Modernization of GHIDRA. Sega Mega Drive ROM Loader

Greetings, comrades. I have not heard of a still-non-open source GHIDRA , probably, only a deaf / blind / dumb / without_internet revers engineer. Its capabilities out of the box are amazing: decompilers for all supported processors, simple addition of new architectures (with immediately active decompilation thanks to competent conversion to IR), a lot of scripts that simplify life, the possibility of Undo / Redo ... And this is only a very small part of all the possibilities. To say that I was impressed is practically nothing to say.
So, in this article I would like to tell you how I wrote my first module for GHIDRA , the Sega Mega Drive / Genesis roms loader. To write it I needed ... just a couple of hours! Go.
I spent some days on understanding the process of writing downloaders for IDA . Then it was version 6.5 , it seems, and in those days there were a lot of problems with the SDK documentation.
Prepare development environment
The developers of GHIDRA thought out almost everything ( Ilfak , where have you been before?). And, just to simplify the implementation of the new functionality, they developed a plug-in for Eclipse - GhidraDev , which actually " helps " to write code. The plugin integrates into the development environment, and allows you to create project templates for scripts, loaders, processor modules and extensions for them, as well as export modules in a few clicks (as I understood, this is some kind of data export from the project).
To install the plugin, download Eclipse for Java , click Help -> Install New Software... , then click the Add button, and open the archive selection dialog with the plugin Archive... button. The archive with GhidraDev is in the $(GHIDRA)/Extensions/Eclipse/GhidraDev . Select it, click Add .

In the list that appears, put a Ghidra on Ghidra , click Next > , agree with the agreements, click Install Anyway (because the plugin has no signature), and restart Eclipse .
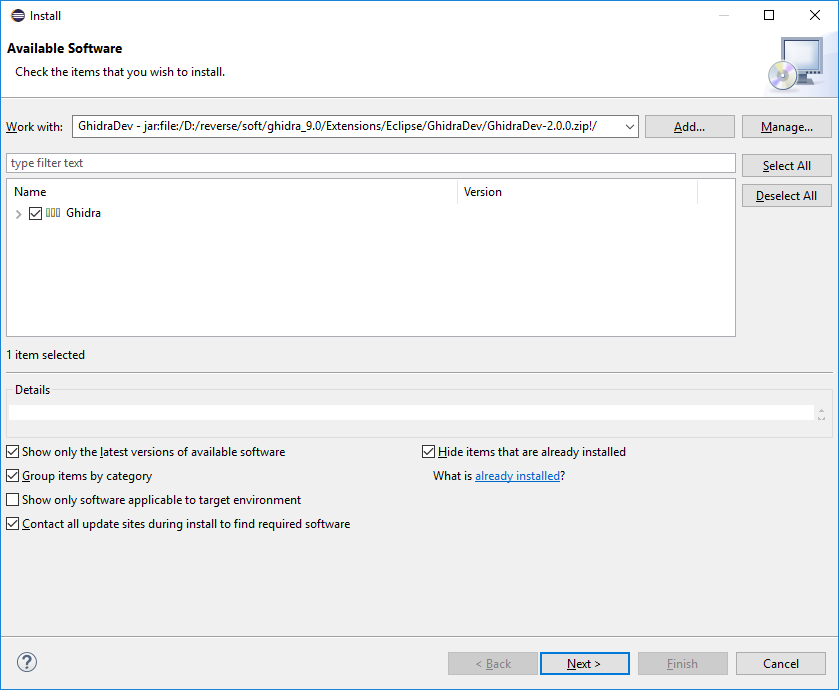
In total, the GhidraDev item will appear in the IDE GhidraDev for easy creation and distribution of your projects (of course, you can also create it through the regular Eclipse project wizard). In addition, we have the opportunity to debug the developed plugin or script.
What really pisses off in the situation with GHIDRA is the fucking copy of the HYIP articles containing almost the same material, which, moreover, does not correspond to reality. Example? Yes please:
The current version of the tool is 9.0. and the tool has options to include additional functionality such as Cryptanalysis, the interaction with OllyDbg, the Ghidra Debugger.
And where is all this? Nope
The second point: open source. In fact, it is almost there, but it is almost there. In the GHIDRA there are source codes for components that were written in Java , but if you look at the Gradle scripts, you can see that there are dependencies on a bunch of external projects from yet-secret ones. laboratories NSA repositories.
At the time of this writing, there are no source codes for the decompiler and SLEIGH (this is a utility for compiling descriptions of processor modules and conversions to IR).
Well, okay, I was distracted by something.
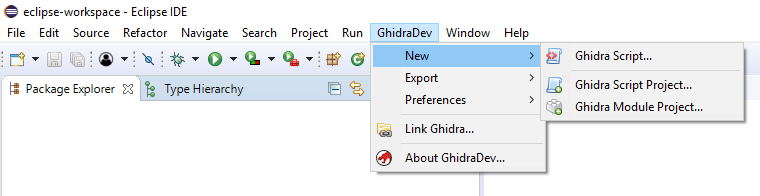
So let's create a new project in Eclipse .
We create the project of the loader
GhidraDev -> New -> Ghidra Module Project...
