Everything (Well, almost) about video cards. Part 1
Recently I came across the fact that there is not much information about video cards.
Well, more precisely, it is, and it is enough, for example, today you can :
But at the same time, this information is scattered across various sources, and it seems to me that it would not hurt to systematize it a little in just two articles.
In the first part I will try to give basic knowledge, in the second there will be a slightly more in-depth level.
')
I will try to touch on various topics related to video cards, in particular - what it is , why it is needed , what it consists of, characteristics and applications in computing

Part 1 : What is a video card? Why is it needed? What is it made of?
Part 2: Characteristics and application of video cards in computing
PS I will attach the link to part 2 as soon as it is
Go:
A video card is a device that converts an image stored in a computer's memory into a video signal for a monitor.
A video card in different sources can be named like: graphics accelerator, graphics card, video adapter, 3D accelerator, GPU and other similar terms. All these are different names for the same device, which is very important in a modern computer.
Why a 3D accelerator or why a graphics accelerator ? Why "important in a modern computer" ? Where is this all from? More on this later
And now look - video cards are divided into 3 types:
In order :
Integrated video cards: These are video chips integrated into the processor core (CPU), (reside on a processor chip) or, less commonly, embedded into the motherboard (as a rule, they are on their own, but generally can be located under a chip called the " north bridge ". video cards give poor performance for those who want good graphics performance.
After all, integrated solutions for this are not calculated and are used in, for example, office computers (or laptops), where it is assumed that there will not be strong loads on the video chip.
The problem of integrated video cards is that they do not have their own random access memory (RAM), and they use the computer’s single RAM together with the processor, while the signal transmission goes through the same system bus - both of which, in fact, greatly hinder the operation .
The integrated video card goes instead of with all the other components on the board, since, obviously, it is located on this board
Example 1:

Example 2:

Example 3:
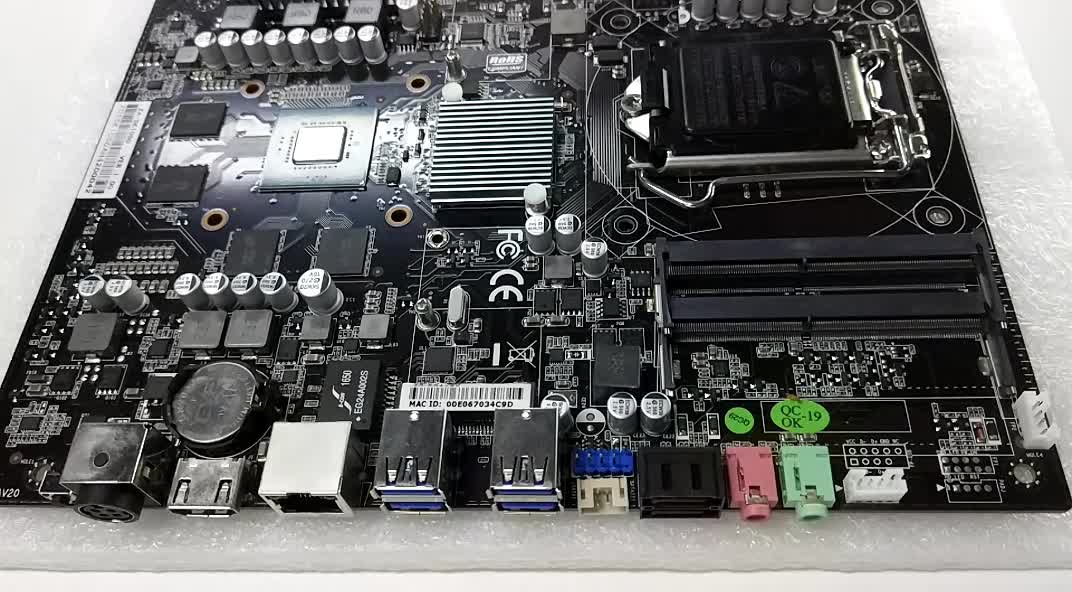
Discrete video cards: This is just an option for those who just need good graphics performance.
Discrete video cards differ in their computing power in comparison with integrated video adapters, since I have my own memory - therefore there is no need to climb and take a couple of computer memory with a processor, although a discrete video card also knows how
The discrete card is not integrated into the motherboard, but is located separately, being independent (wanted-pulled out and carried with itself) and connecting to the system data bus using expansion cards (in other words, slots ), which
View all images
used to connect external devices (aka adapters or controllers of these connected devices)
Speaking of slots , I mean :

