5 mistakes to avoid when creating 3D models for 3D printing

It is known that the process of modeling for additive production is not always simple: in 3D modeling, as in 3D printing, there is no one right solution. We use different software, we print from different materials and we use different 3D-printers and additive technologies. Therefore, it is not unusual that users sometimes feel confused, and creating the perfect 3D model for 3D printing is not as easy as it sounds. That is why we have compiled this list of errors that should be avoided by creating a 3D model for manufacturing using additive methods.
1. Do not take into account the features of the material
Each material for 3D printing has its own characteristics. Materials are fragile or strong, flexible or rigid, smooth or rough, heavy or light, and so on. This means that, ideally, the product should be modeled for a specific material. For example, if we are going to print a 3D model of steel, we must follow certain modeling-related recommendations for modeling, which include creating supports for overhanging parts, strengthening protruding elements of the product, rounding corners, etc.
The choice of print material predetermines some of the basic principles of modeling that must be adhered to.

')
2. Disregard 3D printing technology
Not only the basic chemical properties of materials for 3D printing differ, but also the technologies used for manufacturing using each of the materials. Interconnecting parts are a good example. Materials such as ABS, polyamide, aluminum or rubber-like materials are suitable for printing interconnecting parts, while gold, silver, bronze or photopolymer resin are not suitable for this. The reason is not in the material itself, but in 3D printing technology .
For example, polyamide, aluminum and rubber-like materials are used in selective laser sintering (using powder); precious metals are used in investment casting (using wax 3D models and molds), and photopolymers in stereolithography .
This may seem strange, but it is important to remember: it cannot be assumed that stainless steel and silver have similar features in 3D printing only because both are metals. For 3D printing, these metals use different technologies, and therefore, inevitable differences in the design features of the models. Materials that are compatible with the same technology, such as gold, silver, bronze and brass ( casting ), are more likely to have similar design requirements for the model.
In addition, it should be borne in mind that the maximum size of the printed model also depends on the 3D printer used and the 3D printing technology.
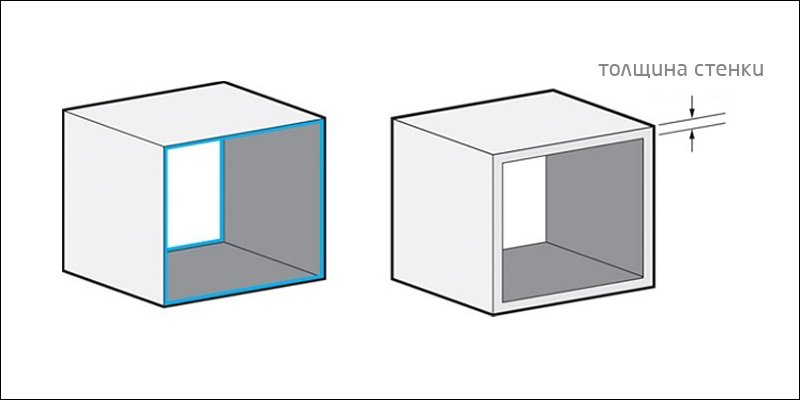
Proper selection of wall thickness is crucial for successful 3D printing.
3. Disregard wall thickness
The problems associated with wall thickness are by far the most common reason why 3D models cannot print. In some cases, the wall thickness is excessively small. Too thin walls make it impossible to print small elements of the model or make them too fragile. Too thick walls, on the contrary, create excessive internal stresses that can lead to the formation of cracks or even to the destruction of the model.
4. Disregard file resolution
Do you know the features of the material? Wall thickness selected right? Perfectly! But now you need to take into account something else: the resolution of the file. The most common format in 3D printing is STL. This means that your model will be represented in three-dimensional space as a set of triangles. In most 3D modeling programs , it is possible to export a project to an STL file and set the desired resolution. Too low or too high resolution can cause problems.
Low-resolution STL file: it is important to understand that the exported file of unsatisfactory quality will not allow printing a high-quality product. Low resolution means that the triangles in the STL file are too large and the surface of the printed model will not be smooth. The product will be a little "mosaic".
The STL file is too high resolution: if the file resolution is too high, it will be too large and in some cases you will not be able to process it. It may also have a too high level of detail that the 3D printer simply cannot reproduce.
In most 3D modeling programs, it is proposed to specify a tolerance when exporting a file. Tolerance is defined as the maximum distance between the original form and the STL mesh exported. We recommend setting 0.01 mm to get a quality STL file. Export with a tolerance of less than 0.01 mm does not make sense, since 3D printers are not yet able to print with such a high level of detail. When exporting with a tolerance of more than 0.01 mm, there is a risk that triangles will be visible in the product.

Choosing the correct file resolution is crucial to get a good quality product. The photo clearly shows the different resolutions - from high (left) to low (right)
5. Disregard software recommendations.
There are many different software products for 3D modeling. Some of them are designed to create models for subsequent 3D printing, others are used mainly by 3D designers, whose models require additional editing before obtaining a model for 3D printing. So, in some programs, the wall thickness is set automatically, while in others it must be specified manually.
Even if you are using software for beginners designed exclusively for 3D printing (for example, Tinkercad), creating a hollow model may not be so easy. In the case of software products such as Blender (used for 3D graphics and animation), SketchUp (popular among architects and fans of large-scale modeling) or ZBrush (modeling software popular among 3D designers), additional file preparation is required.
Materialise Magics offers the most complete set of functions - a comprehensive, innovative solution for preparing data for 3D printing for professionals in additive manufacturing. This software allows you to edit and create separate layers of components based on three-dimensional data from CAD or data obtained using 3D scanning. Magics provides a full cycle of additive manufacturing - from data import (in STL and other formats) and quality analysis to support creation, platform preparation and post-processing.
Briefly: how to create 3D models for printing
Do not worry: in reality everything is simpler than it seems. Just make sure you know the software well and the material selected. If you are experiencing difficulties trying to master 3D modeling, you can always contact our specialists for help. If you created a 3D model and want to print it, contact the iQB Technologies RP Center. We will check your model and, if it contains errors, correct them and print a quality product.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/442270/
All Articles