VMware NSX for the smallest. Part 4. Configure Routing

Part one. Introductory
Part two. Configuring Firewall and NAT Rules
Part Three DHCP setup
NSX Edge supports static and dynamic (ospf, bgp) routing.
Initial setup
Static routing
Ospf
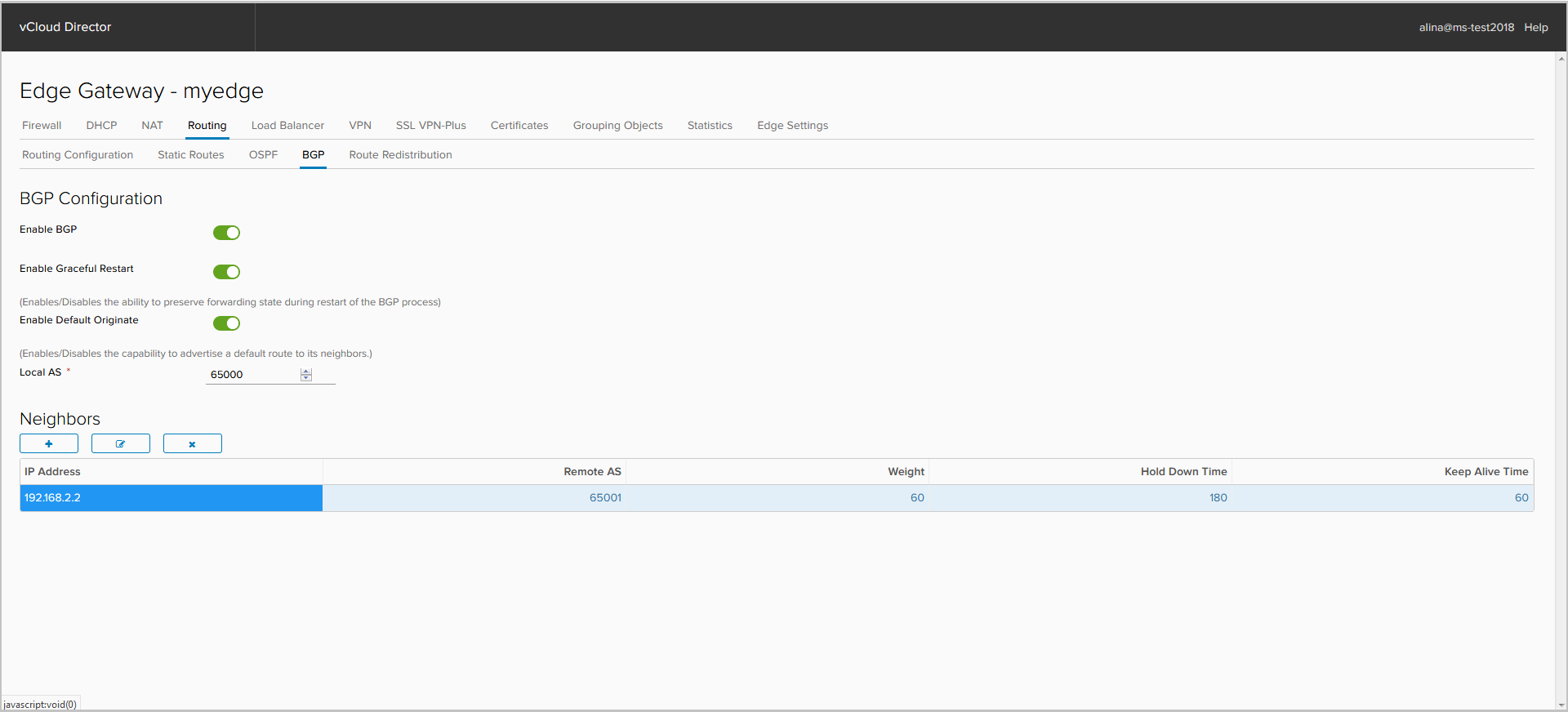
Bgp
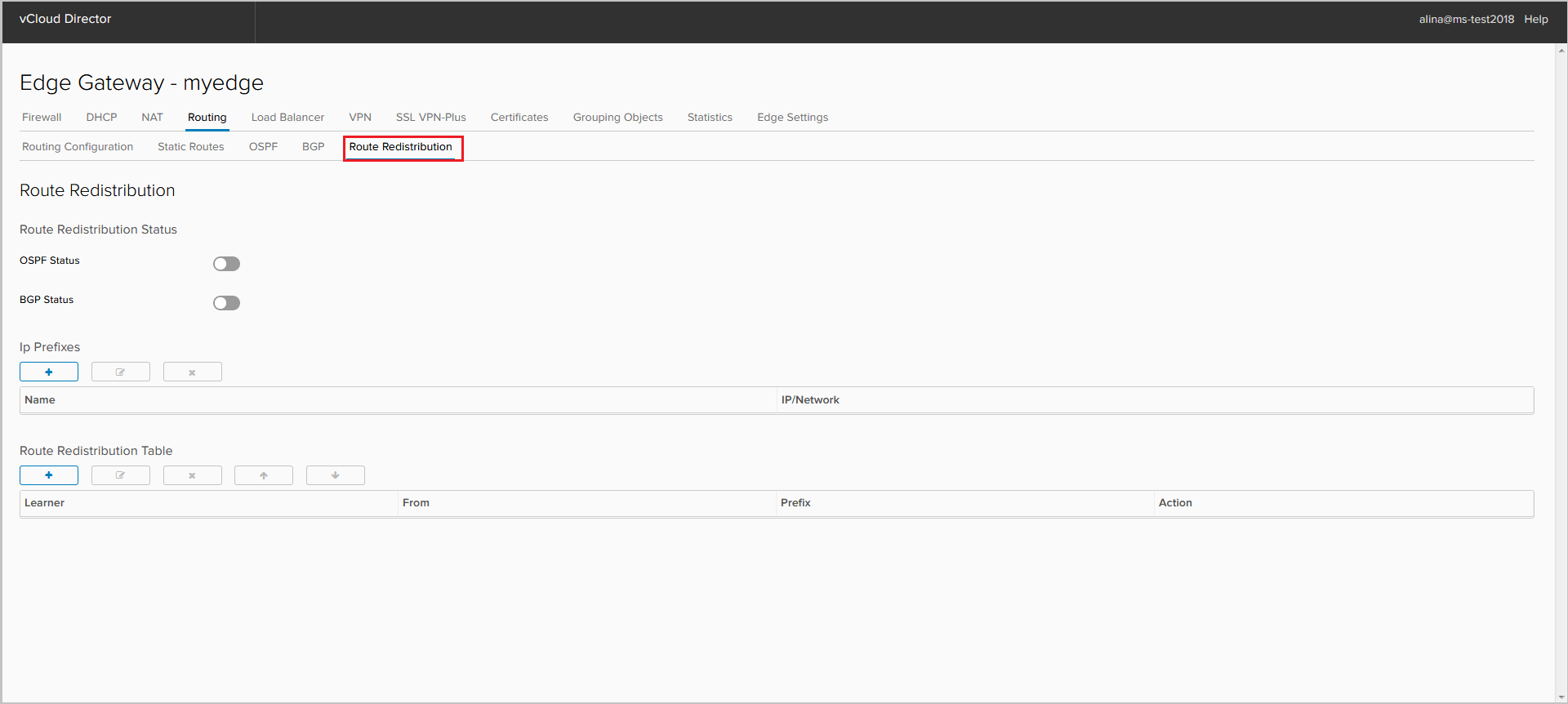
Route Redistribution
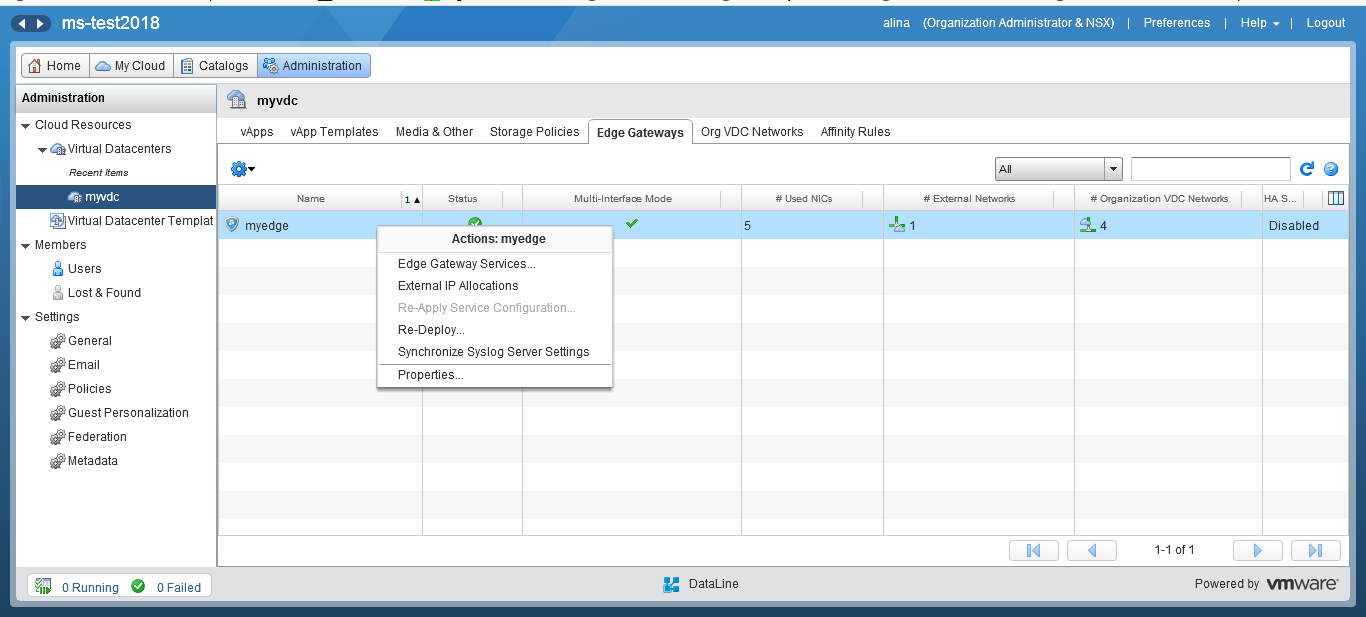
To configure routing, go to the Administration section in vCloud Director and click on the virtual data center. In the horizontal menu, select the Edge Gateways tab. Right-click on the desired network and select the Edge Gateway Services option.
')
Go to the Routing menu.
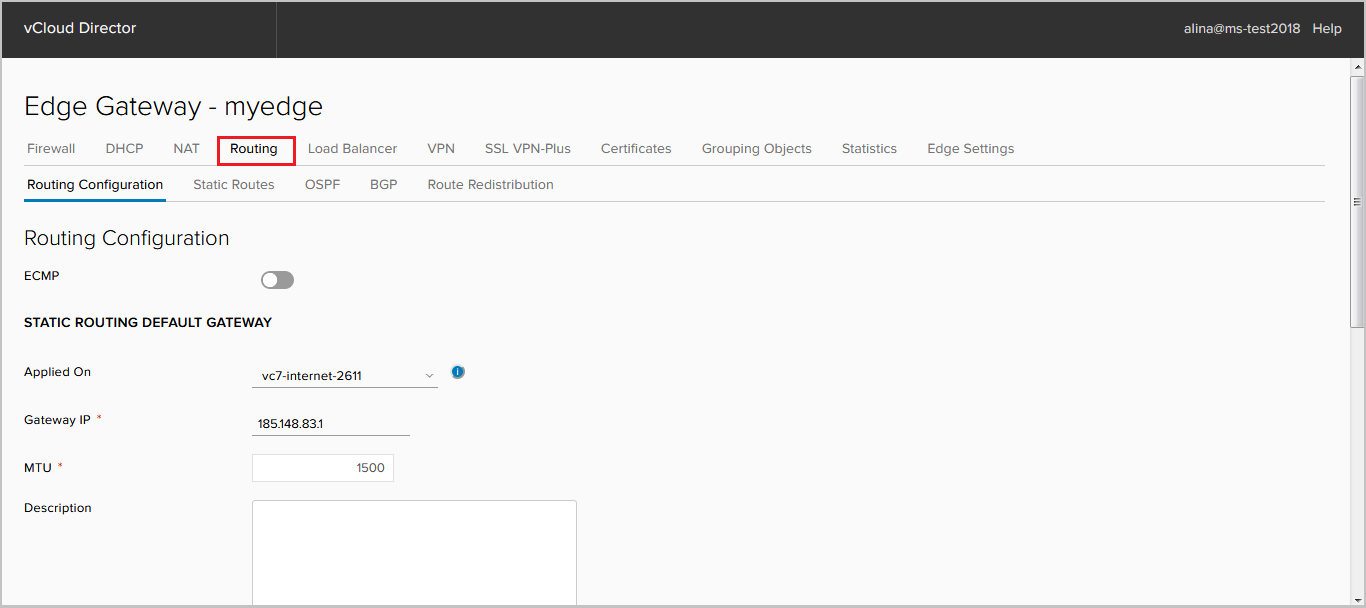
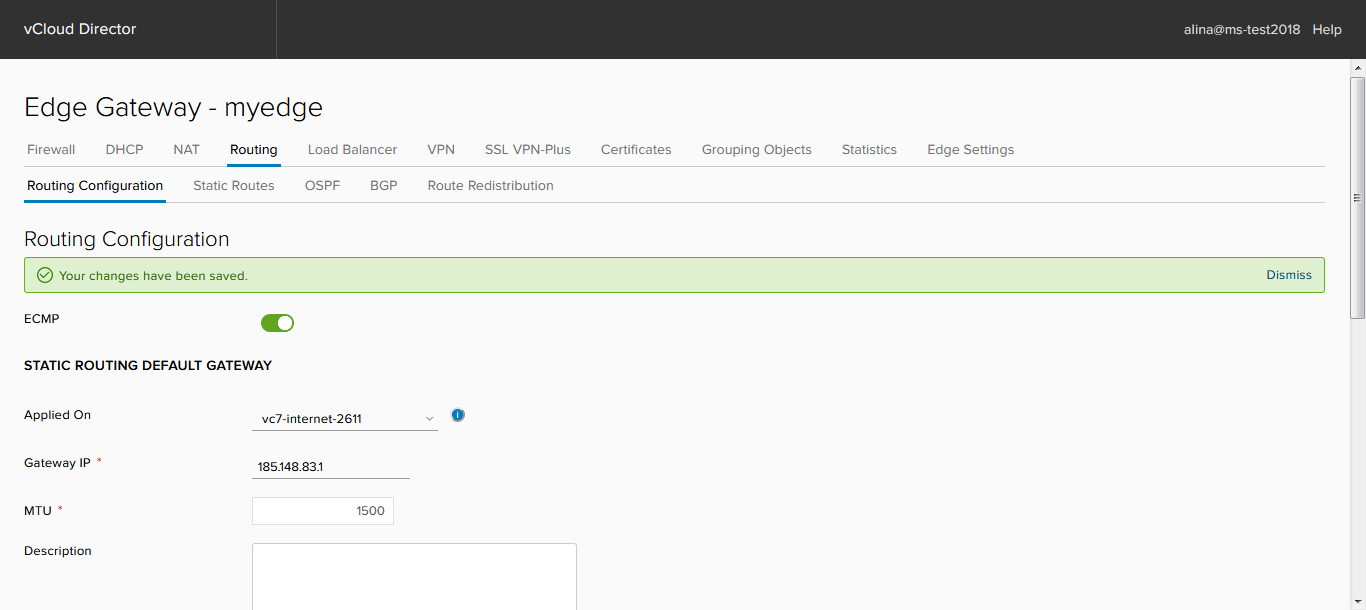
Routing Configuration
In this contribution you can:
- activate the ECMP parameter, which allows to set up to 8 equivalent routes in the RIB.