The discrete map is obviously different from the integrated one and looks like this:
Example 1:

Example 2:
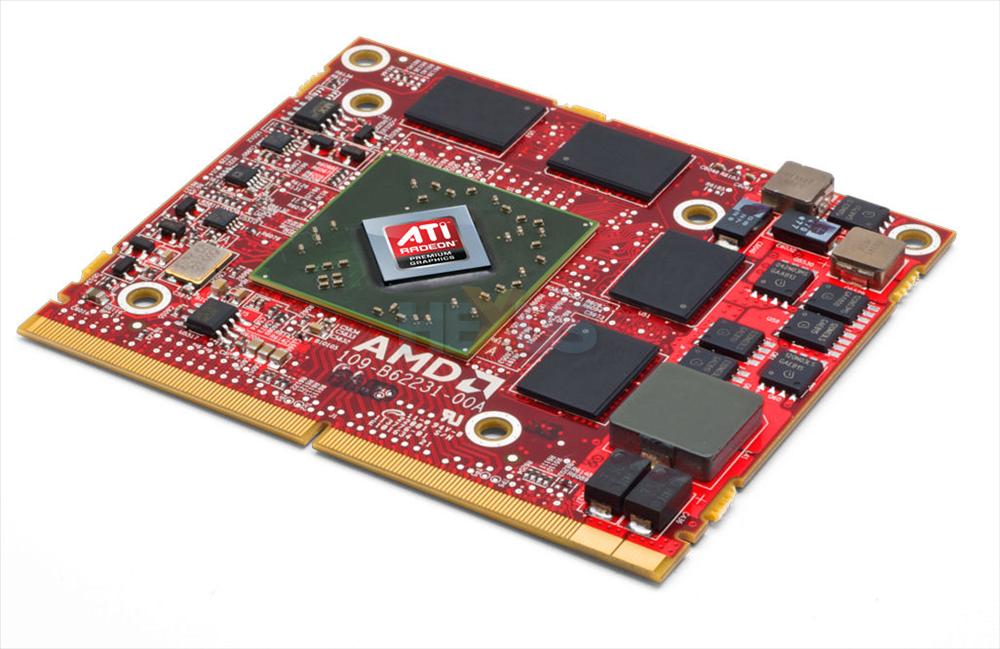

Example 3:

Example 4:

As you can see, discrete cards, unlike integrated ones, are not an integral part of the board and are made as a separate chip.
Hybrid solutions: This option (well, or this solution) implies in itself, as, actually, it is clear from the name - the combination of an integrated video card and a discrete one (only the work does not take place simultaneously, but in turn, while resources requiring large computing powers are given discretely, and Smaller - weak, integrated video card (there should be a switch - should )
And in this case, the video card (just usually they mean discrete) can be considered a graphics accelerator, a 3D accelerator, because the speed of work increases noticeably, and with the passage of games there are fewer problems.
It is for its computing power that a discrete card plays the role of a very important component in a modern computer.
If you do not plan to heavily load your computer (or laptop), for example, you just need to sit on the Internet, run light games, sometimes program, using editors, and maybe even IDE, edit tables - then you can take a computer (or laptop) with an integrated video card - they are cheaper than discrete ones, and, you see, it is reasonable if you do not overpay for opportunities that will not be used.
The disadvantages can be attributed to the fact that if for some reason your video chip fails, it will be painful, since it is already in the processor, which is quite problematic
If you want to get high power from a computer, because you need, for example, to play new games, freely watch videos in the best quality, render videos and a whole lot more that warms up your “machine” well, then you should definitely take a discrete video card, let it cost you more.
In the event of a chip failure on a discrete card, since a discrete card is pulled out as freely as it is inserted - it can be re-soldered or replaced, initially, of course, taking out this video card (you shouldn’t warm it up, I think this is nonsense and then it will only get worse)
An integrated video card uses the same resources as other components on this board, but with a discrete card, things are more interesting, it has its own components.
Who cares,in the context of it looks like this:
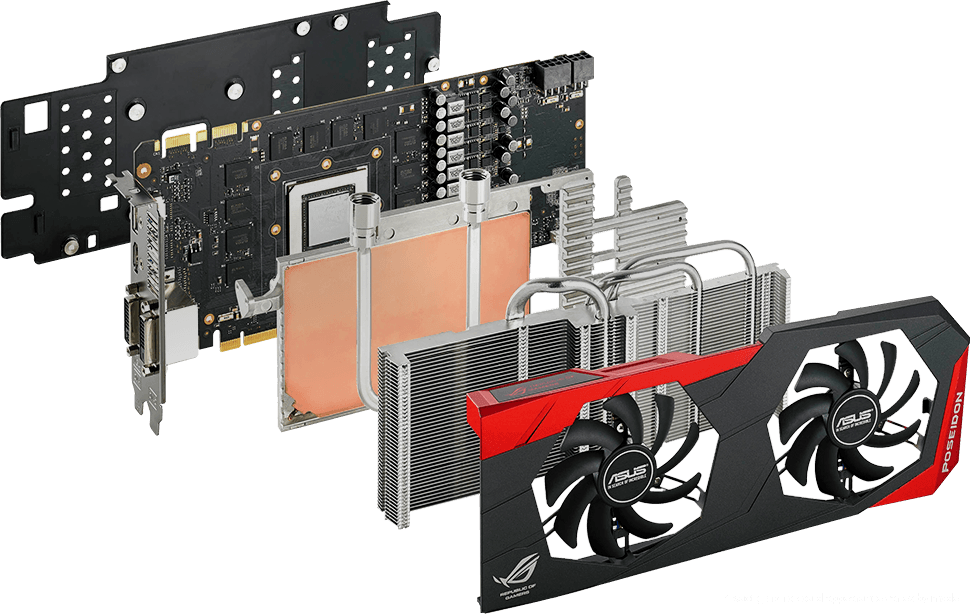