Specify the name of the project (we take into account that words of the Loader type will be pasted to the file names, and in order not to get something like sega_loaderLoader.java , we call them appropriately).
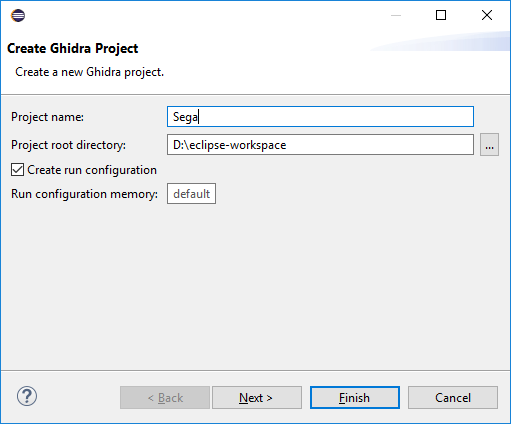
Click Next > . Here we put daws in front of the categories we need. In my case, this is just a Loader . Click Next > .

Here we indicate the path to the catalog with . Click Next > .
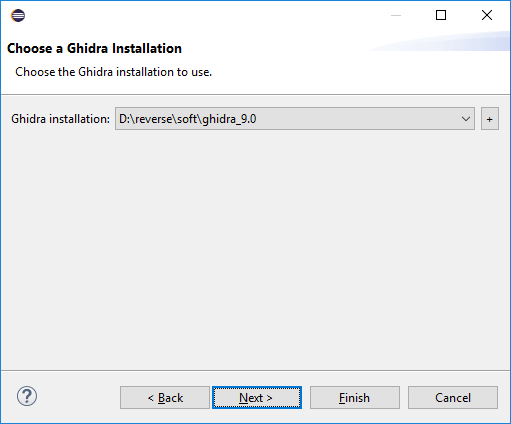
GHIDRA allows GHIDRA to write scripts in python (via Jython ). I will write in Java , so I do not put a daw. Shake Finish .

Write the code
The tree of an empty project looks impressive:

All files with java code are in the /src/main/java branch:
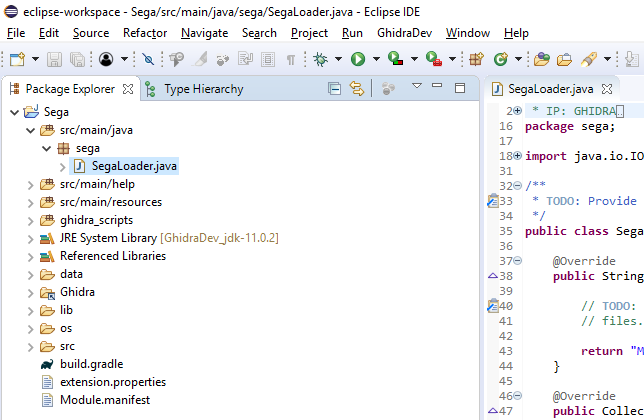
getName ()
First, let's choose a name for the bootloader. It is returned by the getName() method:
@Override public String getName() { return "Sega Mega Drive / Genesis Loader"; } findSupportedLoadSpecs ()
The findSupportedLoadSpecs() method decides (based on the data contained in the binary file) which processor module should be used for disassembling (as well as in the IDA ). In GHIDRA terminology GHIDRA this is called Compiler Language . It includes: processor, endianness, bitness and compiler (if known).
This method returns a list of supported architectures and languages. If the data is in the wrong format, we will simply return an empty list.
So, in the case of the Sega Mega Drive , the word " SEGA " is most often present at the offset of the 0x100 header (this is not a mandatory condition, but it is performed in 99% of cases). It is necessary to check whether this line is in the imported file. To do this, the input findSupportedLoadSpecs() is supplied by the ByteProvider provider , with which we will work with the file.
Create a BinaryReader object for easy reading of data from a file:
BinaryReader reader = new BinaryReader(provider, false); Argument false in this case indicates the use of Big Endian when reading. Now let's read the line. To do this, we use the readAsciiString(offset, size) method of the reader object:
reader.readAsciiString(0x100, 4).equals(new String("SEGA")) If equals() returns true , then we are dealing with a Segum rum, and in the List<LoadSpec> loadSpecs = new ArrayList<>(); You can add a motorola m68k . To do this, we create a new object of type LoadSpec , the constructor of which accepts a loader object (in our case, this ) in the ImageBase , an ImageBase into which the ROM will be loaded, an object of type LanguageCompilerSpecPair and a flag — whether this LoadSpec is preferred among the others in the list (yes, in the list there may not be one LoadSpec ).
