Situation: virtual GPUs are not inferior in performance to iron solutions
In February, a high-performance computing (HPC) conference was held at Stanford. VMware representatives said that when working with a GPU, the system based on the modified ESXi hypervisor is not inferior in speed to bare metal solutions.
We talk about the technologies that allowed to achieve this.

/ photo Victorgrigas CC BY-SA
')
According to analysts, about 70% of workloads in data centers are virtualized . However, the remaining 30% still work on bare metal without hypervisors. These 30% for the most part consist of high-load applications associated, for example, with the training of neural networks, and using graphics processors.
Experts explain this trend by the fact that the hypervisor, as an intermediate layer of abstraction, can affect the performance of the entire system. In studies five years ago, you can find data on the reduction in the speed of work by 10%. Therefore, companies and data center operators are in no hurry to transfer HPC-load into a virtual environment.
But virtualization technologies are evolving and improving. At the conference a month ago in VMware, they said that the ESXi hypervisor does not have a negative impact on GPU performance. The computation speed can be reduced by three percent, and this is comparable with bare metal.
To increase the performance of HPC systems with graphics processors, VMware made a number of changes to the work of the hypervisor. In particular, he was relieved of the vMotion function. It is needed for load balancing and usually transfers virtual machines (VMs) between servers or GPUs. Disabling vMotion led to the fact that each VM is now assigned a specific graphics processor. This helped reduce the cost of data sharing.
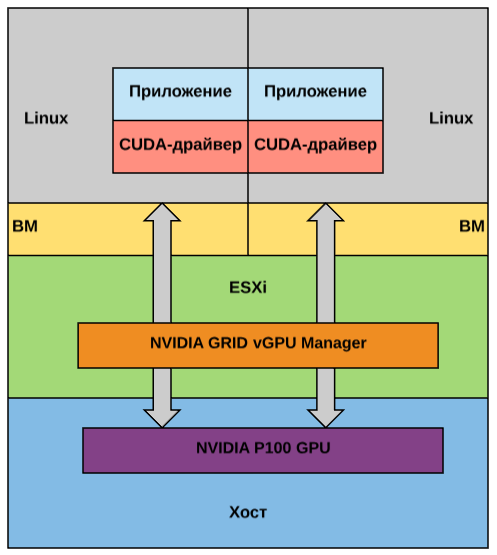
Another key component of the system is DirectPath I / O technology . It allows the CUDA parallel computing driver to interact with virtual machines directly, bypassing the hypervisor. When several VMs are required to run on one GPU at once, the GRID vGPU solution is enabled. It divides the memory card into several segments (but the computational cycles are not divided).
The operation scheme of two virtual machines in this case will look as follows:
The company conducted tests of the hypervisor, having trained the language model based on TensorFlow . "Damage" performance was only 3-4%, compared with bare metal. At the same time, in exchange, the system was able to allocate resources on demand, depending on current loads.
The IT giant also conducted container tests . Company engineers trained neural networks to recognize images. At the same time, the resources of one GPU were distributed among four container VMs. As a result, the performance of individual machines has decreased by 17% (compared to a single VM, which has full access to GPU resources). However, the number of processed images per second increased three times. It is expected that such systems will find application in the field of data analysis and computer modeling.
Among the potential problems that VMware may encounter, experts highlight a rather narrow target audience. With high-performance systems while working a small number of companies. Although Statista notes that by 2021 94% of the workloads of the world data centers will be virtualized. According to analysts, the cost of the HPC-market will increase from 32 to 45 billion dollars in the period from 2017 to 2022.

/ Global Access Point PD Photo
There are several analogues on the market that are developed by large IT companies: AMD and Intel.
The first company to virtualize GPUs offers an approach based on SR-IOV (single-root input / output virtualization). This technology provides VM access to parts of the system's hardware capabilities. The solution allows you to divide the graphics processor between 16 users with equal performance of virtualized systems.
As for the second IT giant, their technology is based on the Citrix XenServer 7 hypervisor. It combines the work of a standard GPU driver and a virtual machine, which allows the latter to display 3D applications and desktops on devices of hundreds of users.
The developers of virtual graphics processors are betting on the introduction of AI systems and the growing popularity of high-performance solutions in the business technology market. They hope that the need for processing large amounts of data will increase the demand for vGPU.
Now manufacturers are looking for a way to combine the functionality of CPU and GPU in one core in order to speed up the solution of tasks related to graphics, performing mathematical calculations, logical operations, data processing. The appearance on the market of such cores in the future will change the approach to resource virtualization and their distribution between workloads in a virtual and cloud environment.
What to read on the topic in our corporate blog:
A couple of posts from our Telegram channel:
We talk about the technologies that allowed to achieve this.

