3D scanners in the automotive industry: 4 advantages and 4 successful projects

In our material on the application of additive technologies in the automotive industry, we examined in detail their main advantages and potential for the Russian industry. And if the introduction of 3D printing still poses certain difficulties (for example, the need for large investments and insufficient automation), then three-dimensional scanning is seen today as the most preferred and affordable 3D technology for the automotive industry.
A 3D scanner is a device designed to quickly analyze a physical object and create its exact computerized 3D model. The principle of its work is based on the calculation of the distance to the object using two cameras. In addition to the cameras used backlight - LED or laser. Both types of scanners are applicable in the automotive industry.
3D scanners provide an opportunity to significantly reduce the time and costs of the development stage, improve the quality of products and, ultimately, speed up the release of the product to the market. They can be used at any stage of product lifecycle management and can help optimize the production process to any branch of the industry - from large manufacturers of cars, engines, machinery and components to small companies performing tuning, maintenance and repair.
')
3D scanning devices can remove many of the limitations that traditional measurement equipment has. Tools such as templates, micrometers, and calipers that are familiar to a metrologist are inexpensive, but they are distinguished by their subjectivity and are not suitable for complex measurements. Coordinate measuring machines are more accurate than 3D scanners, but they are more expensive, more dimensional and require special operator training.
Optical control systems, which include 3D-scanners, are the best solution in terms of price and quality, as they provide:
- measurement speed
- high accuracy of digitization of objects of complex geometry ,
- can work autonomously,
- easy to operate.
Thanks to the 3D scanner, the work of the designer, technologist, and designer is greatly facilitated: the implementation of laborious, complex measurements and the creation of design from scratch are a thing of the past.
In this article, we will demonstrate the benefits of this technology with specific examples, and in the videos below you will be able to track the process of 3D scanning in real time.
What tasks does 3D scanning do?
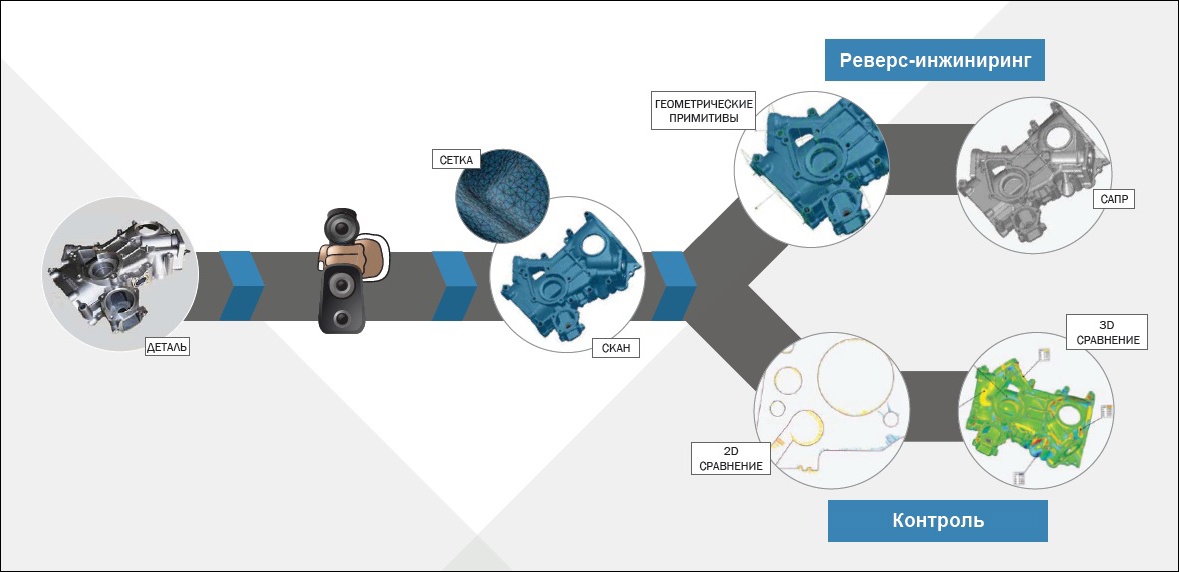
- Quality control : the ability to check any geometric parameters, including input and output control, metrological control of parts, housings and production equipment.
- The reverse engineering of automotive components for the rapid receipt of project documentation and product upgrades.
- Designing and modeling for auto-tuning, prototyping and evaluation of the appearance of products, modernization of production workshops and equipment.
- Digital archiving of any necessary assortment (for example, discontinued parts). Models stored in digital libraries are available remotely from anywhere in the world.