The format of the LanguageCompilerSpecPair constructor is as follows:
- The first argument,
languageIDis a string of the form " ProcessorName: Endianness: Bits: ExactCpu ". In my case it should be the string " 68000: BE: 32: MC68020 " (unfortunately, there is noMC68000in the delivery, but this is not such a problem).ExactCpumay bedefault - The second argument,
compilerSpecIDis to find what you need to specify here in theprocessor description directory ($(GHIDRA)/Ghidra/Processors/68000/data/languages) in the file68000.opinion. We see that onlydefaultis listed here. Actually, we specify it
As a result, we have the following code (as we can see, so far nothing complicated):
@Override public Collection<LoadSpec> findSupportedLoadSpecs(ByteProvider provider) throws IOException { List<LoadSpec> loadSpecs = new ArrayList<>(); BinaryReader reader = new BinaryReader(provider, false); if (reader.readAsciiString(0x100, 4).equals(new String("SEGA"))) { loadSpecs.add(new LoadSpec(this, 0, new LanguageCompilerSpecPair("68000:BE:32:MC68020", "default"), true)); } return loadSpecs; } There is a difference, and it is really very strong. In GHIDRA you can write one project that will understand different architectures, different data formats, be a loader, a processor module, an extension of the decompiler functionality, and other buns.
In IDA , this is a separate project for each type of add-on.
How comfortable is it? In my opinion, GHIDRA - at times!
load ()
In this method we will create segments, process input data, create code, and pre-known labels. For this, the following objects are served to help us at the entrance:
ByteProvider provider: we already know it. Work with binary file dataLoadSpec loadSpec: specification of the architecture that was selected at the stage of importing the file using thefindSupportedLoadSpecsmethod. It is necessary, if we, for example, are able to work with several data formats in one module. ConvenientlyList<Option> options: a list of options (including custom ones). I have not learned to work with them yet.Program program: the main object that provides access to all the necessary functionality: listing, address space, segments, tags, creating arrays, etc.MemoryConflictHandler handlerandTaskMonitor monitor: we rarely have to work directly with them (usually, it’s enough to transfer these objects to ready-made methods)MessageLog log: logger itself
So, first we will create some objects that will simplify our work with GHIDRA entities and the available data. Of course, we definitely need the BinaryReader :
BinaryReader reader = new BinaryReader(provider, false); Further. It will be very useful to us and simplify almost all objects of the FlatProgramAPI class (hereafter you will see what you can do with it):
FlatProgramAPI fpa = new FlatProgramAPI(program, monitor); Rum header
To begin with, let us define what the title of a regular Segovsky rum is. In the first 0x100 bytes there is a table of 64 DWORD-pointers to vectors, for example: Reset , Trap , DivideByZero , VBLANK and others.
Next comes the structure with the name of the Roma, the regions, the addresses of the beginning and end of the ROM and RAM blocks, the cheksumma (the field is checked at the request of the developers, not the prefix) and other information.
Let's create java classes to work with these structures, as well as to implement the data types that will be added to the list of structures.
VectorsTable
Create a new class VectorsTable , and attention, we indicate that it implements the StructConverter interface. In this class we will store the addresses of the vectors (for future use) and their names.

We announce the list of vectors names and their number:
private static final int VECTORS_SIZE = 0x100; private static final int VECTORS_COUNT = VECTORS_SIZE / 4; private static final String[] VECTOR_NAMES = { "SSP", "Reset", "BusErr", "AdrErr", "InvOpCode", "DivBy0", "Check", "TrapV", "GPF", "Trace", "Reserv0", "Reserv1", "Reserv2", "Reserv3", "Reserv4", "BadInt", "Reserv10", "Reserv11", "Reserv12", "Reserv13", "Reserv14", "Reserv15", "Reserv16", "Reserv17", "BadIRQ", "IRQ1", "EXT", "IRQ3", "HBLANK", "IRQ5", "VBLANK", "IRQ7", "Trap0", "Trap1", "Trap2", "Trap3", "Trap4", "Trap5", "Trap6", "Trap7", "Trap8", "Trap9", "Trap10", "Trap11", "Trap12", "Trap13","Trap14", "Trap15", "Reserv30", "Reserv31", "Reserv32", "Reserv33", "Reserv34", "Reserv35", "Reserv36", "Reserv37", "Reserv38", "Reserv39", "Reserv3A", "Reserv3B", "Reserv3C", "Reserv3D", "Reserv3E", "Reserv3F" }; Create a separate class to store the address and name of the vector:
package sega; import ghidra.program.model.address.Address; public class VectorFunc { private Address address; private String name; public VectorFunc(Address address, String name) { this.address = address; this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public String getName() { return name; } } The list of vectors will be stored in the vectors array:
private VectorFunc[] vectors; The constructor for VectorsTable will accept:
FlatProgramAPI fpafor convertinglongaddresses into the HydraAddressdata type (in fact, this data type complements the simple numeric value of the address by binding it to another chip — the address space)BinaryReader reader- reading dvordov
