RuNet architecture
As our readers know, Qrator.Radar tirelessly explores the global connectivity of the BGP protocol, as well as the regional one. Since the Internet is short for interconnected networks - interconnected networks, the best way to ensure high quality and speed of its work is the rich and diverse connectivity of individual networks, whose development is motivated primarily by competition.
The fault tolerance of the Internet connection in any particular region or country is related to the number of alternative routes between autonomous systems - AS. However, as we have repeatedly stated in our studies of the national sustainability of the global network segments, some of the paths become more important than others (for example, the paths to Tier-1 transit providers or AS that host authoritative DNS servers) mean that having as many alternative routes as possible is ultimately the only viable way to ensure the reliability of the system (in the sense of AS).
This time, we will take a closer look at the device of the Internet segment of the Russian Federation. There are reasons to keep an eye on this segment: according to the data provided by the RIPE registrar database, 6183 AS out of 88664 globally registered belong to the Russian Federation, which is 6.87%.
')
This percentage puts Russia in second place in the world in this indicator, immediately after the United States (30.08% of registered AS) and before Brazil, which owns 6.34% of all autonomous systems. The effects that arise as a result of changes in Russian connectivity can be observed in other countries dependent on or adjacent to this connectivity and, finally, at the level of almost any Internet service provider.
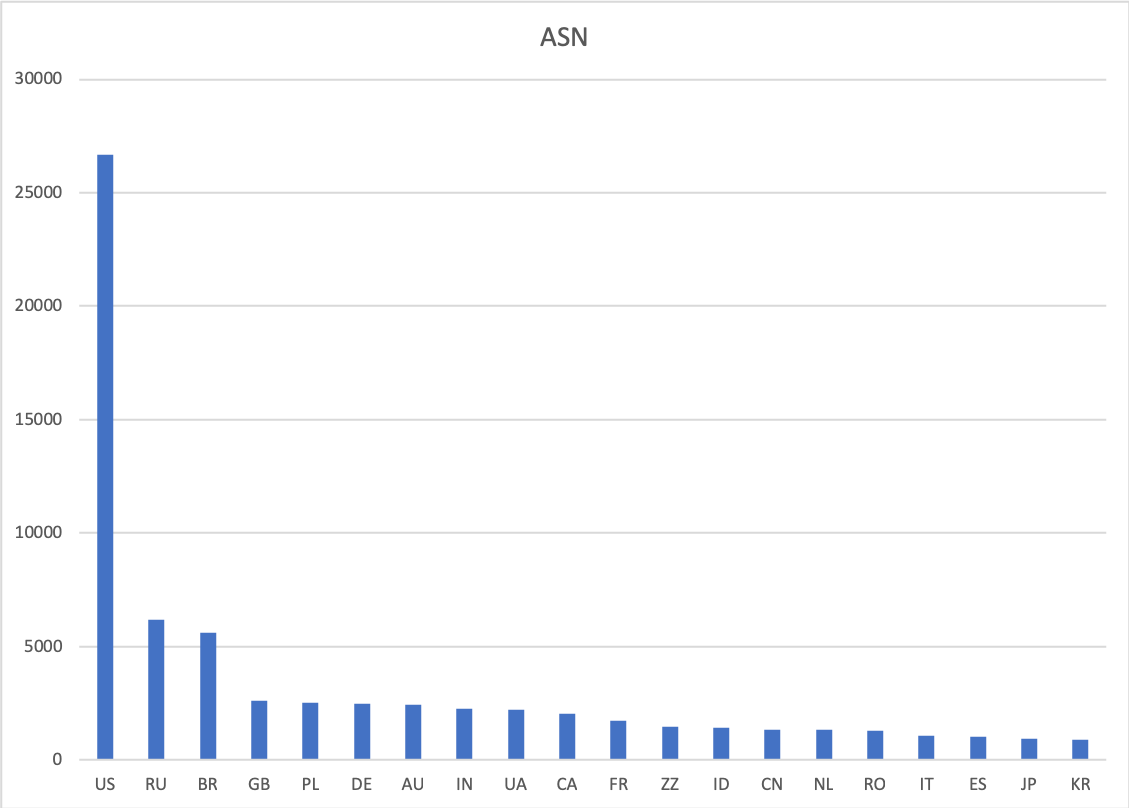
Chart 1. Distribution of autonomous systems between countries in IPv4 and IPv6, top 20 countries
In IPv4, Internet providers from the Russian Federation announce 33933 of the 774859 globally visible network prefixes, which represents 4.38% and places the Russian Internet segment in fifth place in the ranking. These prefixes, advertised exclusively from the RU segment, cover 4.3 * 10 ^ 7 unique IP addresses from 2.9 * 10 ^ 9 globally advertised - 1.51%, 11th place.