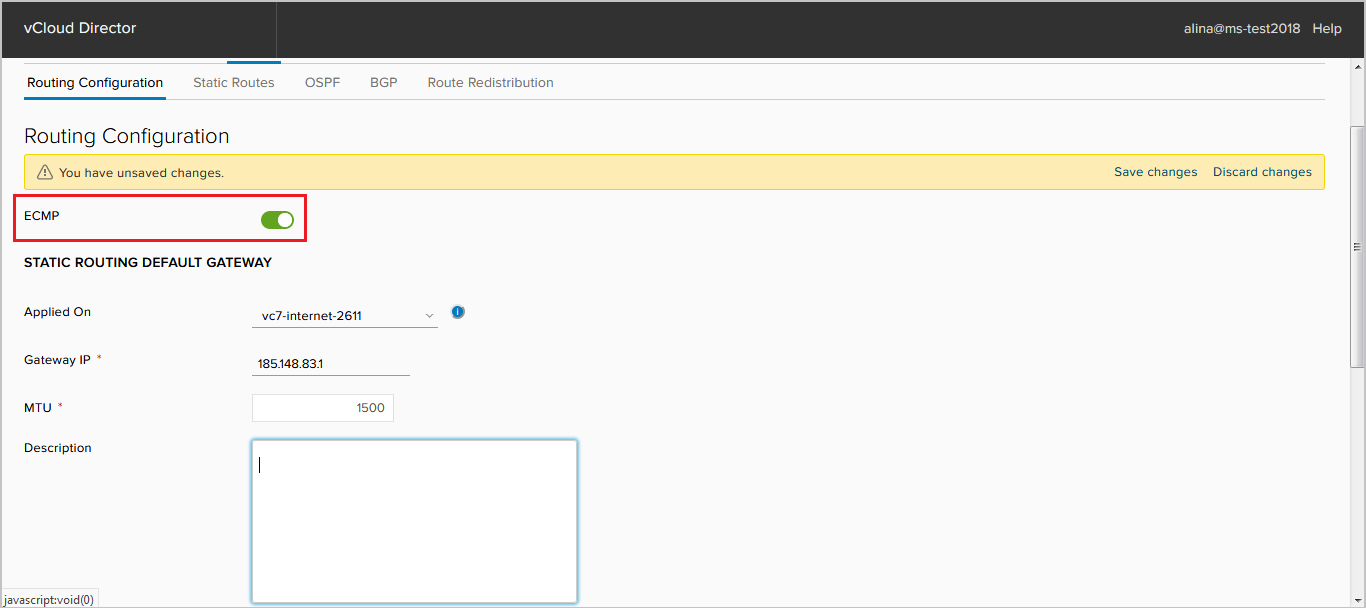
- change or disable the default route.
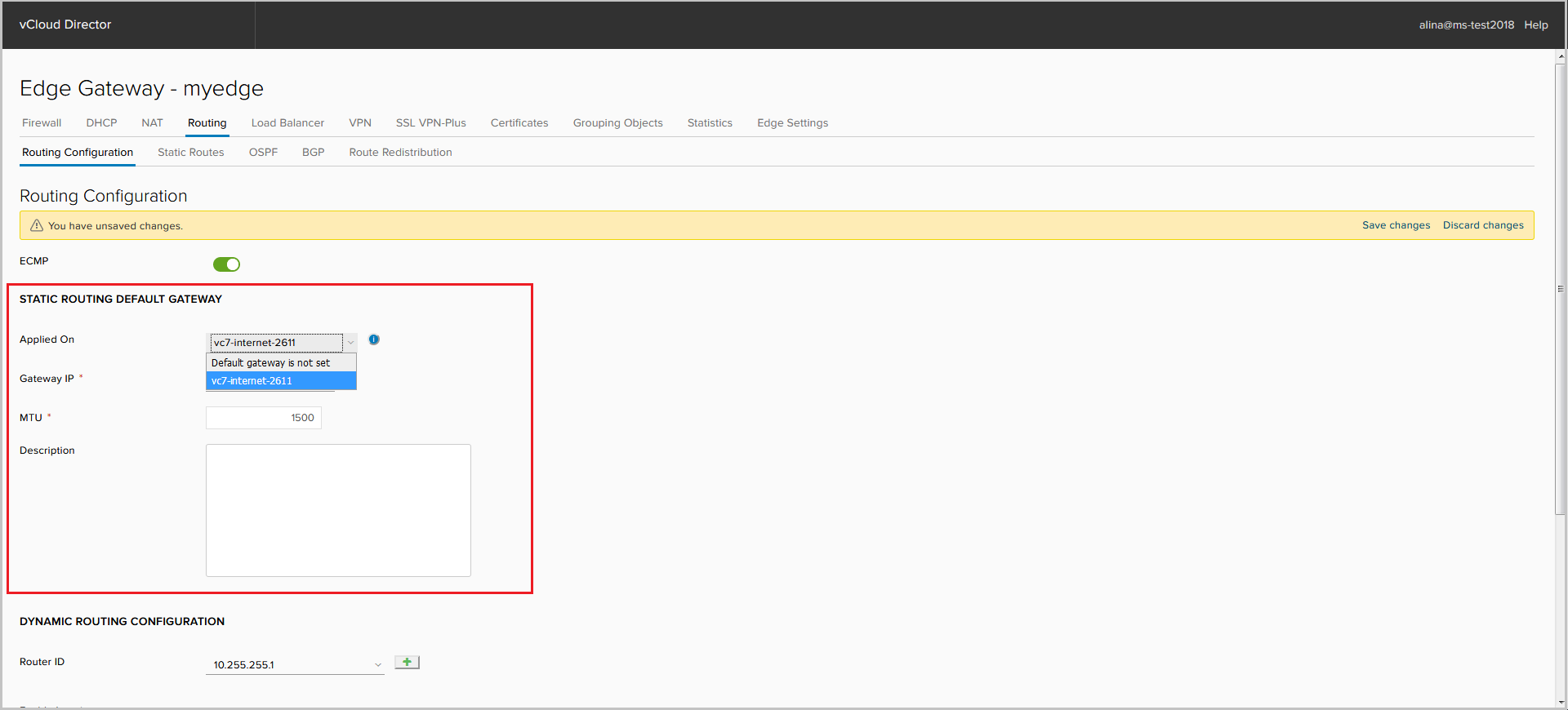
- select Router-ID. As the Router-ID, you can select the external address of the interface. Without specifying the Router-ID, it is not possible to start OSPF or BGP processes.
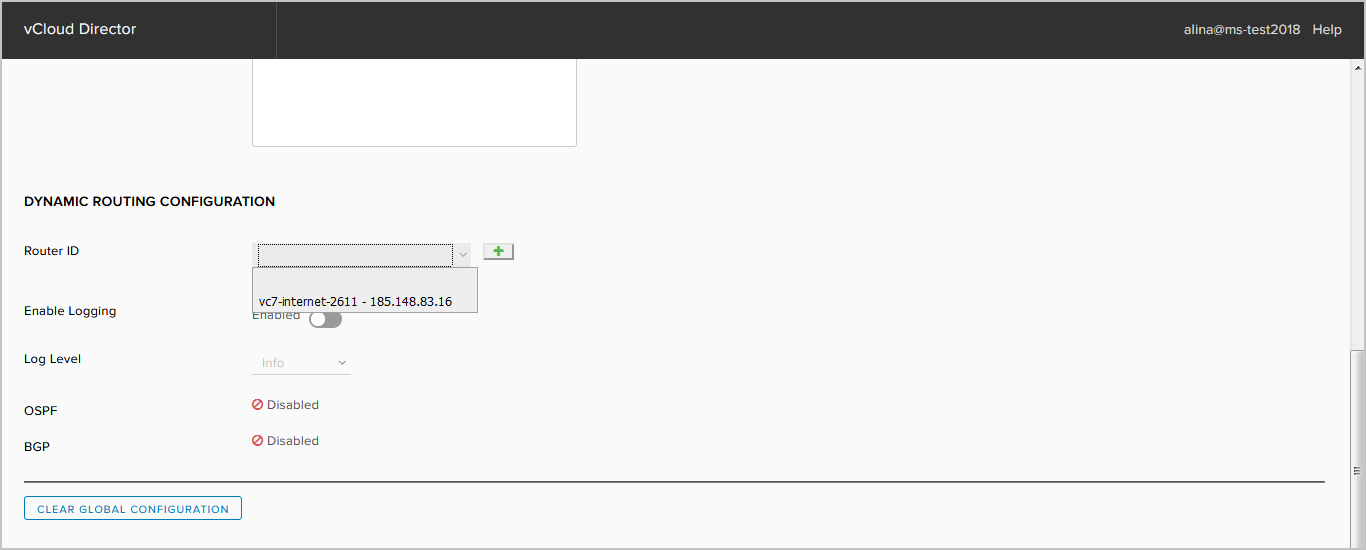
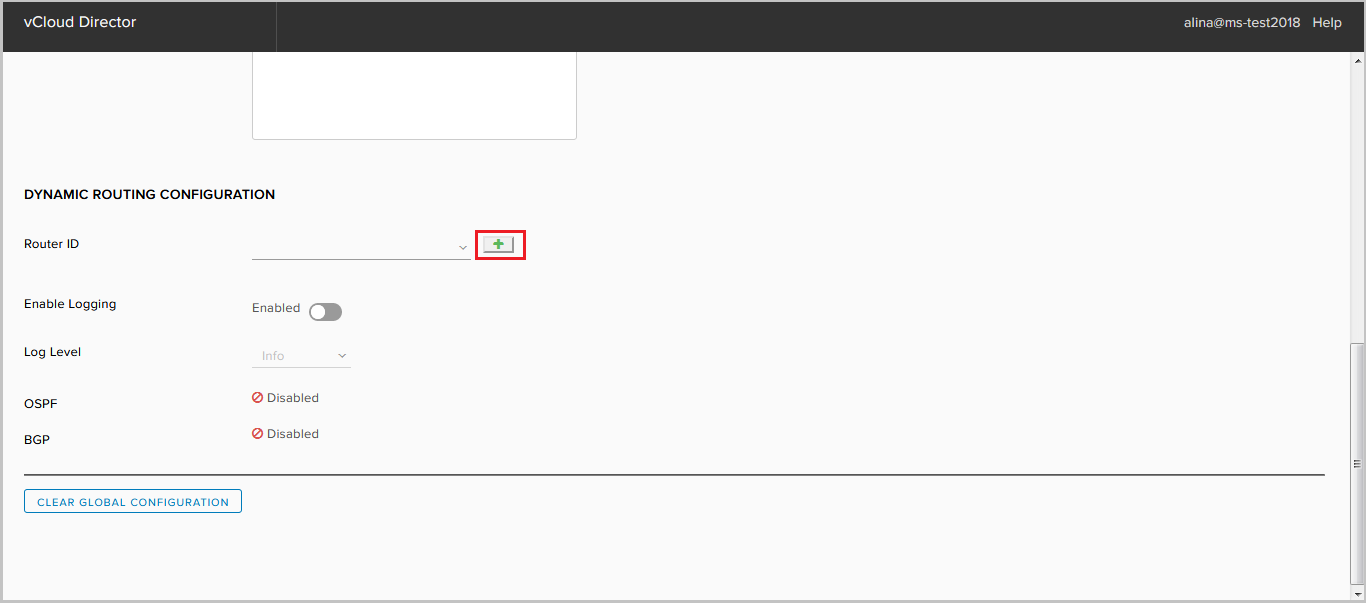
Or add your own by clicking +.
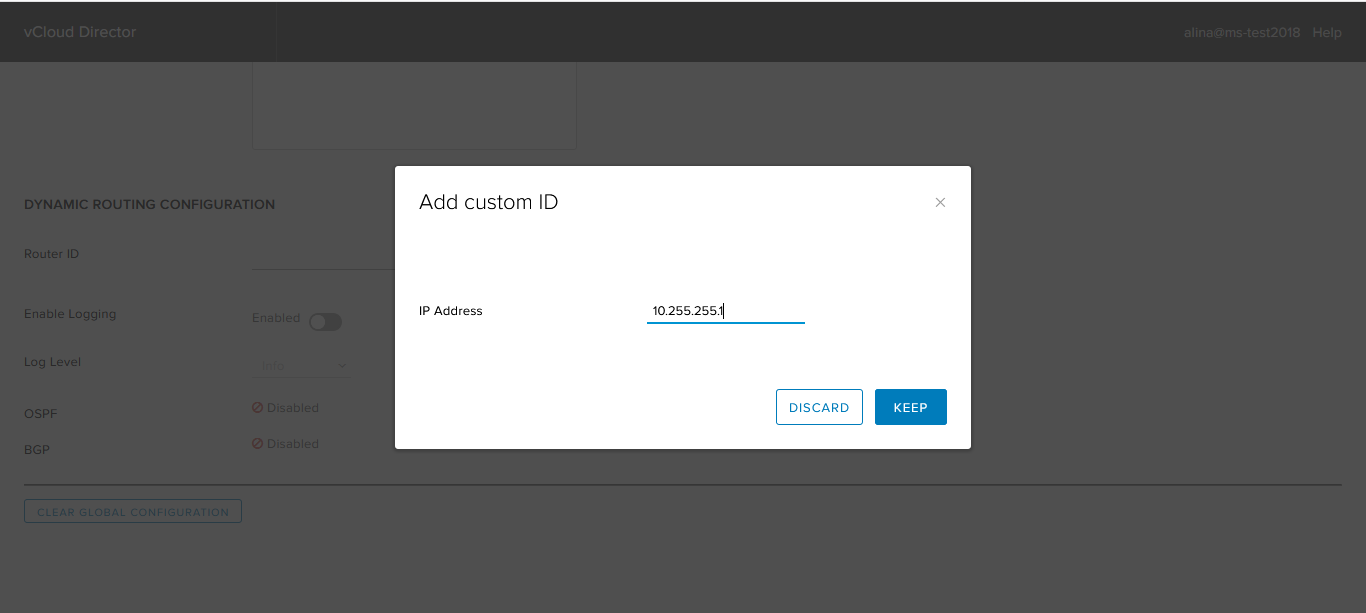
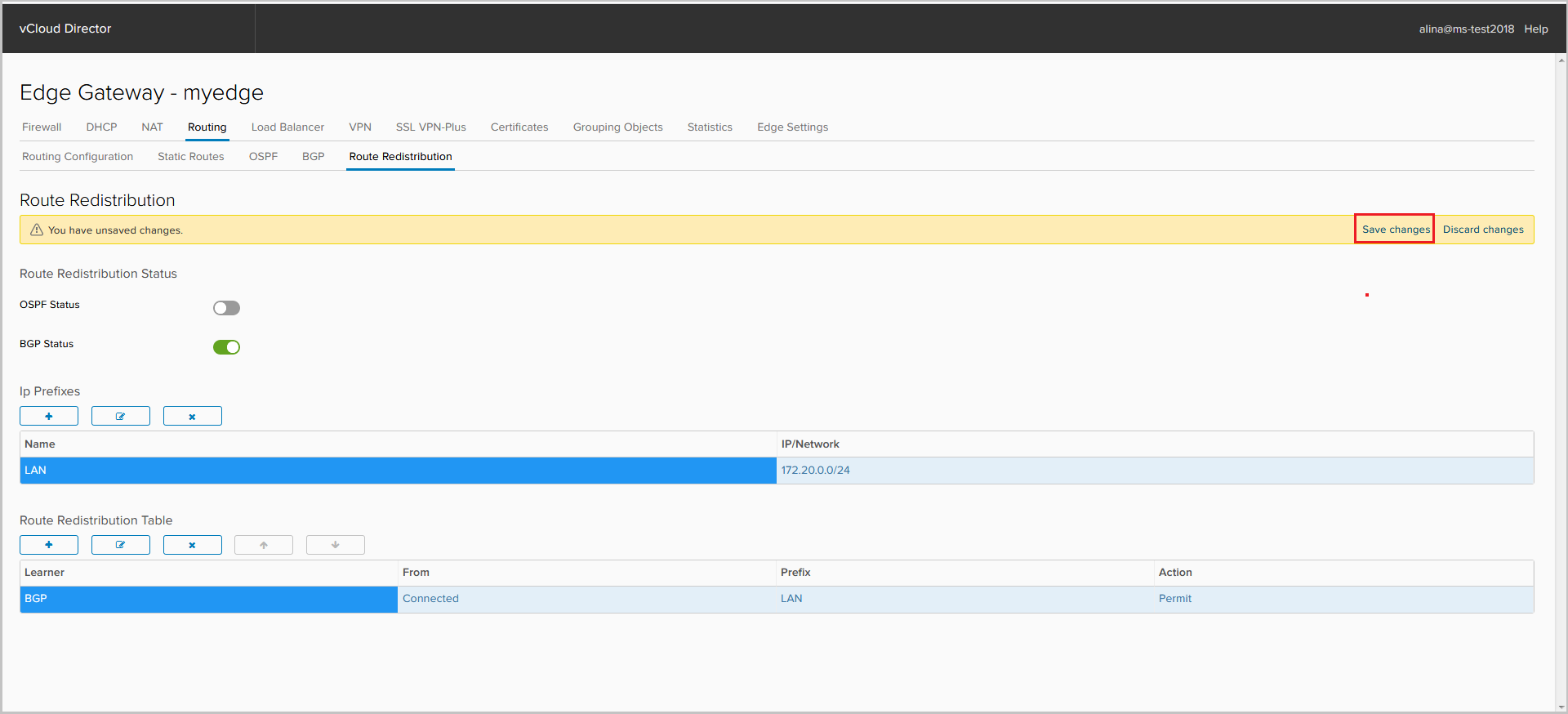
Save the configuration.