The main advantages of 3D scanning for the automotive industry
- Accuracy
Certainly, accuracy is a fundamental criterion for metrology. 3D scanners allow you to efficiently perform measurements with metrological accuracy from 20 to 80 microns (depending on the device and the size of the object). - Speed
Speed is productivity. 3D scanning takes the measurement speed to a new level: the process of digitizing and processing in a software component of a component such as a car door takes about 20 minutes instead of 4 hours of measurements on a CMM. You not only save time, but also reduce production costs. - Reliability
Modern professional and industrial 3D scanners are characterized by increased stability and reliability. Handheld devices are designed for transportation to remote objects and can operate in conditions of industrial vibration. All portable 3D scanners that iQB Technologies uses in its work regularly travel around Russia and the near abroad without a single breakdown. - Simplicity
Working with a 3D scanner does not require skills, and an inexperienced user — whether an OTC specialist, chief engineer, designer, or technologist — takes 20 minutes to master the device. Point cloud processing requires knowledge of software, and if there is no staff member with CAD skills, you can send the scan result to an outsource network.

Quality control of Ariel Atom racing cars using Solutionix 3D scanner
Quality control in the automotive industry
The main task of 3D-scanning, which will help to optimize automobile production, is the control of geometry for the purpose of verification with the reference model. You can control not only automotive components, but also molds and tooling, as well as carry out a tool wear analysis.
The use of 3D-scanners allows you to quickly track the defective parts coming from suppliers, and the availability of metrological certificates and methods of verification - to get a report on deviations from the declared geometry. When a marriage is detected, it will be possible to find its cause, compare the scan with the reference CAD-model and provide a report to the manufacturer or a third-party organization.
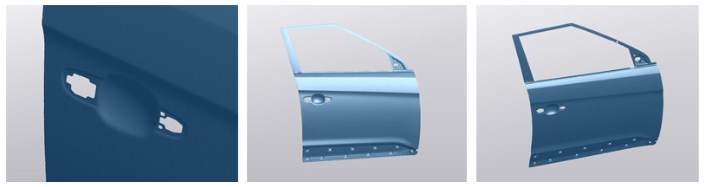
Automobile plant carried out measurements with the help of CMM on control points with obtaining information in the form of a numerical table.
The operating time of the equipment and processing of results: 4 hours.
Solution proposed by iQB Technologies:
Handheld 3D scanner Creaform HandyScan 700 + software Geomagic Control X.
Preparation time for work, including calibration and labeling of tags - 7 minutes.
The time for receiving a scan of a car door (taking into account the work of an operator) is 5 minutes
Inspection analysis (comparison with the CAD-model) - 10 minutes.
Total time spent: 22 minutes.
Automated control on the conveyor
Automated scanning systems , including a 3D scanner, a robotic arm, and software, can perform not only random inspection, but also monitor all products on the production line. The result is a reduction in time and resources for quality control procedures and a significant reduction in reject rates.
Advanced automated quality control systems on a conveyor belt are offered by Creaform. This MetraSCAN 3D-R is an optical 3D scanner mounted on the robot, and CUBE-R is a turnkey solution consisting of a turntable, a robotic arm with a scanner, a tracking device and a control stand. Both systems are already operational at the Daimler plant in Stuttgart and at the factories of the Renault-Nissan concern in France.
See how MetraSCAN 3D-R allows you to get a scan of a car door with a report in just 2 minutes and 27 seconds:
Another similar solution, which has no analogues in Russia, was developed by our company. This is an automated scanning system that includes the Fanuc LR Mate 200iD robotic arm, the Creaform HandySCAN 700 portable 3D scanner, and the Geomagic Control X software. The system was first demonstrated at the Metalworking Exhibition 2018.
Reverse engineering
The second important production problem solved by a 3D scanner is reverse engineering, or reverse engineering. Using 3D-scanning and specialized software, you can modify existing products without drawings, including models that were discontinued, and upgrade individual parts of the vehicle body to quickly bring the updated model to market. For example, a scanner would be great when releasing a new “Grants”, developed on the basis of “Kalina”.
In addition, reverse engineering performs the task of replacing production equipment due to obsolescence, wear or absence, as well as evaluating the current and selecting the optimal placement of production equipment and engineering communications in the workshop.