The fpa object has a method toAddr() , and the reader has setPointerIndex() and readNextUnsignedInt() . In principle, nothing else is required. Get the code:
public VectorsTable(FlatProgramAPI fpa, BinaryReader reader) throws IOException { if (reader.length() < VECTORS_COUNT) { return; } reader.setPointerIndex(0); vectors = new VectorFunc[VECTORS_COUNT]; for (int i = 0; i < VECTORS_COUNT; ++i) { vectors[i] = new VectorFunc(fpa.toAddr(reader.readNextUnsignedInt()), VECTOR_NAMES[i]); } } The toDataType() method that we need to override to implement the structure should return a Structure object, in which the structure field names, their sizes, and comments for each field should be declared (you can use null ):
@Override public DataType toDataType() { Structure s = new StructureDataType("VectorsTable", 0); for (int i = 0; i < VECTORS_COUNT; ++i) { s.add(POINTER, 4, VECTOR_NAMES[i], null); } return s; } Well, and let's implement the methods for getting each of the vectors, or the entire list (a bunch of sample code):
public VectorFunc[] getVectors() { return vectors; } public VectorFunc getSSP() { if (vectors.length < 1) { return null; } return vectors[0]; } public VectorFunc getReset() { if (vectors.length < 2) { return null; } return vectors[1]; } public VectorFunc getBusErr() { if (vectors.length < 3) { return null; } return vectors[2]; } public VectorFunc getAdrErr() { if (vectors.length < 4) { return null; } return vectors[3]; } public VectorFunc getInvOpCode() { if (vectors.length < 5) { return null; } return vectors[4]; } public VectorFunc getDivBy0() { if (vectors.length < 6) { return null; } return vectors[5]; } public VectorFunc getCheck() { if (vectors.length < 7) { return null; } return vectors[6]; } public VectorFunc getTrapV() { if (vectors.length < 8) { return null; } return vectors[7]; } public VectorFunc getGPF() { if (vectors.length < 9) { return null; } return vectors[8]; } public VectorFunc getTrace() { if (vectors.length < 10) { return null; } return vectors[9]; } public VectorFunc getReserv0() { if (vectors.length < 11) { return null; } return vectors[10]; } public VectorFunc getReserv1() { if (vectors.length < 12) { return null; } return vectors[11]; } public VectorFunc getReserv2() { if (vectors.length < 13) { return null; } return vectors[12]; } public VectorFunc getReserv3() { if (vectors.length < 14) { return null; } return vectors[13]; } public VectorFunc getReserv4() { if (vectors.length < 15) { return null; } return vectors[14]; } public VectorFunc getBadInt() { if (vectors.length < 16) { return null; } return vectors[15]; } public VectorFunc getReserv10() { if (vectors.length < 17) { return null; } return vectors[16]; } public VectorFunc getReserv11() { if (vectors.length < 18) { return null; } return vectors[17]; } public VectorFunc getReserv12() { if (vectors.length < 19) { return null; } return vectors[18]; } public VectorFunc getReserv13() { if (vectors.length < 20) { return null; } return vectors[19]; } public VectorFunc getReserv14() { if (vectors.length < 21) { return null; } return vectors[20]; } public VectorFunc getReserv15() { if (vectors.length < 22) { return null; } return vectors[21]; } public VectorFunc getReserv16() { if (vectors.length < 23) { return null; } return vectors[22]; } public VectorFunc getReserv17() { if (vectors.length < 24) { return null; } return vectors[23]; } public VectorFunc getBadIRQ() { if (vectors.length < 25) { return null; } return vectors[24]; } public VectorFunc getIRQ1() { if (vectors.length < 26) { return null; } return vectors[25]; } public VectorFunc getEXT() { if (vectors.length < 27) { return null; } return vectors[26]; } public VectorFunc getIRQ3() { if (vectors.length < 28) { return null; } return vectors[27]; } public VectorFunc getHBLANK() { if (vectors.length < 29) { return null; } return vectors[28]; } public VectorFunc getIRQ5() { if (vectors.length < 30) { return null; } return vectors[29]; } public VectorFunc getVBLANK() { if (vectors.length < 31) { return null; } return vectors[30]; } public VectorFunc getIRQ7() { if (vectors.length < 32) { return null; } return vectors[31]; } public VectorFunc getTrap0() { if (vectors.length < 33) { return null; } return vectors[32]; } public VectorFunc getTrap1() { if (vectors.length < 34) { return null; } return vectors[33]; } public VectorFunc getTrap2() { if (vectors.length < 35) { return null; } return vectors[34]; } public VectorFunc getTrap3() { if (vectors.length < 36) { return null; } return vectors[35]; } public VectorFunc getTrap4() { if (vectors.length < 37) { return null; } return vectors[36]; } public VectorFunc getTrap5() { if (vectors.length < 38) { return null; } return vectors[37]; } public VectorFunc getTrap6() { if (vectors.length < 39) { return null; } return vectors[38]; } public VectorFunc getTrap7() { if (vectors.length < 40) { return null; } return vectors[39]; } public VectorFunc getTrap8() { if (vectors.length < 41) { return null; } return vectors[40]; } public VectorFunc getTrap9() { if (vectors.length < 42) { return null; } return vectors[41]; } public VectorFunc getTrap10() { if (vectors.length < 43) { return null; } return vectors[42]; } public VectorFunc getTrap11() { if (vectors.length < 44) { return null; } return vectors[43]; } public VectorFunc getTrap12() { if (vectors.length < 