Multi-level lighting control based on the CTS NPL
Multi-site lighting control and multi-level lighting control in the residential sector is becoming increasingly popular. Standard solutions are the use of impulse relays or PLC, but there is another solution - the Non-Programmable Logic Hardware Complex (CTS NPL) based on contactors , here I want to show the difference and features of such a solution.
Technical task
Everything said below makes sense for multi-level load management without remote access and without creating scripts, because for such tasks the choice is obvious to everyone. The functionality of the considered systems: centralized multi-level sectional control, while maintaining local control. Here is a fragment of what the customer wants and what the designer has painted:
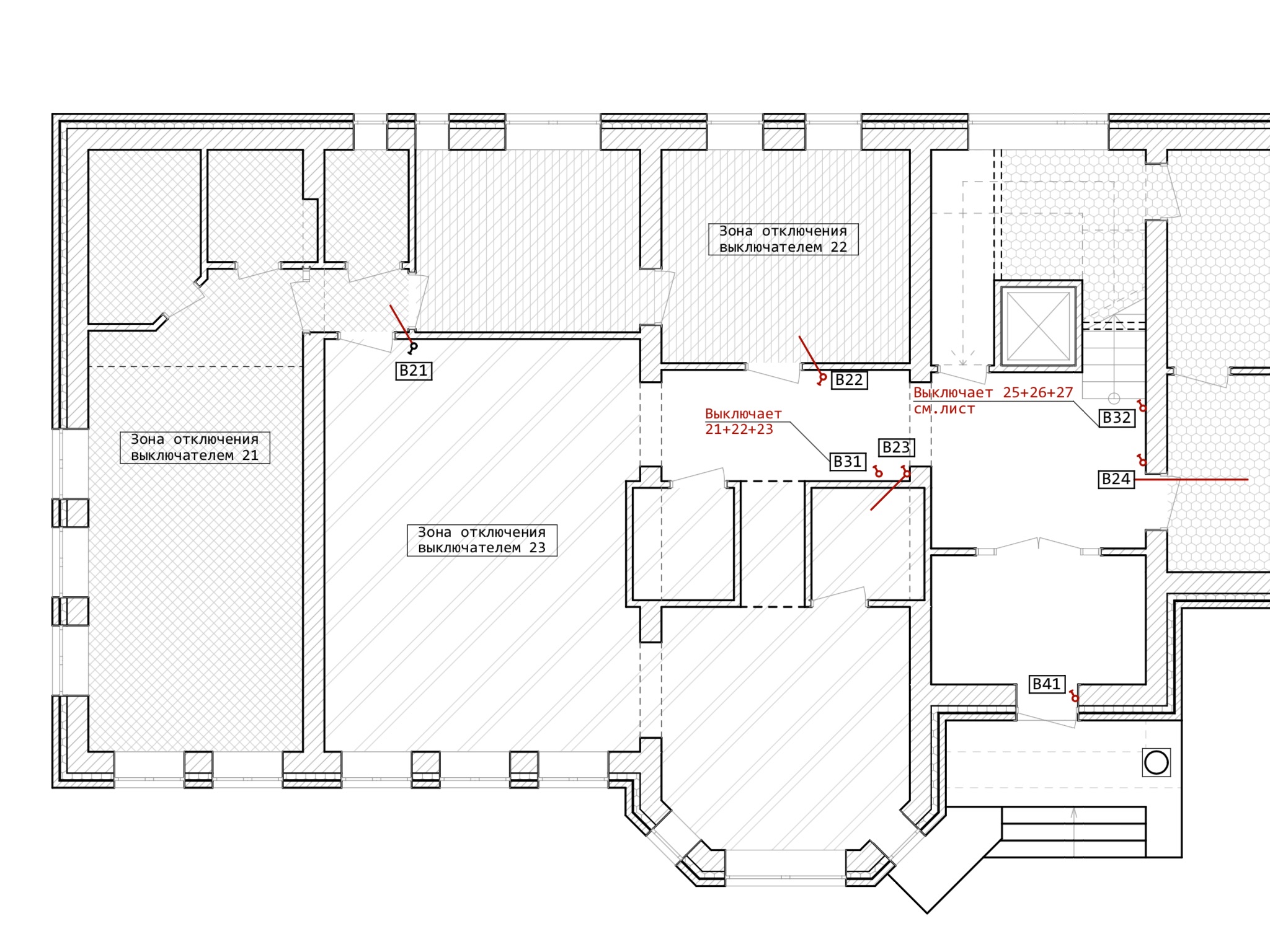
')
Calculate the total cost of equipment
For a more illustrative analysis, below I have indicated the average cost of equipment for each of the systems. I also provide a formula by which the total equipment cost for the system can be calculated. Naturally the price does not include protection apparatuses, wardrobe, etc.