/ photo Victorgrigas CC BY-SA
')
Performance problem
According to analysts, about 70% of workloads in data centers are virtualized . However, the remaining 30% still work on bare metal without hypervisors. These 30% for the most part consist of high-load applications associated, for example, with the training of neural networks, and using graphics processors.
Experts explain this trend by the fact that the hypervisor, as an intermediate layer of abstraction, can affect the performance of the entire system. In studies five years ago, you can find data on the reduction in the speed of work by 10%. Therefore, companies and data center operators are in no hurry to transfer HPC-load into a virtual environment.
But virtualization technologies are evolving and improving. At the conference a month ago in VMware, they said that the ESXi hypervisor does not have a negative impact on GPU performance. The computation speed can be reduced by three percent, and this is comparable with bare metal.
How it works
To increase the performance of HPC systems with graphics processors, VMware made a number of changes to the work of the hypervisor. In particular, he was relieved of the vMotion function. It is needed for load balancing and usually transfers virtual machines (VMs) between servers or GPUs. Disabling vMotion led to the fact that each VM is now assigned a specific graphics processor. This helped reduce the cost of data sharing.
Another key component of the system is DirectPath I / O technology . It allows the CUDA parallel computing driver to interact with virtual machines directly, bypassing the hypervisor. When several VMs are required to run on one GPU at once, the GRID vGPU solution is enabled. It divides the memory card into several segments (but the computational cycles are not divided).
The operation scheme of two virtual machines in this case will look as follows:

Results and forecasts
The company conducted tests of the hypervisor, having trained the language model based on TensorFlow . "Damage" performance was only 3-4%, compared with bare metal. At the same time, in exchange, the system was able to allocate resources on demand, depending on current loads.
The IT giant also conducted container tests . Company engineers trained neural networks to recognize images. At the same time, the resources of one GPU were distributed among four container VMs. As a result, the performance of individual machines has decreased by 17% (compared to a single VM, which has full access to GPU resources). However, the number of processed images per second increased three times. It is expected that such systems will find application in the field of data analysis and computer modeling.
Among the potential problems that VMware may encounter, experts highlight a rather narrow target audience. With high-performance systems while working a small number of companies. Although Statista notes that by 2021 94% of the workloads of the world data centers will be virtualized. According to analysts, the cost of the HPC-market will increase from 32 to 45 billion dollars in the period from 2017 to 2022.

/ Global Access Point PD Photo
Similar solutions
There are several analogues on the market that are developed by large IT companies: AMD and Intel.
The first company to virtualize GPUs offers an approach based on SR-IOV (single-root input / output virtualization). This technology provides VM access to parts of the system's hardware capabilities. The solution allows you to divide the graphics processor between 16 users with equal performance of virtualized systems.
As for the second IT giant, their technology is based on the Citrix XenServer 7 hypervisor. It combines the work of a standard GPU driver and a virtual machine, which allows the latter to display 3D applications and desktops on devices of hundreds of users.
Future technology
The developers of virtual graphics processors are betting on the introduction of AI systems and the growing popularity of high-performance solutions in the business technology market. They hope that the need for processing large amounts of data will increase the demand for vGPU.
Now manufacturers are looking for a way to combine the functionality of CPU and GPU in one core in order to speed up the solution of tasks related to graphics, performing mathematical calculations, logical operations, data processing. The appearance on the market of such cores in the future will change the approach to resource virtualization and their distribution between workloads in a virtual and cloud environment.
What to read on the topic in our corporate blog:
- Why companies use virtual machines, not containers
- "How are VMware?": A review of new solutions
- VMware vSphere 6.7: What Are the New Functions of the Hypervisor?
A couple of posts from our Telegram channel:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/443946/
All Articles