5 features of metal powders for 3D printing
One of the important advantages of 3D metal printing technology is the ability to create a product from virtually any alloy. In addition to standard metals, there is a wide range of special alloys - unique high-tech materials that are manufactured for specific customer tasks.
The most progressive and popular technology of 3D-printing metals - selective laser melting (SLM / DMP). It consists in sequential layer-by-layer melting of metal powders with the help of high-power radiation from an ytterbium laser.
The technology is patented by the leaders of the 3D industry - companies SLM Solutions and 3D Systems. Metal 3D-printers of these manufacturers, depending on the functionality and tasks, can be used as production machines for mass production, and as laboratory facilities with flexible settings and the ability to quickly change materials for 3D printing.
')
Equipment:
SLM Solutions (SLM-technology): SLM 125, SLM 280, SLM 500, SLM 800;
3D Systems (DMP technology): ProX DMP 100, ProX DMP 200, ProX DMP 300, ProX DMP 320, DMP 8500.
The main advantages of 3D printing with metals:
- high density: 1.5 times higher than during casting;
- the possibility of creating miniature and geometrically complex objects and other unique forms in the form of closed bionic structures;
- a wide range of metal alloys, both standard and special;
- reduction of production cycles and acceleration of finished product output.
Application areas:
- aerospace industry;
- engineering;
- automotive industry ;
- oil and gas industry;
- electronics;
- the medicine;
- food industry;
- research and experimental work in design offices, research and educational centers.
Types of metals used in additive manufacturing
Modern additive technologies involve the use of about twenty tested and ready-to-use materials, including instrumental, stainless, heat-resistant alloys, aluminum and titanium alloys, medical cobalt-chromium and titanium.
Since there are a lot of metals, and each of them has certain properties, one metal can be replaced by another on the basis of technological problems. For example, if it is necessary to use a titanium alloy in the technological chain, the process engineer will be able to choose one of the many titanium alloys with the properties that are needed for the production of a particular product.
- Stainless alloys: 17-4PH, AISI 410, AISI 304L, AISI 316L, AISI 904L
This category includes complex alloyed steels with a chromium content (at least 12%). Chromium oxide forms a corrosion-resistant film on the surface of the metal, which can be destroyed by mechanical damage or chemical media, but is restored by reaction with oxygen. Stainless alloys are used in the manufacture of valves for hydraulic presses, cracking fittings fittings, springs, welded equipment operating in corrosive environments, and products used at high temperatures (+ 550… 800 ° C). - Tool alloys: 1.2343, 1.2367, 1.2709
The main purpose of tool alloys is the manufacture of various types of tools (cutting, measuring, die, etc.), inserts in the mold during hot deformation of structural steels and non-ferrous alloys in high-volume production, molds for injection molding of aluminum, zinc and magnesium alloys. . These alloys contain at least 0.7% carbon and have increased hardness, wear resistance, toughness, thermal conductivity and hardenability. - Nickel alloys: Inconel 625, Inconel 718
Nickel has the ability to dissolve many other metals, while maintaining plasticity, so there are many nickel alloys. For example, in conjunction with chromium, they are widely used in aircraft engines, of which workers and nozzle vanes, turbine rotor disks, parts of the combustion chamber , etc. are made. The most heat-resistant are foundry complex-alloyed nickel-based alloys, which can withstand temperatures up to + 1100 ° C for hundreds and thousands of hours under high static and dynamic loads. - Cobalt Chrome: CoCr
CoCr is a high-quality cobalt-chrome alloy for model casting that meets modern technical requirements. Due to its excellent mechanical properties, it is well suited for the manufacture of buildings of complex geometry in electronics, food production, aircraft, rocket and mechanical engineering, as well as clasp prostheses. - Non-ferrous metals: CuSn6
CuSn6 is an alloy of copper and 6% tin, which has high heat-conducting properties and corrosion resistance and is ideal for creating unique cooling systems . - Aluminum Alloys: AlSi12
It is the cheapest of cast alloys. Their advantages include high corrosion resistance, fluidity, electrical and thermal conductivity. In industry, they are used, as a rule, for the manufacture of large-sized thin-walled castings of complex shape. - Titanium alloys: Ti6Al4V, Ti6Al7Nb
Ti6Al4V is the most common alloy of titanium with excellent mechanical properties. It is considered the most durable and tough titanium alloy, characterized by a particularly high complexity of processing. It has a density of 4500 kg / m³ and tensile strength of more than 900 MPa. The Ti6Al4V alloy provides undeniable advantages in terms of weight reduction products in industries such as aerospace, automotive and shipbuilding. These metals are used, in particular, in the manufacture of inlays in the mold, turbine blades, combustion chambers, as well as products intended for operation at high temperatures (up to + 1100 ° C).
