Can digital medicine resist hackers
The introduction of digital technologies in medicine offers great promise, allowing to significantly improve the quality of treatment and fundamentally change the approach to the early diagnosis of dangerous diseases. It is not surprising, therefore, that today in the most technologically advanced medical institutions there are up to 12 digital devices per bed. At the same time, when connected to a computer network, medgadgets are turned into convenient objects for cyber attacks because of the many vulnerabilities in the embedded software. Let us figure out what the organizers of these attacks need and how to defend against them?
Why attackers need medical data
The mere fact of the existence of a vulnerability is not enough to become an object of attack. For the attack criminals need a clear motivation. Today, the main driving force of cybercrime is money . Data from medical information systems are of particular value because they contain sensitive information about people's health, as well as complete personal, financial, and possibly biometric data. Criminals can resell them or use them for their own purposes, for example, open a bank account in order to cash out funds or arrange a loan for a patient.
')
Another reason for cyber attacks on health is attacks on public reputations. Publication of medical information about famous people can compromise them and lead to the collapse of a public or sports career. In 2016, hackers broke into the base of the World Anti-Doping Agency and published information about the athletes who used the illicit drugs "for medical reasons" under the heading "License for doping." Despite the fact that the athletes formally did not break anything, this greatly affected their reputation among the fans.
The threat of publishing intimate or mental health information stolen from medical databases can be a leverage for blackmailers and extortionists (that is, money is in the game again). And in case they manage to intercept the management of medical implants, then the life and health of patients may be at stake. And this is a violent crime or even an act of terrorism.
There are other reasons for attacks on medical institutions, such as the revenge of disgruntled employees and industrial espionage. Access to the results of new drug trials on patients can save competing companies time and huge amounts of money to conduct similar studies.
Where our data is stored in digital health conditions
In the short term, the development of digital medicine involves the widespread introduction of electronic medical cards, the development of the “connected patient” concept - monitoring the condition of patients using IoT implants - and the extensive use of telemedicine.
The storage of medical information in the Russian Federation is regulated by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 05.05.2018 No. 555 “On the unified state information system in the field of health care” . In accordance with the document, personalized integrated electronic medical records (IEMCs) will be maintained and stored in the medical information systems of medical organizations (IIA MO), and in the same name EGISZ subsystem this data will be kept in anonymized form.
For the exchange of information of the medical organization IEMC subsystem with external systems, the Electronic Medical Record Register (SEMD) will be used - the subsystem that is part of EGISZ.
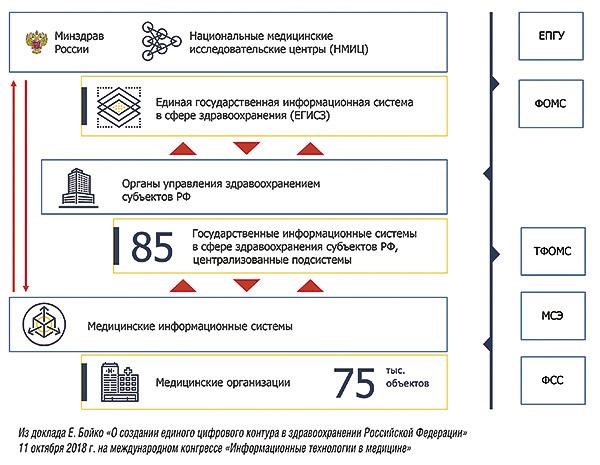
Source: Elena Boyko's report “On the creation of a single digital circuit in the health care system of the Russian Federation” at the international congress “Information technologies in medicine” 11.09.2018. Currently, Elena Boyko is the Deputy Minister of Health of the Russian Federation and is responsible for the digitization of the medical industry in the country.
In fact, this means that the responsibility for the safety of medical data is transferred from the federal to the regional level, and each hospital will decide the issues of protection against cyber attacks on its own information systems.
Basic cyber threats of digital medicine
Health care in Russia and around the world has a complex organizational structure. This provides attackers with a significant number of vectors for penetrating medical information systems:
While implant cracking and seizure of control for extortion and harm to the patient’s health has not been used in practice - cybersecurity experts only warn about the possibility of this and filmmakers shoot SciFi films, but the vulnerabilities of hospital networks have already caused financial and reputational damage.
Thus, in spring 2017, the UK National Health Service (NHS) reported that 16 medical facilities from London, Nottingham, Cumbria, Hertfordshire, Derbyshire, Blackpool and Blackburn were victims of the extortionist WannaCry . In January 2018, the SamSam encryption company penetrated the networks of several US hospitals through compromised web servers. As a result of this attack, extortionists received more than 300 thousand dollars for decrypting data. In either case, the hospitals were not the main victims of the attack, but rather were hit by carpet bombing.
It is much more important that if the attackers set a goal to attack the medical infrastructure, they can inflict enormous damage on it, on its operators and owners, and, most importantly, on the patients. Here is an example: the thousands of climate control systems produced by Resource Data Management, which are used in many hospitals around the world, have proven vulnerable to remote cyber attacks . Hypothetically, attackers can change the temperature regime of medical refrigerators and destroy the stored blood supplies, donor organs and vaccines.
Recommendations for protection against cyber attacks
Given the critical nature of the effects of cyber attacks on hospitals, the organization of protection should be approached systematically, turning information security into an integral part of the treatment process.