Let's look at the external (discrete) card again:

Modern discrete graphics card consists of the following parts:
1. Graphic processor
The graphics processor (well, or the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) - a graphics processor unit) is engaged in the calculations of the displayed image , relieving the central processor of this responsibility, and makes calculations for processing 3D graphics commands. It is the basis of the graphics card , it depends on it the speed and capabilities of the entire device.
Modern graphics processors are not inferior in complexity to the central processor of a computer, and often surpass it in computing power , thanks to a large number of universal computing units (more cores)
Looks like a GPU, for example, like this :
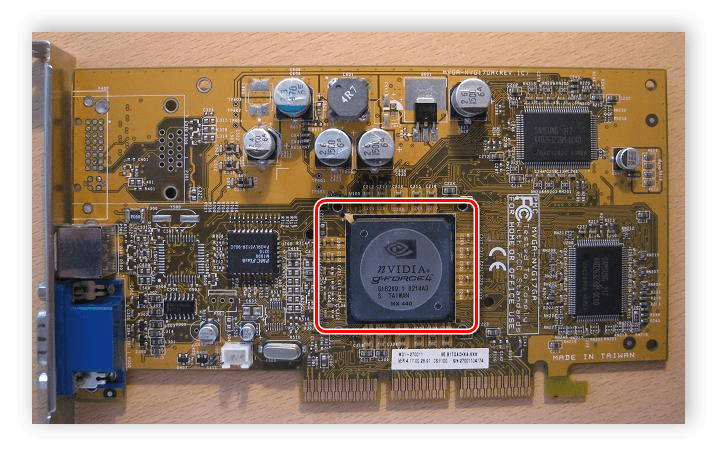

We ’ll talk about its architecture and, in principle, the differences between CPU and GPU, after I have reviewed all the components
Going further :
2.Video controller
The video controller is responsible for the image formation in the video memory, it sends commands to the digital-to-analog converter (RAMDAC) and processes the CPU commands

If we talk about a discrete card, it uses VRAM (video memory)
Modern graphics adapters (video cards) - for example, AMD, NVidia - usually have at least two video controllers operating independently of each other and controlling simultaneously one or several displays each.
Pictures :
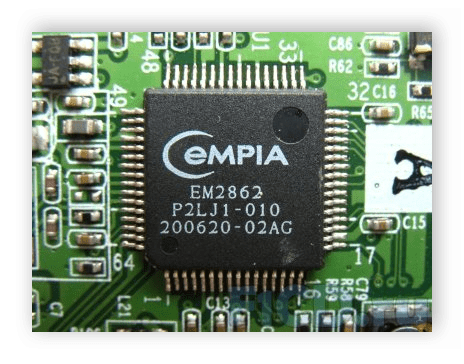




