Random databases. Oracle Enterprise Data Quality Quality - Corporate Vault Shield and Sword
1. The concept of a random database.
The first person’s business relations are described by formal and informal documents such as a statement, a declaration, a labor contract, an application for placement, an application for a resource. These documents create logical connections between business processes, but, as a rule, are the product of thinking of office managers and are poorly formalized.
')
The task of any complex optimization is not only to understand formal and informal rules, but, often, to bring disparate knowledge to a common information base.
Definition A random database is a set of facts, documents, manual notes, formal documents that are processed by a person for a particular business process, but cannot be fully automatically processed due to the strong influence of the human factor.
Example. The secretary formally takes the call. The caller is interested in a product or service. The caller is not known CRM. Question: what should the caller say to be heard by a specialist?
To be more precise: how can the secretary’s business instructions allow for a formal dialogue about the business if the responsible specialist is not ready for this type of activity?
It turns out that we again come to the definition of a random database.
Maybe it contains more facts than the secretary can know. But the extra information received in it can not be. In general, when random facts of a random database arrive at the input of a formalized system, then there is such a thing as information overload - and the entire information overload can affect the performance of not only the secretary, but the entire company.
If it is used for processing purposes, the machine that reads the states of this information comes on the basis of logical conclusions to the state opposite to the person - information overload. Human logic is more flexible.
2. Application of the definition to real problems.
Imagine a store in which the price tags for random goods are noticeably overpriced or undervalued. When you exit this store, the price of 5-7 (or even 3) of the most popular goods whose price may affect the size of the total check will remain in the head of an inexperienced buyer’s shopping list. It turns out that if it were possible to know the list of goods, the price of which is most often remembered by buyers, then the rest of the prices could be varied in a relatively wide range.
Have you ever wondered why, before Lent, the meat first becomes sharply cheaper, and then it can rise in price sharply, and then disappear? The price of a product, the demand for which can fall to zero, is artificially heated first, then, passing a certain level of demand, begins to be fixed, and after a while it grows forcefully, since greed does not allow to give illiquid goods at a fair price.
The situation is almost the same in the data market. The most useful information is almost always under the surface of secondary hypotheses about its applicability and recoverability.
It is enough to lay out any information that is interesting to 5000-7000 people on any relatively unprotected resource, copypaster sites will definitely be found.
Or the famous game with phone codes "Who called me?". About a thousand sites in runet consist only of telephone numbers of various operators, to be a little higher in the search results, trying to at least sell the domain name and advertising more expensive.
