What shines Crew Dragon Roscosmos
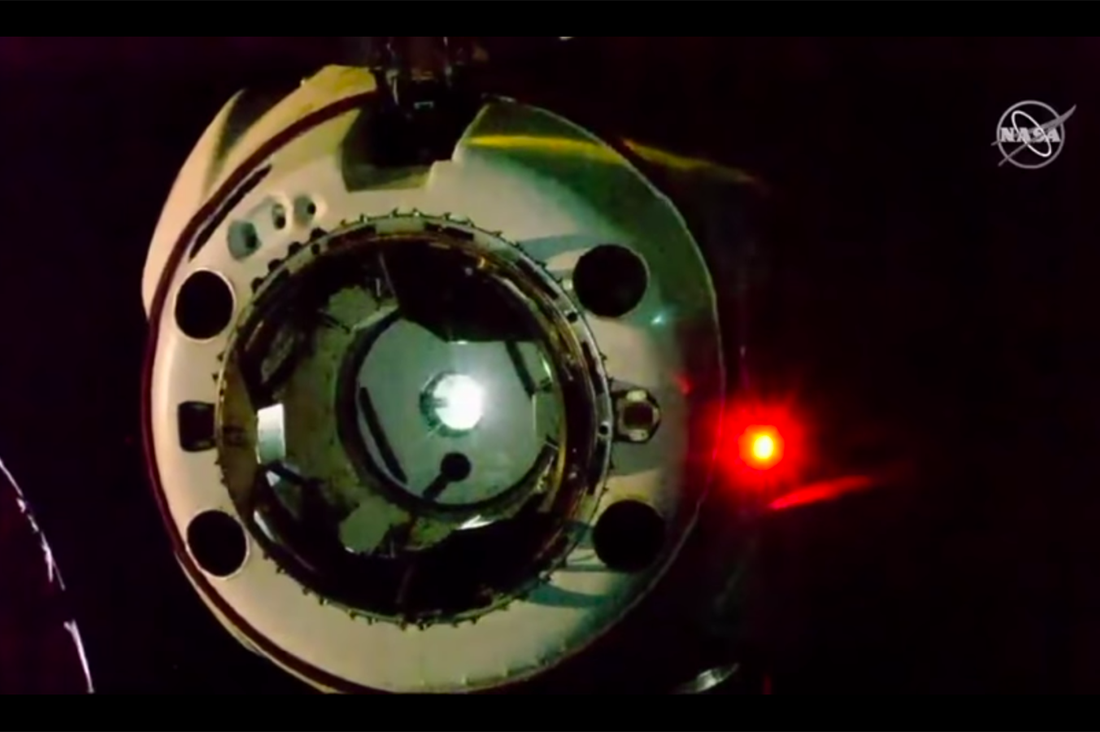
The unmanned spacecraft Crew Dragon docked to the International Space Station after a daily flight. So far, only the Ripley mannequin and 180 kg of cargo have arrived on the ship, but if the tests are successful, the first astronauts should go there in six months. Today's success is very important for the United States, but it will also have a significant impact on the Russian space program.

After launch and docking, the next important phase of the flight - landing - is expected in five days. A few weeks later, a new launch for testing an emergency landing system during a rocket flight in the atmosphere. And only then the spacecraft will receive a safety certificate and the first crew. When a manned Dragon flight becomes a reality, it will mean that the United States has regained its ability to fly into space from its territory, which they have not had since 2011. Then the Space Shuttle program ended and Roskosmos took over the delivery of all international crews.
')
The Russian "Unions" from 2011 to the present fly not only on the feeling of mutual assistance and cooperation, but also generously funded by the American side. Under the ISS program, NASA pays for American, Canadian, European, and Japanese astronauts. In general, the flights of the Americans on the Russian Soyuz ships began as early as the 1990s, but then they were exchange flights — instead, Russian cosmonauts flew shuttles. Since 2006, paid expeditions began. Since then, seven dozen people have flown.
At first, the price tag for astronauts on the Soyuz began with a moderate $ 25 million per seat — a bit more expensive than the first tourists' tickets. However, the program of astronauts differs significantly from entertainment: they need to work, i.e. preparation is complicated, and the duration of the expedition is not 10 days, but six months. Yes, and money from NASA was clearly more than private traders. After the final flight of the Space Shuttle, “tickets” to Russian ships were constantly becoming more expensive. By 2018, the price for an astronaut reached $ 82 million. For example, the cost of the Soyuz rocket and the Soyuz-MS three-seater is about $ 70 million, i.e. one astronaut more than paid for the flight for the entire crew.
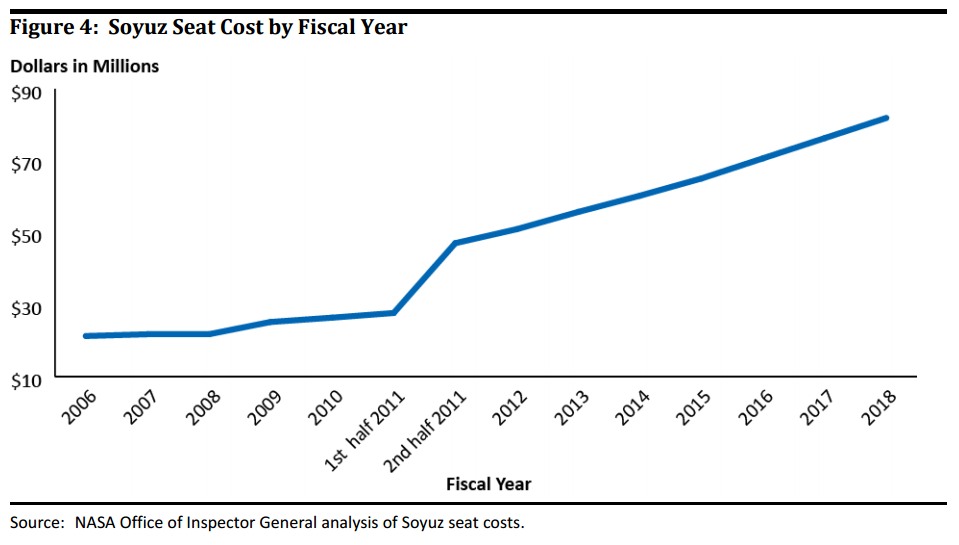
On average, after 2011, Roskosmos earned $ 300–400 million per year on the “izvoz” to the ISS. Considering that the total amount of state funding of Roscosmos (the Federal Space Program, defense order, federal targeted programs) is about $ 3-4 billion a year, it turns out that about 10% of the total funding of Russian cosmonautics was provided by the American manned cosmonautics.
Accordingly, if the flow of American “alliance dollars” dries up, then Roskosmos will face a choice - to keep the former production volumes of manned ships at a loss or to reduce the series. It is not planned to increase the Russian crew until the launch of the MLM Nauka module, and without this module there won't be much practical sense in them. And there are doubts that he will fly at all and will be used regularly. Therefore, the Roscosmos sees the solution in short-term flights of all comers who can pay for the flight.
The first group of clients has already been found - a detachment of astronauts from the United Arab Emirates (the cost of their tickets has not been disclosed). The second source of paying passengers is tourism. Recently, the idea of launching manned spacecraft "along the Gagarin route", i.e. without docking with the ISS and the duration of tens of minutes or a few hours. From the point of view of science, such flights will be practically useless; at best, they are suitable for some student projects and cosmonaut training. From a practical point of view, this is simply a program for the preservation of jobs at RSC Energia and RCC Progress, which are launching Soyuz ships and missiles.