3.Video ROM
Video ROM — do not confuse with video memory — a permanent memory device (ROM) in which video cards BIOS, screen fonts, service tables, etc. are written to the ROM. The video controller is not used by the video controller directly — it is accessed only by the central processor
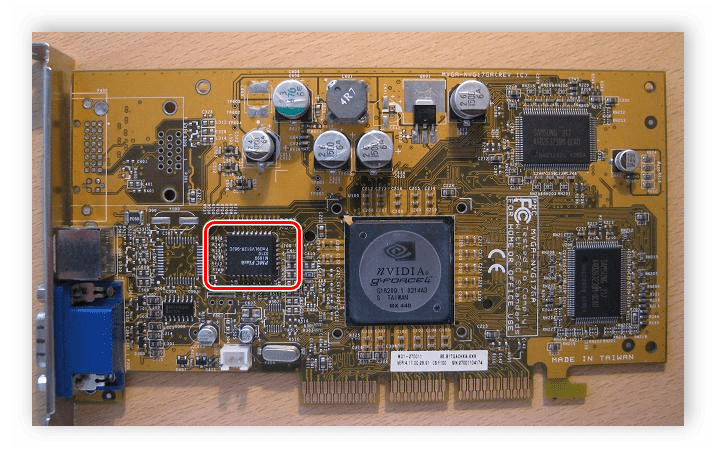


4.Video memory (VRAM) is an internal memory allocated for storing data used to form an image on a monitor screen.
Video memory serves as a frame buffer, which stores the image created and constantly changed by the graphics processor until it is displayed on the monitor (or multiple monitors).
Intermediate, invisible on the screen elements of the image and other data are also stored in the video memory.
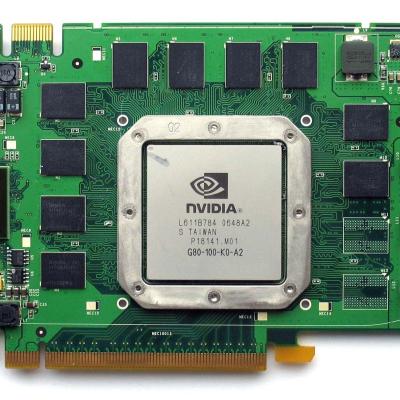
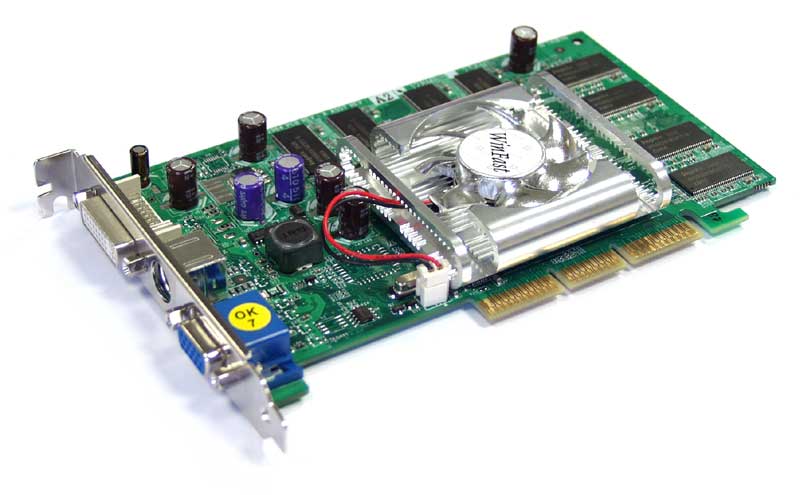