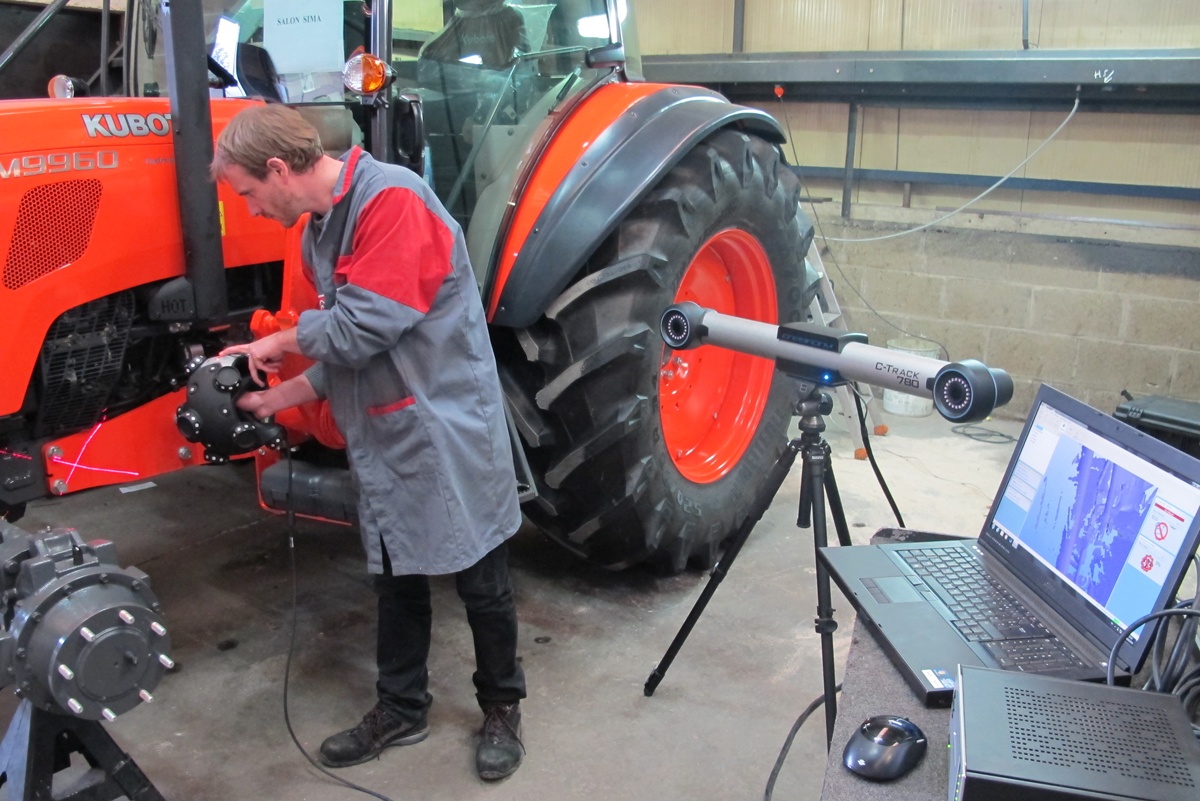

3D scan of a tractor for attachment development at MX
We give an example of the introduction of 3D scanning in the French company MX, which manufactures loading equipment for agricultural tractors. Tractor manufacturers rarely share information about their new products, and getting the CAD models of these tractors is even more difficult because they are intellectual property. However, for the development and production of attachments such as MX loading arms, it is absolutely necessary to have 3D models. Therefore, the company has to perform 3D measurements of all the tractors for which it wants to design and produce attachments, and until recently, these tasks were solved with the help of manipulators for 3D measurements. Today, MX uses 3D scanning technology to digitize all areas needed to design adaptable structures, including bracket attachment points and their surroundings. Creaform 3D solutions made it possible to reduce the measurement time by more than 2 times, and, consequently, reduce the time to market for the product.
Creation of CAD-models and digital archives
Getting design documentation and drawings by hand takes a lot of time. Digital archiving and acquisition of CAD-models of products is one of the possibilities that 3D scanners offer. You can take any part out of production, quickly perform a scan and get a 3D model for further reproduction and preservation in the archive. Digital libraries are very convenient to use: the designer or technologist at any time and in any place will get access to the necessary model and easily make adjustments to it.
If you have a digital model of the finished product, you can compare the result obtained after functional testing or a crash test with the original product or with a reference CAD model. This will allow the analysis of damage and wear and make appropriate modifications to the design.
By storing information about objects scanned at production, an enterprise is able to form a picture of its products, predict the further production cycle and reduce costs.
Here is an example from my personal experience. I am fond of motorcycles and for my Ducati Monster I purchased at the eBay auction a long-overdue rear suspension arm from the Ducati 888 model, which has less weight and a number of adjustments. The video above shows the process of scanning a part that took 10 minutes. The result is a polygonal model in .stl format. From the model we get the sketched dimensions of the part and create a parametric CAD model in the CAD system. Then the control program for CNC machines is written, which is transmitted to the turner-milling machine. As a result, we have a copy of the part, which ceased to be released 25 years ago, and its 3D model is stored in a digital archive.
Towards Industry 4.0
Our company conducted research among more than 100 automakers operating in the Russian market. We found that 37% use, and 32% plan to implement 3D scanning. More and more automotive enterprises are thinking about the introduction of innovative technologies, including 3D scanners - first of all this concerns Russian car factories of foreign manufacturers. There is a clear understanding that without the acceleration of production not to withstand competition. It can be said that the domestic automotive industry is following the global trend of transition to digital production and is ready for change.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/444138/
All Articles