The total cost of equipment = the average cost of equipment x (number of light sources + number of control sections).
Lighting control system based on entry-level PLC
System composition:
Logic module, logic module expansion unit, intermediate relays, modular contactors.
System characteristics:
In the event of a malfunction of the logic module - the complete absence of lighting until the malfunction is eliminated
Electrical wear resistance: 100 thousand cycles for AC-1.
Maximum switching frequency limit of 2 Hz.
Limiting the number of relay outputs and the number of control levels.
The average cost of equipment is $ 72.
Lighting control system based on impulse relays
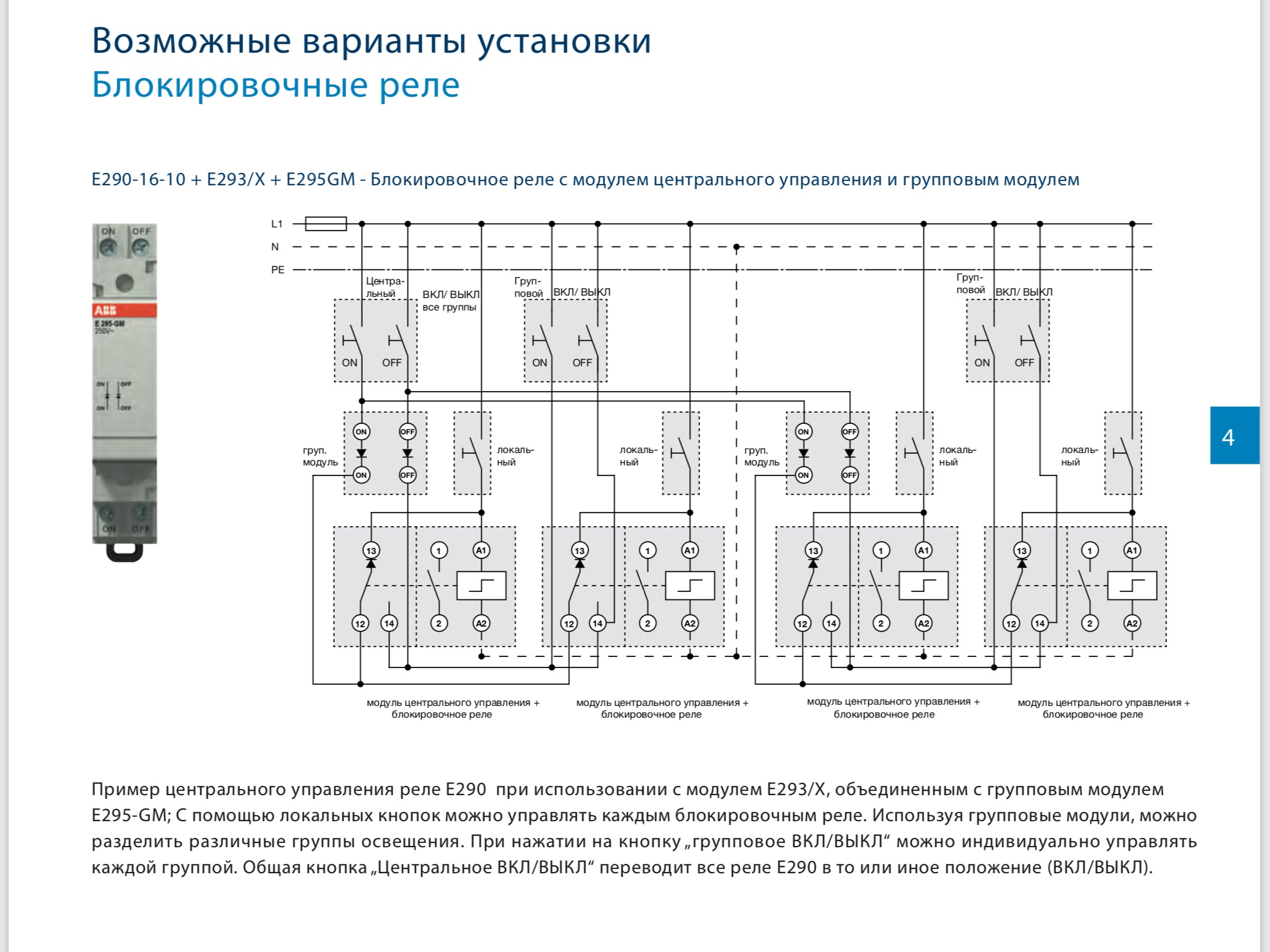
System composition:
Pulse relays, central control modules, group control modules.
System characteristics:
In the event of a malfunction, the elements of the system fail one at a time.