These black chips located around the GPU are the video memory.
Here is another example:
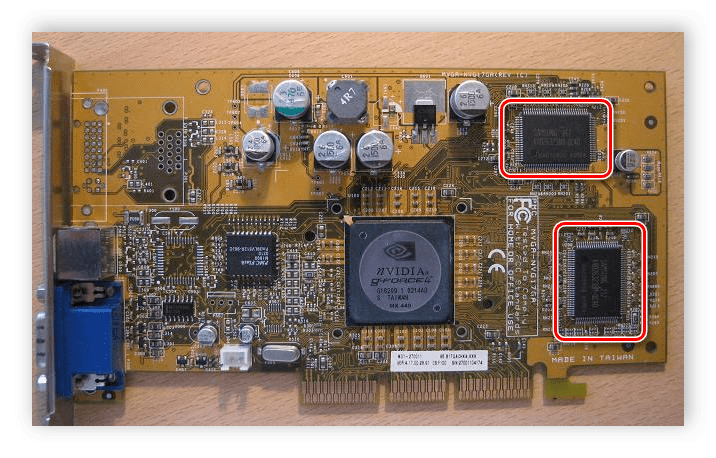
Video memory is of several types, differing in access speed and operating frequency, we'll talk about it later when I touch on the characteristics of video cards
5. Digital to analog converter (D / A converter)
The video controller generates an image, but it needs to be converted into a necessary signal with certain color levels.
This process performs the DAC.
There is also TMDS:
TMDS - briefly: differential signal transmission with minimization of level differences - a digital signal transmitter with no DAC conversions (no need to convert a signal from analog to digital).
Used with DVI-D, HDMI, DisplayPort connections.
The fact is that with the proliferation of liquid crystal monitors and plasma panels, the need to transmit this very analog signal disappeared - unlike cathode ray tubes, they no longer have an analog component and work inside with digital data right away .
More information about TMDS here
Actually, DAC:

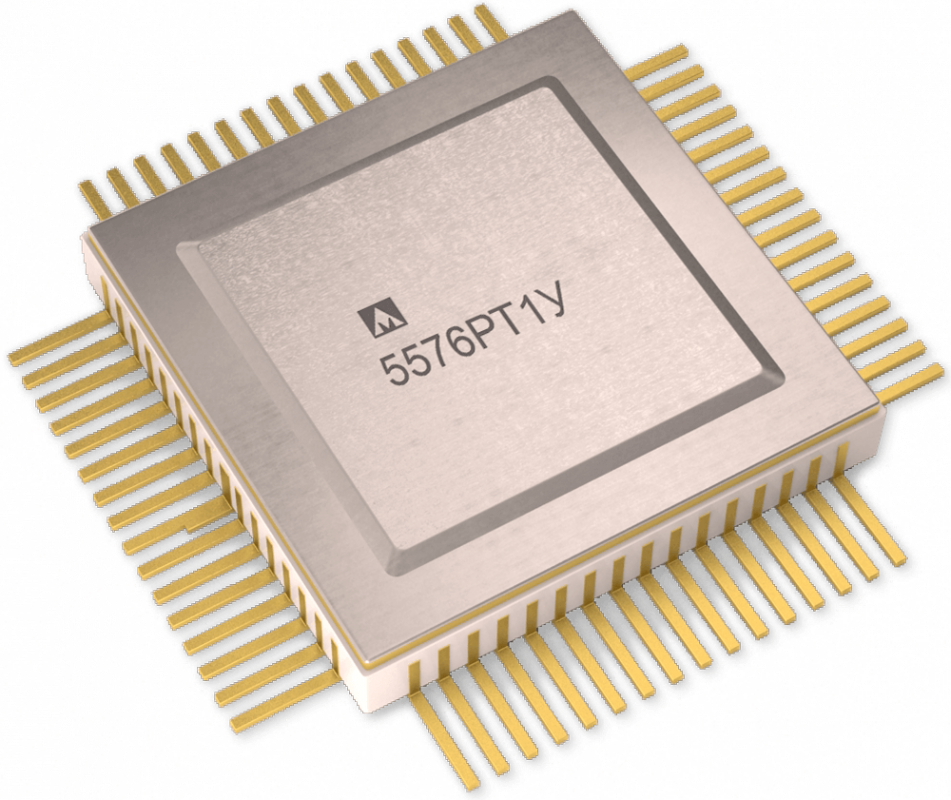


6.Video connectors
Video cards have the ability to transfer images to other output devices by connecting, via interfaces (outputs):
VGA (Video Graphics Adapter) is used to output an analog signal

Connector for called VGA or D-Sub 15 (15-pin connector)
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) interface for high-definition multimedia, allowing you to transfer high-resolution digital video data and copy-protected multi-channel digital audio signals


