without the use of anti-aliasing, at a resolution of 1280 × 720
Reducing the number of calls to the pixel shader saves energy and improves performance, that is, the frame rate, by 20-40%.

In this image, the objects in the red frames are identified as being sufficiently distant from the camera and having little importance for the overall image quality, so the detailing can be reduced without noticeably affecting the image quality with a consequent increase in frame rate
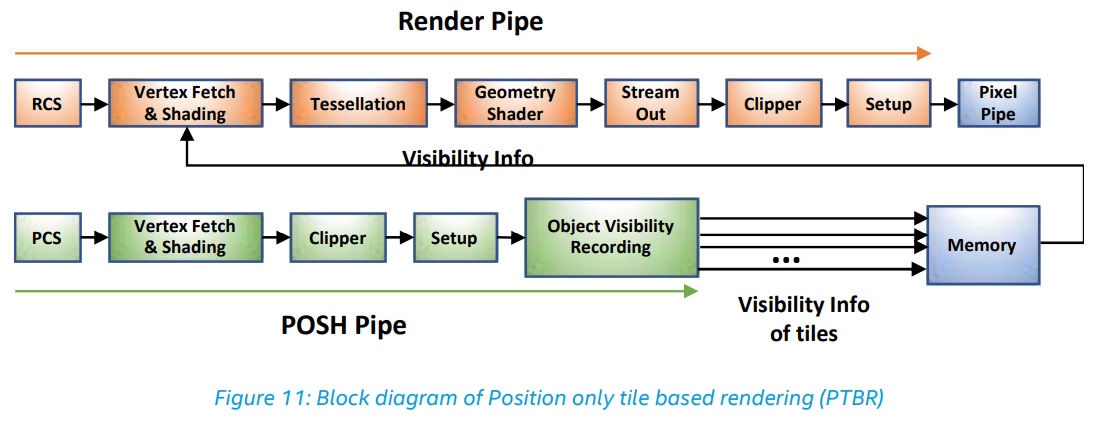
The POSH pipeline starts the position shader in parallel with the main application, which usually allows you to generate a result much faster, the documentation says. This is part of the tile positioning system (Position Only Tile-Based Rendering, PTBR).
Overall, Gen11 will be a significant upgrade for Intel processors. The first two generations of AMD Ryzen Mobile competed with weak Skylake graphics. The third generation of the Ryzen Mobile APU, whenever it comes out, will have to compete with a much more powerful Intel chip, writes the ExtremeTech edition.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/444972/
All Articles