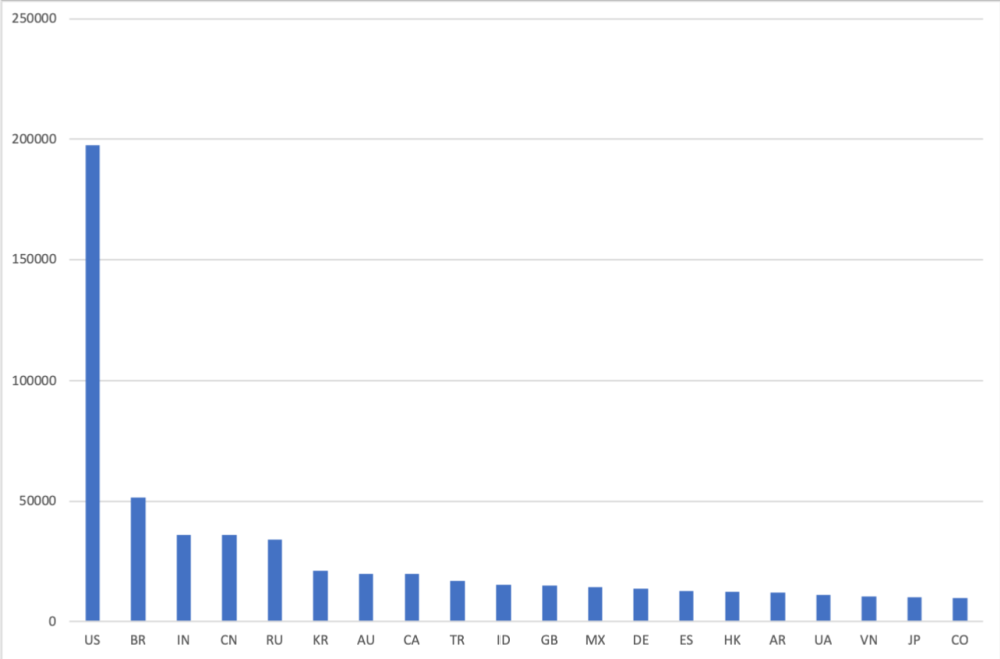
Chart 2. Distribution of network prefixes between countries in IPv4, top 20 countries
In the framework of IPv6, Internet service providers from the Russian Federation announce 1831 of 65532 globally visible prefixes, which represents 2.79% and 7th place. These prefixes cover 1.3 * 10 ^ 32 unique IPv6 addresses from 1.5 * 10 ^ 34 globally advertised - 0.84% and 18th place.
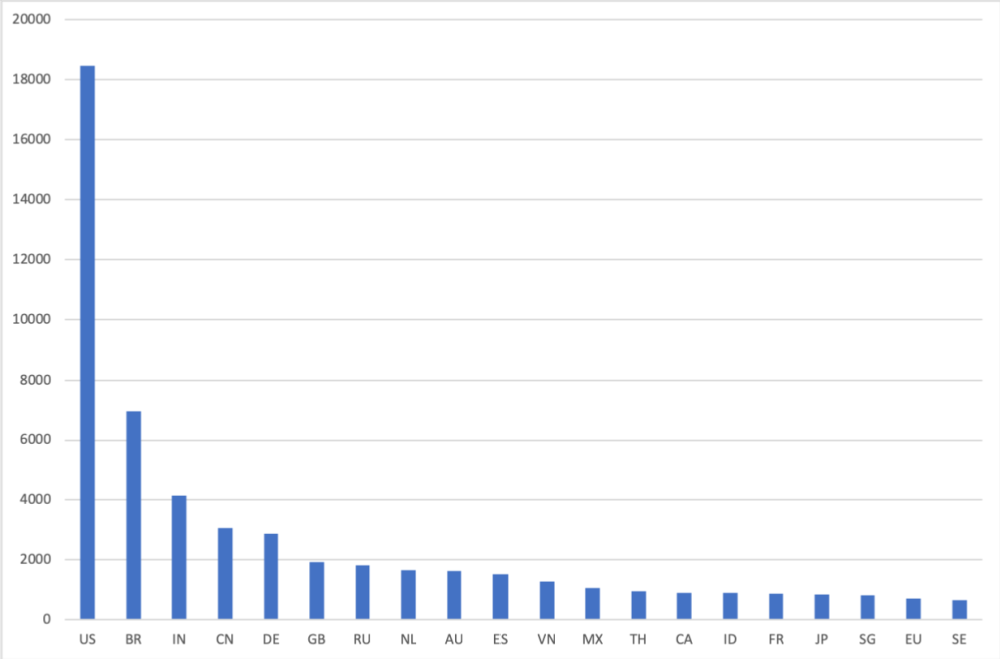
Diagram 3. Distribution of network prefixes between countries in IPv6, top 20 countries
One of the many ways to assess the connectivity and reliability of the Internet in a particular country is to rank autonomous systems belonging to a given region by the number of announced prefixes. This technique, however, is vulnerable to route deaggregation, which is gradually balanced by filtering redundantly degraded prefixes on the equipment of Internet service providers, primarily due to the constant and inevitable growth of memory-occupied routing tables.
