How did Fukuoka Airport learn which measures would be effective in reducing queues
Here is not a fictional picture from the “Airports of the Future” advertising magazine. This is actually operating airport of the Japanese city of Fukuoka, which offers passengers a lot of free space to move. Thanks to a special modeling technology, the causes of queuing were identified and optimization measures were taken. Who cares how this technology works, please under the cat.

Photo courtesy of Fukuoka City
Professor Takahashi (Shingo Takahashi), head of the department of developing industrial systems and control systems at Waseda University and Fujitsu Laboratories have developed a technology that allows you to identify the reasons for the accumulation of people in public places. The solution automatically analyzes the factors that led to the formation of a large mass of people, based on the results of modeling human behavior.
')
Back in 2015, Fujitsu and Professor Takahashi used this technology in a system for modeling human behavior, which analyzed measures to eliminate queues at the airport in Fukuoka. They managed to find 4 times more reasons for the emergence of crowds compared with the analysis of experts. For example, when analyzing a crowd of people during a control inspection of passengers and baggage, the system was able to detect for the first time that passengers gathered at a certain check-in counter caused an unexpected crowd of people in the control inspection zone. During the simulation, it was confirmed that this technology allows to reduce the number of people awaiting the passage of control inspection, one-sixth. In addition, the number of staff can be reduced by one third. And the analysis time was significantly reduced, from several months to several minutes.
The new development brings together categories that have a certain commonality, and expresses the characteristics of the relevant "agents" (modeled behavior, human actions) in the form of a small number of combinations of categories without making lists of movement results or routes of tens or hundreds of thousands of agents. This approach makes it easier to isolate the characteristics of agents associated with the causes of clusters of people, and makes it possible to create parameters related to certain characteristic features and examples of movement.

Diagram of the simulation of human behavior and the forecast of the formation of crowds at the airport
Previously, due to the fact that the data relating to the distinctive features, perceptions and actions of agents (for example, the agent’s task is to “have lunch” or the agent saw the pointer at a point), which were expressed in dozens of records in the database, were combined to create the characteristics of the agent, this process created a large number of combinatorial examples. With the new technology, which creates logical groups, which include similarities in the characteristics, and creates clusters of agent characteristics for each group, it was possible to reduce the number of combinatorial examples. This allows you to search for causes that are directly related to countermeasures, and get an answer to the question of what measures will be effective in reducing crowds.
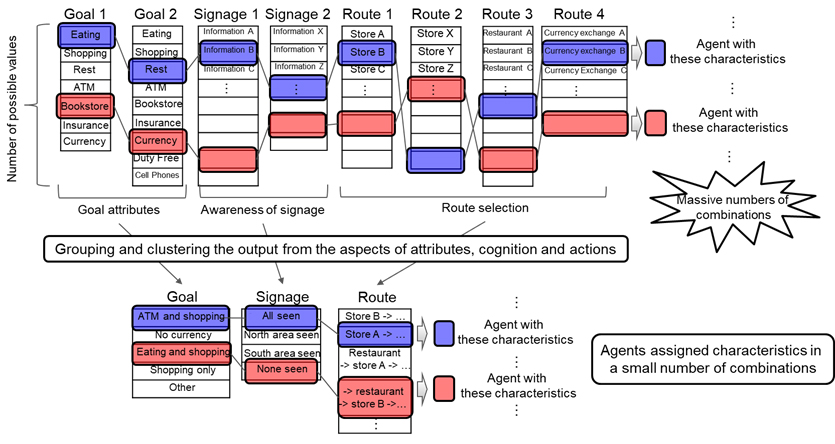
Identification of the full range of reasons for the formation of clusters of people based on distinctive features, actions and ways of perception
For example, with regard to crowds that occur in store A and B in a mall, when a bunch of people are detected, it can be determined that the cluster in store A was caused by people who saw the pointer, and the cluster in store B was caused by people who had finished eating lunch in cafe and all came to the store. Thus, the accumulation of people in store A can be eliminated by installing new signs, and the accumulation in store B can be eliminated by increasing the number of staff and speed of service.

Identify the causes and examples of oppositions that have been received thanks to technology
When modeling human behavior, experts tend to repeat the process of trial and error, analyzing large amounts of data that were obtained as a result of modeling, and offer hypotheses about the reasons for the formation of crowds and possible countermeasures, based on their experience and information, and then rerunning the modeling to assess proposed hypotheses. Accordingly, the analysis of the proposed causes and the determination of countermeasures may take several months. And in some cases, when the analyst missed certain reasons, additional problems may arise. New technology professors Takahashi and Fujitsu Laboratories provides a comprehensive selection of the characteristics of agents that are relevant to the crowds. Consequently, the number of combinatorial examples decreases. This allows you to search for causes that are directly related to countermeasures, and get to quickly develop measures to combat queues.
The technology allows the rapid assessment of parameters to prevent the formation of clusters of people in places of trade, places of various events and in other places where people may form clusters due to their high attendance or centralization. Thus, the new development makes it possible to improve the safety and comfort of urban environments.
Event venues, airports and shopping centers, which often have large masses of people, can have a negative effect on customer satisfaction and, ultimately, sales. Currently, in addition to ways to solve this problem, such as increasing the number of personnel deployed at entrances, exits and points of sale to assist visitors, there are a number of other measures that include installing special signposts and schemes for moving visitors to less loaded rooms. However, to implement more effective means of reducing the flow, it is important to understand which types of people will take what types of actions in response to what types of information.
To do this, increasingly used technology "modeling human behavior." Specialists perform modeling of the distinctive features, perceptions, and actions of various groups of people as “agents”. And with the help of computerized virtual modeling of queuing situations, scientists can analyze the causes and evaluate solutions that will prevent crowds.