45) { return null; } return vectors[44]; } public VectorFunc getTrap13() { if (vectors.length < 46) { return null; } return vectors[45]; } public VectorFunc getTrap14() { if (vectors.length < 47) { return null; } return vectors[46]; } public VectorFunc getTrap15() { if (vectors.length < 48) { return null; } return vectors[47]; } public VectorFunc getReserv30() { if (vectors.length < 49) { return null; } return vectors[48]; } public VectorFunc getReserv31() { if (vectors.length < 50) { return null; } return vectors[49]; } public VectorFunc getReserv32() { if (vectors.length < 51) { return null; } return vectors[50]; } public VectorFunc getReserv33() { if (vectors.length < 52) { return null; } return vectors[51]; } public VectorFunc getReserv34() { if (vectors.length < 53) { return null; } return vectors[52]; } public VectorFunc getReserv35() { if (vectors.length < 54) { return null; } return vectors[53]; } public VectorFunc getReserv36() { if (vectors.length < 55) { return null; } return vectors[54]; } public VectorFunc getReserv37() { if (vectors.length < 56) { return null; } return vectors[55]; } public VectorFunc getReserv38() { if (vectors.length < 57) { return null; } return vectors[56]; } public VectorFunc getReserv39() { if (vectors.length < 58) { return null; } return vectors[57]; } public VectorFunc getReserv3A() { if (vectors.length < 59) { return null; } return vectors[58]; } public VectorFunc getReserv3B() { if (vectors.length < 60) { return null; } return vectors[59]; } public VectorFunc getReserv3C() { if (vectors.length < 61) { return null; } return vectors[60]; } public VectorFunc getReserv3D() { if (vectors.length < 62) { return null; } return vectors[61]; } public VectorFunc getReserv3E() { if (vectors.length < 63) { return null; } return vectors[62]; } public VectorFunc getReserv3F() { if (vectors.length < 64) { return null; } return vectors[63]; } Gameheader
Do the same, and create a GameHeader class that implements the StructConverter interface.
| Start Offset | End offset | Description |
|---|---|---|
| $ 100 | $ 10F | Console name (usually 'SEGA MEGA DRIVE' or 'SEGA GENESIS') |
| $ 110 | $ 11F | Release date (usually '© XXXX YYYY.MMM' where XXXX is the company code, YYYY is the year and MMM - month) |
| $ 120 | $ 14F | Domestic name |
| $ 150 | $ 17F | International name |
| $ 180 | $ 18D | Version ('XX YYYYYYYYYYYY' where XX is the game type and YY the game code) |
| $ 18E | $ 18F | Checksum |
| $ 190 | $ 19F | I / O support |
| $ 1A0 | $ 1A3 | ROM start |
| $ 1A4 | $ 1A7 | ROM end |
| $ 1A8 | $ 1AB | RAM start (usually $ 00FF0000) |
| $ 1AC | $ 1AF | RAM end (usually $ 00FFFFFF) |
| $ 1B0 | $ 1b2 | 'RA' and $ F8 enables SRAM |
| $ 1B3 | ---- | unused ($ 20) |
| $ 1B4 | $ 1B7 | SRAM start (default $ 00200000) |
| $ 1B8 | $ 1BB | SRAM end (default $ 0020FFFF) |
| $ 1BC | $ 1FF | Notes (unused) |
We get fields, check for sufficient length of input data, use two new methods for us readNextByteArray() , readNextUnsignedShort() of reader object for reading data, and create a structure. The resulting code is obtained as follows:
package sega; import java.io.IOException; import ghidra.app.util.bin.BinaryReader; import ghidra.app.util.bin.StructConverter; import ghidra.program.flatapi.FlatProgramAPI; import ghidra.program.model.address.Address; import ghidra.program.model.data.DataType; import ghidra.program.model.data.Structure; import ghidra.program.model.data.StructureDataType; public class GameHeader implements StructConverter { private byte[] consoleName = null; private byte[] releaseDate = null; private byte[] domesticName = null; private byte[] internationalName = null; private byte[] version = null; private short checksum = 0; private byte[] ioSupport = null; private Address romStart = null, romEnd = null; private Address ramStart = null, ramEnd = null; private byte[] sramCode = null; private byte unused = 0; private Address sramStart = null, sramEnd = null; private byte[] notes = null; FlatProgramAPI fpa; public GameHeader(FlatProgramAPI fpa, BinaryReader reader) throws IOException { this.fpa = fpa; if (reader.length() < 0x200) { return; } reader.setPointerIndex(0x100); consoleName = reader.readNextByteArray(0x10); releaseDate = reader.readNextByteArray(0x10); domesticName = reader.readNextByteArray(0x30); internationalName = reader.readNextByteArray(0x30); version = reader.readNextByteArray(0x0E); checksum = (short) reader.readNextUnsignedShort(); ioSupport = reader.readNextByteArray(0x10); romStart = fpa.toAddr(reader.readNextUnsignedInt()); romEnd = fpa.toAddr(reader.readNextUnsignedInt()); ramStart = fpa.toAddr(reader.readNextUnsignedInt()); ramEnd = fpa.toAddr(reader.readNextUnsignedInt()); sramCode = reader.readNextByteArray(0x03); unused = reader.readNextByte(); sramStart = fpa.toAddr(reader.readNextUnsignedInt()); sramEnd = fpa.toAddr(reader.readNextUnsignedInt()); notes = reader.readNextByteArray(0x44); } @Override public DataType toDataType() { Structure s = new StructureDataType("GameHeader", 0); s.add(STRING, 0x10, "ConsoleName", null); s.add(STRING, 0x10, "ReleaseDate", null); s.add(STRING, 0x30, "DomesticName", null); s.add(STRING, 0x30, "InternationalName", null); s.add(STRING, 0x0E, "Version", null); s.add(WORD, 0x02, "Checksum", null); s.add(STRING, 0x10, "IoSupport", null); s.add(POINTER, 