Why exactly 4 years ago NASA shot Atlas V rocket at the night sky of Cape Canaveral?

On March 12, 2015, another NASA mission to study the dynamics of the Earth’s magnetic field started from Cape Canaveral. This time the subject of research was the process of re-closure of the magnetic field lines .
As a result of the bombardment of the Earth by charged particles from the Sun, the lines of force of the magnetic field of our mother can undergo ruptures and reconnections, which causes huge bursts of energy that are reflected in the atmosphere in the form of beautiful auroras .
')
In order to better understand the physics of this process, NASA uses American taxpayers' money to permeate the sky with expensive equipment. You, in order to dive into the topic, just look under the cat.
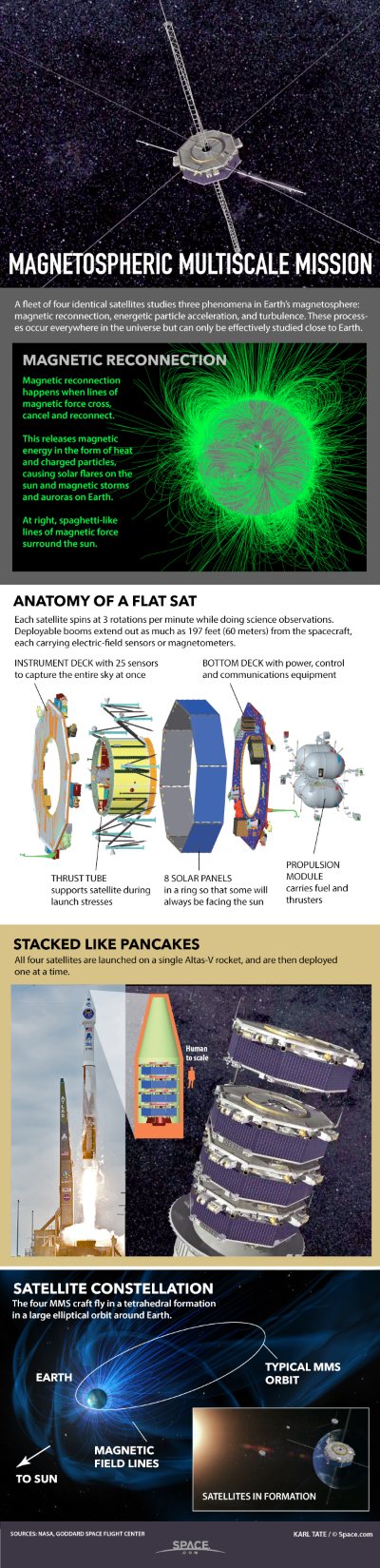
Onboard the Atlas V were 4 mission satellites called Magnetospheric Multiscale mission (MMS), the main purpose of which is to study the phenomenon of reconnection of the magnetic field lines of the Sun’s magnetic field in the Earth’s magnetosphere, resulting in a rather dangerous explosive process, may damage operating devices in orbit.
This mission is one of a kind, dealing with this issue. Its remarkable feature is the geometric choreography of the location of the satellites relative to each other. In order for the equipment to be able to collect adequate data, satellites must form a regular pyramid on the path of the phenomenon that is unfolding before the cold eyes of cosmic wanderers.
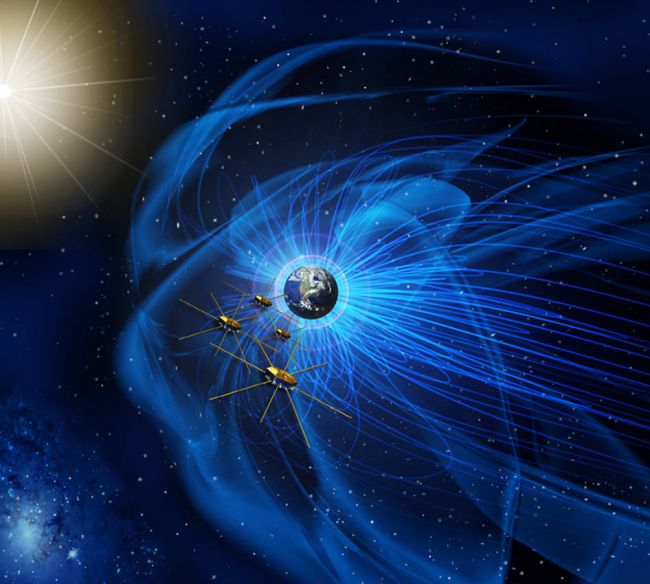
Magnetic fields can be found in every corner of the universe. Planets, stars, galaxies, black holes and many other bodies create magnetic fields that entwine their creators or freely wander around the surrounding space.
