Virtual Check Points: Customization Checklist
Many clients who rent cloud resources from us use virtual Check Points. With their help, clients solve various tasks: someone controls the output of the server segment to the Internet or publishes their services for our equipment. Someone needs to push all traffic through the IPS blade, while someone needs Check Point as a VPN gateway to access internal resources in the data center from the branches. There are those who need to protect their infrastructure in the cloud in order to pass certification on FZ-152, but I will tell you about this separately.
On duty, I am engaged in the support and administration of Check Points. Today I will tell you what to consider when deploying a cluster of Check Points in a virtual environment. I will touch on the moments of the level of virtualization, network, settings of Check Point itself and monitoring.
I do not promise to discover America - there are many things in the recommendations and best practices of the vendor. But nobody reads them), so they drove.
Cluster mode
We Check Point live in clusters. The most frequent installation is a cluster of two nodes in active-standby mode. If something happens to an active node, it becomes inactive, and a standby-node is activated. Switching to a “spare” node usually occurs due to synchronization problems between the cluster members, the state of the interfaces, the established security policy, simply because of the heavy load on the equipment.
')
In a cluster of two nodes, we do not use active-active mode.
If one of the nodes falls, the surviving node may simply not sustain a double load, and then we will lose everything. If you really want active-active, then there should be at least 3 nodes in the cluster.
Network and virtualization settings
On network equipment, multicast traffic is allowed between SYNC interfaces of cluster members. If multicast traffic is not possible, then synchronization protocol (CCP) is used by broadcast. Nodes in the Check Point cluster synchronize with each other. Change messages are transmitted from node to node through multicast. Check Point has a non-standard multicast implementation (a non-multicast IP address is used). Because of this, some equipment, such as the Cisco Nexus switch, does not understand these messages and therefore blocks them. In this case, switch to broadcast.
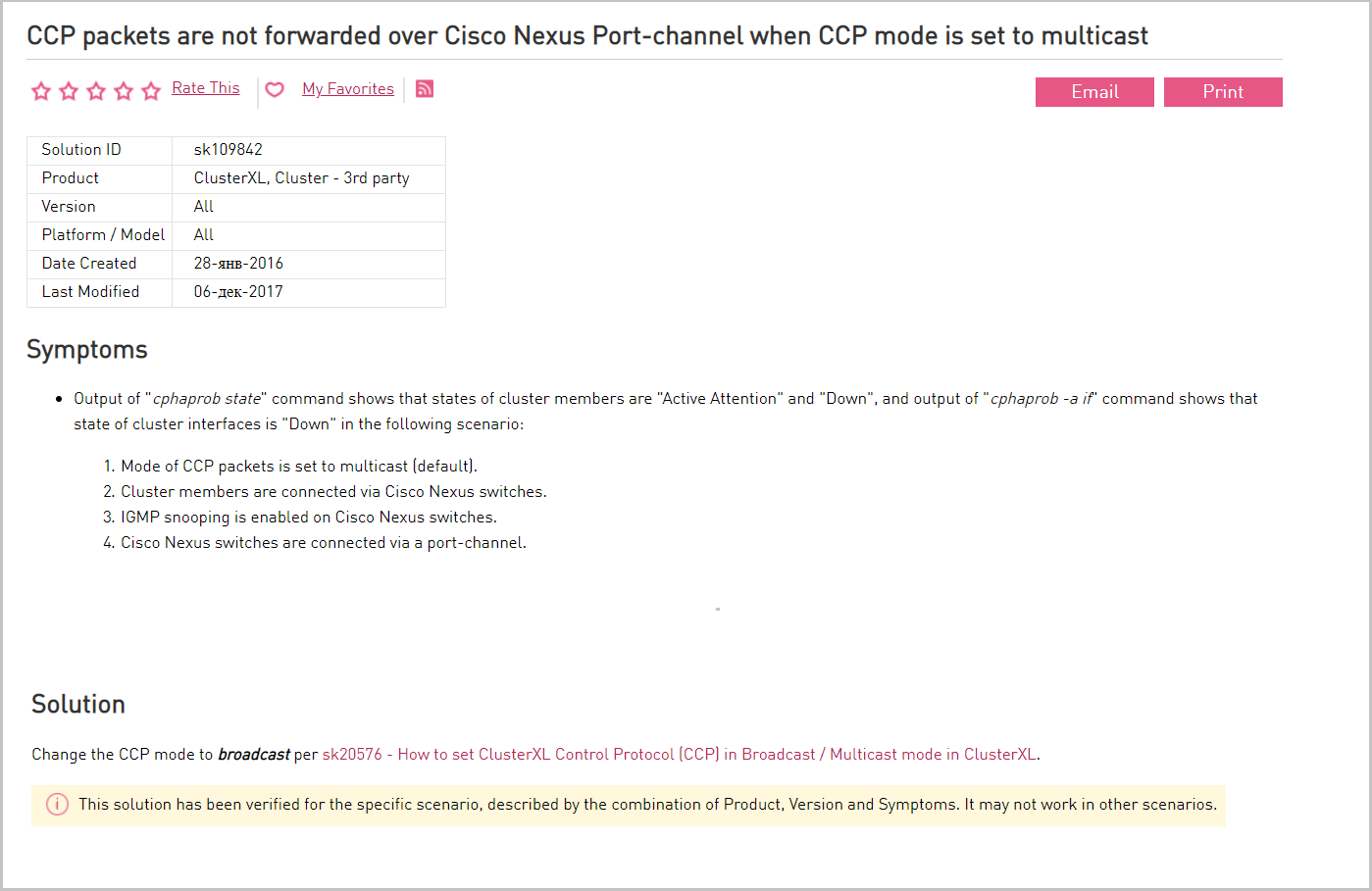
Description of the problem with Cisco Nexus and its solutions on the vendor portal.
At the level of virtualization, we also allow the passage of multicast traffic. If multicast is not allowed for cluster synchronization (CCP), then we use broadcast.