Electrical wear resistance: 100 thousand cycles for AC-1.
Limit the number of switching: 5-15 switching per minute / 100 switching per day.
Limit pulse duration: 50 ms - 1 s.
Power load limit
Vibrations can lead to spontaneous switching, that is, if necessary, install contactors in such a control cabinet will not work.
With an increase in the number of management levels, the complexity of constructing a scheme increases.
The average cost of equipment is $ 73.
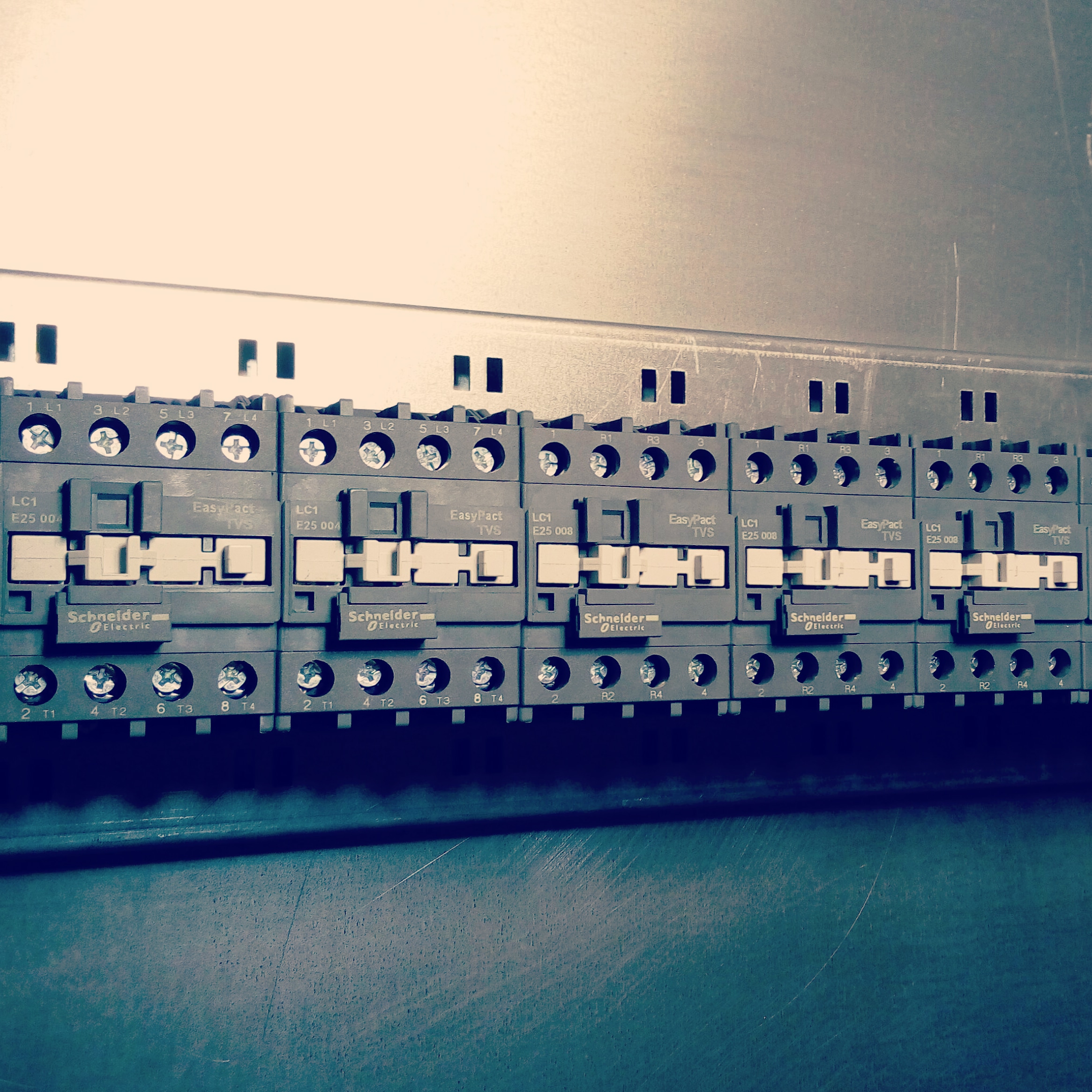
Lighting control system based on contactors
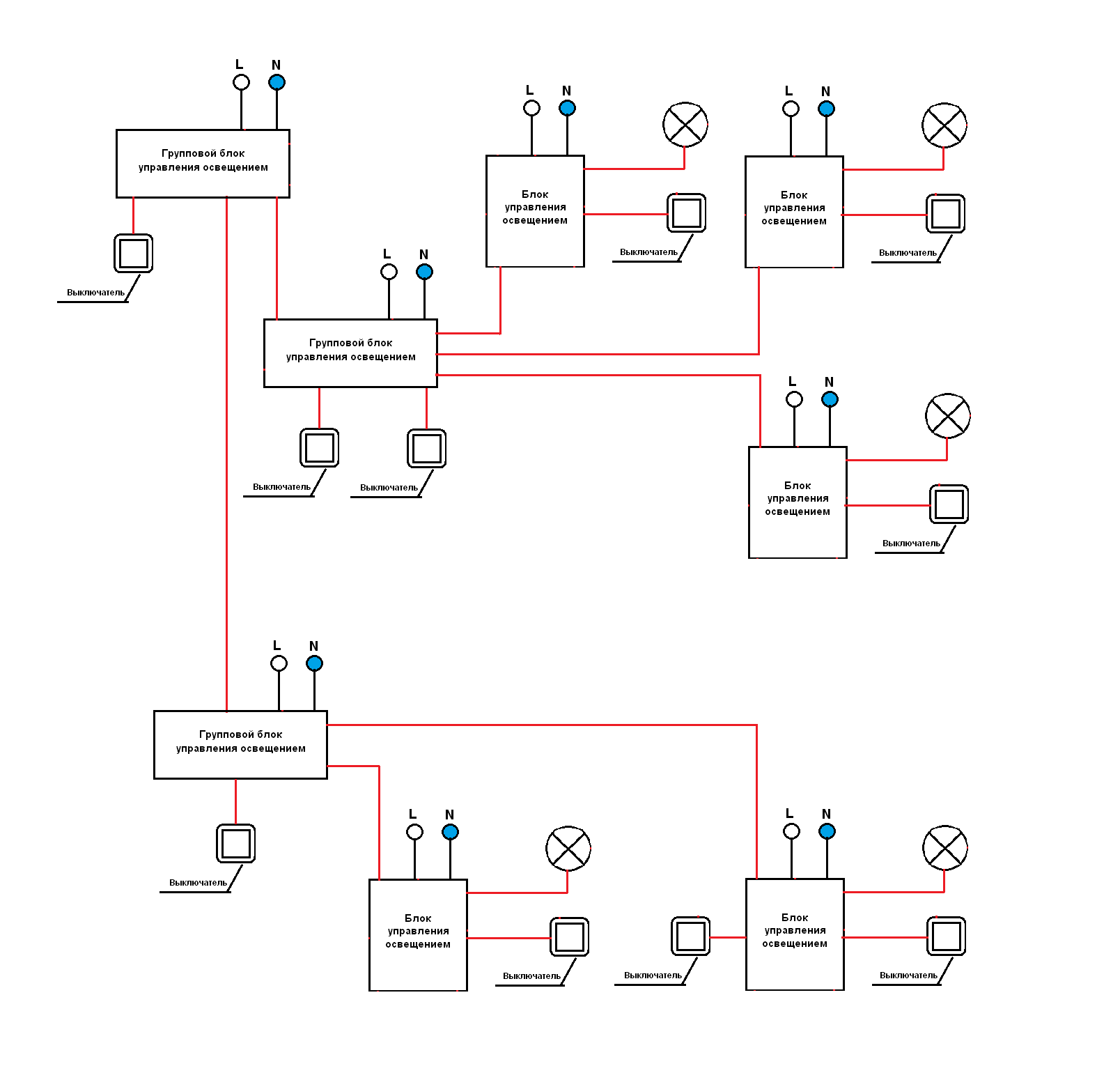
System composition:
Contactors - each lighting control unit consists of two contactors: the first to turn on the load, the second to turn off.
System characteristics:
Electrical wear resistance: 1.4 million cycles for AC-3, 150 thousand cycles for AC-1.
Number of switching per hour: 1800 cycles.
At malfunction elements of the system fail one at a time.
Unlimited plug-in power.
Unlimited levels of management.
With an increase in the number of system management levels, the scheme is not complicated.
The average cost of equipment is $ 53.
Comparison
PLC vs. Impulse relays
Comparability of cost and load switching resource. When using a PLC, if it fails, the entire lighting system will be de-energized until troubleshooting, but despite this, the impulse relays have too many shortcomings for such a cost: limiting the duration of the pulse, limiting the number of switches per minute, limiting the load, the complexity of building a large number of levels, limiting the level of vibration.
PLC vs. KTS NPL on the basis of contactors
The CTS NPL has a larger load switching resource, the ability to build a circuit with any number of light sources, any number of control levels, without complicating the circuit, and at a lower cost, if one of the system elements fails, the rest of the system will continue to work, unlike PLC.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/443388/
All Articles