Table 1. AS size by the number of announced prefixes
We use the aggregated size of the announced address space as a more reliable metric for comparing the sizes of autonomous systems, which determines its potential and the limits to which it can scale. This metric is not always relevant in IPv6 due to the current IPv6 RIPE NCC address allocation policy and redundancy protocol.
Gradually, this situation will be balanced by the growth in the use of IPv6 in the Russian segment of the Internet and the development of practices for working with the IPv6 protocol.
Table 2. AS size by the number of announced IP addresses
Both metrics — the number of announced prefixes and the aggregated size of the address space — are manipulable. Although we did not see such behavior from the mentioned AS during the study.
There are 3 main types of relationships between autonomous systems:
Usually, these types of relationships are the same for any two Internet providers, which is confirmed in the region of the Russian Federation under consideration. However, sometimes it happens that two Internet providers have different types of relationships in different regions, for example, exchanging for free in Europe, but having commercial relations in Asia.
Table 3. AS connectivity by the number of clients
The number of customers given by AS reflects its role as a direct provider of Internet connectivity services to commercial consumers.
Table 4. AS connectivity by the number of peering partners
A large number of peering partners can significantly improve the coherence of an entire region. Here, traffic exchange points (IX - Internet Exchange) are important, though not obligatory - the largest Internet providers usually do not participate in regional exchanges (with a few exceptions worthy of mention, such as NIXI) due to the nature of their business.
For a content provider, the number of peering partners can indirectly serve as an indicator of the volume of generated traffic - the incentive to exchange large amounts of it for free is a factor of motivation (sufficient for most local Internet providers) to see a worthy peering partner in the content provider. There are also opposite cases when content providers do not support the policy of a significant number of regional connections, which makes this indicator not too accurate for estimating the size of content providers, that is, the volume of traffic generated by them.
Table 5. AS connectivity by client cone size
The client cone is the set of all ASs that are directly or indirectly dependent on the autonomous system under consideration. From an economic point of view, each AS within the client cone is, directly or indirectly, a paying customer. At a higher level, the number of AS within the client cone, as well as the number of direct consumers, is a key indicator of connectivity.
Finally, we have prepared for you another table that looks at the connectivity up to the Runet core. Understanding the structure of the core of regional connectivity, based on the number of direct customers and the size of the client cone for each autonomous system in the region, we can calculate how far they are from the region’s largest transit Internet service providers. The lower the number, the higher the connectivity. “1” means that for all visible paths there is a direct connection with the regional core.
Table 6. AS connectivity in distance to the core of regional connectivity
What can be done to improve the overall connectivity and, as a result, the stability, reliability and security of any country, the Russian Federation in particular? Here are just some of the measures:
The fault tolerance of the Internet connection in any particular region or country is related to the number of alternative routes between autonomous systems - AS. However, as we have repeatedly stated in our studies of the national sustainability of the global network segments, some of the paths become more important than others (for example, the paths to Tier-1 transit providers or AS that host authoritative DNS servers) mean that having as many alternative routes as possible is ultimately the only viable way to ensure the reliability of the system (in the sense of AS).