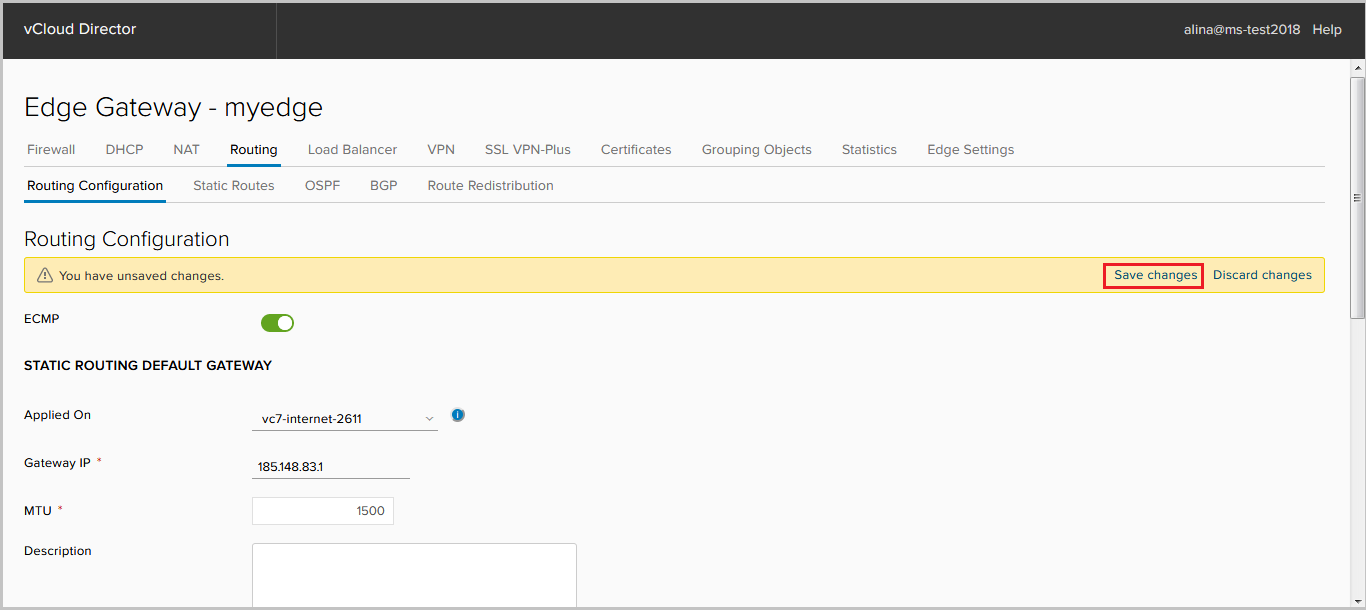
Is done.
Configure static routing
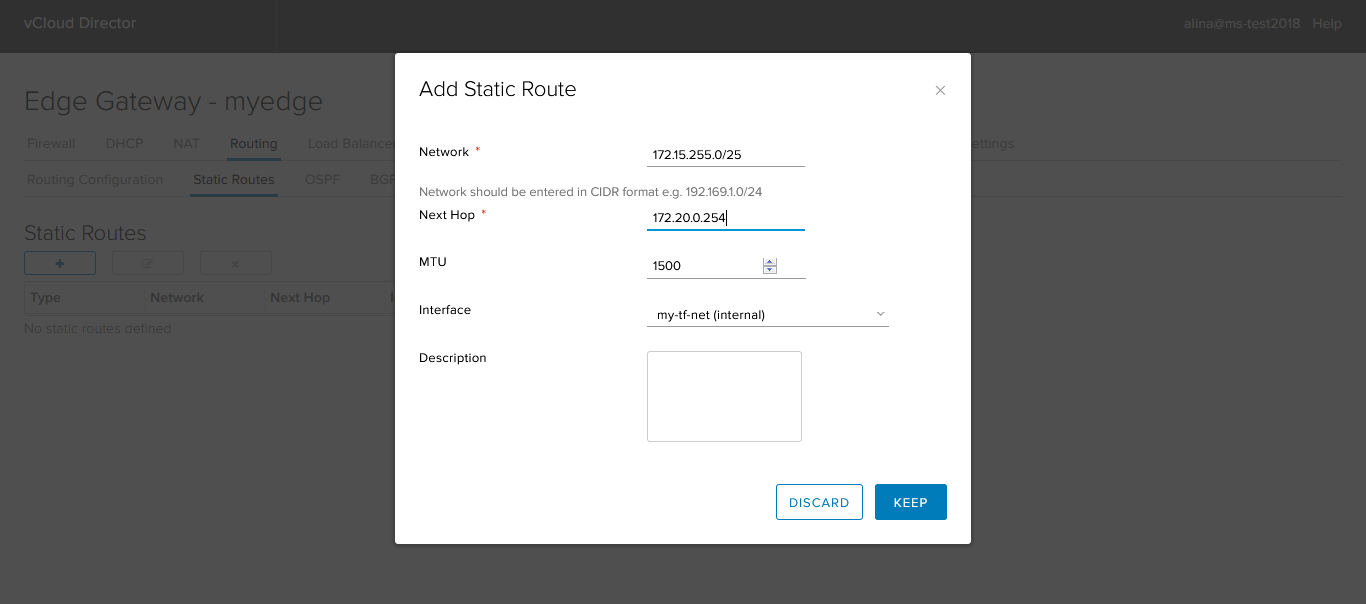
Go to the Static routing tab and click +.

To add a static route, fill in the following required fields:
- Network — destination network;
- Next Hop - IP addresses of the host / router through which traffic will pass to the destination network;
- Interface - the interface for which the Next Hop is located.
Click Keep.
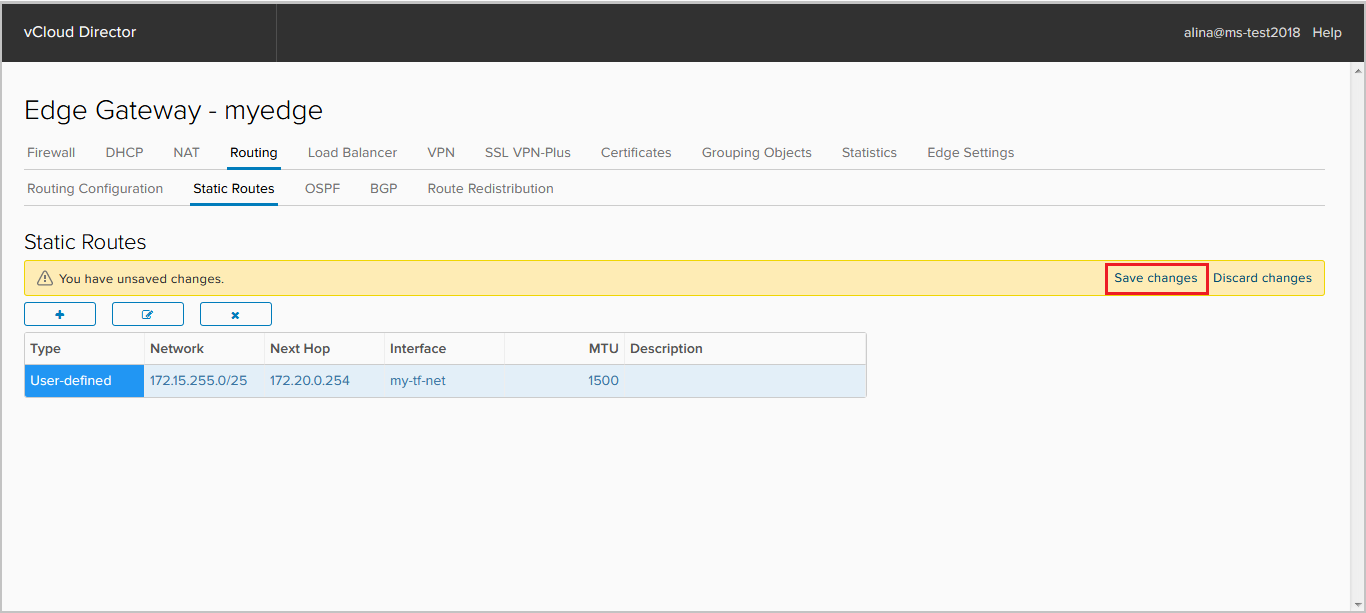
Save the configuration.
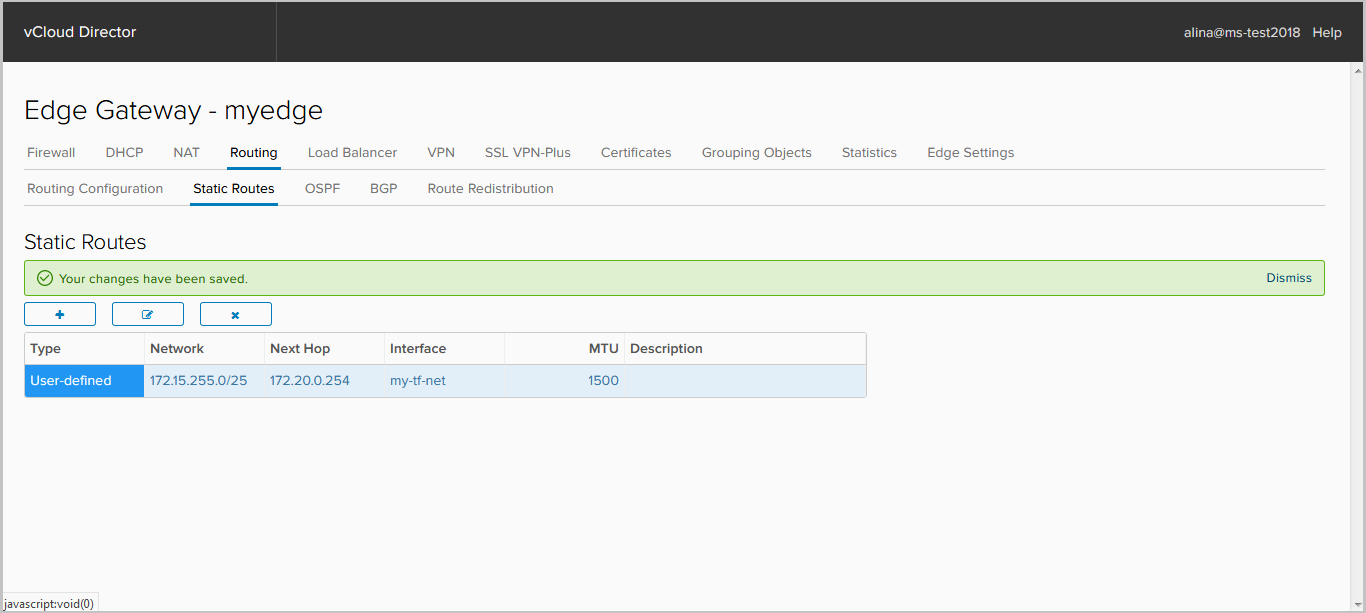
Is done.
OSPF Setup
Click the OSPF tab. We include the OSPF process.
If required, disable Graceful restart, which is enabled by default. Graceful restart is a protocol that allows you to continue forwarding traffic during the convergence of the control plane.
Here you can activate the default route announcement if it is in the RIB - the default originate option.
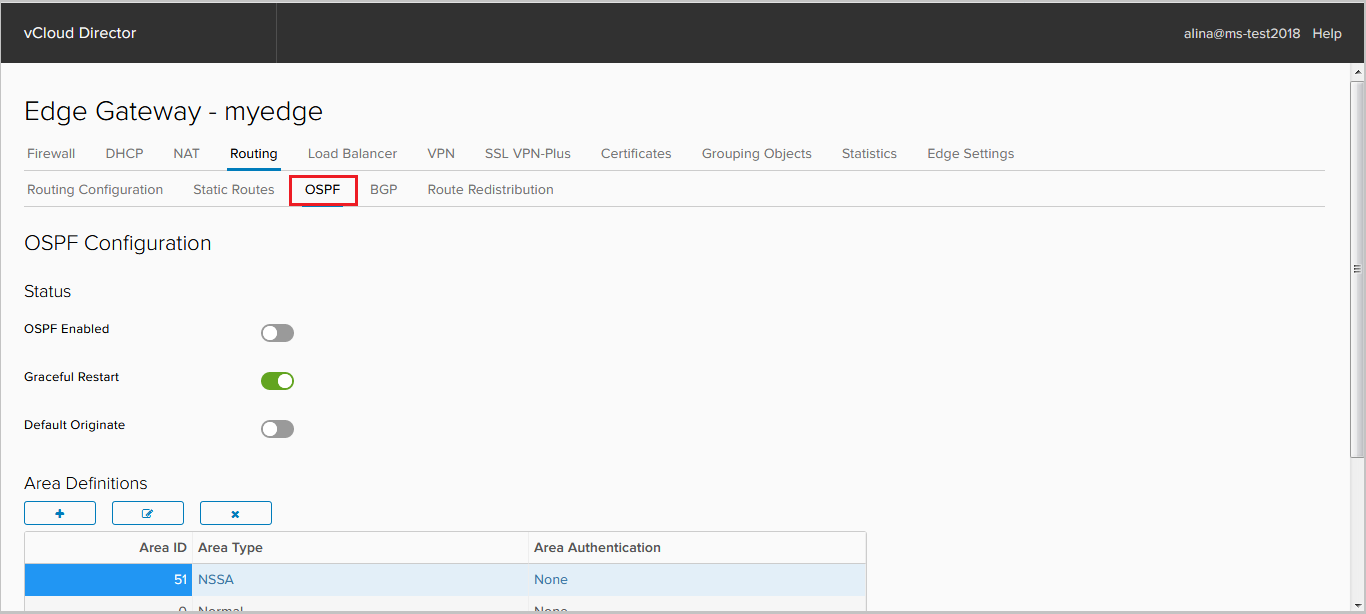
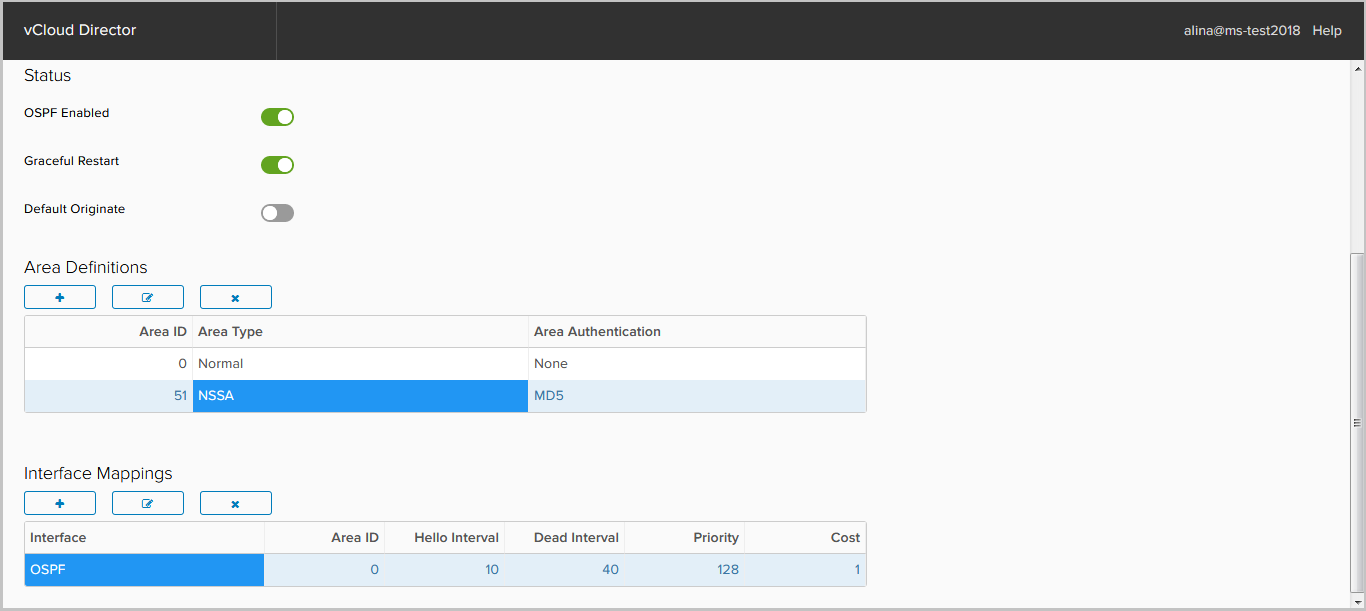
Next, add the Area. By default, Area 0 is added. NSX Edge supports 3 types of Area:
- Backbone area (area 0 + Normal);
- Standard area (Normal);
- Not-so-stubby area (NSSA).