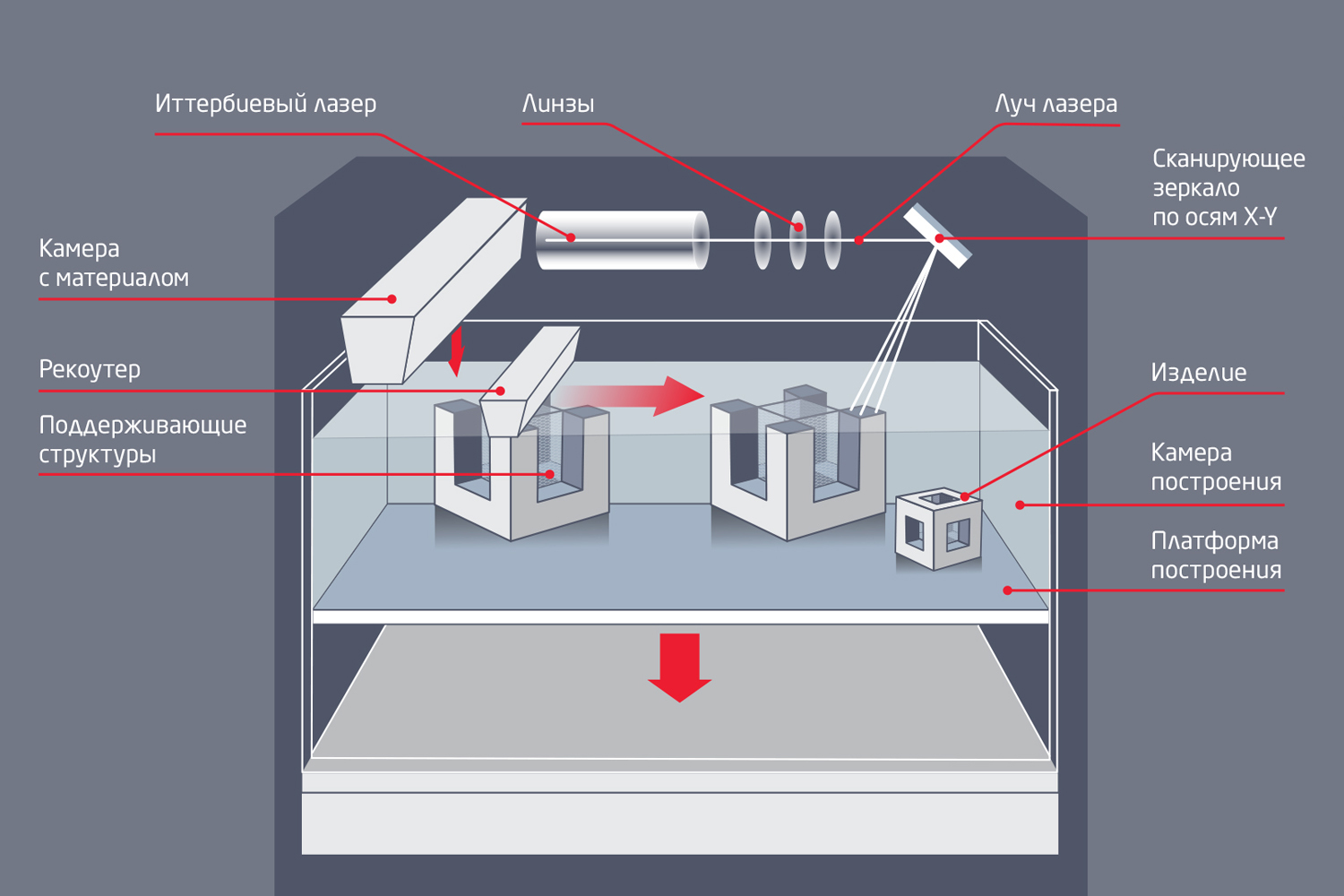
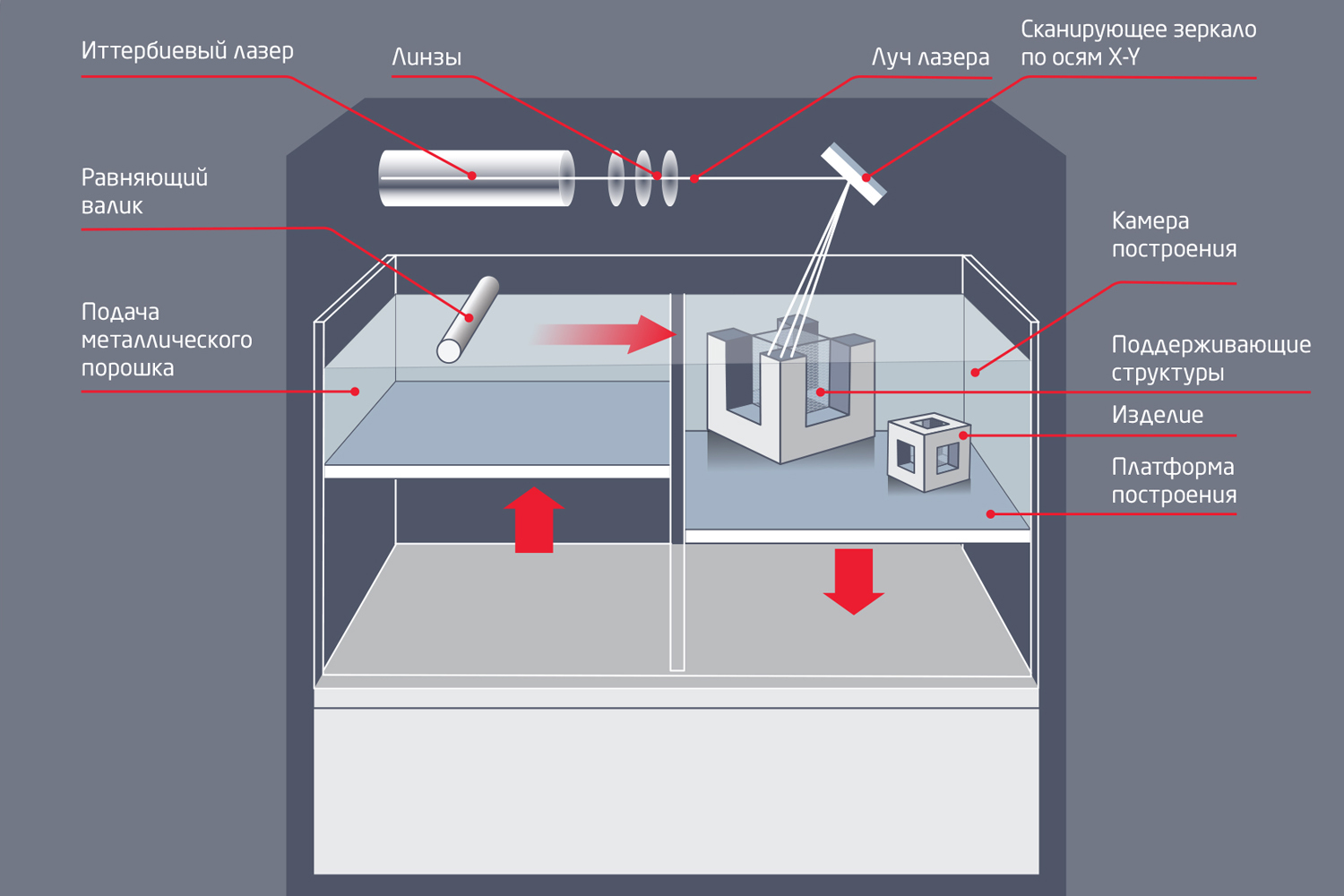
Installation diagrams for SLM Solutions (above) and 3D Systems (below)
Features of metal powders
- Metal for additive plants is produced in the form of fine spherical granules with a grain size from 4 to 80 microns. This indicator determines the thickness of the object to be grown in an additive plant. When creating the powder, the size and composition of the grain is specified, since it is necessary to observe a certain percentage of large and small grains. This determines the fluidity of the metal, which is checked using a Hall device (a funnel with a calibrated hole). If the grain has a too small fraction, the metal will not flow through the funnel and, accordingly, poorly fed to the construction table, and this directly affects the uniformity of the layers and the quality of the grown product.