 Attached at one end to the positively charged side and the other to the negatively charged, the magnetic field lines are usually closed and form loops. But sometimes there is a break in the line, followed by a closure in the new loop. The opening and closing of these lines releases a large amount of energy, accelerating the surrounding charged particles to speeds close to the speed of light.
Attached at one end to the positively charged side and the other to the negatively charged, the magnetic field lines are usually closed and form loops. But sometimes there is a break in the line, followed by a closure in the new loop. The opening and closing of these lines releases a large amount of energy, accelerating the surrounding charged particles to speeds close to the speed of light.To quote the words of Jim Burch, the principal investigator of MMS, he said on March 10, 2015:
Exactly how the magnetic line is broken and then closed is a completely unknown process.When a similar phenomenon occurs with the magnetic lines of the Sun, solar flares occur, which send a massive piece of the solar atmosphere to outer space as free-floating, sometimes straight to Earth. Such an event is called the ejection of coronal masses and is quite a dangerous phenomenon that can cause significant problems with electronics on Earth and damage satellites in orbit.
The reconnection of magnetic lines also occurs much closer to the Earth: from time to time the magnetic lines of the Sun reach the Earth's magnetic lines. This is a catalyst for the redistribution of magnetic lines and as a result of their reconnection.
 In most cases, the result of this process is the flow of charged particles, directed towards the Earth's atmosphere, which generates one of the most spectacular events on Earth - the northern lights. But the same effect is also the cause of geomagnetic storms, which are a source of strong electromagnetic waves that can destroy electronics and cause a power outage.
In most cases, the result of this process is the flow of charged particles, directed towards the Earth's atmosphere, which generates one of the most spectacular events on Earth - the northern lights. But the same effect is also the cause of geomagnetic storms, which are a source of strong electromagnetic waves that can destroy electronics and cause a power outage.With the help of the MMS mission, mankind wants to understand how this simultaneously beautiful and dangerous phenomenon works.
Let's go to the details
- The cost of the mission: $ 1.1 billion
- Weight of each satellite: 1.36 tons
- Packed size of each satellite: Oktogonal shape (regular octagon) 1.2 meters high, 3.65 meters wide
- The method of packaging in the carrier rocket: wedding cake
- Operational size of each satellite: 28.65 meters high, 120.7 meters wide
Impressive, isn't it?
How?
In orbit, the satellites formed a pyramid, being at a distance of 10 km from each other, to compile a 3d image of the process under study. Each satellite has a GPS module, which provides positioning accuracy up to 100 meters.
Mission vehicles collect data in places where the probability of detecting such events is maximum - on the Sun-Earth line in a magnetopause .
What is the result
A year after the launch of the mission, it was possible to fix the first reconnection event. Flying in close proximity to the re-locked lines in the so-called dissipation region, the satellites detected the event itself and the flow of charged particles rushing in a straight line from the scene at a speed of thousands of kilometers per second, breaking through the Earth's magnetic field, usually holding them. As soon as the particles pass through the magnetic barrier, they unfold by 180 degrees, which signals the formation of new magnetic lines after the old ones were destroyed by the sun.
These results completely coincided with computer simulations.
Since the launch of MMS, it has flown through these regions in the Earth’s magnetic field thousands of times already, each time collecting information on the dynamics of the magnetic field lines of the Earth. After the first direct observation of this phenomenon, about a dozen more similar cases were recorded, which provided more data to study this fundamental phenomenon.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/443502/
All Articles