In the Check Point console with the help of the command cphaprob -a if you can see the CPP settings and its mode of operation (multicast or broadcast). To change the mode of operation, use the command cphaconf set_ccp broadcast.

Cluster nodes must reside on different ESXi hosts. Everything is clear: when the physical host drops, the second node continues to work. This can be achieved using DRS anti-affinity rules.
Sizes of the virtual machine on which Check Point will work. Recommendations vendor - 2 vCPU and 6 GB, but it is for the minimum configuration, for example, if you have a firewall running with a minimum bandwidth. According to our implementation experience, when using several software blades, it is desirable to use at least 4 vCPU, 8 GB RAM.
On the node, we allocate an average of 150 GB of disk. When deploying a virtual Check Point, the disk is divided into partitions, and we can adjust how much space to allocate for System Swap, System Root, Logs, Backup and Upgrade.
As System Root increases, the Backup and Upgrade partition also needs to be increased in order to keep the proportion between them. If the proportion is not met, then the next backup may not fit the disk.
Disk Provisioning - Thick Provision Lazy Zeroed. Check Point generates many events and logs, 1000 entries appear every second. It is better to reserve a place for them right away. To do this, when creating a virtual machine, we allocate a disk using the Thick Provisioning technology; there is a place in the physical storage at the time of the disk creation.
Configured 100% reservation resources for Check Point when migrating between ESXi hosts. We recommend that you reserve 100% of the resources so that the virtual machine to which Check Point is deployed does not compete for resources with other VMs on the host.
Other We use the Check Point version of the R77.30. It is recommended to use RedHat Enterprise Linux version 5 (64-bit) as a guest OS on a virtual machine. From network drivers - VMXNET3 or Intel E1000.
Check Point Settings
The latest Check Point updates are installed on the gateways and the management server. Check for updates via CPUSE.
With Verifier, we verify that the update package we are about to install does not conflict with the system.

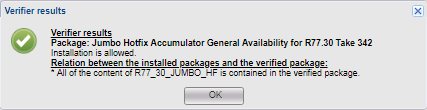
Verifier, of course, is a good thing, but there are nuances. Some updates are incompatible with add-ons, but Verifier will not show these conflicts and allow for updates. At the end of the update you will have an error, and only from it you will learn what prevents the update. For example, this situation arose with the MABDA_001 (Mobile Access Blade Deployment Agent) update package, which solves the problem of launching the Java Plugin in browsers other than IE.