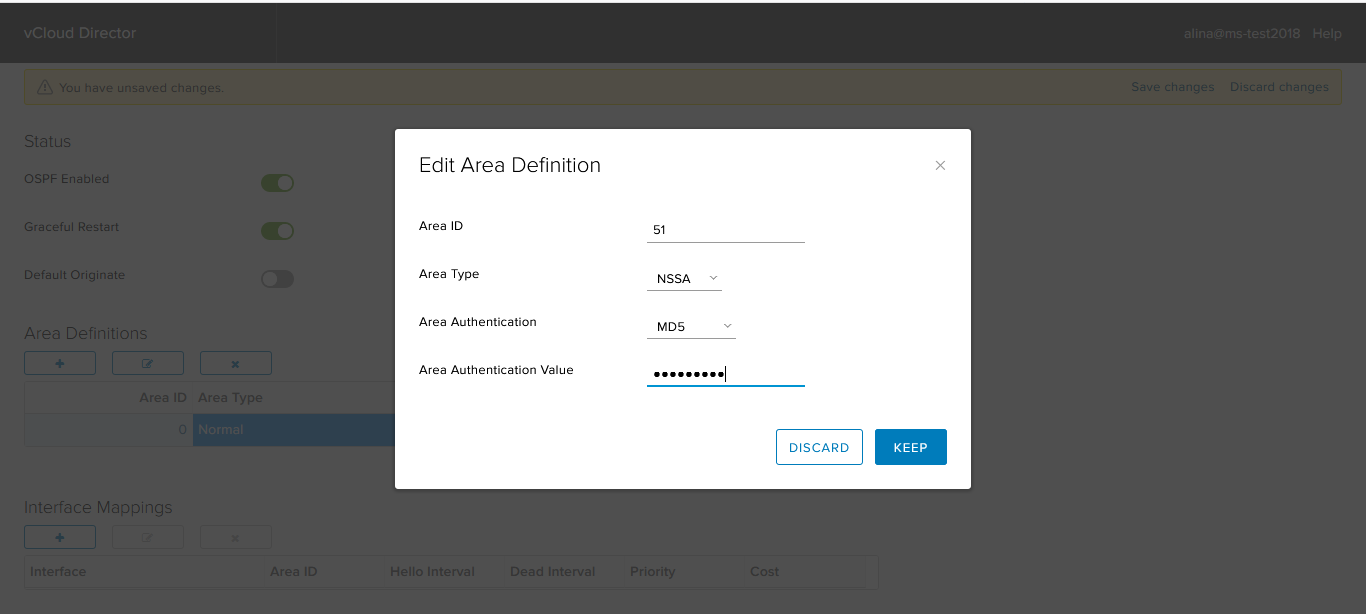
Click + in the Area Definition field to add a new Area.
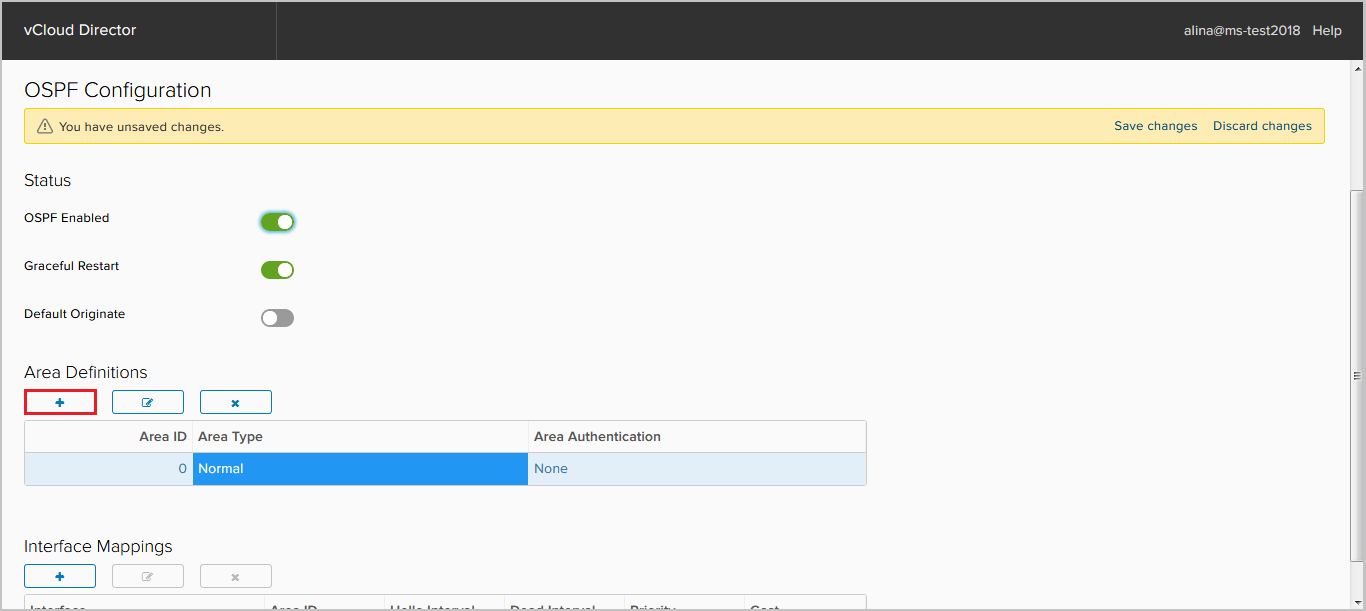
In the window that appears, specify the following required fields:
- Area ID;
- Area type.
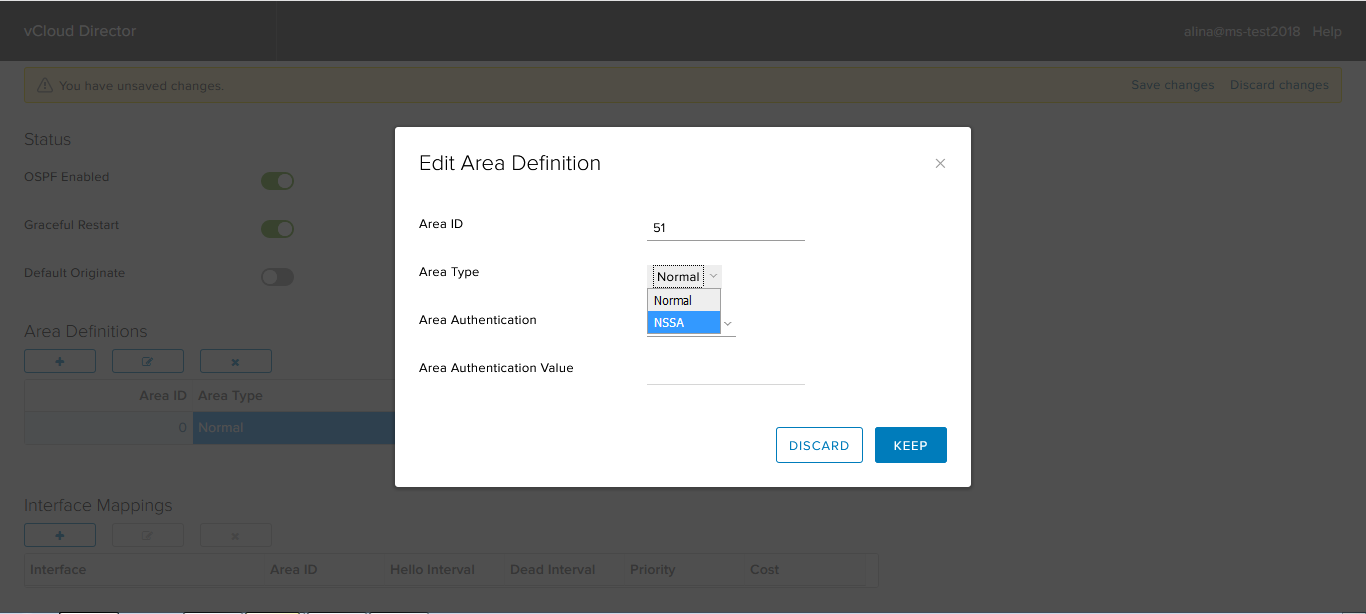
If required, configure authentication. NSX Edge supports two types of authentication: clear text (password) and MD5.
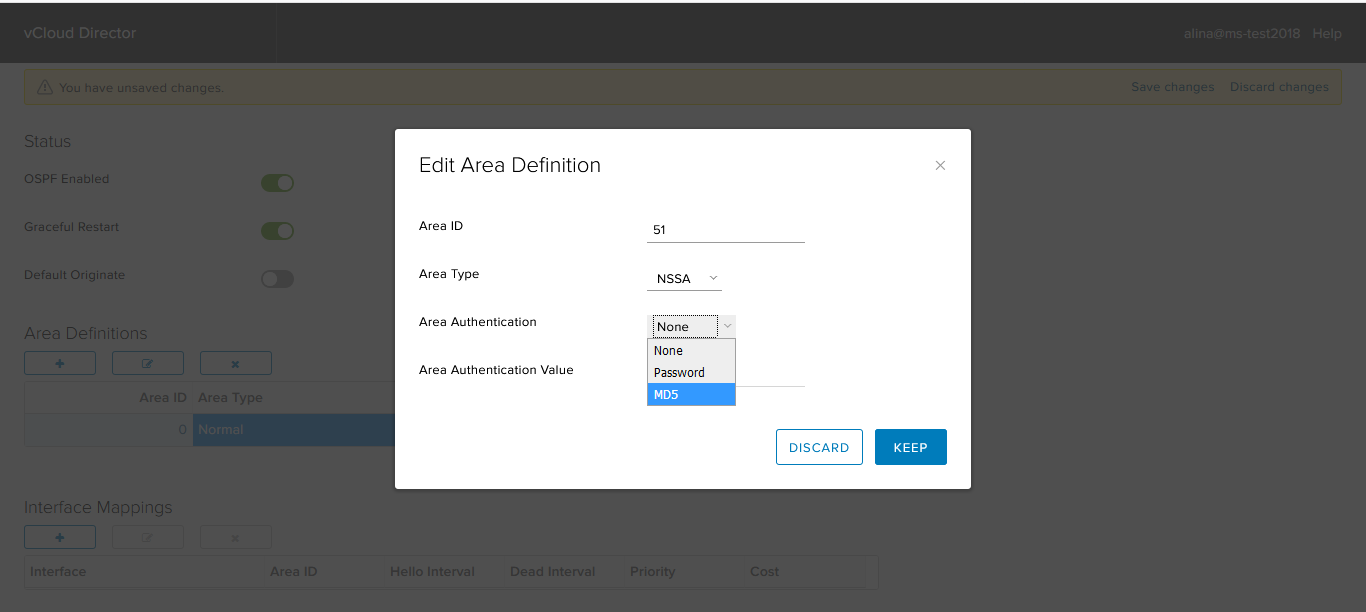
Click Keep.
Save the configuration.
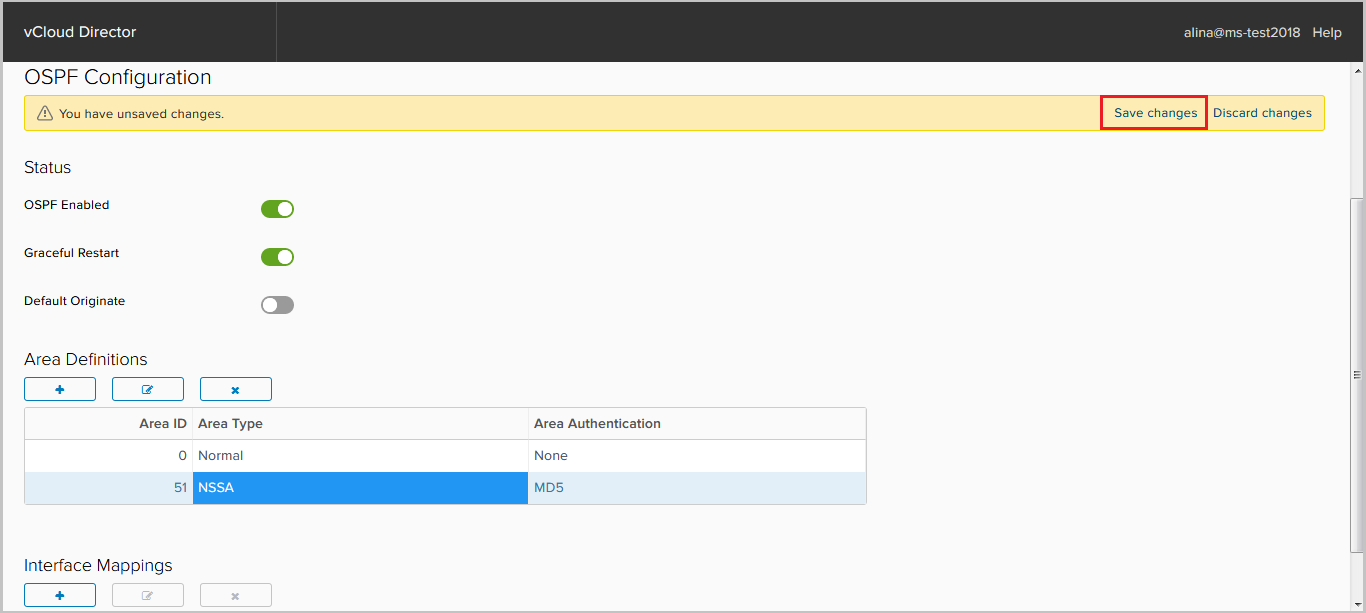
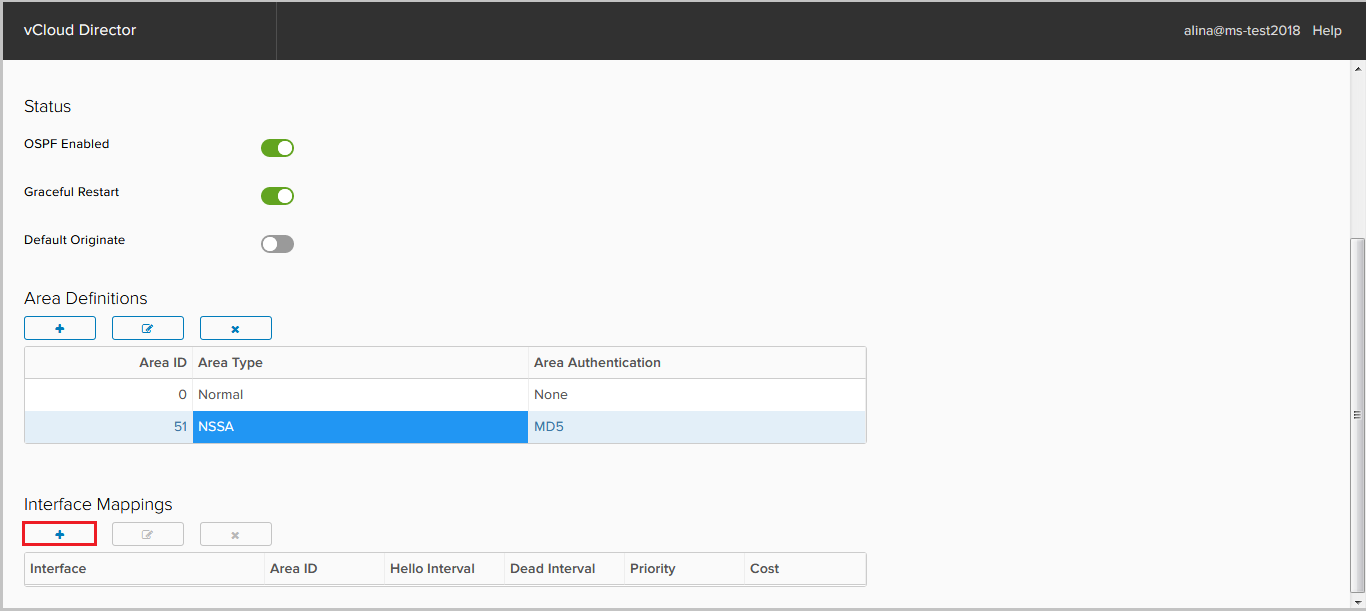
Now add the interfaces on which the OSPF neighborhood will climb. To do this, click + in the Interface Mapping field.