0x04, "RomStart", null); s.add(POINTER, 0x04, "RomEnd", null); s.add(POINTER, 0x04, "RamStart", null); s.add(POINTER, 0x04, "RamEnd", null); s.add(STRING, 0x03, "SramCode", null); s.add(BYTE, 0x01, "Unused", null); s.add(POINTER, 0x04, "SramStart", null); s.add(POINTER, 0x04, "SramEnd", null); s.add(STRING, 0x44, "Notes", null); return s; } public byte[] getConsoleName() { return consoleName; } public byte[] getReleaseDate() { return releaseDate; } public byte[] getDomesticName() { return domesticName; } public byte[] getInternationalName() { return internationalName; } public byte[] getVersion() { return version; } public short getChecksum() { return checksum; } public byte[] getIoSupport() { return ioSupport; } public Address getRomStart() { return romStart; } public Address getRomEnd() { return romEnd; } public Address getRamStart() { return ramStart; } public Address getRamEnd() { return ramEnd; } public byte[] getSramCode() { return sramCode; } public byte getUnused() { return unused; } public Address getSramStart() { return sramStart; } public Address getSramEnd() { return sramEnd; } public boolean hasSRAM() { if (sramCode == null) { return false; } return sramCode[0] == 'R' && sramCode[1] == 'A' && sramCode[2] == 0xF8; } public byte[] getNotes() { return notes; } } Create objects for the title:
vectors = new VectorsTable(fpa, reader); header = new GameHeader(fpa, reader); Segments
Segui has a well-known map of memory regions, which I, perhaps, will not give here in the form of a table, but only give the code that is used to create segments.
So, the FlatProgramAPI class FlatProgramAPI has a createMemoryBlock() method, with which it is convenient to create memory regions. It takes the following arguments as input:
name: region nameaddress: address of the beginning of the regionstream: an object of typeInputStreamthat will be the basis for data in the memory region. If you specifynull, then an uninitialized region will be created (for example, for68K RAMorZ80 RAMwe will need this onesize: size of the region to be createdisOverlay: acceptstrueorfalse, and indicates that the memory region is overlayed. Where is it necessary except for executable files I do not know
At the exit, createMemoryBlock() returns an object of the type MemoryBlock , which can additionally be set with flags of access rights ( Read , Write , Execute ).
As a result, the following function will be obtained:
private void createSegment(FlatProgramAPI fpa, InputStream stream, String name, Address address, long size, boolean read, boolean write, boolean execute) { MemoryBlock block = null; try { block = fpa.createMemoryBlock(name, address, stream, size, false); block.setRead(read); block.setWrite(read); block.setExecute(execute); } catch (Exception e) { Msg.error(this, String.format("Error creating %s segment", name)); } } Here, we additionally called the static error method of the Msg class to display an error message.
A segment containing game rum may have a maximum size of 0x3FFFFF (everything else will already belong to other regions). Create it:
InputStream romStream = provider.getInputStream(0); createSegment(fpa, romStream, "ROM", fpa.toAddr(0x000000), Math.min(romStream.available(), 0x3FFFFF), true, false, true); InputStream , 0.
, ( SegaCD Sega32X ). OptionDialog . , showYesNoDialogWithNoAsDefaultButton() YES NO - NO .
:
if (OptionDialog.YES_OPTION == OptionDialog.showYesNoDialogWithNoAsDefaultButton(null, "Question", "Create Sega CD segment?")) { if (romStream.available() > 0x3FFFFF) { InputStream epaStream = provider.getInputStream(0x400000); createSegment(fpa, epaStream, "EPA", fpa.toAddr(0x400000), 0x400000, true, true, false); } else { createSegment(fpa, null, "EPA", fpa.toAddr(0x400000), 0x400000, true, true, false); } } if (OptionDialog.YES_OPTION == OptionDialog.showYesNoDialogWithNoAsDefaultButton(null, "Question", "Create Sega 32X segment?")) { createSegment(fpa, null, "32X", fpa.toAddr(0x800000), 0x200000, true, true, false); } :
createSegment(fpa, null, "Z80", fpa.toAddr(0xA00000), 0x10000, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "SYS1", fpa.toAddr(0xA10000), 16 * 2, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "SYS2", fpa.toAddr(0xA11000), 2, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "Z802", fpa.toAddr(0xA11100), 2, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "Z803", fpa.toAddr(0xA11200), 2, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "FDC", fpa.toAddr(0xA12000), 0x100, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "TIME", fpa.toAddr(0xA13000), 0x100, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "TMSS", fpa.toAddr(0xA14000), 4, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "VDP", fpa.toAddr(0xC00000), 2 * 9, true, true, false); createSegment(fpa, null, "RAM", fpa.toAddr(0xFF0000), 0x10000, true, true, true); if (header.hasSRAM()) { Address sramStart = header.getSramStart(); Address sramEnd = header.getSramEnd(); if (sramStart.getOffset() >= 0x200000 && sramEnd.getOffset() <= 0x20FFFF && sramStart.getOffset() < sramEnd.getOffset()) { createSegment(fpa, null, "SRAM", sramStart, sramEnd.getOffset() - sramStart.getOffset() + 1, true, true, false); } } ,
CreateArrayCmd . , :
address: ,numElements:dataType:elementSize:
applyTo(program) , .