Configured daily automatic update of signatures for IPS and other software blades. Check Point releases signatures that can be used to detect or block new vulnerabilities. Vulnerabilities are automatically assigned a severity level. In accordance with this level and the set filter, the system decides whether to detect or block the signature. Here it is important not to overdo the filters, periodically check and make adjustments so as not to block legitimate traffic.
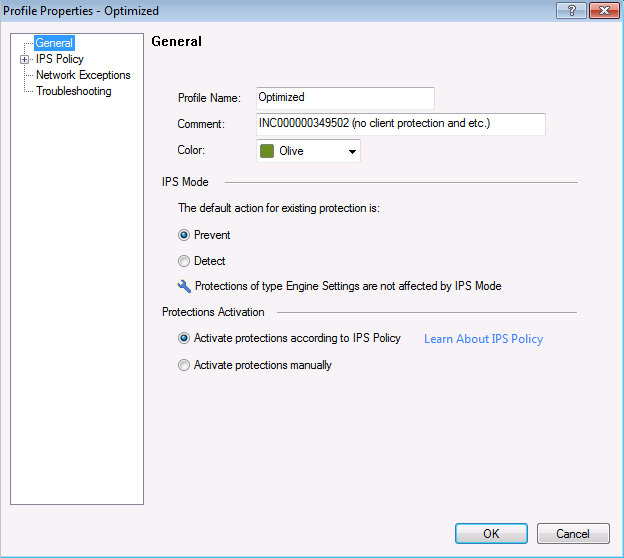
IPS profile, where we choose the action in relation to the signature in accordance with its parameters.
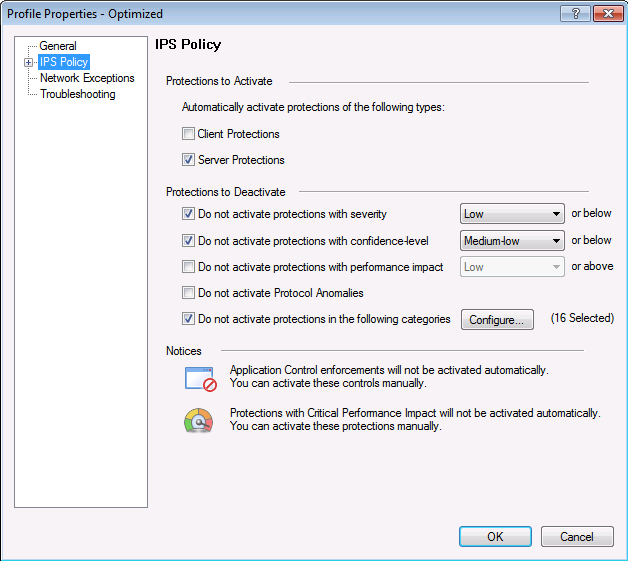
Policy settings for this IPS profile in accordance with the signature parameters: severity level, performance impact, etc.
On the Check Point hardware, the NTP time synchronization protocol is configured. As recommended , Check Point should use an external NTP server to synchronize the time on the hardware. This can be done through the gaia web portal.
Inaccurately set time can lead to a cluster out of sync. If the time is wrong, it is extremely inconvenient to look for the record of interest to us in the logs. Each entry in the event logs is marked by a so-called timestamp.
Configured Smart Event for notification of IPS, App Control, Anti-Bot, etc. operations. This is a separate module with its own license. If you have one, then with its help it is convenient to visualize information about the operation of all software blades and devices. For example, attacks, the number of IPS attacks, the level of threat criticality, which prohibited applications are used by users, etc.