A travel ticket is likely to be cheaper than for NASA, because the flight to the ISS will last no more than 10 days, and the flight without docking is even less. One of the pilots of the spacecraft will always be a professional astronaut, i.e. for one round, it will turn out to bring no more than two “vacationers”, this gives the lower bar of the price - not less than $ 35 million, any discount will be at the expense of Russian taxpayers. The ten-day tourist flight to the ISS in 2015 was estimated at $ 55 million, which is also lower than NASA payments.
There are also organizational problems with tourist visits to the ISS: since the ships fly once every 4 months, the tourist can only be brought by one ship and returned to Earth by another, at this time the astronaut who lost the seat remains at the station until the next flight. So more than two tourists a year to live at the station will not take.
It turns out that even if Roskosmos finds new passengers for all future Unions, it is waiting for funding cuts by 5%, if it does not, then by 10%. Reducing the number of launched "Unions" will lead to an increase in their cost for the state budget due to overhead costs.
The Roscosmos problem is that Ilon Musk will be able to compete in space tourism, launching those who want along the “John Glenn's route”, i.e. making short-term flights without docking with the ISS. Now for NASA, the launch of one manned four-seater Dragon is estimated at $ 405 million. If we compare the difference between the commercial value of rockets ($ 62 million) and launches in the interests of NASA ($ 89-99 million), the commercial launch price of Dragon can be about $ 250 million. in the seven-seater version and without a professional “driver”, the price per flight is close to the same $ 35 million. Using reusable Falcon 9 steps and inhabited Dragon compartments may promise a price reduction, so Roscosmos can give way to SpaceX.
However, piloted astronautics, with rare exceptions, is a deliberately unprofitable activity, therefore, to the detriment of finances, Roskosmos can save face and previous production volumes by returning the practice of exchange flights. So our cosmonauts will get experience of flying on Dragon SpaceX and Starliner Boeing, and our officials according to the old tradition will be able to publicly emphasize "Americans cannot do without us." The truth is, there is a danger of the “Tesla effect” when motorists ride on Tesla electric cars lose interest in driving gasoline cars.
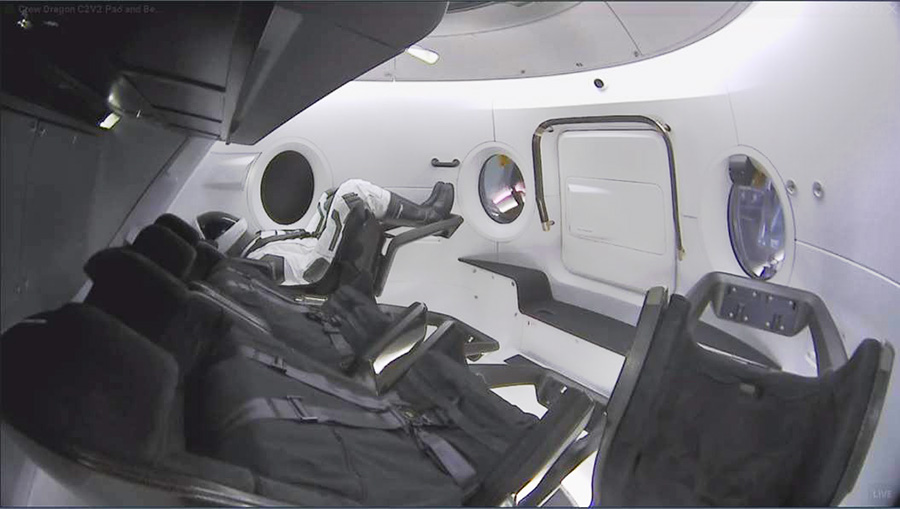

In general, the success of SpaceX can be welcomed, the world is indeed entering a new era of manned flights, but this promises nothing good for the current leader.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/442484/
All Articles