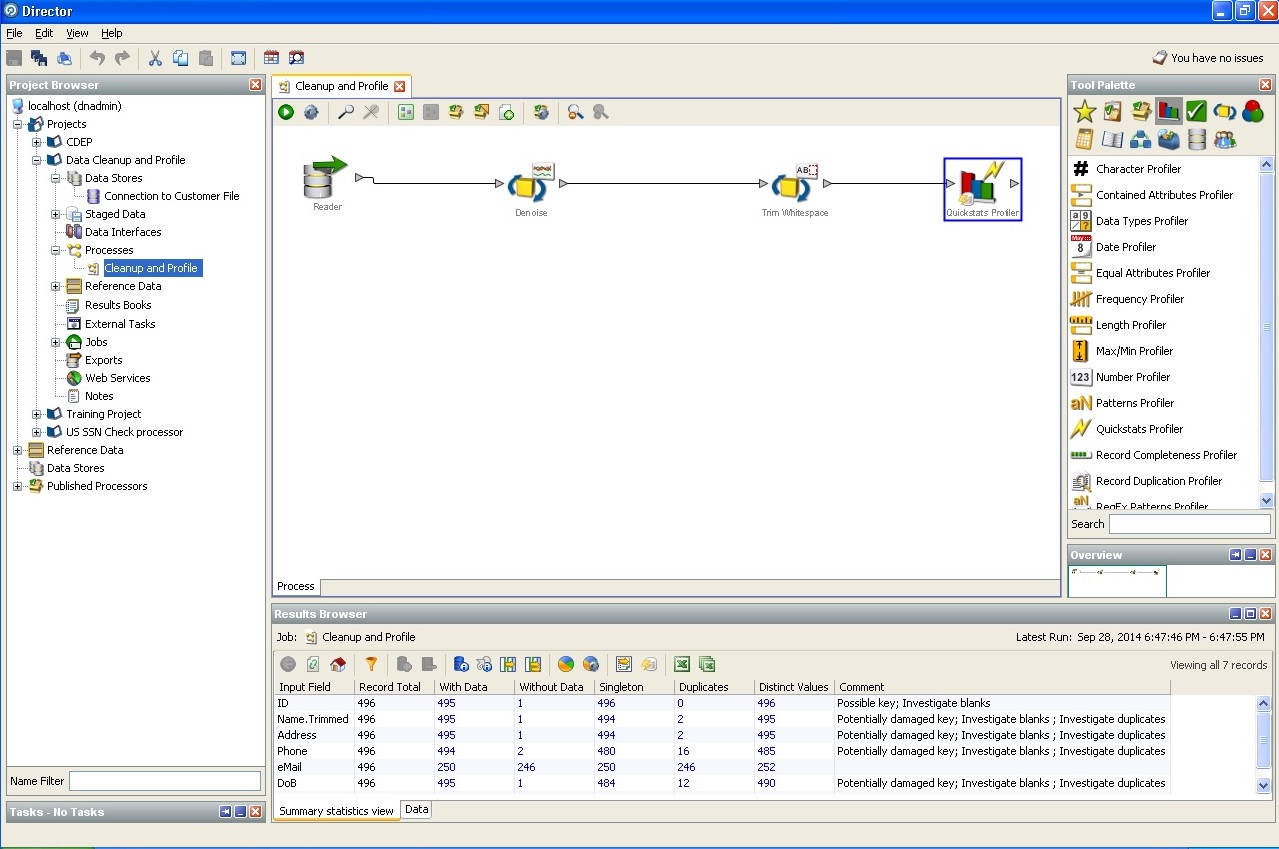
3. The price of the issue when working with "dirty" data.
According to the research of the author of the article, up to 10% of the workforce of each project is diverted to writing certain data cleaning procedures. If you don’t dwell on a completely banal type and length, there are still unique identifiers, database integrity rules and business integrity rules, quantitative and qualitative unit scales, systems of units of labor-intensiveness and any other states, influences, transitions, the compilation of which requires as usual statistical , and logical and serious business analysis. Formalizing the requirements comes to the need to formalize the fact-measurement relationship both for building repositories and for solving issues on the frontend.