Based on health facility safety research, Trend Micro, for example, developed the following guidelines for ensuring information security in the health sector :

Why attackers need medical data
The mere fact of the existence of a vulnerability is not enough to become an object of attack. For the attack criminals need a clear motivation. Today, the main driving force of cybercrime is money . Data from medical information systems are of particular value because they contain sensitive information about people's health, as well as complete personal, financial, and possibly biometric data. Criminals can resell them or use them for their own purposes, for example, open a bank account in order to cash out funds or arrange a loan for a patient.
')
Another reason for cyber attacks on health is attacks on public reputations. Publication of medical information about famous people can compromise them and lead to the collapse of a public or sports career. In 2016, hackers broke into the base of the World Anti-Doping Agency and published information about the athletes who used the illicit drugs "for medical reasons" under the heading "License for doping." Despite the fact that the athletes formally did not break anything, this greatly affected their reputation among the fans.
The threat of publishing intimate or mental health information stolen from medical databases can be a leverage for blackmailers and extortionists (that is, money is in the game again). And in case they manage to intercept the management of medical implants, then the life and health of patients may be at stake. And this is a violent crime or even an act of terrorism.
There are other reasons for attacks on medical institutions, such as the revenge of disgruntled employees and industrial espionage. Access to the results of new drug trials on patients can save competing companies time and huge amounts of money to conduct similar studies.
Where our data is stored in digital health conditions
In the short term, the development of digital medicine involves the widespread introduction of electronic medical cards, the development of the “connected patient” concept - monitoring the condition of patients using IoT implants - and the extensive use of telemedicine.
The storage of medical information in the Russian Federation is regulated by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 05.05.2018 No. 555 “On the unified state information system in the field of health care” . In accordance with the document, personalized integrated electronic medical records (IEMCs) will be maintained and stored in the medical information systems of medical organizations (IIA MO), and in the same name EGISZ subsystem this data will be kept in anonymized form.
For the exchange of information of the medical organization IEMC subsystem with external systems, the Electronic Medical Record Register (SEMD) will be used - the subsystem that is part of EGISZ.

Source: Elena Boyko's report “On the creation of a single digital circuit in the health care system of the Russian Federation” at the international congress “Information technologies in medicine” 11.09.2018. Currently, Elena Boyko is the Deputy Minister of Health of the Russian Federation and is responsible for the digitization of the medical industry in the country.
In fact, this means that the responsibility for the safety of medical data is transferred from the federal to the regional level, and each hospital will decide the issues of protection against cyber attacks on its own information systems.
Basic cyber threats of digital medicine
Health care in Russia and around the world has a complex organizational structure. This provides attackers with a significant number of vectors for penetrating medical information systems:
- phishing attacks, including targeted;
- DDoS attacks;
- network attacks on vulnerable software;
- malware — extortionists, spyware, worms, trojans and other malware;
- equipment firmware vulnerabilities, including wearable medical devices and implants, such as infusion pumps , brain implants and pacemakers ;
- compromise of mobile medical applications;
- the compromise of public web servers and their subsequent use to infiltrate the hospital network;
- insider attacks by hospital staff and service companies;
- attacks on infrastructure, for example, on the cooling system.
While implant cracking and seizure of control for extortion and harm to the patient’s health has not been used in practice - cybersecurity experts only warn about the possibility of this and filmmakers shoot SciFi films, but the vulnerabilities of hospital networks have already caused financial and reputational damage.
Thus, in spring 2017, the UK National Health Service (NHS) reported that 16 medical facilities from London, Nottingham, Cumbria, Hertfordshire, Derbyshire, Blackpool and Blackburn were victims of the extortionist WannaCry . In January 2018, the SamSam encryption company penetrated the networks of several US hospitals through compromised web servers. As a result of this attack, extortionists received more than 300 thousand dollars for decrypting data. In either case, the hospitals were not the main victims of the attack, but rather were hit by carpet bombing.
It is much more important that if the attackers set a goal to attack the medical infrastructure, they can inflict enormous damage on it, on its operators and owners, and, most importantly, on the patients. Here is an example: the thousands of climate control systems produced by Resource Data Management, which are used in many hospitals around the world, have proven vulnerable to remote cyber attacks . Hypothetically, attackers can change the temperature regime of medical refrigerators and destroy the stored blood supplies, donor organs and vaccines.
Recommendations for protection against cyber attacks
Given the critical nature of the effects of cyber attacks on hospitals, the organization of protection should be approached systematically, turning information security into an integral part of the treatment process.
Based on health facility safety research, Trend Micro, for example, developed the following guidelines for ensuring information security in the health sector :
- Separate network segments. Allocating medical devices in a separate segment from the hospital network will protect this part of the hospital infrastructure from a significant part of cyber attacks.
- Use firewalls, ideally - UTM systems - new generation firewalls that combine the functionality of the firewall itself, intrusion prevention and detection systems, antivirus, filtering web traffic and application control.
- Implement an email protection system against malware and phishing emails.
- Use the vulnerability scanner network equipment, operating systems and software. Allows you to identify existing network vulnerabilities before they can take advantage of attackers.
- Upgrade your operating system and hardware firmware in a timely manner. This will fix the detected errors in the software and provide protection against hacking. Develop a plan for installing updates and follow it.
- Explore the safety of new medical devices. This will reduce the risk that the device will become a springboard for breaking into the hospital.
- Perform a hospital penetration testing network to identify and eliminate all weaknesses.
- Back up your important data. In the event of a cipher attack, the ability to quickly recover the necessary information can be of immense benefit.
- Share information about attacks and threats . The better this exchange is organized, the sooner the attack can be eliminated and the less people will suffer from its consequences.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/441908/
All Articles