In the window that appears, specify the following parameters:
- Interface - the interface that will be involved in the OSPF process;
- Area ID;
- Hello / Dead interval - protocol timers;
- Priority - the priority required to select DR / BDR;
- Cost - the metric required to calculate the best path. Click Keep.
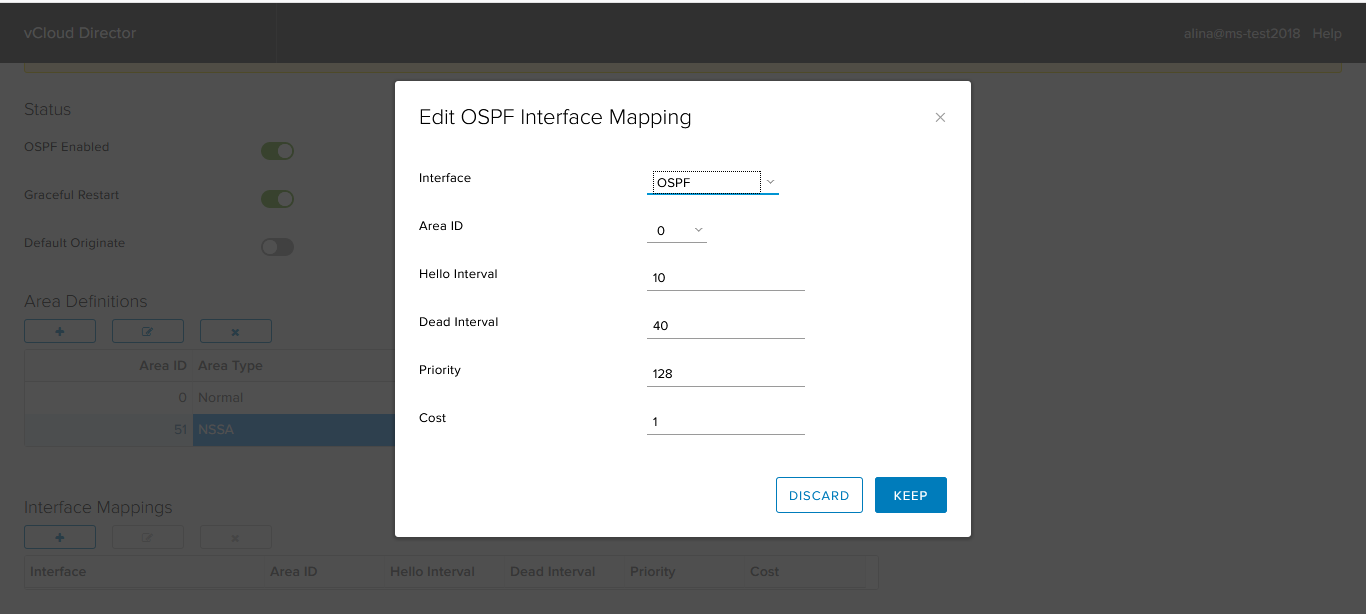
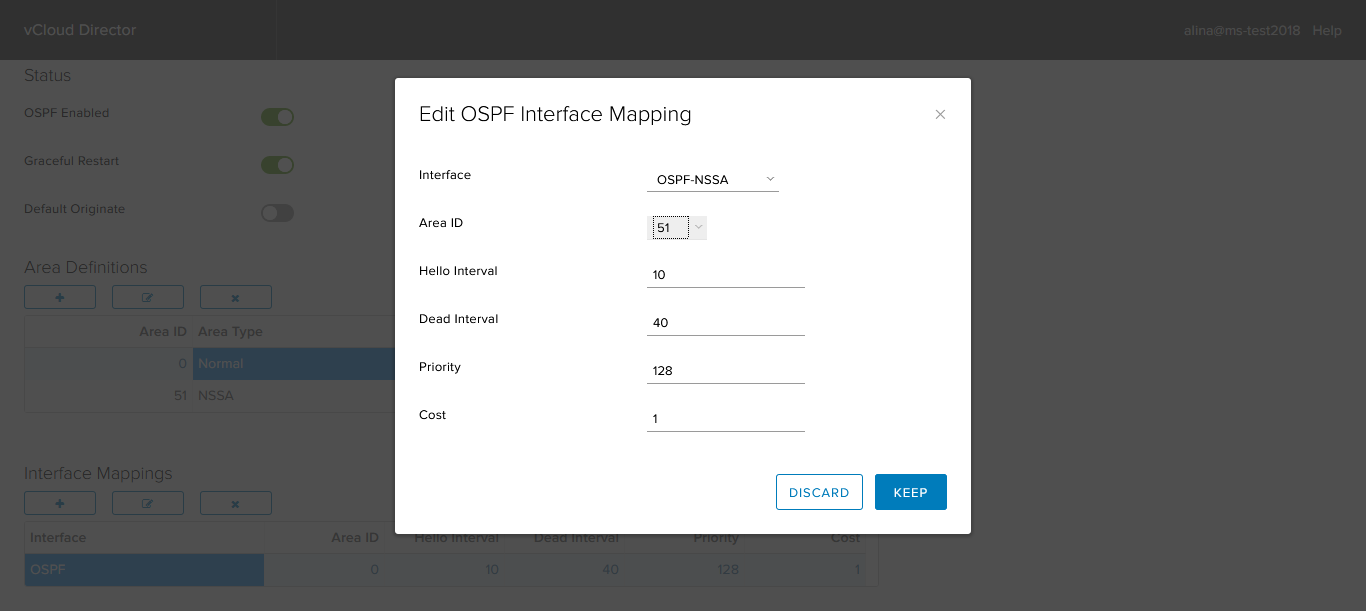
Add our router NSSA Area.
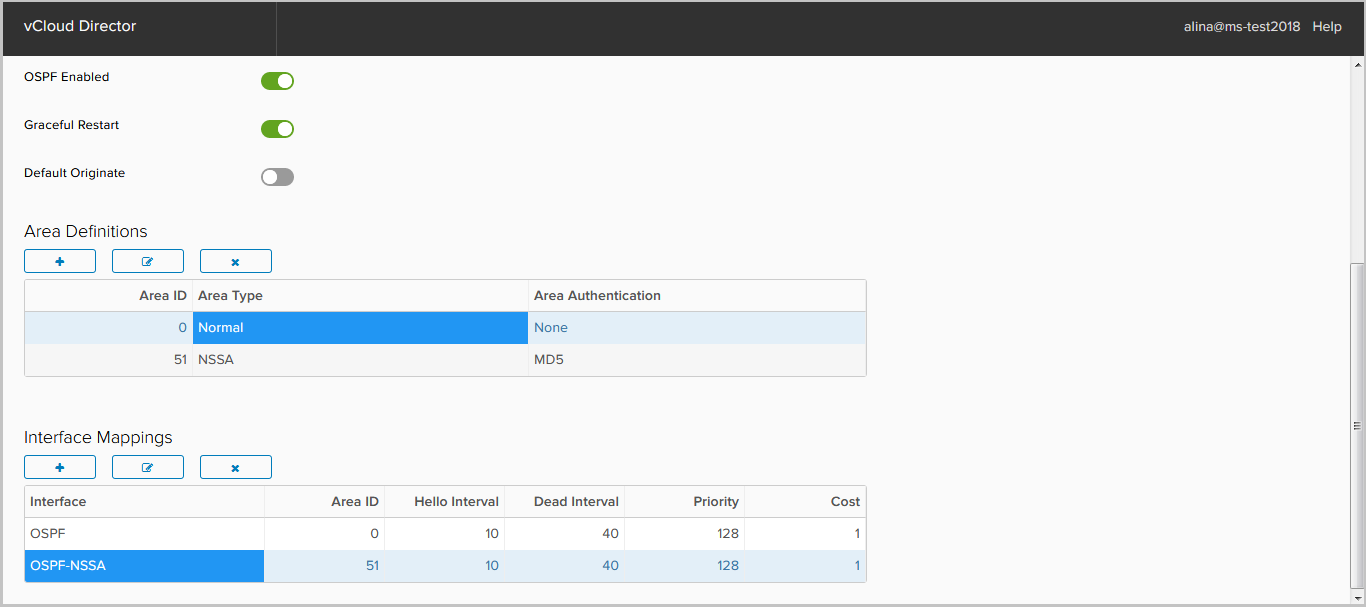
Save the configuration.
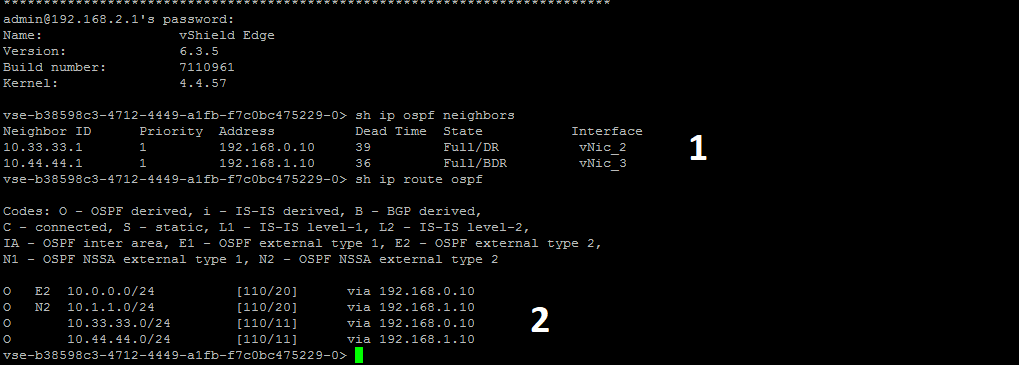
In the screenshot below we see:
1. established sessions;
2. installed routes in the RIB.
BGP Setup
Click the BGP tab.
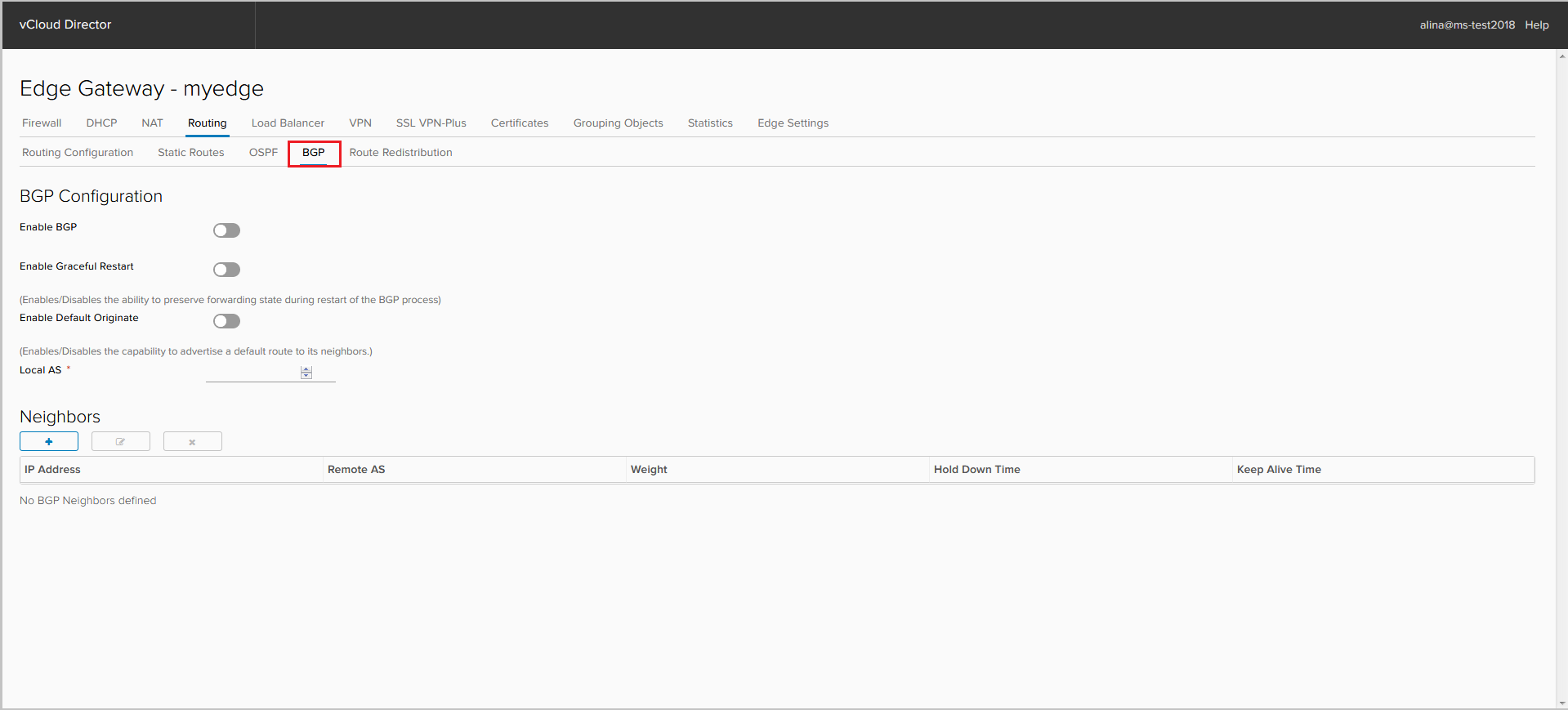
We include the BGP process.
If required, disable Graceful Restart, which is enabled by default. Here you can activate the default route announcement, even if it is not in the RIB - the option Default Originate.
We specify AS of ours NSX Edge. 4-byte AS support is available only with NSX 6.3.

To add peer neighbors, click +.