Photo courtesy of Fukuoka City
Professor Takahashi (Shingo Takahashi), head of the department of developing industrial systems and control systems at Waseda University and Fujitsu Laboratories have developed a technology that allows you to identify the reasons for the accumulation of people in public places. The solution automatically analyzes the factors that led to the formation of a large mass of people, based on the results of modeling human behavior.
')
Back in 2015, Fujitsu and Professor Takahashi used this technology in a system for modeling human behavior, which analyzed measures to eliminate queues at the airport in Fukuoka. They managed to find 4 times more reasons for the emergence of crowds compared with the analysis of experts. For example, when analyzing a crowd of people during a control inspection of passengers and baggage, the system was able to detect for the first time that passengers gathered at a certain check-in counter caused an unexpected crowd of people in the control inspection zone. During the simulation, it was confirmed that this technology allows to reduce the number of people awaiting the passage of control inspection, one-sixth. In addition, the number of staff can be reduced by one third. And the analysis time was significantly reduced, from several months to several minutes.
The new development brings together categories that have a certain commonality, and expresses the characteristics of the relevant "agents" (modeled behavior, human actions) in the form of a small number of combinations of categories without making lists of movement results or routes of tens or hundreds of thousands of agents. This approach makes it easier to isolate the characteristics of agents associated with the causes of clusters of people, and makes it possible to create parameters related to certain characteristic features and examples of movement.

Diagram of the simulation of human behavior and the forecast of the formation of crowds at the airport
Previously, due to the fact that the data relating to the distinctive features, perceptions and actions of agents (for example, the agent’s task is to “have lunch” or the agent saw the pointer at a point), which were expressed in dozens of records in the database, were combined to create the characteristics of the agent, this process created a large number of combinatorial examples. With the new technology, which creates logical groups, which include similarities in the characteristics, and creates clusters of agent characteristics for each group, it was possible to reduce the number of combinatorial examples. This allows you to search for causes that are directly related to countermeasures, and get an answer to the question of what measures will be effective in reducing crowds.

Identification of the full range of reasons for the formation of clusters of people based on distinctive features, actions and ways of perception
For example, with regard to crowds that occur in store A and B in a mall, when a bunch of people are detected, it can be determined that the cluster in store A was caused by people who saw the pointer, and the cluster in store B was caused by people who had finished eating lunch in cafe and all came to the store. Thus, the accumulation of people in store A can be eliminated by installing new signs, and the accumulation in store B can be eliminated by increasing the number of staff and speed of service.

Identify the causes and examples of oppositions that have been received thanks to technology
When modeling human behavior, experts tend to repeat the process of trial and error, analyzing large amounts of data that were obtained as a result of modeling, and offer hypotheses about the reasons for the formation of crowds and possible countermeasures, based on their experience and information, and then rerunning the modeling to assess proposed hypotheses. Accordingly, the analysis of the proposed causes and the determination of countermeasures may take several months. And in some cases, when the analyst missed certain reasons, additional problems may arise. New technology professors Takahashi and Fujitsu Laboratories provides a comprehensive selection of the characteristics of agents that are relevant to the crowds. Consequently, the number of combinatorial examples decreases. This allows you to search for causes that are directly related to countermeasures, and get to quickly develop measures to combat queues.
The technology allows the rapid assessment of parameters to prevent the formation of clusters of people in places of trade, places of various events and in other places where people may form clusters due to their high attendance or centralization. Thus, the new development makes it possible to improve the safety and comfort of urban environments.
Relevance
Event venues, airports and shopping centers, which often have large masses of people, can have a negative effect on customer satisfaction and, ultimately, sales. Currently, in addition to ways to solve this problem, such as increasing the number of personnel deployed at entrances, exits and points of sale to assist visitors, there are a number of other measures that include installing special signposts and schemes for moving visitors to less loaded rooms. However, to implement more effective means of reducing the flow, it is important to understand which types of people will take what types of actions in response to what types of information.
To do this, increasingly used technology "modeling human behavior." Specialists perform modeling of the distinctive features, perceptions, and actions of various groups of people as “agents”. And with the help of computerized virtual modeling of queuing situations, scientists can analyze the causes and evaluate solutions that will prevent crowds.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/443820/
All Articles