Agree, if the ETL processes take up 70% of the operating time of any repository, then saving 5-7% of resources on properly clearing data on conditional storage of 200,000 clients is a good bonus?
We will cover a little the questions of “dirty” data in ready-made systems. Let's say you send greetings on a national holiday to 10,000 clients via mail. How many people throw your letter with the best postcard in the mailbox, if you make a mistake in the name, surname, or incorrectly fill in the form in the form? The price of your efforts can reduce the mood of any user to zero!
4. Oracle Enterprise Data Quality - shield and sword of the corporate repository.
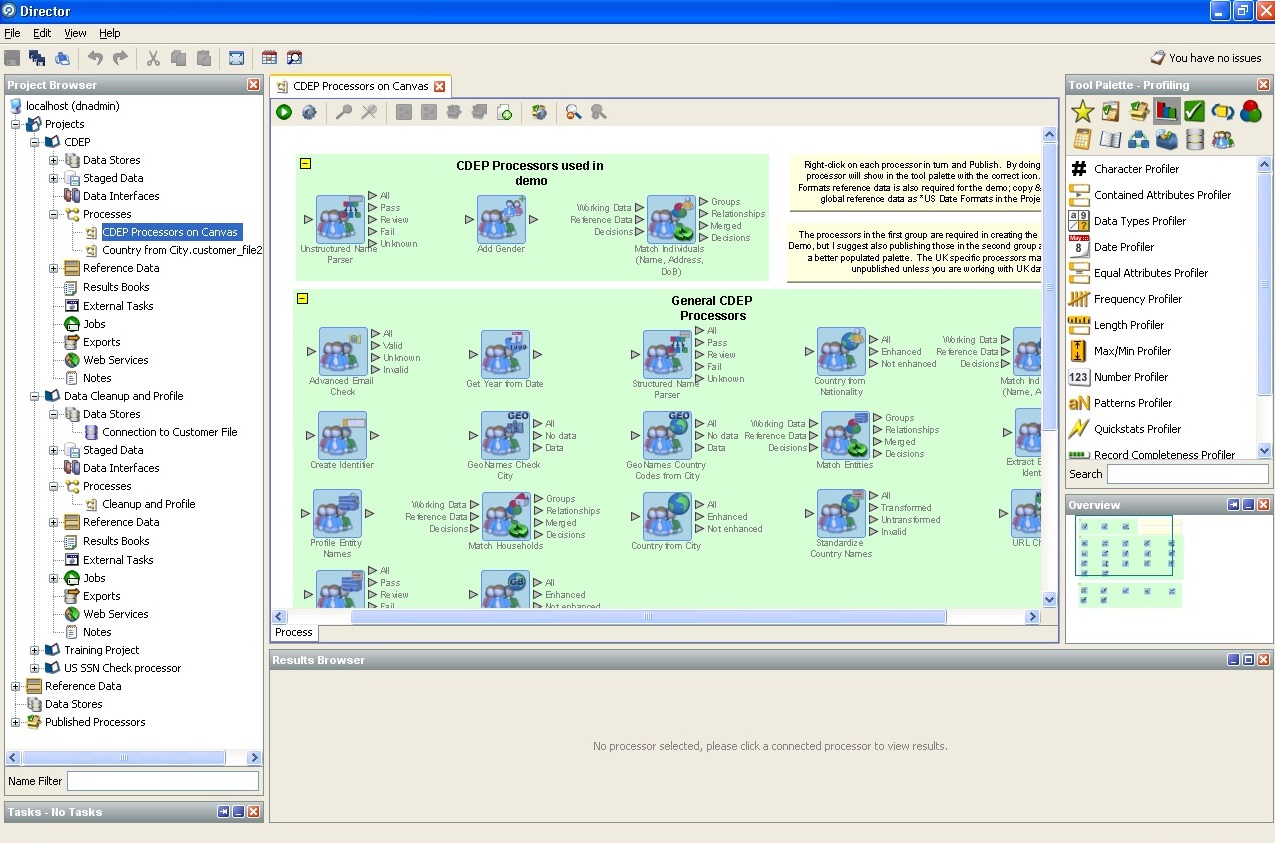
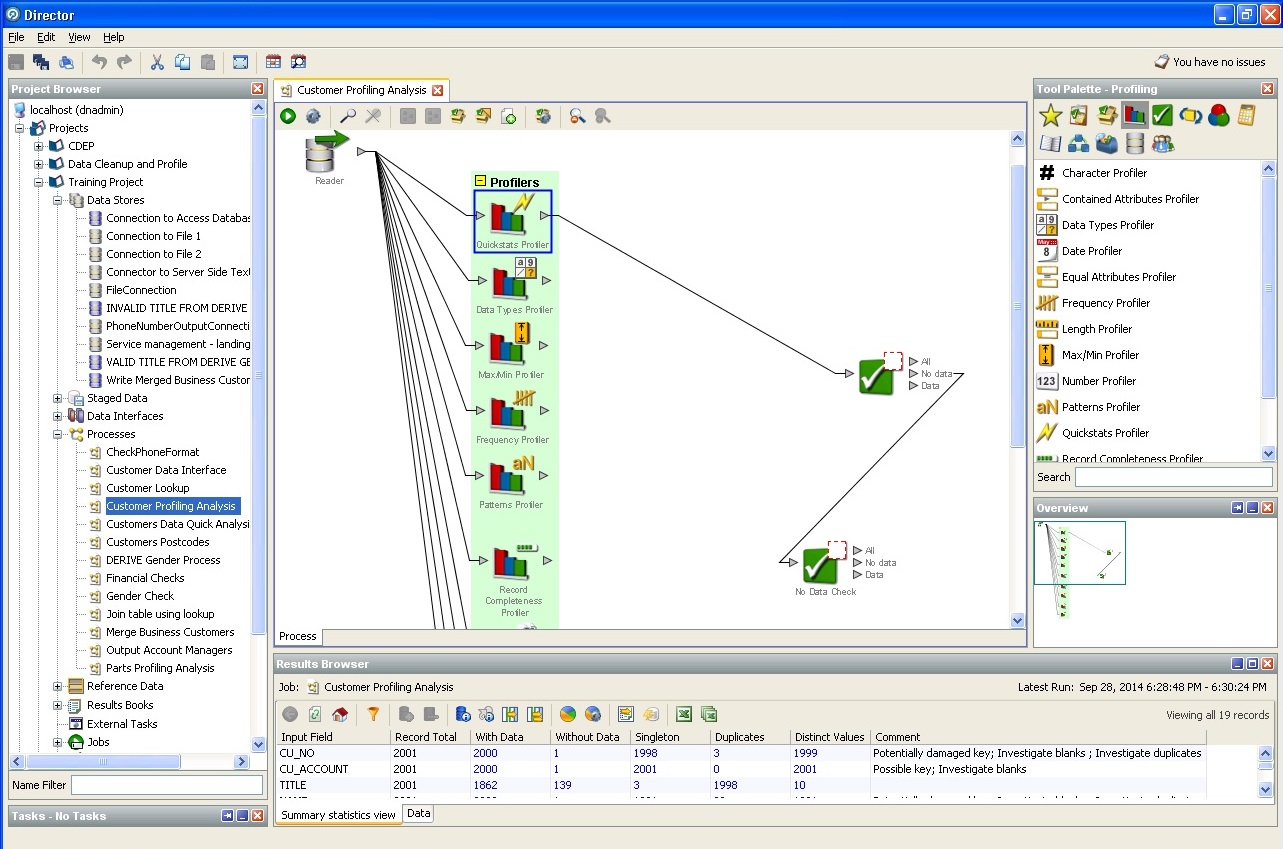
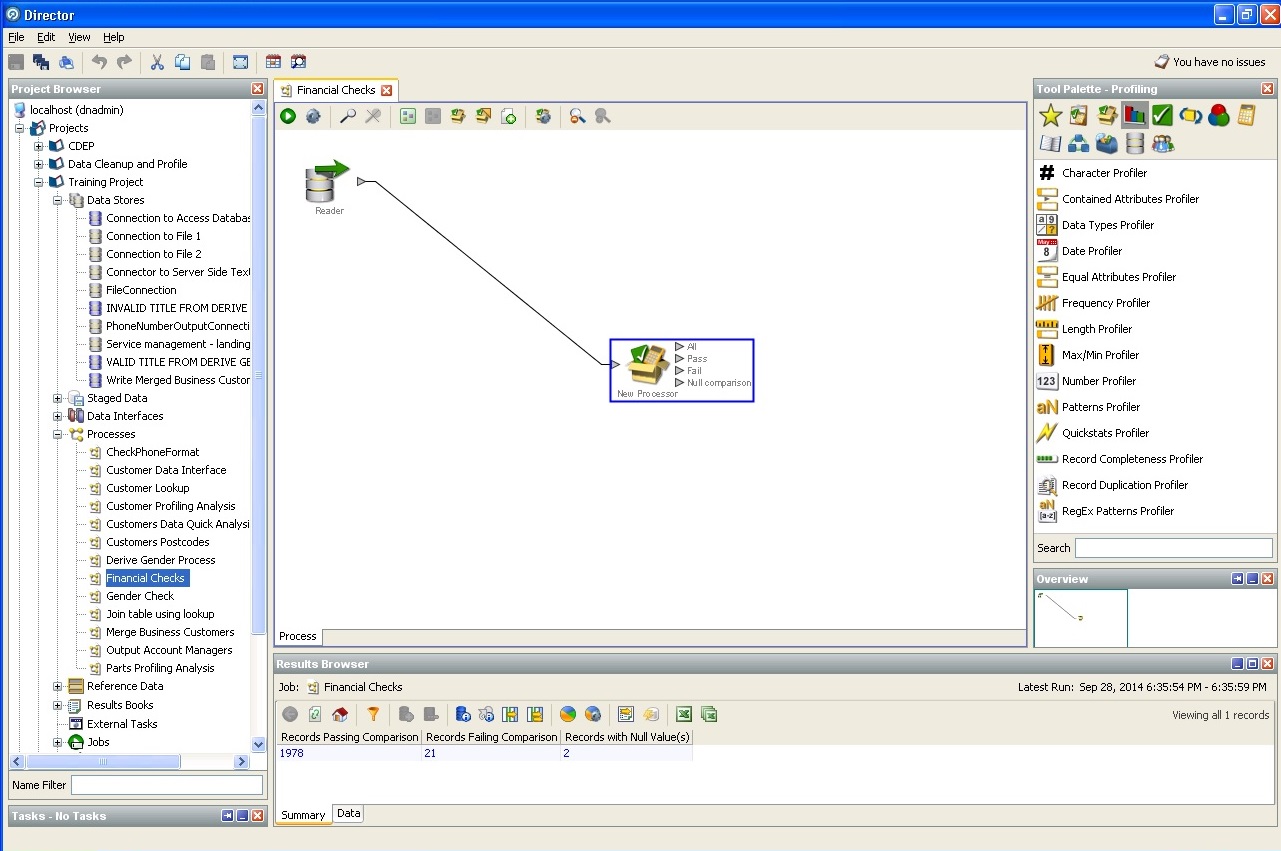
The screenshots we provide describe the capabilities of Oracle Enterprise Data Quality.
So, let someone have spilled water on your database or text document.
Here is a list of standard processors (logical units that allow
data or other hypotheses, or search for the required):
Random database profiler action:
Basic check of financial solvency:
Work with zip code:
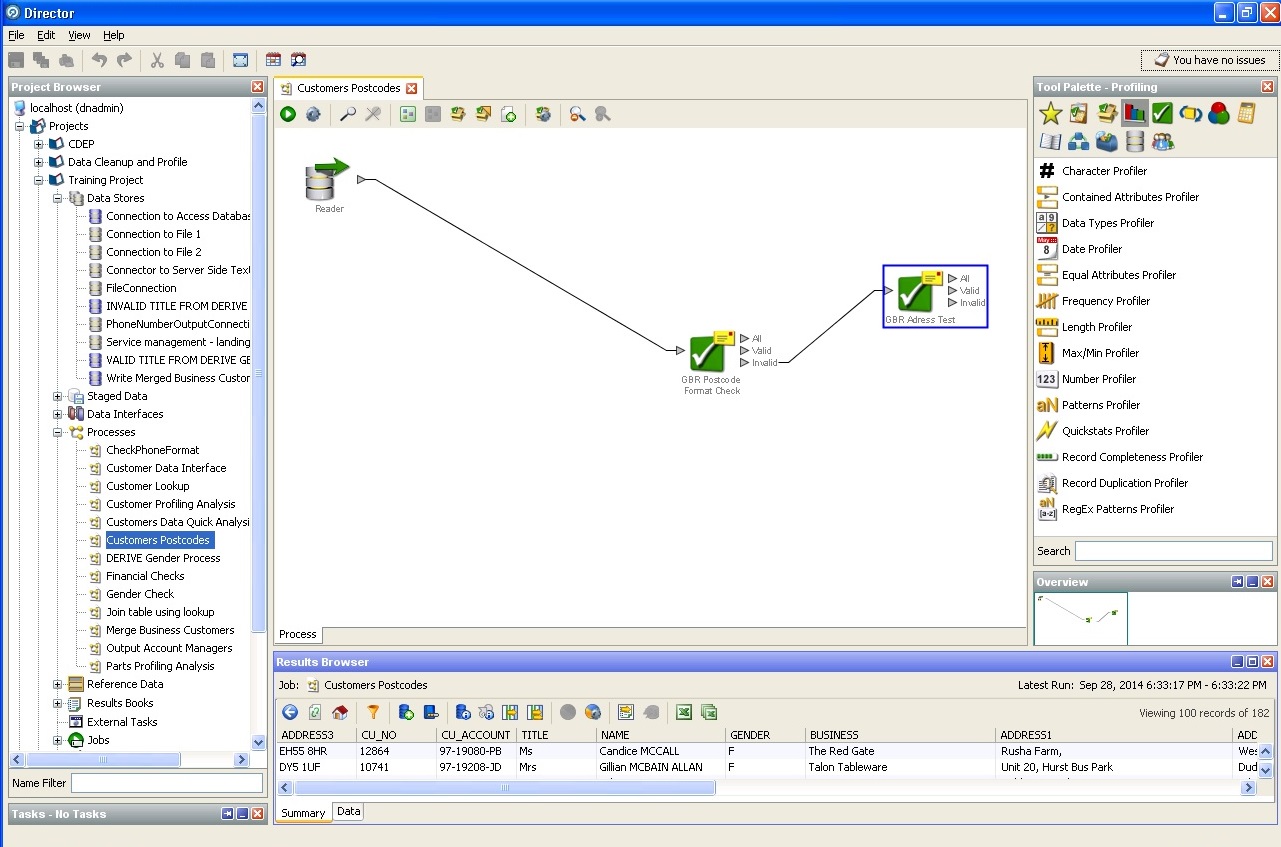
Cleaning the mailing address:
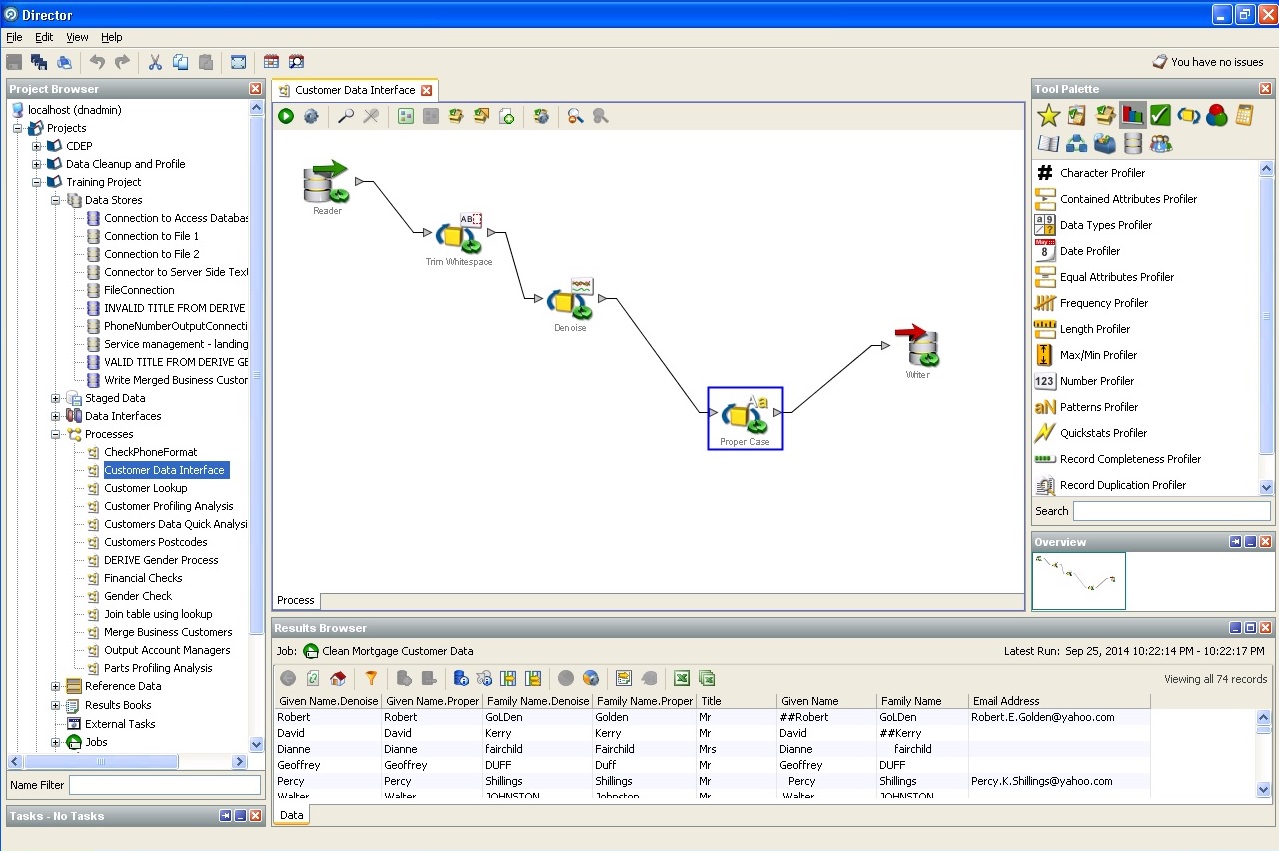
Clearing user data:
Assigning a record to a certain confidence interval:
Determining user gender from indirect data:
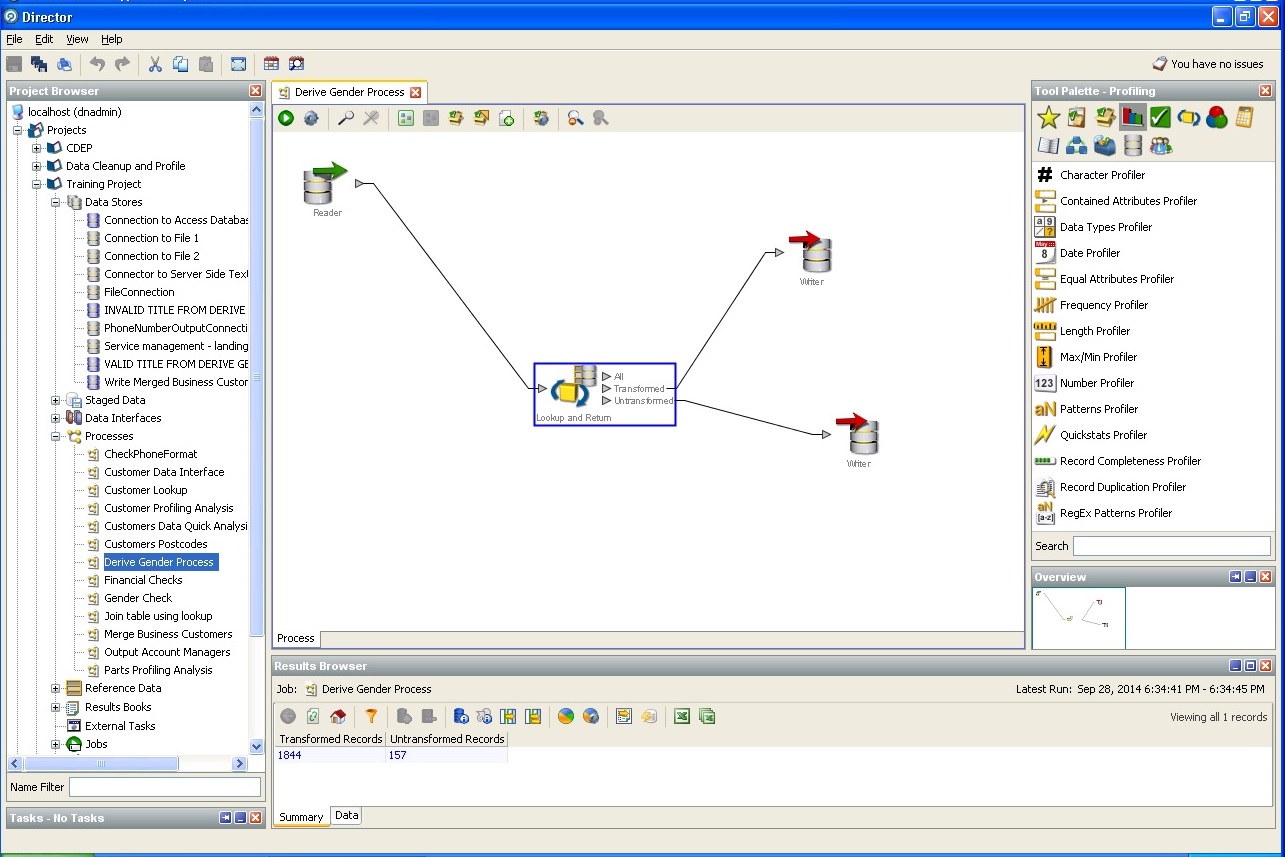
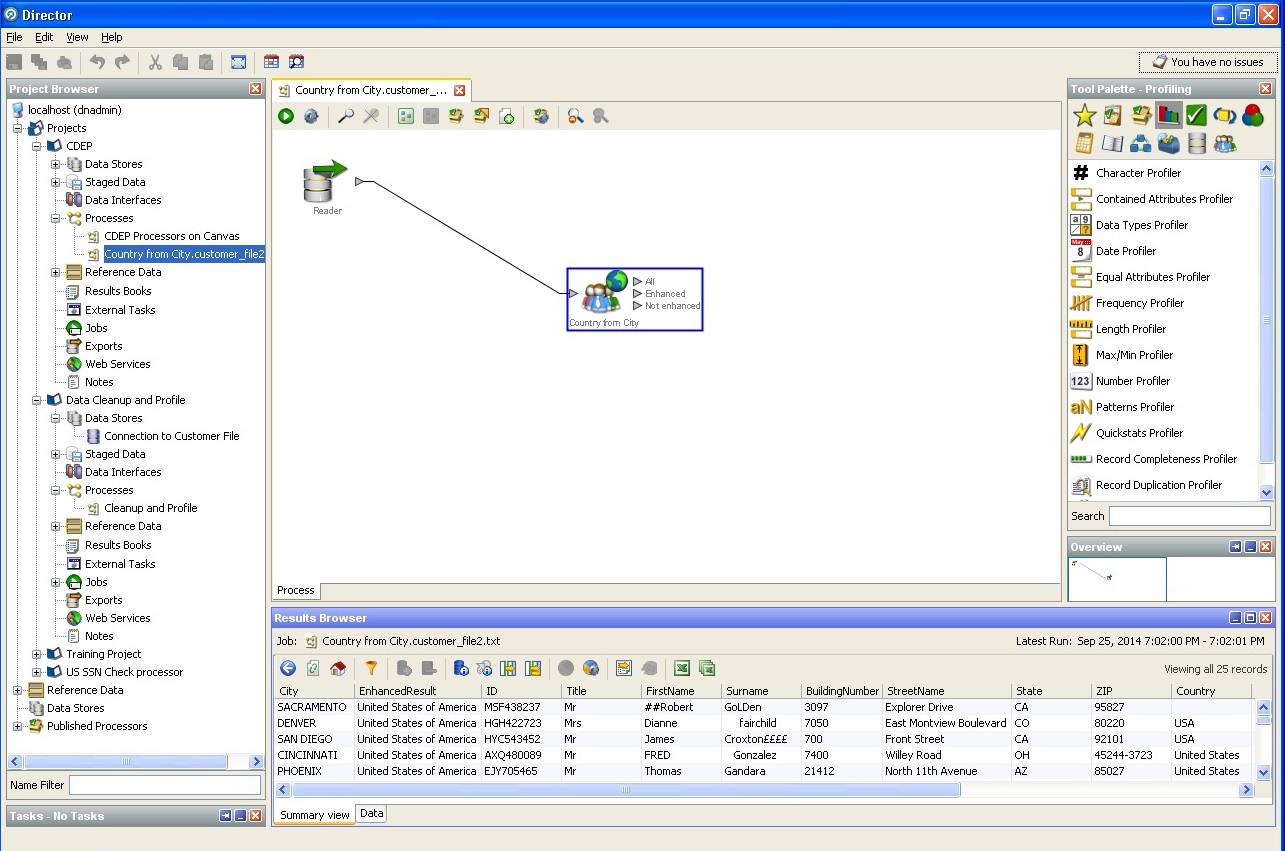
Definition of the city and country, state:
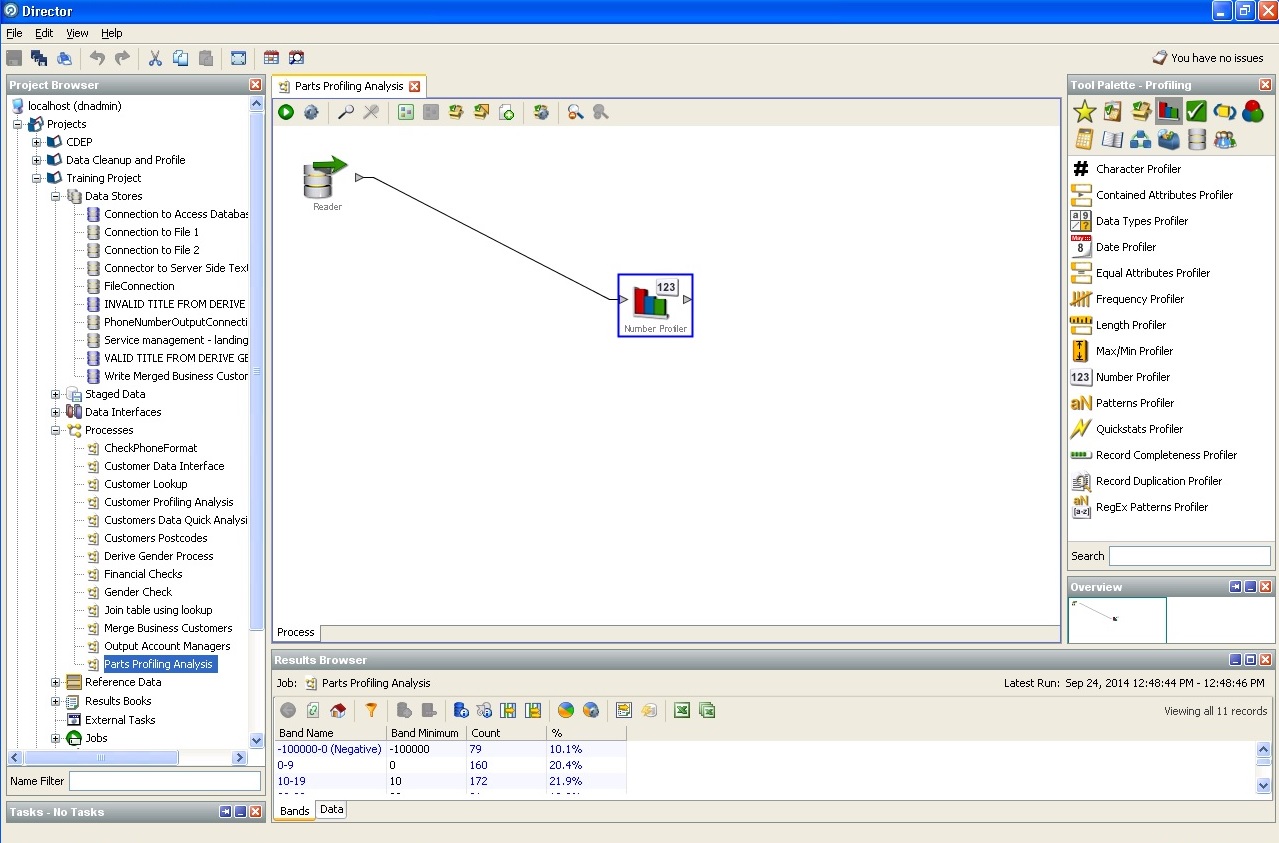
Simplest search for keys in a random database:
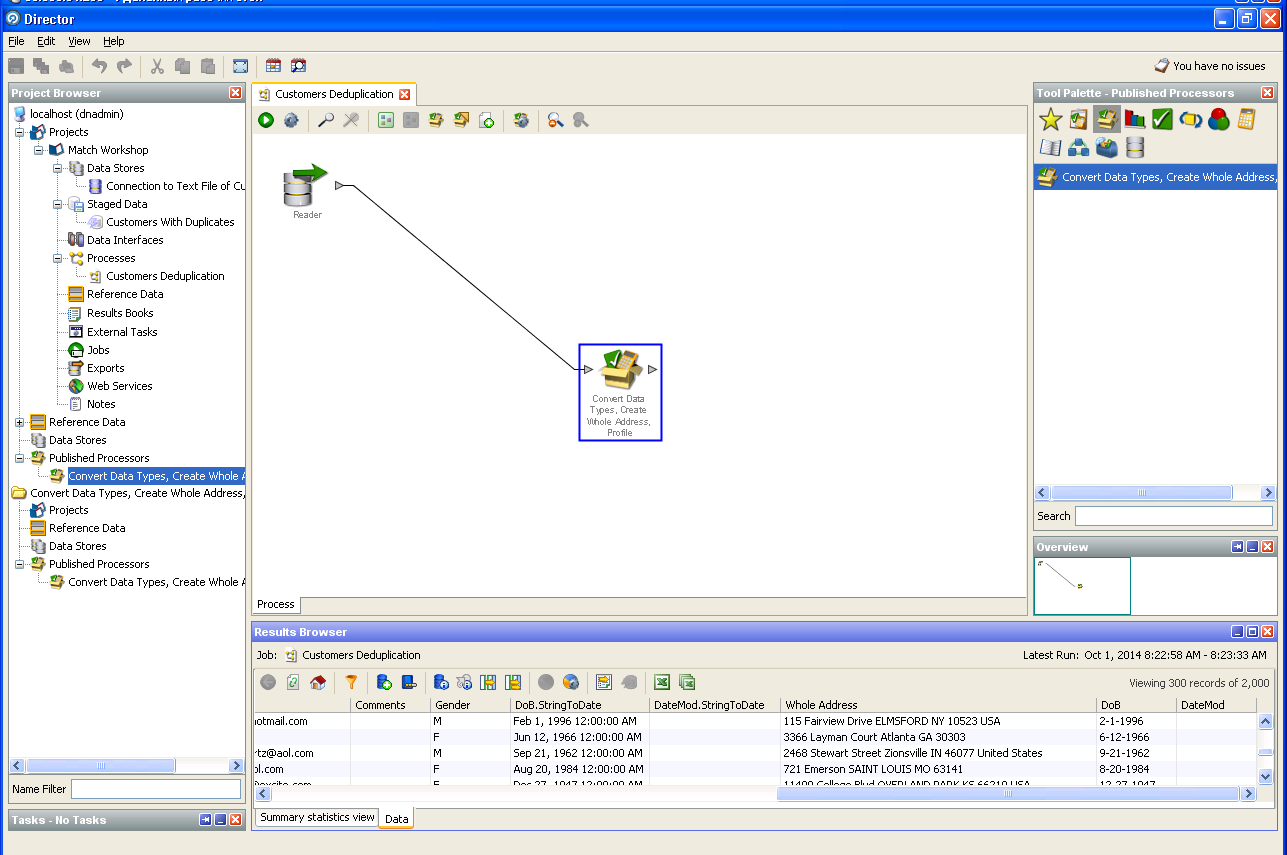
Deduplication of user data:

5. Funny observations made on the results of work on Oracle EDQ.
One of the principles of comparing the contribution of writers and poets to literature is the comparison of their poetic and writing dictionaries. We give a number of dictionaries compiled in free time for tests of ready-made solutions for Oracle EDQ, Python, Java. We will be grateful if the authors-philologists in the comments lay out their results.