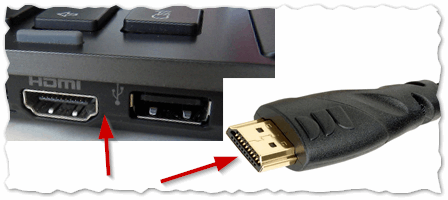
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) - a digital interface that is used to connect a video card to LCD monitors, televisions, projectors, and plasma panels
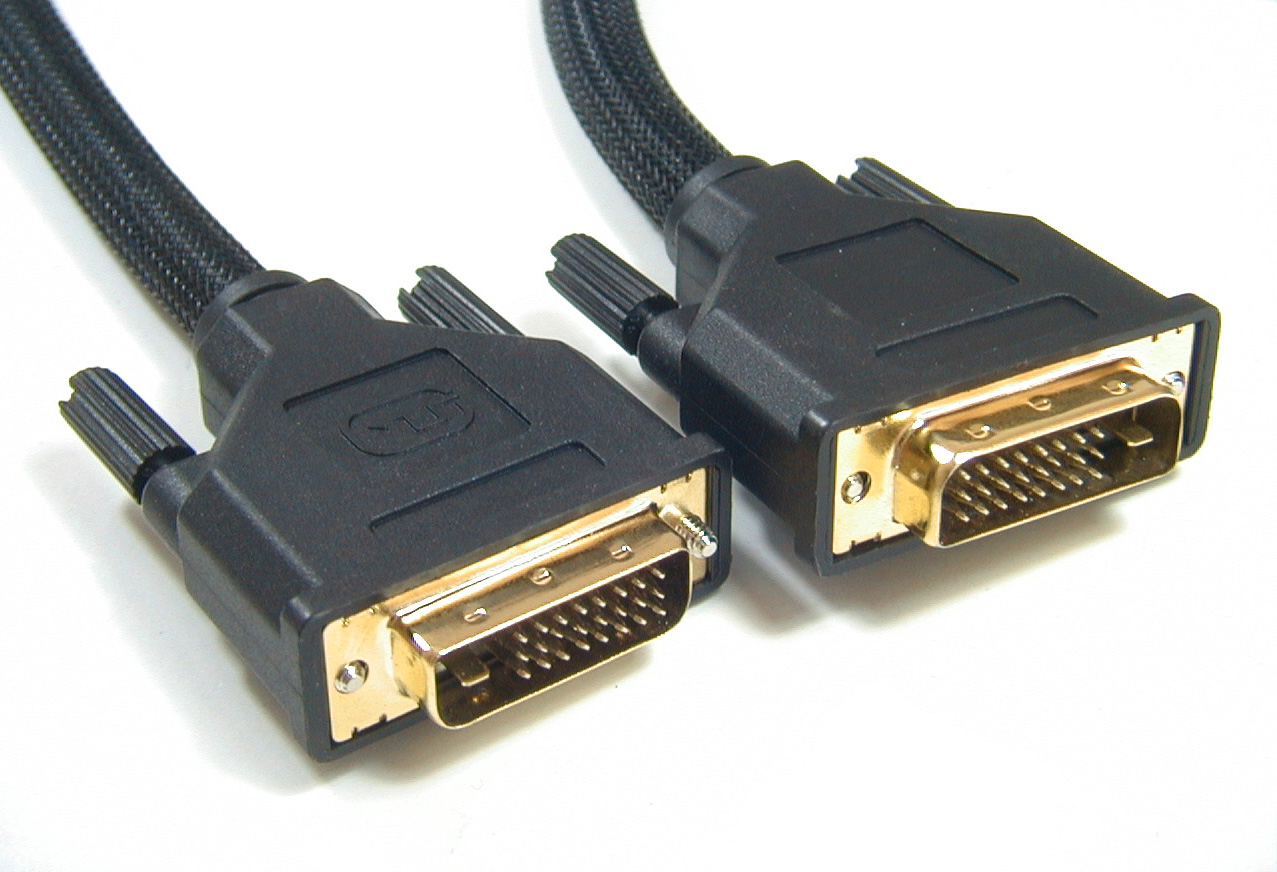



S-Video (or S-VHS)
S-Video (or S-VHS) is an analog connector that is used to output images to televisions and video equipment.