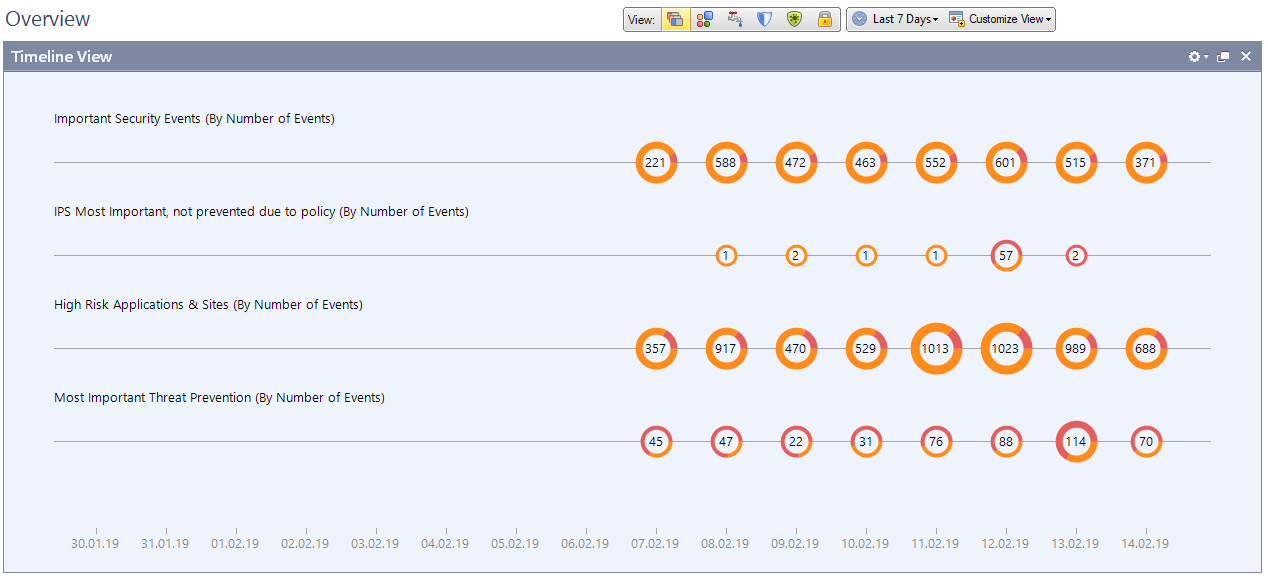
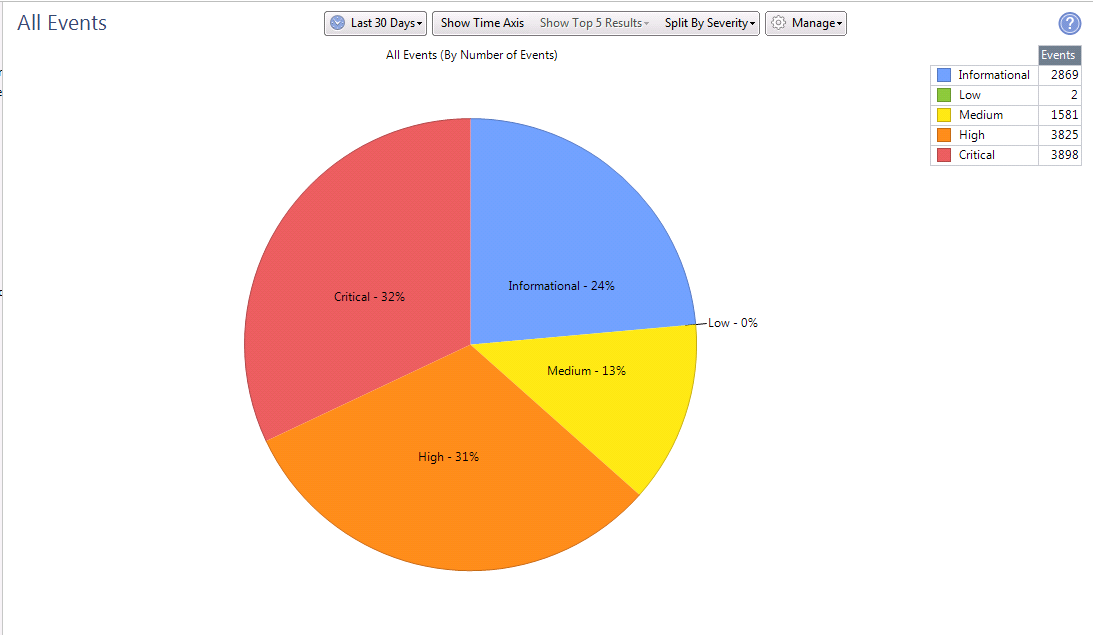
These are statistics for 30 days by the number of signatures and the degree of their criticality.