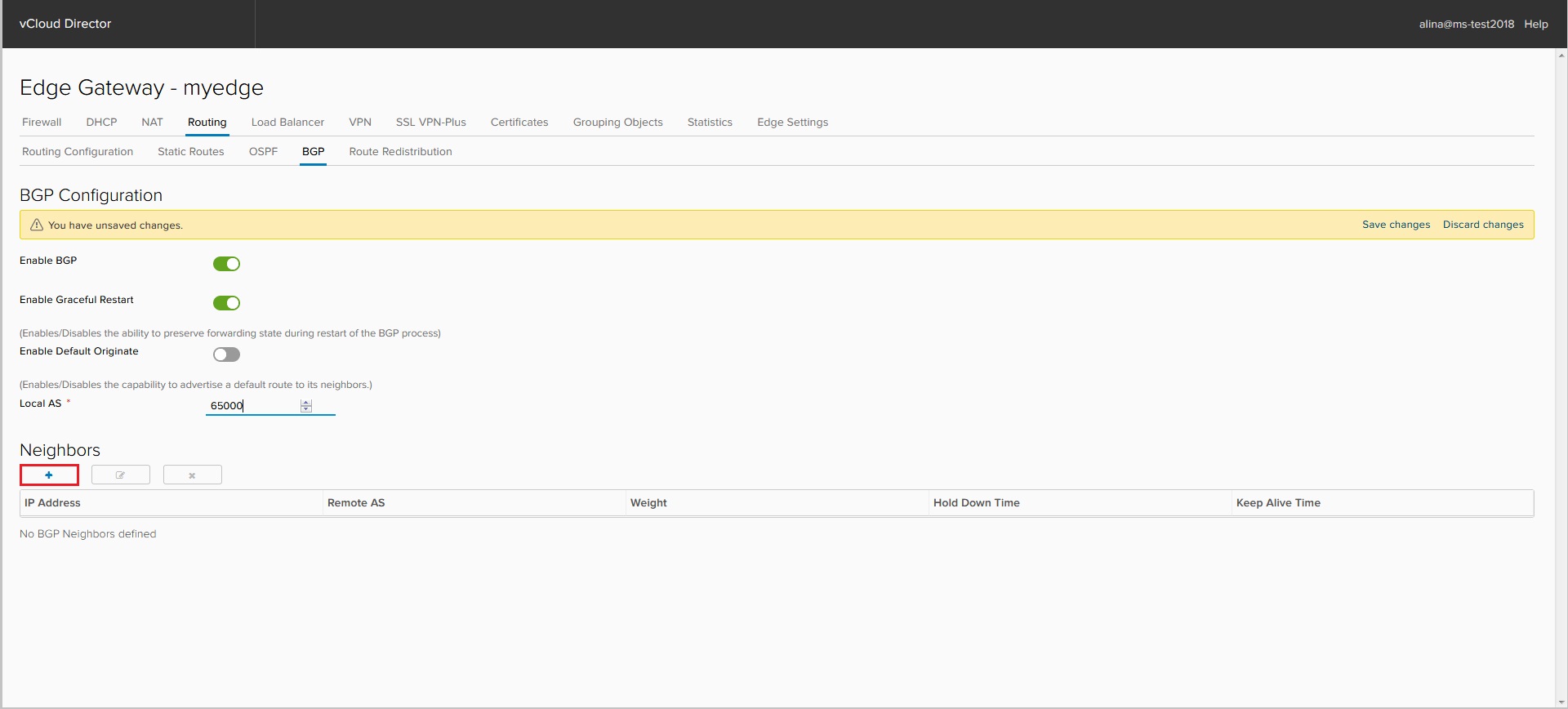
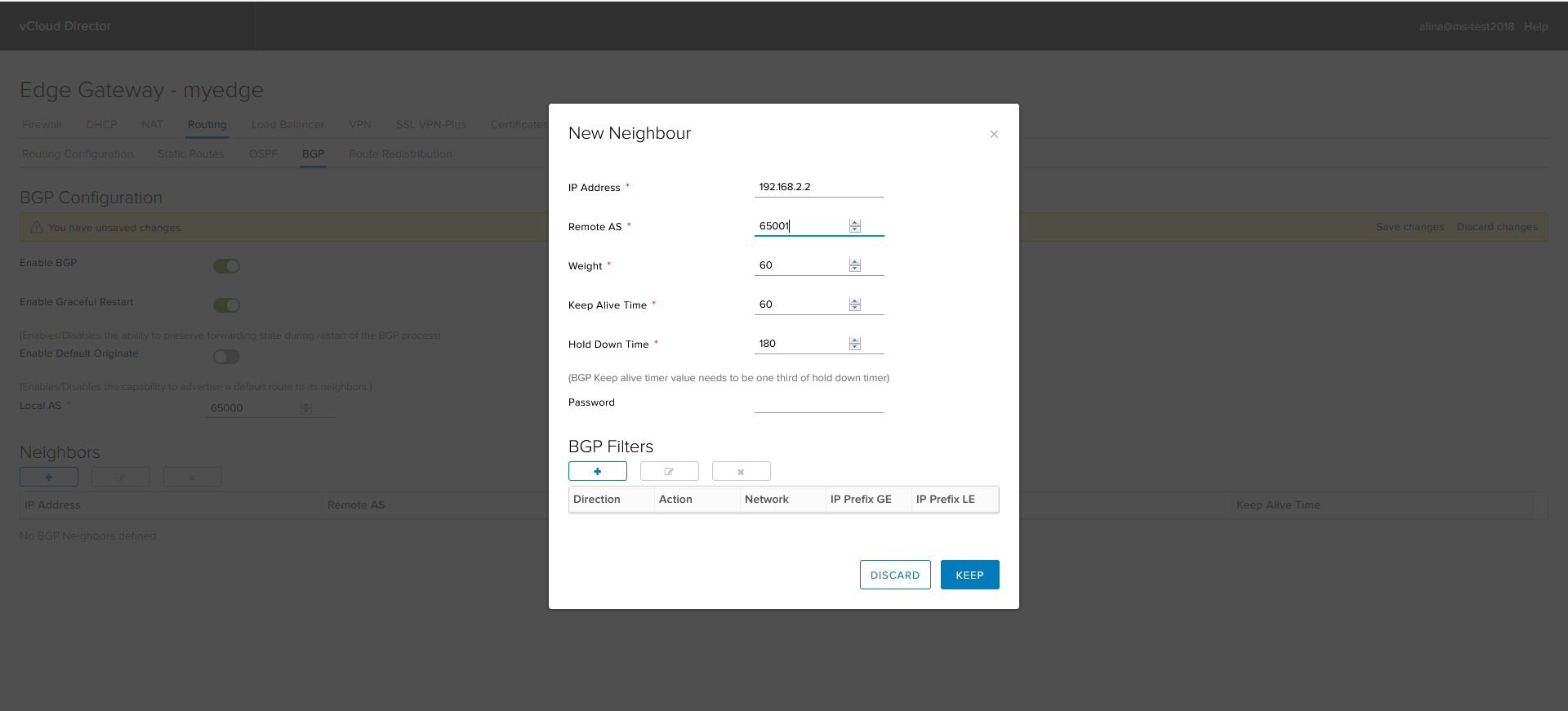
In the window that appears, specify the following parameters:
- IP Address - BGP peer address;
- Remote AS — AS BGP peer number;
- Weight is a metric with which you can control outgoing traffic;
- Keep Alive / Hold Down Time - protocol timers.
Next, configure BGP Filters. For eBGP sessions, the default is to filter all advertised and accepted prefixes on this router, except the default route. It is advertised using the default originate option.
Click + to add BGP Filter.
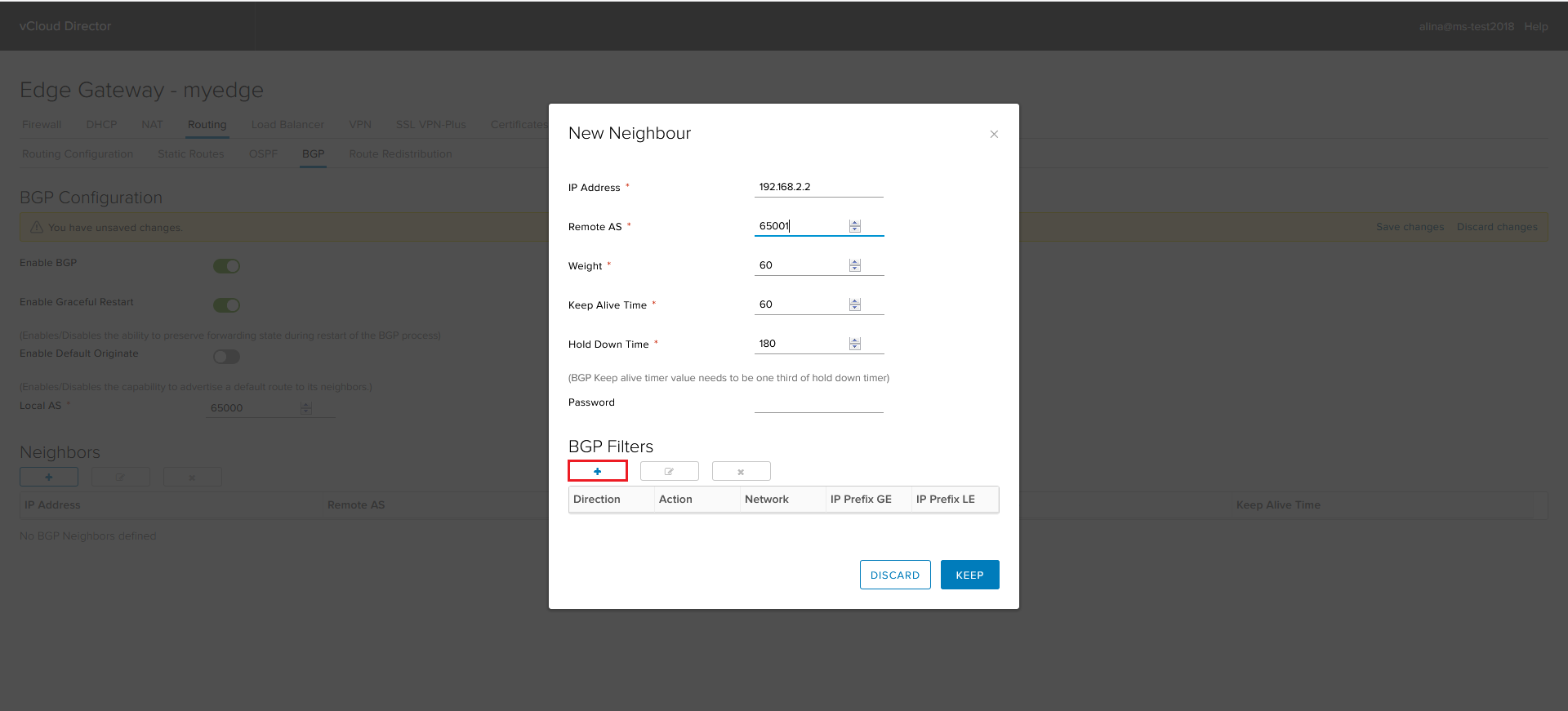
Configure the filter for outgoing update.
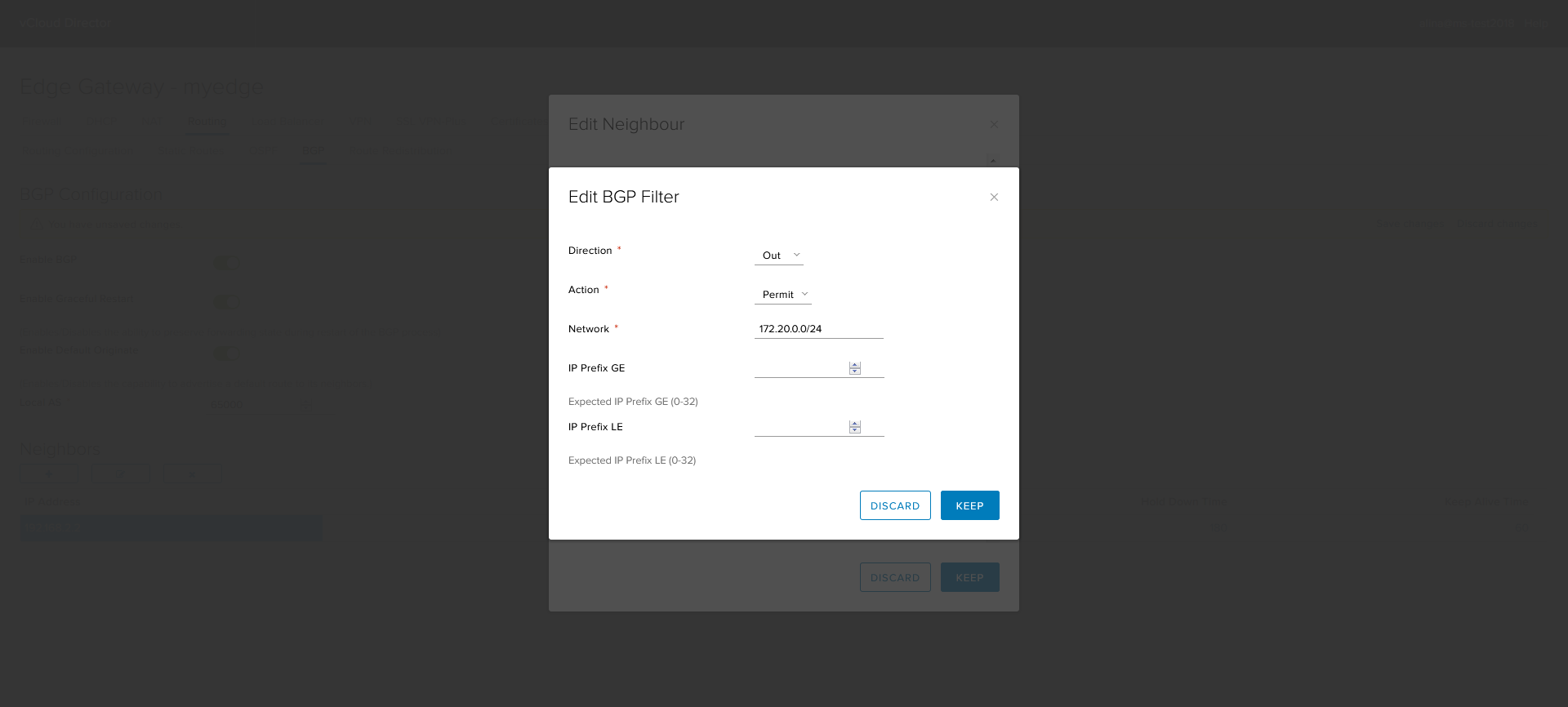
We configure the filter on the incoming update.

Click Keep to complete the setup.
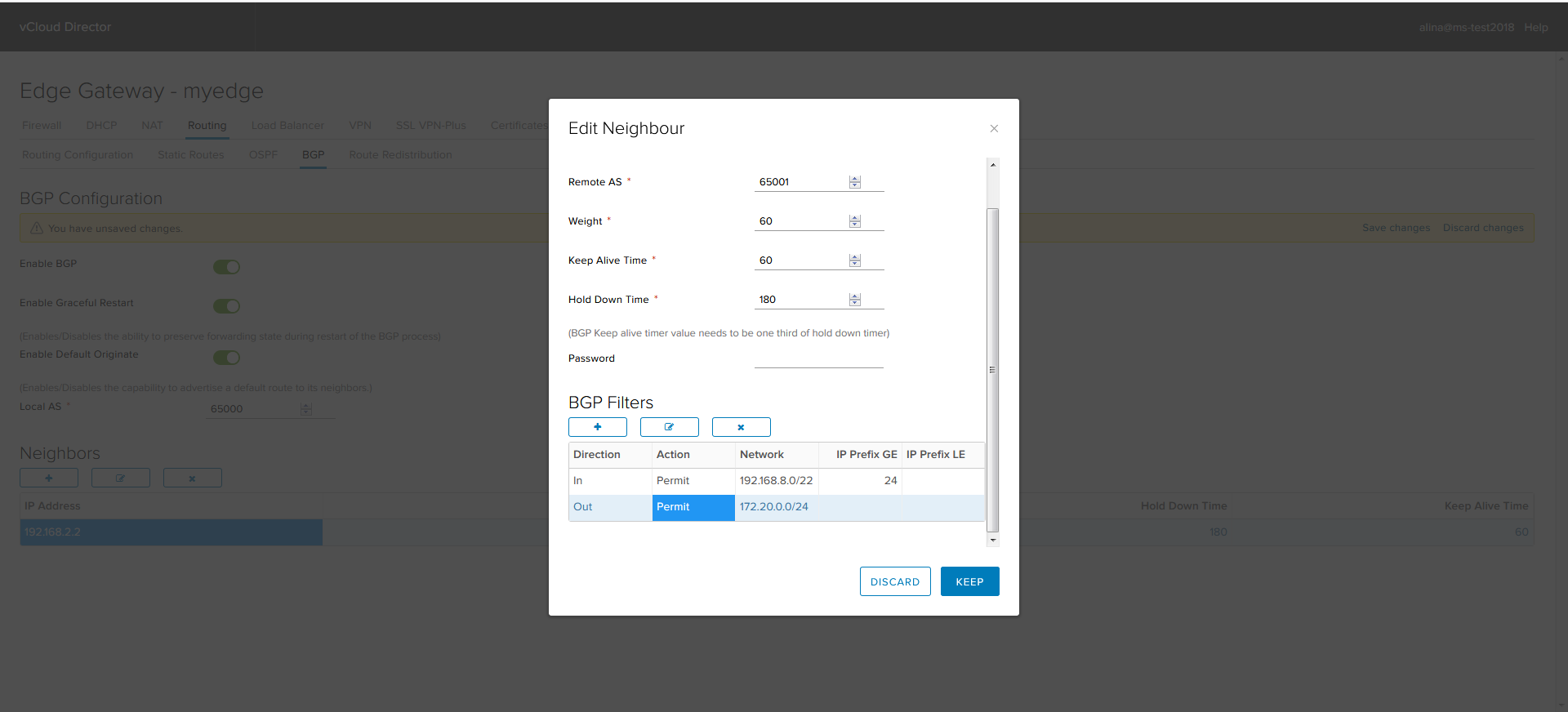
Save the configuration.