, , BYTE , WORD , DWORD . , FlatProgramAPI createByte() , createWord() , createDword() ..
, , (, VDP ). , :
ProgramgetSymbolTable(), , ..createLabel(), , . , ,SourceType.IMPORTED
, :
private void createNamedByteArray(FlatProgramAPI fpa, Program program, Address address, String name, int numElements) { if (numElements > 1) { CreateArrayCmd arrayCmd = new CreateArrayCmd(address, numElements, ByteDataType.dataType, ByteDataType.dataType.getLength()); arrayCmd.applyTo(program); } else { try { fpa.createByte(address); } catch (Exception e) { Msg.error(this, "Cannot create byte. " + e.getMessage()); } } try { program.getSymbolTable().createLabel(address, name, SourceType.IMPORTED); } catch (InvalidInputException e) { Msg.error(this, String.format("%s : Error creating array %s", getName(), name)); } } private void createNamedWordArray(FlatProgramAPI fpa, Program program, Address address, String name, int numElements) { if (numElements > 1) { CreateArrayCmd arrayCmd = new CreateArrayCmd(address, numElements, WordDataType.dataType, WordDataType.dataType.getLength()); arrayCmd.applyTo(program); } else { try { fpa.createWord(address); } catch (Exception e) { Msg.error(this, "Cannot create word. " + e.getMessage()); } } try { program.getSymbolTable().createLabel(address, name, SourceType.IMPORTED); } catch (InvalidInputException e) { Msg.error(this, String.format("%s : Error creating array %s", getName(), name)); } } private void createNamedDwordArray(FlatProgramAPI fpa, Program program, Address address, String name, int numElements) { if (numElements > 1) { CreateArrayCmd arrayCmd = new CreateArrayCmd(address, numElements, DWordDataType.dataType, DWordDataType.dataType.getLength()); arrayCmd.applyTo(program); } else { try { fpa.createDWord(address); } catch (Exception e) { Msg.error(this, "Cannot create dword. " + e.getMessage()); } } try { program.getSymbolTable().createLabel(address, name, SourceType.IMPORTED); } catch (InvalidInputException e) { Msg.error(this, String.format("%s : Error creating array %s", getName(), name)); } } createNamedDwordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA04000), "Z80_YM2612", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10000), "IO_PCBVER", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10002), "IO_CT1_DATA", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10004), "IO_CT2_DATA", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10006), "IO_EXT_DATA", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10008), "IO_CT1_CTRL", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA1000A), "IO_CT2_CTRL", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA1000C), "IO_EXT_CTRL", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA1000E), "IO_CT1_RX", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10010), "IO_CT1_TX", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10012), "IO_CT1_SMODE", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10014), "IO_CT2_RX", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10016), "IO_CT2_TX", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA10018), "IO_CT2_SMODE", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA1001A), "IO_EXT_RX", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA1001C), "IO_EXT_TX", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA1001E), "IO_EXT_SMODE", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA11000), "IO_RAMMODE", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA11100), "IO_Z80BUS", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA11200), "IO_Z80RES", 1); createNamedByteArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA12000), "IO_FDC", 0x100); createNamedByteArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA13000), "IO_TIME", 0x100); createNamedDwordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xA14000), "IO_TMSS", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC00000), "VDP_DATA", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC00002), "VDP__DATA", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC00004), "VDP_CTRL", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC00006), "VDP__CTRL", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC00008), "VDP_CNTR", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC0000A), "VDP__CNTR", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC0000C), "VDP___CNTR", 1); createNamedWordArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC0000E), "VDP____CNTR", 1); createNamedByteArray(fpa, program, fpa.toAddr(0xC00011), "VDP_PSG", 1); createData() DataUtilities . :
program:Programaddress: ,dataType:dataLength: .-1stackPointers:true, - .falseclearDataMode: , (, )
: .. (, ), . FlatProgramAPI createFunction() , .