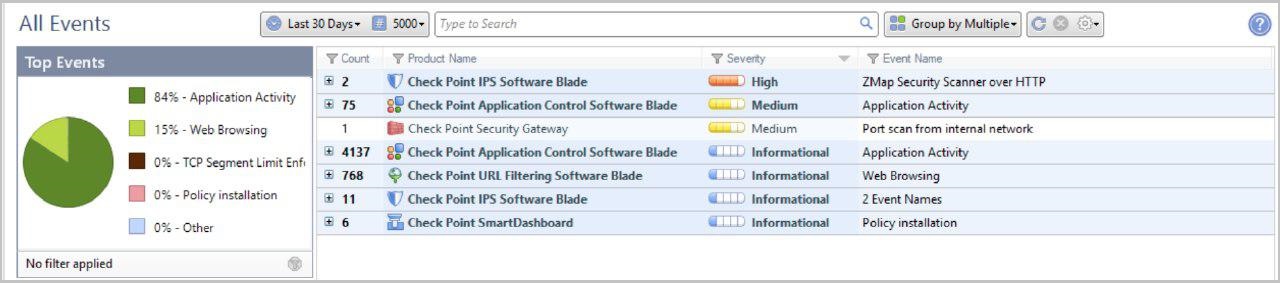
More information on detected signatures on each software blade.
Monitoring
It is important to track at least the following parameters:
- cluster status;
- availability of Check Point components;
- CPU load
- remaining disk space;
- free memory.
Check Point has a separate software blade - Smart Monitoring (separate license). It can additionally monitor the availability of Check Point components, loads on individual blades, license status.
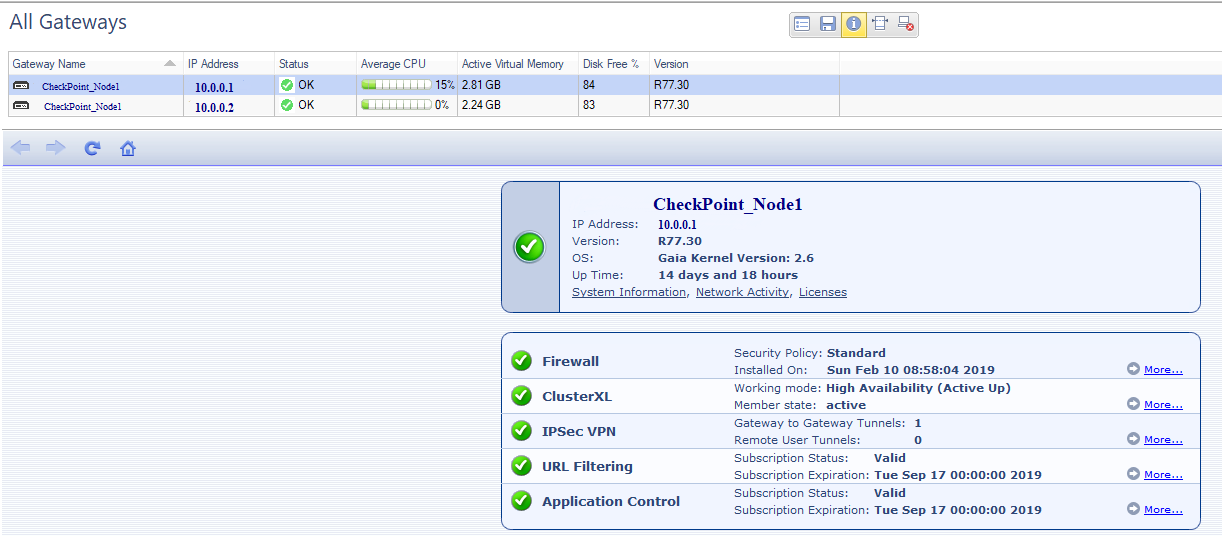
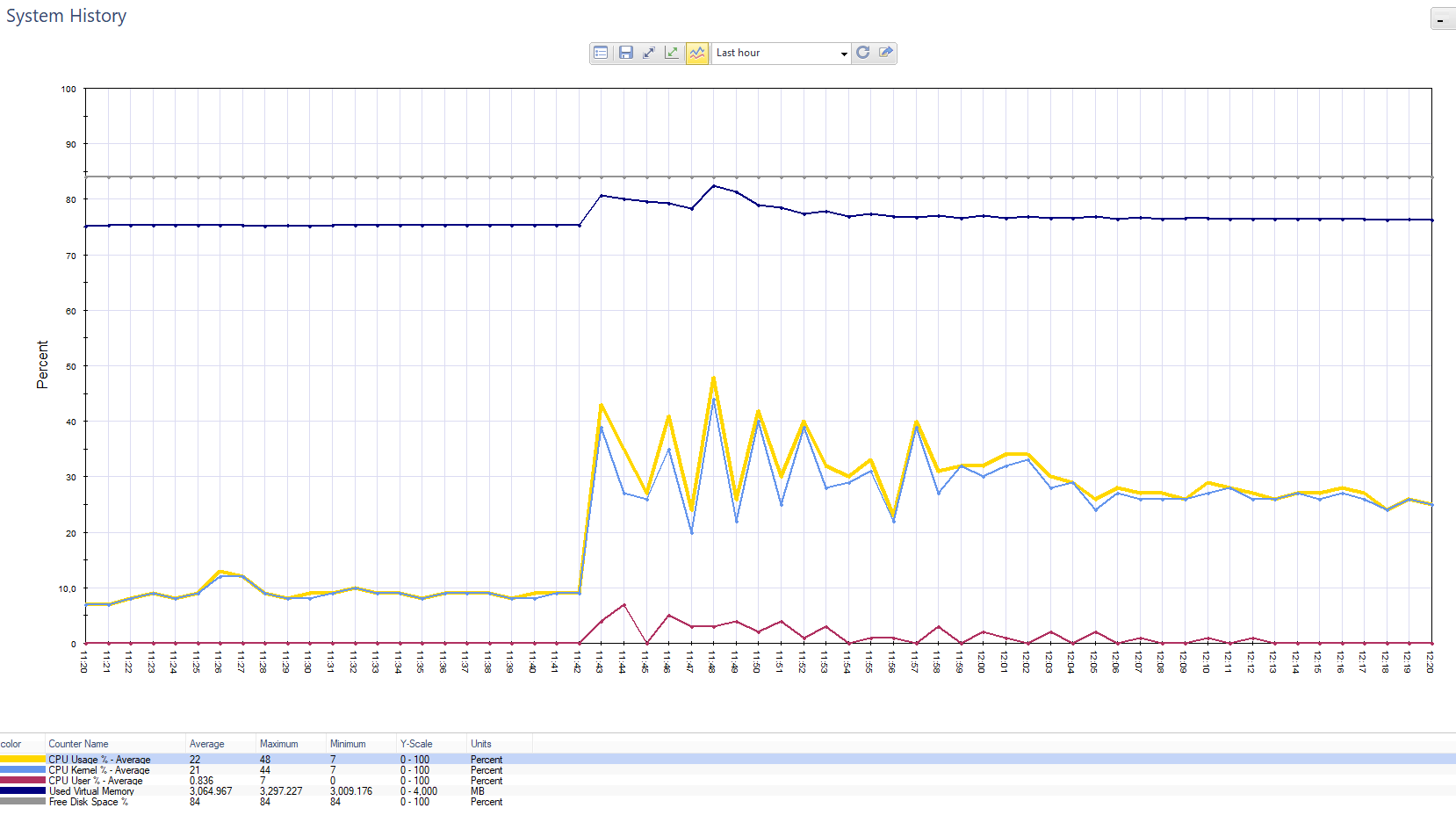
Schedule for load on Chek Point. Splash - this customer sent push-notifications to 800 thousand customers.

The graph for the load on the Firewall blade in the same situation.
Monitoring can be configured through third-party services. We, for example, also use Nagios, where we monitor:
- network availability of equipment;
- availability of a cluster address;
- CPU load by cores When loading more than 70% comes an alert in the mail. Such a high load may indicate specific traffic (vpn, for example). If this is often repeated, then perhaps there are not enough resources and it is worth expanding the pool.
- free RAM If less than 80% remains, then we will find out.
- disk loading on certain partitions, for example var / log. If it scores soon, it must be expanded.