Number pp | Word | Entry frequency | |||
a lion | AND. | AND. | N. | ||
one. | and | 10351 | at | at | and |
3 | at | 5185 | and | and | at |
four. | not | 4292 | not | not | not |
five. | what | 3845 | on | on | I |
6 | he | 3730 | as | as | with |
7 | on | 3305 | with | with | on |
eight. | with | 3030 | what | what | as |
9. | as | 2097 | to | AND | what |
ten. | I | 1896 | from | I | he |
eleven. | him | 1882 | of | to | you |
12. | to | 1771 | I | from | but |
13. | that | 1600 | Where | everything | but |
14. | she is | 1564 | than | by | So |
15. | but | 1234 | behind | you | to |
sixteen. | this | 1208 | by | AT | everything |
17 | said | 1135 | But | behind | behind |
18. | It was | 1125 | neither | of | to me |
nineteen. | So | 1032 | would | but | Yes |
20. | the prince | 1012 | that | he | him |
21. | behind | 985 | you | But | that |
22 | but | 962 | about | that | was |
23. | his | 918 | but | about | by |
24 | everything | 908 | there is | this | not |
25 | by | 895 | I | I | neither |
26 | her | 885 | but | about | |
27. | of | 845 | Where | their | |
28 | than | of | |||
29. | BUT | from | |||
thirty. | same | we | |||
Conclusion: the statistics of the Russian language over the past hundred years has hardly changed in terms of the frequency of individual words, and the poets have more “singing” words. By the way, Darya Dontsova’s statistics largely coincide with Leo Tolstoy in the frequency dictionary of the complete works.
6. Several formal calculations as a conclusion.
About 60 thousand Ivanov Ivanovich Ivanovich live in our country. Assuming that 100 tables are stored hypothetically in an average database, 10 key fields in each table, and each key can take 60,000 values, we find that the total number of unique key states within the database is approximately 60 million. If even in one table two keys are confused, then they can generate up to 20 unique states in one table. In total, the database of unique states can run up to several thousand. Agree that spending 10% of development time and 5-7% of ETL execution time to catch such trifles is an unaffordable luxury?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/444700/
All Articles