This time, we will take a closer look at the device of the Internet segment of the Russian Federation. There are reasons to keep an eye on this segment: according to the data provided by the RIPE registrar database, 6183 AS out of 88664 globally registered belong to the Russian Federation, which is 6.87%.
')
This percentage puts Russia in second place in the world in this indicator, immediately after the United States (30.08% of registered AS) and before Brazil, which owns 6.34% of all autonomous systems. The effects that arise as a result of changes in Russian connectivity can be observed in other countries dependent on or adjacent to this connectivity and, finally, at the level of almost any Internet service provider.
Overview

Chart 1. Distribution of autonomous systems between countries in IPv4 and IPv6, top 20 countries
In IPv4, Internet providers from the Russian Federation announce 33933 of the 774859 globally visible network prefixes, which represents 4.38% and places the Russian Internet segment in fifth place in the ranking. These prefixes, advertised exclusively from the RU segment, cover 4.3 * 10 ^ 7 unique IP addresses from 2.9 * 10 ^ 9 globally advertised - 1.51%, 11th place.

Chart 2. Distribution of network prefixes between countries in IPv4, top 20 countries
In the framework of IPv6, Internet service providers from the Russian Federation announce 1831 of 65532 globally visible prefixes, which represents 2.79% and 7th place. These prefixes cover 1.3 * 10 ^ 32 unique IPv6 addresses from 1.5 * 10 ^ 34 globally advertised - 0.84% and 18th place.

Diagram 3. Distribution of network prefixes between countries in IPv6, top 20 countries
Individual size
One of the many ways to assess the connectivity and reliability of the Internet in a particular country is to rank autonomous systems belonging to a given region by the number of announced prefixes. This technique, however, is vulnerable to route deaggregation, which is gradually balanced by filtering redundantly degraded prefixes on the equipment of Internet service providers, primarily due to the constant and inevitable growth of memory-occupied routing tables.
| Top 20 IPv4 | Top 20 IPv6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASN | AS Name | Number of prefixes | ASN | AS Name | Number of prefixes |
| 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 2279 | 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 56 |
| 8402 | CORBINA-AS | 1283 | 59504 | vpsville-AS | 51 |
| 24955 | UBN-AS | 1197 | 39811 | MTSNET-FAR-EAST-AS | thirty |
| 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 930 | 57378 | ROSTOV-AS | 26 |
| 35807 | SkyNet-SPB-AS | 521 | 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 20 |
| 44050 | PIN-AS | 366 | 42385 | RIPN-RU | 20 |
| 197695 | AS-REGRU | 315 | 51604 | EKAT-AS | nineteen |
| 12772 | ENFORTA-AS | 291 | 51819 | YAR-AS | nineteen |
| 41704 | OGS-AS | 235 | 50543 | SARATOV-AS | 18 |
| 57129 | RU-SERVERSGET-KRSK | 225 | 52207 | TULA-AS | 18 |
| 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 216 | 206066 | TELEDOM-AS | 18 |
| 49505 | SELECTEL | 213 | 57026 | CHEB-AS | 18 |
| 12714 | TI-AS | 195 | 49037 | MGL-AS | 17 |
| 15774 | TTK-RTL | 193 | 41682 | ERTH-TMN-AS | 17 |
| 12418 | QUANTUM | 191 | 21191 | ASN-SEVERTTK | sixteen |
| 50340 | SELECTEL-MSK | 188 | 41843 | ERTH-OMSK-AS | 15 |
| 28840 | TATTELECOM-AS | 184 | 42682 | ERTH-NNOV-AS | 15 |
| 50113 | SuperServersDatacenter | 181 | 50498 | LIPETSK-AS | 15 |
| 31163 | MF-KAVKAZ-AS | 176 | 50542 | VORONEZH-AS | 15 |
| 21127 | ZSTTKAS | 162 | 51645 | IRKUTSK-AS | 15 |
We use the aggregated size of the announced address space as a more reliable metric for comparing the sizes of autonomous systems, which determines its potential and the limits to which it can scale. This metric is not always relevant in IPv6 due to the current IPv6 RIPE NCC address allocation policy and redundancy protocol.