- Split Brain (at the cluster level). We track the state when both nodes become active and synchronization between them disappears.
- High availability mode - we monitor that the cluster is operating in active-standby mode. We look at the status of the node - active, standby, down.
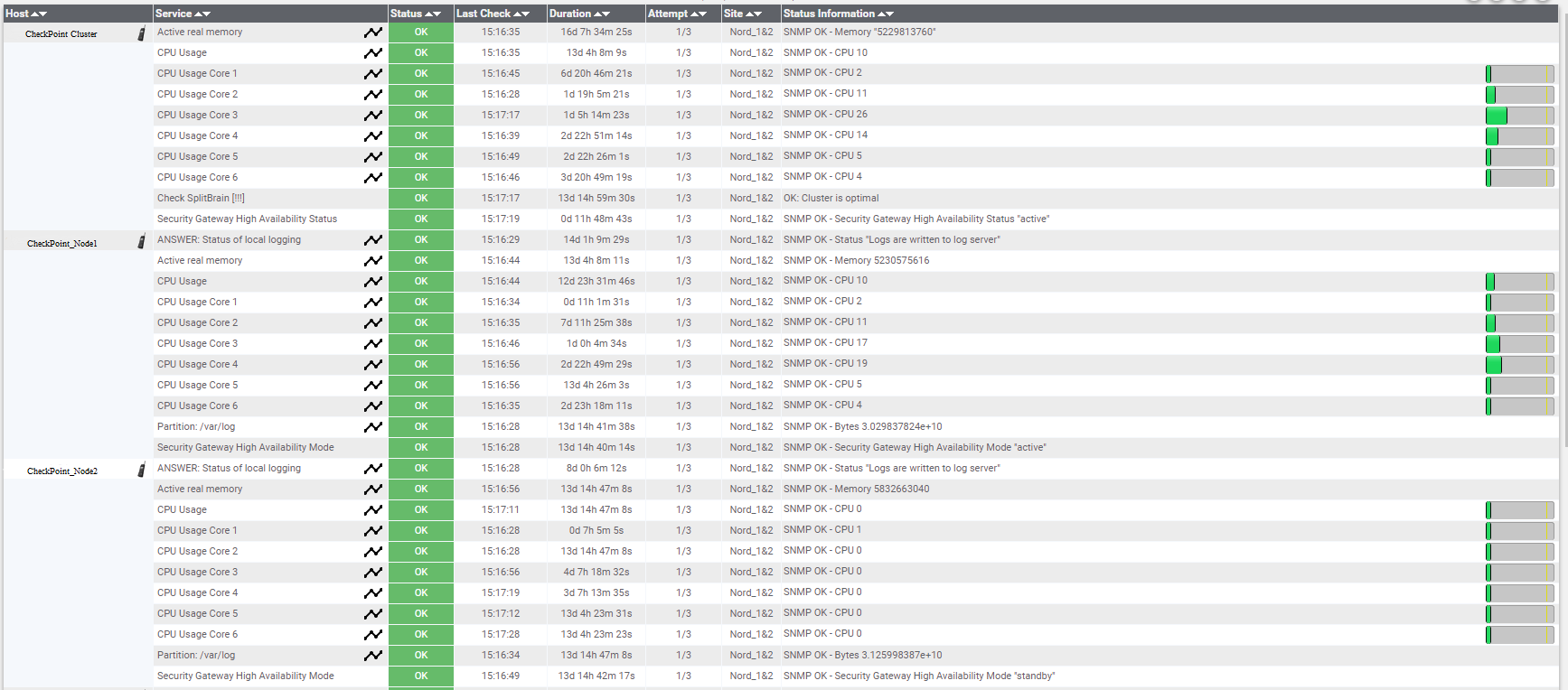
Monitoring options in Nagios.
It is also worth monitoring the status of the physical servers on which ESXi hosts are deployed.
Backup
The vendor himself recommends making a snapshot immediately after installing the update (Hotfixies).
Depending on the frequency of changes, a full backup is set once a week or a month. In our practice, we do daily incremental copying of Check Point files and a full backup once a week.
That's all. These were the most basic points that need to be taken into account when deploying virtual Check Points. But even the implementation of this minimum will help avoid problems with their work.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/442880/
All Articles