:
private void markVectorsTable(Program program, FlatProgramAPI fpa) { try { DataUtilities.createData(program, fpa.toAddr(0), vectors.toDataType(), -1, false, ClearDataMode.CLEAR_ALL_UNDEFINED_CONFLICT_DATA); for (VectorFunc func : vectors.getVectors()) { fpa.createFunction(func.getAddress(), func.getName()); } } catch (CodeUnitInsertionException e) { Msg.error(this, "Vectors mark conflict at 0x000000"); } } private void markHeader(Program program, FlatProgramAPI fpa) { try { DataUtilities.createData(program, fpa.toAddr(0x100), header.toDataType(), -1, false, ClearDataMode.CLEAR_ALL_UNDEFINED_CONFLICT_DATA); } catch (CodeUnitInsertionException e) { Msg.error(this, "Vectors mark conflict at 0x000100"); } } load()
load() setMessage() TaskMonitor , .
monitor.setMessage(String.format("%s : Start loading", getName())); , :
@Override protected void load(ByteProvider provider, LoadSpec loadSpec, List<Option> options, Program program, MemoryConflictHandler handler, TaskMonitor monitor, MessageLog log) throws CancelledException, IOException { monitor.setMessage(String.format("%s : Start loading", getName())); BinaryReader reader = new BinaryReader(provider, false); FlatProgramAPI fpa = new FlatProgramAPI(program, monitor); vectors = new VectorsTable(fpa, reader); header = new GameHeader(fpa, reader); createSegments(fpa, provider, program, monitor); markVectorsTable(program, fpa); markHeader(program, fpa); monitor.setMessage(String.format("%s : Loading done", getName())); } getDefaultOptions validateOptions
,
Run -> Debug As -> 1 Ghidra . .

GHIDRA
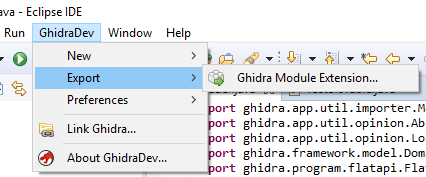
, - . Eclipse extension.properties , :
description=Loader for Sega Mega Drive / Genesis ROMs author=Dr. MefistO createdOn=20.03.2019 GhidraDev -> Export -> Ghidra Module Extension... :


dist zip- (- ghidra_9.0_PUBLIC_20190320_Sega.zip ) GHIDRA .
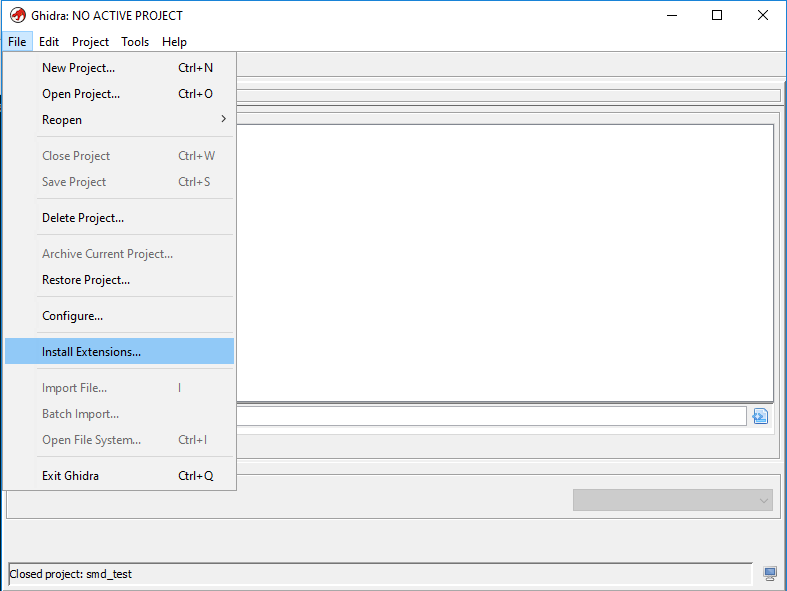
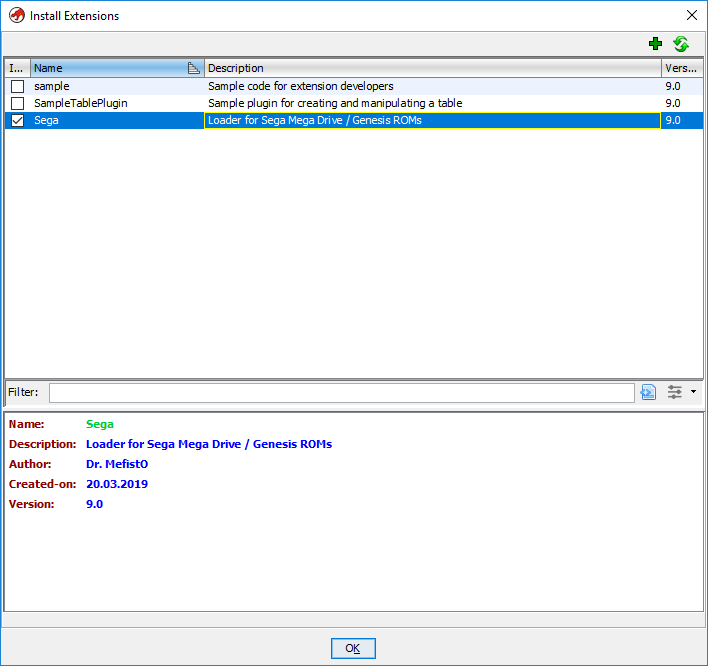
. , File -> Install Extensions... , , . Voila ...
github- , .
: IDA GHIDRA . .
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/444562/
All Articles