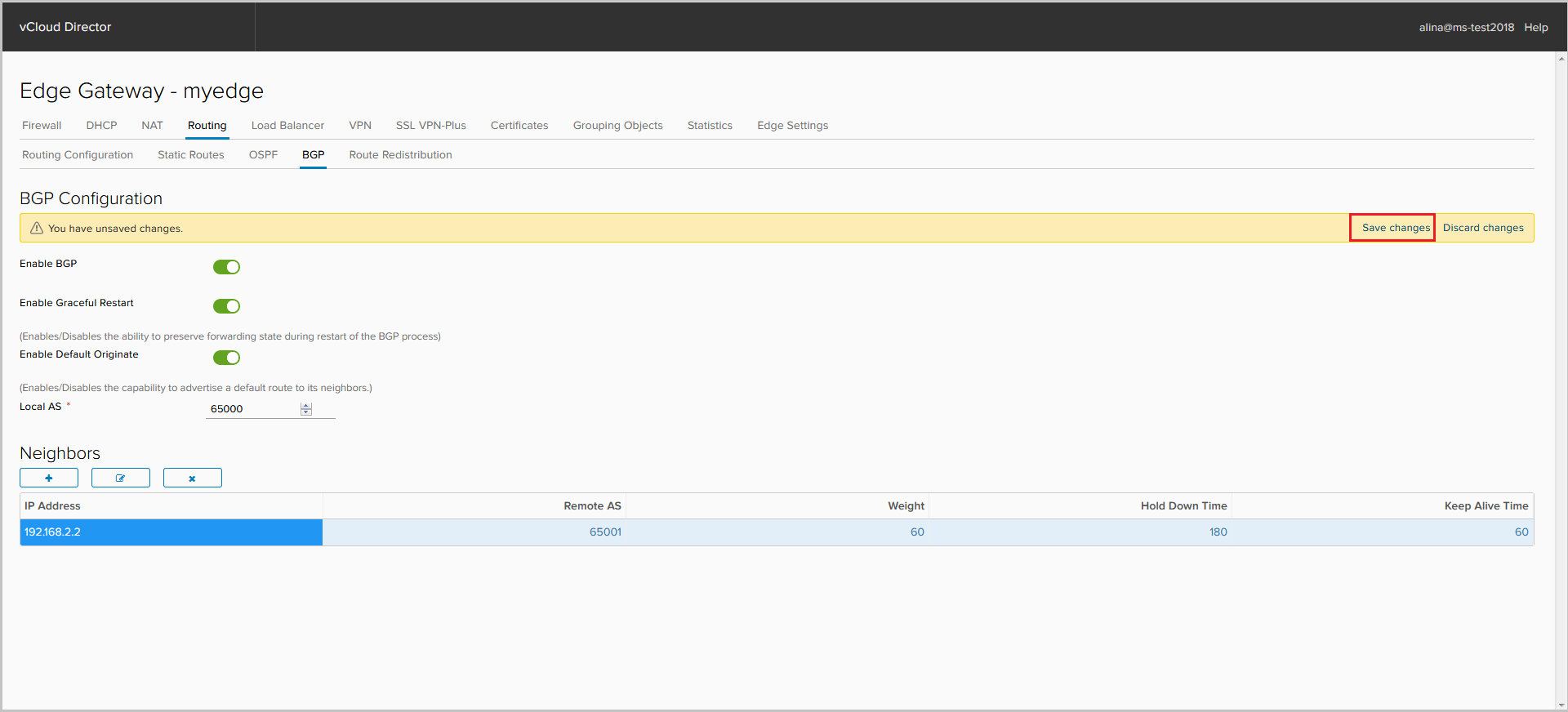
Is done.
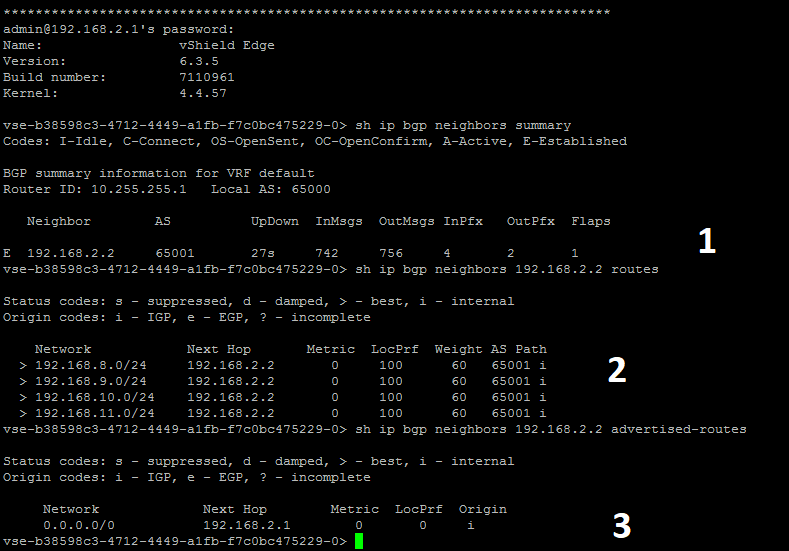
In the screenshot below we see:
1. established session.
2. received prefixes (4 prefixes / 24) from BGP peer.
3. default route announcement. The prefix 172.20.0.0/24 is not announced as it is not added to BGP.
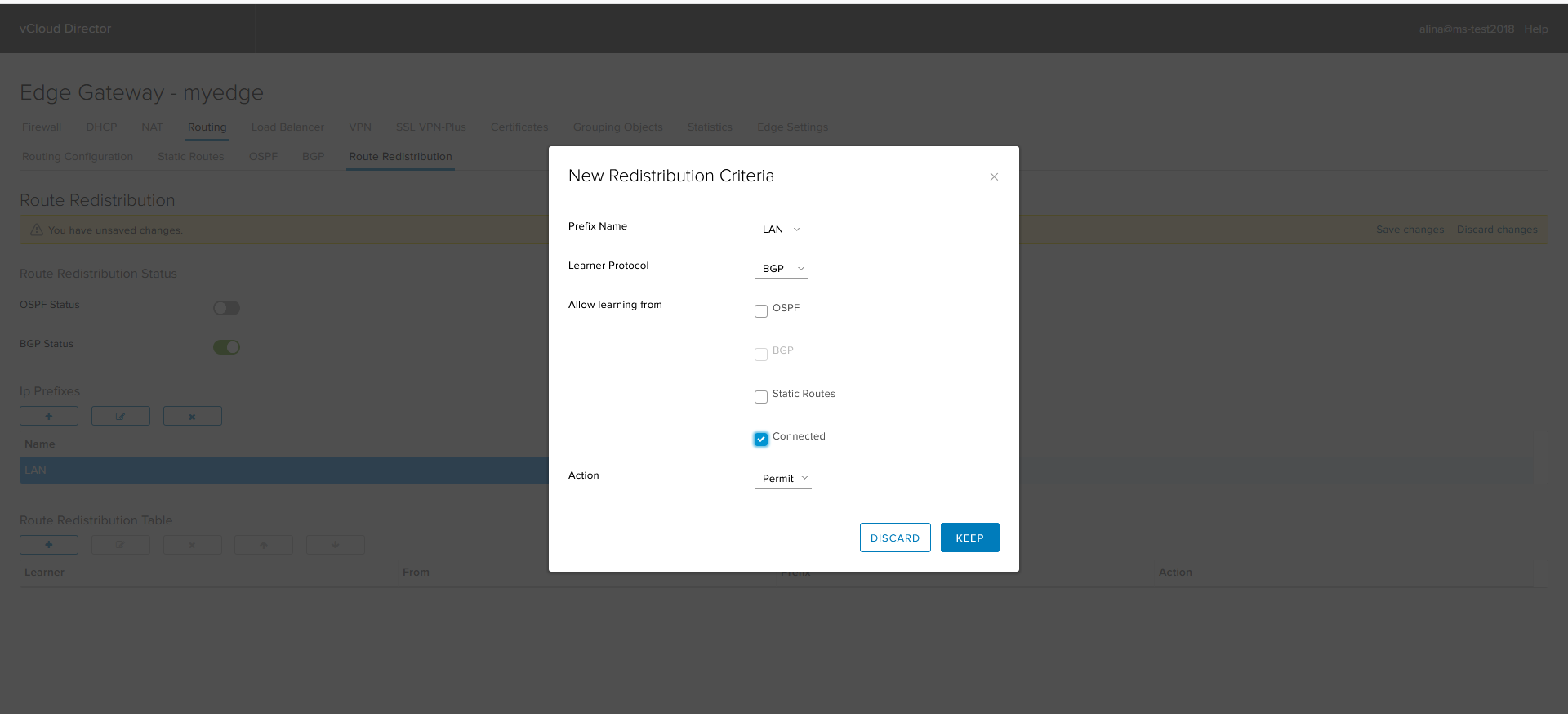
Configuring Route Redistribution
Click the Route Redistribution tab.
Enable route import for protocol (BGP or OSPF).
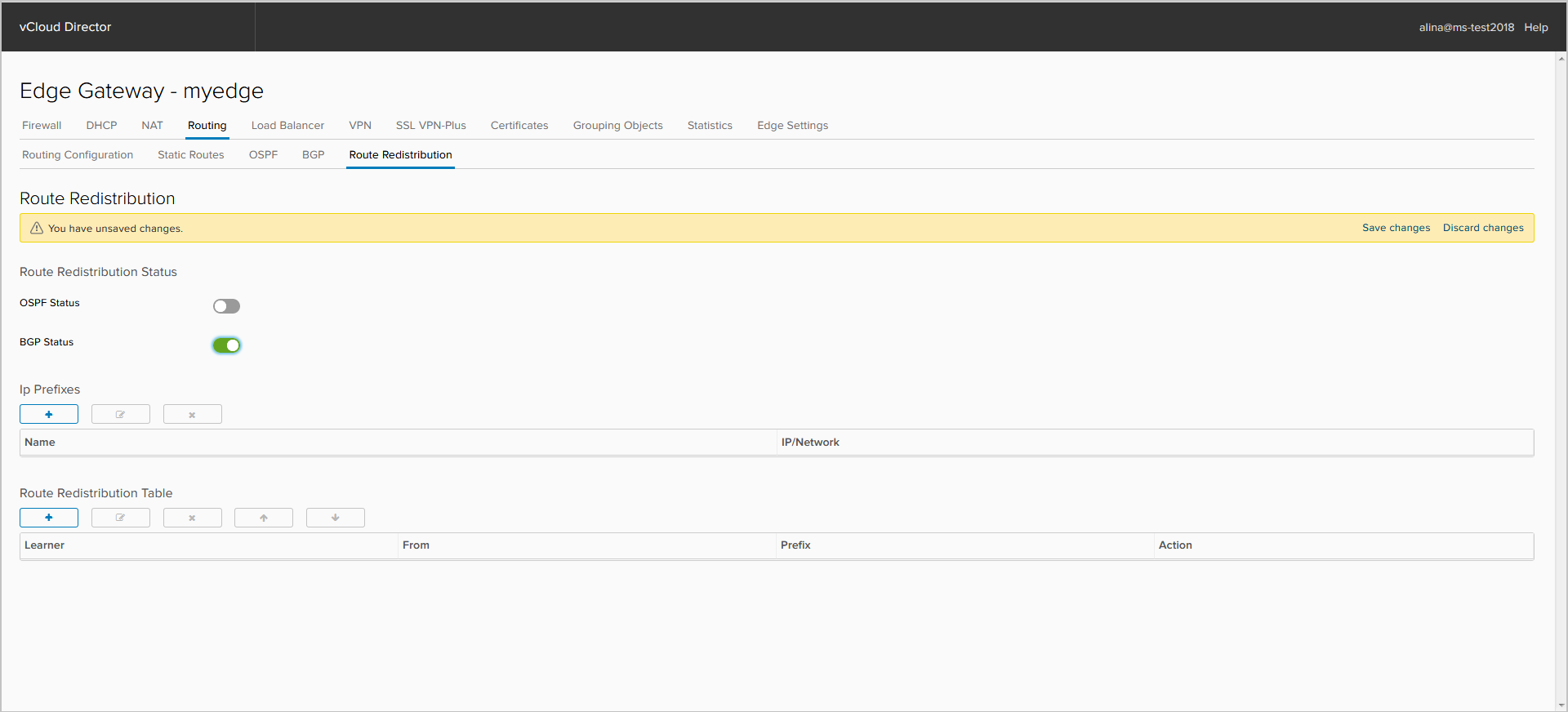
To add an IP prefix, click +.