Gradually, this situation will be balanced by the growth in the use of IPv6 in the Russian segment of the Internet and the development of practices for working with the IPv6 protocol.
| Top 20 IPv4 | Top 20 IPv6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASN | AS Name | Number of IP Addresses | ASN | AS Name | Number of IP Addresses |
| 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 8994816 | 59504 | vpsville-AS | 2.76 * 10 ^ 30 |
| 8402 | CORBINA-AS | 2228864 | 49335 | NCONNECT-AS | 2.06 * 10 ^ 30 |
| 12714 | TI-AS | 1206272 | 8359 | MTS | 1.43 * 10 ^ 30 |
| 8359 | MTS | 1162752 | 50113 | SuperServersDatacenter | 1.35 * 10 ^ 30 |
| 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 872608 | 201211 | DRUGOYTEL-AS | 1.27 * 10 ^ 30 |
| 31200 | NTK | 566272 | 34241 | NCT-AS | 1.27 * 10 ^ 30 |
| 42610 | NCNET-AS | 523264 | 202984 | team-host | 1.27 * 10 ^ 30 |
| 25513 | ASN-MGTS-USPD | 414464 | 12695 | DINET-AS | 9.51 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 39927 | Elight-AS | 351744 | 206766 | INETTECH1-AS | 8.72 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 350720 | 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 7.92 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 8342 | RTCOMM-AS | 350464 | 12722 | RECONN | 7.92 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 28840 | TATTELECOM-AS | 336896 | 47764 | mailru-as | 7.92 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 8369 | INTERSVYAZ-AS | 326912 | 44050 | PIN-AS | 7.13 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 28812 | JSCBIS-AS | 319488 | 45027 | INETTECH-AS | 7.13 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 12332 | PRIMORYE-AS | 303104 | 3267 | RUNNET | 7.13 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 20632 | PETERSTAR-AS | 284416 | 34580 | UNITLINE_MSK_NET1 | 7.13 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 8615 | CNT-AS | 278528 | 25341 | LINIYA-AS | 7.13 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 35807 | SkyNet-SPB-AS | 275968 | 60252 | OST-LLC-AS | 7.13 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 3267 | RUNNET | 272640 | 28884 | MR-SIB-MTSAS | 6.73 * 10 ^ 29 |
| 41733 | ZTELECOM-AS | 266240 | 42244 | ESERVER | 6.44 * 10 ^ 29 |
Both metrics — the number of announced prefixes and the aggregated size of the address space — are manipulable. Although we did not see such behavior from the mentioned AS during the study.
Connectivity
There are 3 main types of relationships between autonomous systems:
- Client: pays another AS for traffic transit;
- Peering partner: AS exchanging its own and client traffic for free;
- Provider: receives payments for traffic transit from other ASs.
Usually, these types of relationships are the same for any two Internet providers, which is confirmed in the region of the Russian Federation under consideration. However, sometimes it happens that two Internet providers have different types of relationships in different regions, for example, exchanging for free in Europe, but having commercial relations in Asia.
| Top 20 IPv4 | Top 20 IPv6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASN | AS Name | Number of customers in the region | ASN | AS Name | Number of customers in the region |
| 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 818 | 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 94 |
| 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 667 | 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 82 |
| 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 589 | 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 77 |
| 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 467 | 20764 | RASCOM-AS | 72 |
| 8359 | MTS | 313 | 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 70 |
| 20764 | RASCOM-AS | 223 | 9049 | ERTH-TRANSIT-AS | 58 |
| 9049 | ERTH-TRANSIT-AS | 220 | 8359 | MTS | 51 |
| 8732 | COMCOR-AS | 170 | 29076 | CITYTELECOM-AS | 40 |
| 2854 | ROSPRINT-AS | 152 | 31,500 | GLOBALNET-AS | 32 |
| 29076 | CITYTELECOM-AS | 143 | 3267 | RUNNET | 26 |
| 29226 | MASTERTEL-AS | 143 | 25478 | IHOME-AS | 22 |
| 28917 | Fiord-AS | 96 | 28917 | Fiord-AS | 21 |
| 25159 | SONICDUO-AS | 94 | 199599 | CIREX | 17 |
| 3267 | RUNNET | 93 | 29226 | MASTERTEL-AS | 13 |
| 31,500 | GLOBALNET-AS | 87 | 8732 | COMCOR-AS | 12 |
| 13094 | SFO-IX-AS | 80 | 35,000 | PROMETEY | 12 |
| 31261 | GARS-AS | 80 | 49063 | DTLN | eleven |
| 25478 | IHOME-AS | 78 | 42861 | FOTONTELECOM | ten |
| 12695 | DINET-AS | 76 | 56534 | PIRIX-INET-AS | 9 |
| 8641 | NAUKANET-AS | 73 | 48858 | Milecom-as | eight |
The number of customers given by AS reflects its role as a direct provider of Internet connectivity services to commercial consumers.