- Each company producing this type of 3D printers has its own requirements for turnover depending on the principle of applying material to the building platform. In additive installations SLM Solutions (SLM technology), metal is fed to the desktop from above, from the feeder (camera with the material), and transferred by the recoater. In this case, the fluidity is very important in order for the powder to flow from the feeder into the recooter and the layers are applied properly. 3D Systems (DMP technology) uses a slightly different principle of operation: the powder container is lifted slightly, transferred with a roller to the building table, then the container is lowered. Thanks to this design, the flow rates are not critical (see the schemes for constructing products in the figures).
- Different metals require different heat treatments , and sometimes specially heated platforms are used for this. In the process of building, during the melting of the metal, a large amount of heat is generated, which must be removed. The role of heat radiators is performed by the supports used in the construction of products. In some cases, the part itself without support is welded to the desktop, as if to a radiator.
- The structure of metal products obtained by the additive method depends on both the construction technology and the equipment settings. Leading manufacturers have achieved a metal density of about 99.9% of theoretical. Along with selective laser melting, there are less efficient, outdated technologies similar to the SLS method, which provide lower density.
- The internal structure of the metal is fine-grained. If in the future we are going to compact the part, that is, to act on it physically, we must bear in mind that it is much more difficult to compress a small grain than a large grain. But at the same time we are very close to the rolled metal - i.e. to the metal that is already sealed. The density of products printed on a 3D printer is 10-15% lower than when rolled, but about 50% higher than that of cast metals.
Safety issues when working on metal 3D-printers
As you know, metals that enter the human body in microscopic doses are useful. In macrodoses, they carry a health hazard - it is very easy to get intoxicated with metals, and in addition, the powders are explosive. When the dispersion of the powder from 4 microns, it penetrates through the pores of the skin, respiratory organs, eyesight, etc. In this regard, when working on metal 3D-printers, you must strictly observe safety precautions. For this, protective clothing is provided - a suit, gloves and shoes. Additive machines, as a rule, are equipped with a vacuum cleaner to remove the base powder, but even after using it, some metal suspension remains.
Manufacturers are striving to improve safety conditions, and now there is a tendency to create so-called closed cycles in the additive production, i.e. completely sealed rooms, outside of which the powder does not fall. The operator works in special clothes, which are then disposed of.

The potential of 3D metal printing
So, we found out that modern technologies allow us to obtain powder for 3D printing with metal with certain properties for solving specific production problems. And since almost any metal can be sprayed, the range of metallic materials for 3D printers is extremely extensive.
Achievements of metallurgy are fully realized in additive manufacturing, allowing the use of unique alloys for the manufacture of geometrically complex products of increased accuracy, density and repeatability. At the same time, the introduction of metal additive plants has constraints, the main of which is the high cost of powders.
3D printing of metals has a serious potential for increasing production efficiency in many industries and is used by an increasing number of companies and research organizations. An example for the global industry is shown by such industrial leaders as General Electric , Airbus, Boeing, Michelin, who have already moved from the manufacture of single metal products to the mass-produced additive production.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/443532/
All Articles