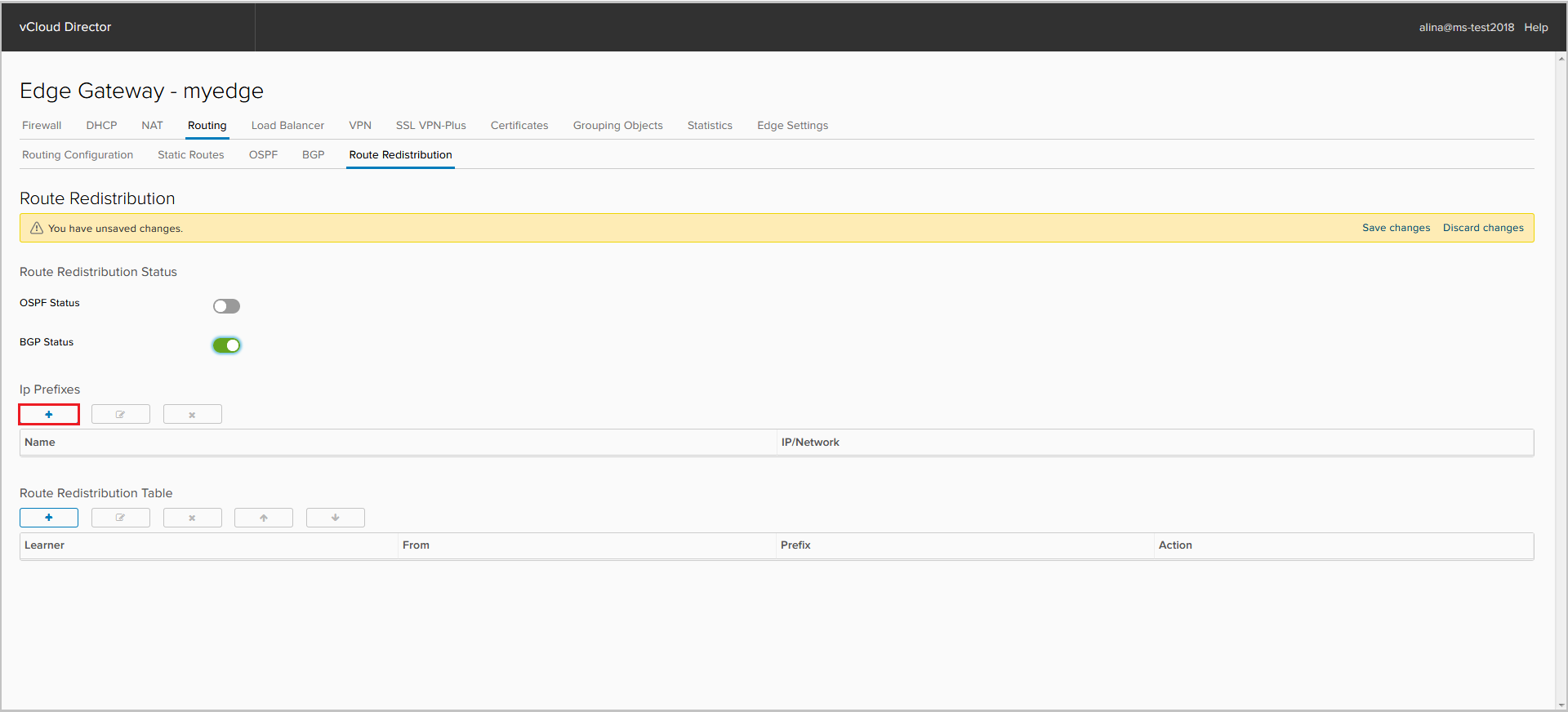
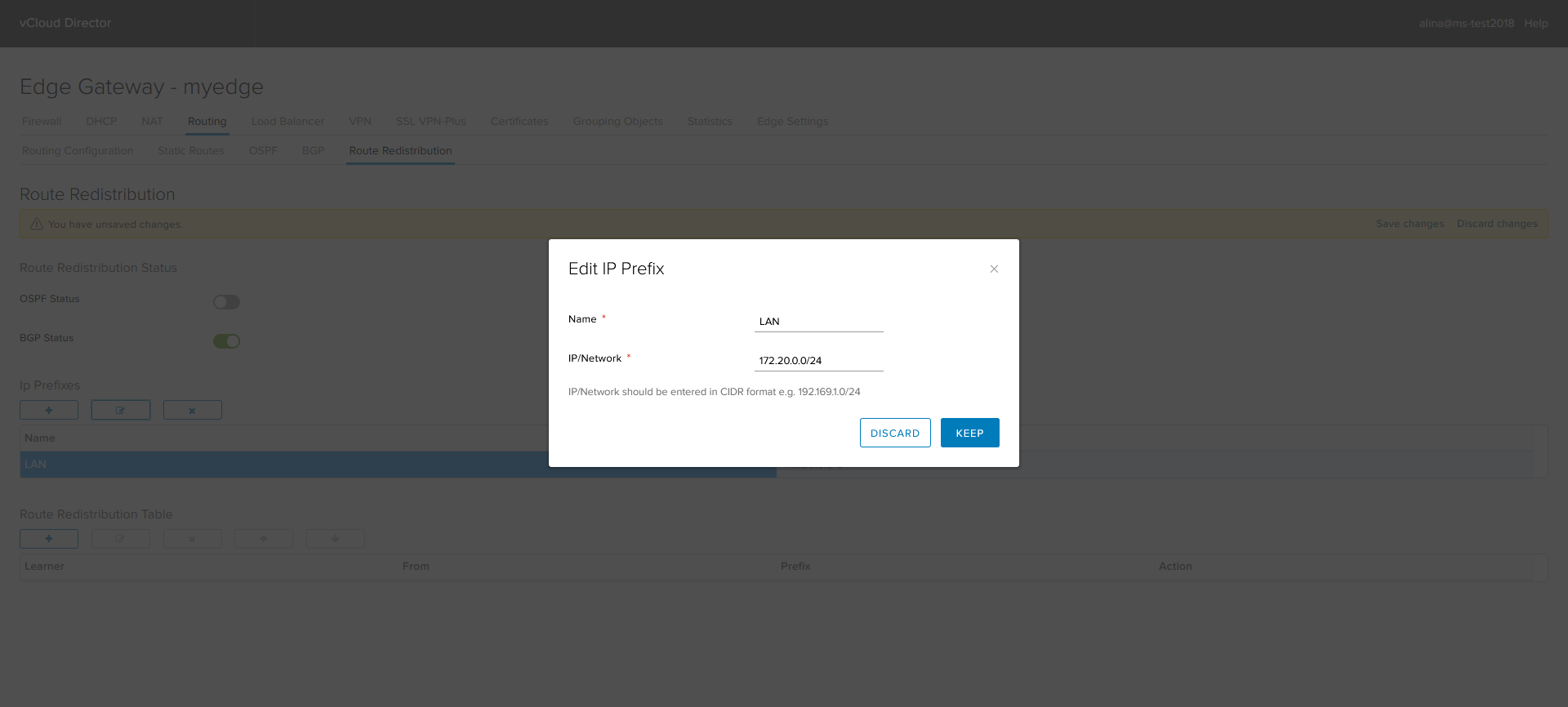
Specify the name of the IP-prefix and the prefkis itself.
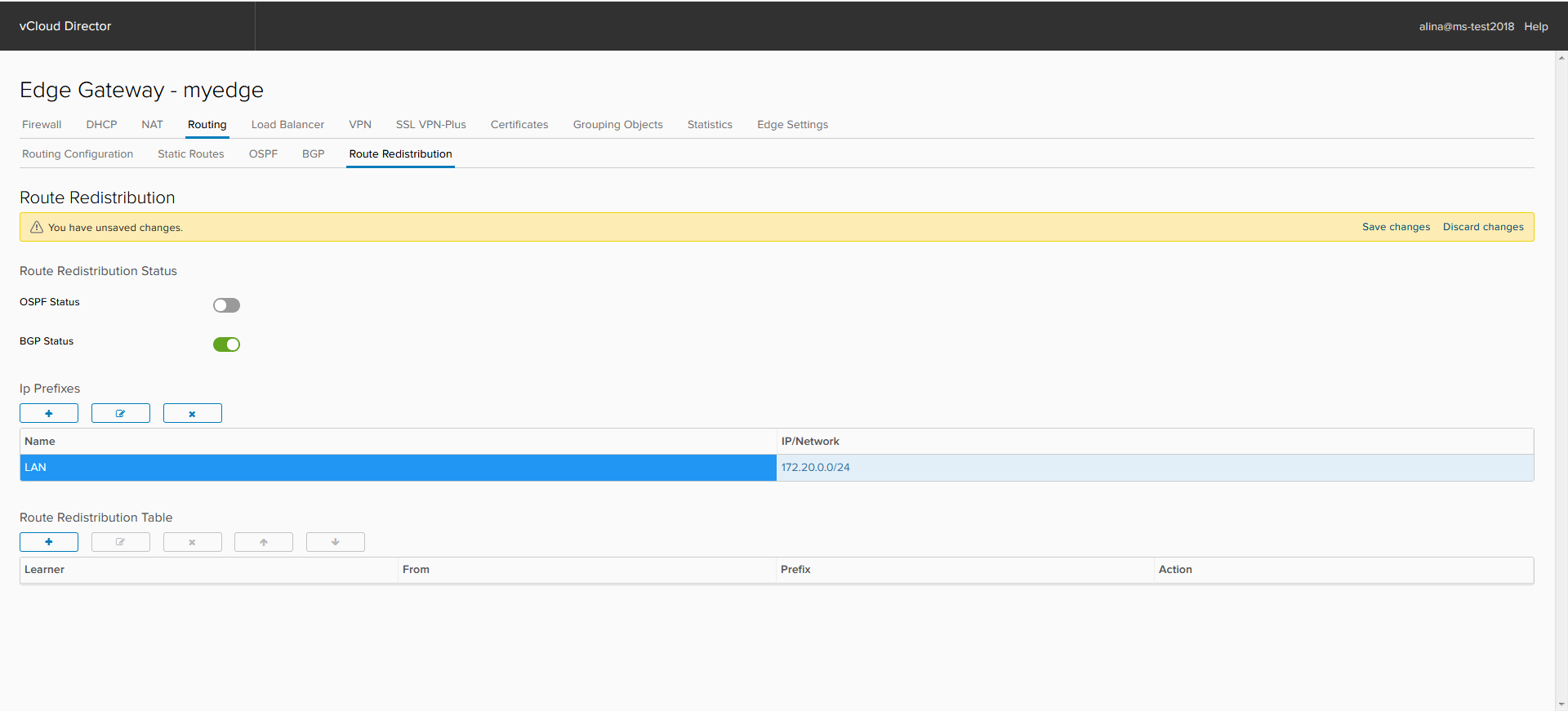
Set up the Route Distribution Table. Click +.
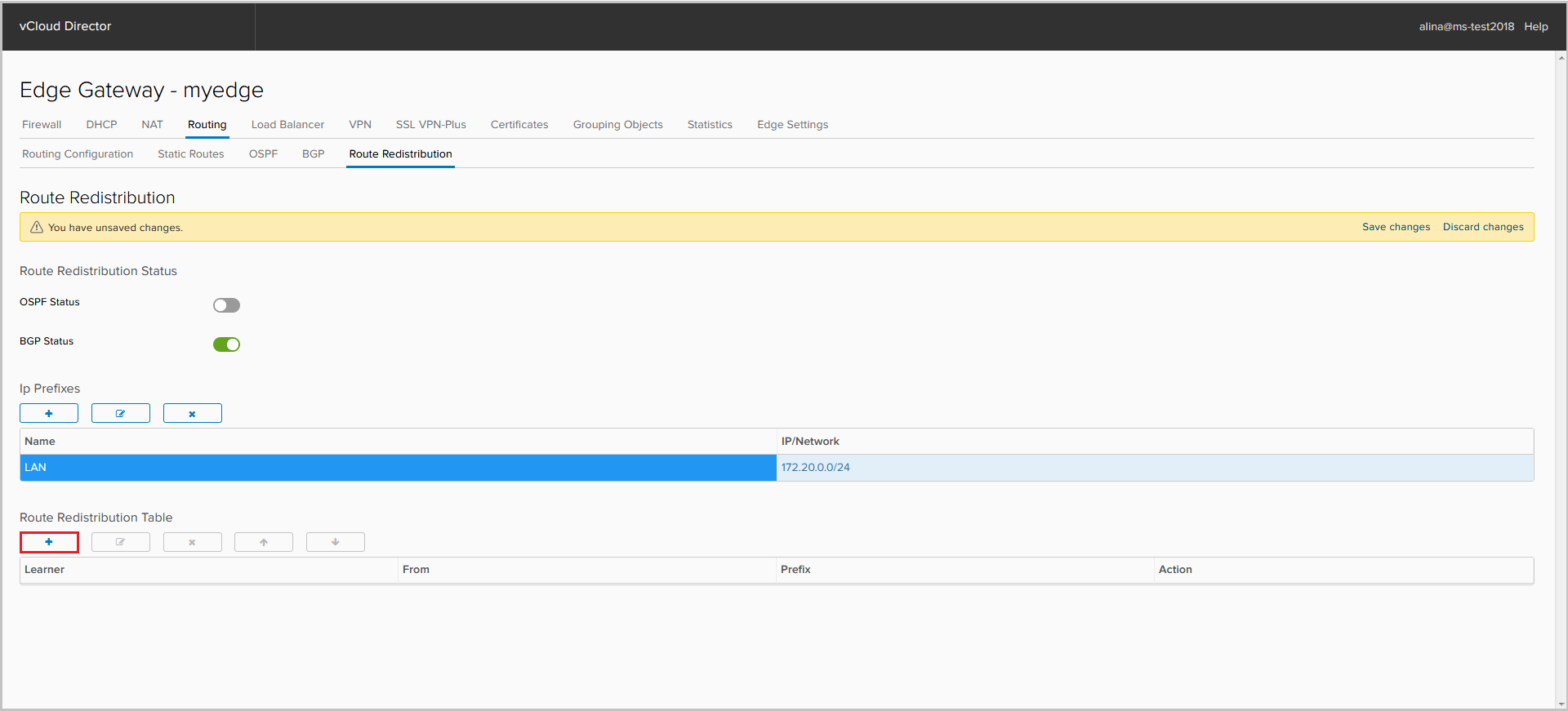
- Prefix Name - select the prefix, which will be imported into the appropriate protocol.
- Learner Protocol - the protocol where we will import the prefix;
- Allow learning - the protocol from which we export the prefix;
- Action - the action that will be applied to this prefix.
Save the configuration.
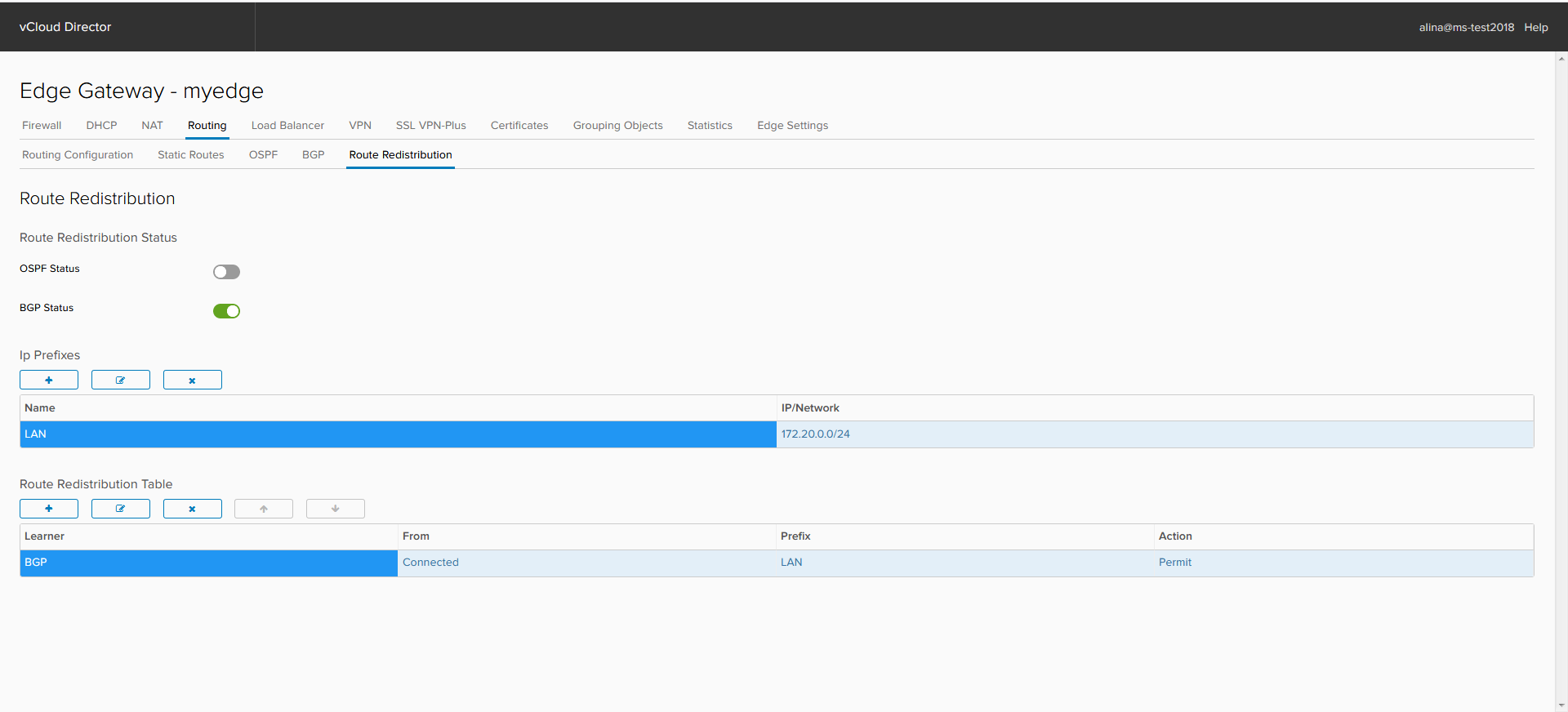
Is done.
The screenshot below shows that the corresponding announcement has appeared in BGP.

On this I have everything about routing using NSX Edge. Ask if something is left incomprehensible. Next time we will deal with the balancer.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/444644/
All Articles