| Top 20 IPv4 | Top 20 IPv6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASN | AS Name | Number of peering partners in the region | ASN | AS Name | Number of peering partners in the region |
| 13238 | Yandex | 638 | 13238 | Yandex | 266 |
| 43267 | First_Line-SP_for_b2b_customers | 579 | 9049 | ERTH-TRANSIT-AS | 201 |
| 9049 | ERTH-TRANSIT-AS | 498 | 60357 | MEGAGROUP-AS | 189 |
| 201588 | MOSCONNECT-AS | 497 | 41617 | SOLID-IFC | 177 |
| 44020 | CLN-AS | 474 | 41268 | LANTA-AS | 176 |
| 41268 | LANTA-AS | 432 | 3267 | RUNNET | 86 |
| 15672 | TZTELECOM | 430 | 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 78 |
| 39442 | UNICO-AS | 424 | 60764 | TK-Telecom | 74 |
| 39087 | PAKT-AS | 422 | 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 52 |
| 199805 | UGO-AS | 418 | 42861 | FOTONTELECOM | 32 |
| 200487 | FASTVPS | 417 | 8359 | MTS | 28 |
| 41691 | SUMTEL-AS-RIPE | 399 | 20764 | RASCOM-AS | 26 |
| 13094 | SFO-IX-AS | 388 | 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 17 |
| 60357 | MEGAGROUP-AS | 368 | 28917 | Fiord-AS | sixteen |
| 41617 | SOLID-IFC | 347 | 31,500 | GLOBALNET-AS | 14 |
| 51674 | Mehanika-AS | 345 | 60388 | TRANSNEFT-TELECOM-AS | 14 |
| 49675 | SKBKONTUR-AS | 343 | 42385 | RIPN-RU | 13 |
| 35539 | INFOLINK-T-AS | 310 | 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 12 |
| 42861 | FOTONTELECOM | 303 | 49063 | DTLN | 12 |
| 25227 | ASN-AVANTEL-MSK | 301 | 44843 | OBTEL-AS | eleven |
A large number of peering partners can significantly improve the coherence of an entire region. Here, traffic exchange points (IX - Internet Exchange) are important, though not obligatory - the largest Internet providers usually do not participate in regional exchanges (with a few exceptions worthy of mention, such as NIXI) due to the nature of their business.
For a content provider, the number of peering partners can indirectly serve as an indicator of the volume of generated traffic - the incentive to exchange large amounts of it for free is a factor of motivation (sufficient for most local Internet providers) to see a worthy peering partner in the content provider. There are also opposite cases when content providers do not support the policy of a significant number of regional connections, which makes this indicator not too accurate for estimating the size of content providers, that is, the volume of traffic generated by them.
| Top 20 IPv4 | Top 20 IPv6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASN | AS Name | Customer cone size | ASN | AS Name | Customer cone size |
| 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 3083 | 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 335 |
| 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 2973 | 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 219 |
| 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 2587 | 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 205 |
| 8732 | COMCOR-AS | 2463 | 8732 | COMCOR-AS | 183 |
| 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 2318 | 20764 | RASCOM-AS | 166 |
| 8359 | MTS | 2293 | 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 143 |
| 20764 | RASCOM-AS | 2251 | 8359 | MTS | 143 |
| 9049 | ERTH-TRANSIT-AS | 1407 | 3267 | RUNNET | 88 |
| 29076 | CITYTELECOM-AS | 860 | 29076 | CITYTELECOM-AS | 84 |
| 28917 | Fiord-AS | 683 | 28917 | Fiord-AS | 70 |
| 3267 | RUNNET | 664 | 9049 | ERTH-TRANSIT-AS | 65 |
| 25478 | IHOME-AS | 616 | 31,500 | GLOBALNET-AS | 54 |
| 43727 | KVANT-TELECOM | 476 | 25478 | IHOME-AS | 33 |
| 31,500 | GLOBALNET-AS | 459 | 199599 | CIREX | 24 |
| 57724 | DDOS-GUARD | 349 | 43727 | KVANT-TELECOM | 20 |
| 13094 | SFO-IX-AS | 294 | 39134 | UNITEDNET | 20 |
| 199599 | CIREX | 290 | 15835 | MAP | 15 |
| 29226 | MASTERTEL-AS | 227 | 29226 | MASTERTEL-AS | 14 |
| 201706 | AS-SERVICEPIPE | 208 | 35,000 | PROMETEY | 14 |
| 8641 | NAUKANET-AS | 169 | 49063 | DTLN | 13 |
The client cone is the set of all ASs that are directly or indirectly dependent on the autonomous system under consideration. From an economic point of view, each AS within the client cone is, directly or indirectly, a paying customer. At a higher level, the number of AS within the client cone, as well as the number of direct consumers, is a key indicator of connectivity.
Finally, we have prepared for you another table that looks at the connectivity up to the Runet core. Understanding the structure of the core of regional connectivity, based on the number of direct customers and the size of the client cone for each autonomous system in the region, we can calculate how far they are from the region’s largest transit Internet service providers. The lower the number, the higher the connectivity. “1” means that for all visible paths there is a direct connection with the regional core.
| IPv4 top 20 | IPv6 top 20 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASN | AS Name | Connectivity rating | ASN | AS Name | Connectivity rating |
| 8997 | ASN-SPBNIT | 1.0 | 21109 | CONTACT-AS | 1.0 |
| 47764 | mailru-as | 1.0 | 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 1.0 |
| 42448 | ERA-AS | 1.0 | 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 1.0 |
| 13094 | SFO-IX-AS | 1.0 | 47541 | VKONTAKTE-SPB-AS | 1.0 |
| 47541 | VKONTAKTE-SPB-AS | 1.07 | 13238 | Yandex | 1.05 |
| 13238 | Yandex | 1.1 | 8470 | MAcomnet | 1.17 |
| 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 1.11 | 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 1.19 |
| 48061 | GPM-TECH-AS | 1.11 | 41722 | MIRAN-AS | 1.2 |
| 31133 | MF-MGSM-AS | 1.11 | 8359 | MTS | 1.22 |
| 8359 | MTS | 1.12 | 60879 | SYSTEMPROJECTS-AS | 1.25 |
| 41268 | LANTA-AS | 1.13 | 41268 | LANTA-AS | 1.25 |
| 9049 | ERTH-TRANSIT-AS | 1.16 | 44020 | CLN-AS | 1.25 |
| 20485 | TRANSTELECOM | 1.18 | 29226 | MASTERTEL-AS | 1.25 |
| 29076 | CITYTELECOM-AS | 1.18 | 44943 | RAMNET-AS | 1.25 |
| 12389 | ROSTELECOM-AS | 1.23 | 12714 | TI-AS | 1.25 |
| 57629 | IVI-RU | 1.25 | 47764 | mailru-as | 1.25 |
| 48297 | DOORHAN | 1.25 | 44267 | Iesv | 1.25 |
| 42632 | MNOGOBYTE-AS | 1.25 | 203730 | SVIAZINVESTREGION | 1.25 |
| 44020 | CLN-AS | 1.25 | 3216 | SOVAM-AS | 1.25 |
| 12668 | MIRALOGIC-AS | 1.25 | 24739 | SEVEREN-TELECOM | 1.29 |
What can be done to improve the overall connectivity and, as a result, the stability, reliability and security of any country, the Russian Federation in particular? Here are just some of the measures:
- Tax deductions and other benefits for local operators of traffic exchange points, as well as free access to them;
- Free or cheap land servitude for laying fiber-optic communication lines;
- Conducting trainings and training sessions for technical staff in remote regions, including workshops and other training formats for the best practices of working with BGP. RIPE NCC organizes a part of them, available by reference .
The data presented above is an excerpt from a study conducted by Qrator Labs on the world's second largest regional Internet segment of the Russian Federation (also known as Runet) based on open data collected and processed in the framework of the Radar project. The presentation of the full study is announced as a workshop at the 10th Asia Pacific Regional Internet Governance Forum in July. Request for similar data for segments of other countries and regions can be sent to the e-mail address mail@qrator.net .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/444724/
All Articles