DisplayPort - a fundamentally new type of digital interface for connecting video cards with display devices


RCA (Radio Corporation of America) aka “Tulip” or “Bell” connector.
Normal output, which can be found on televisions and video equipment


7. Cooling system
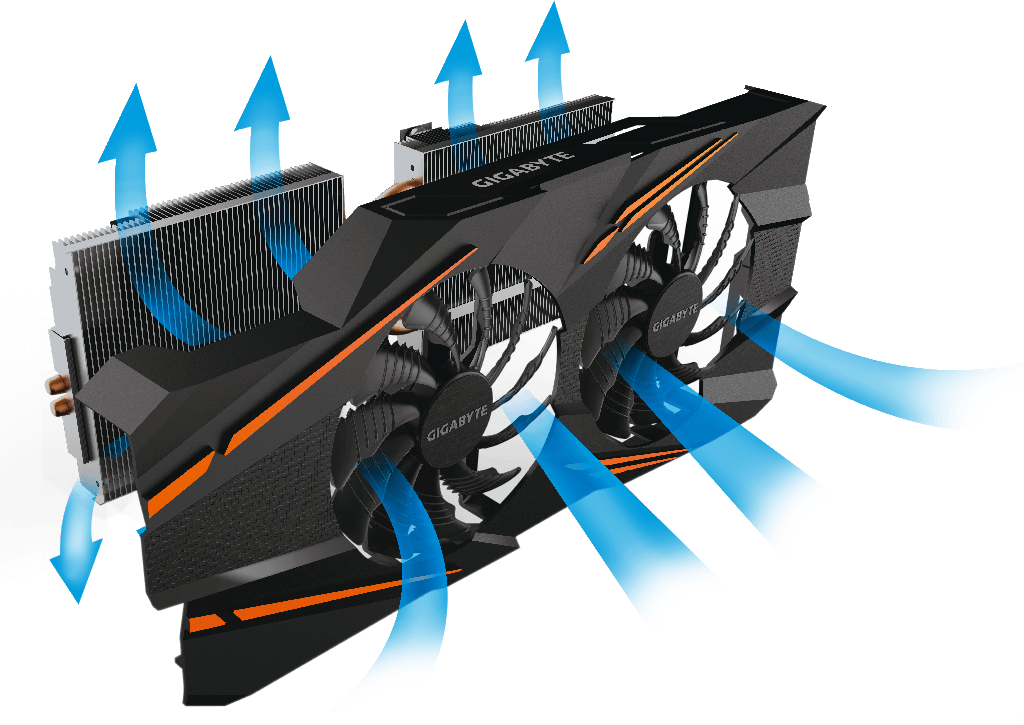
These are the fans that you saw on the discrete cards above - this is the main cooling system (air), the component itself is called a cooler , translated from English ( English cooler) means cooler
The cooling system is designed to preserve the temperature mode of the video processor and (often) the video memory within acceptable limits - obviously
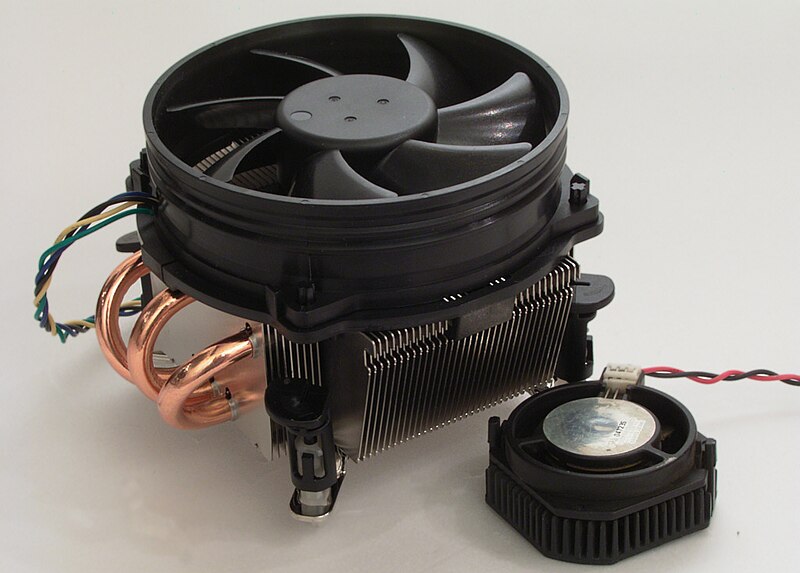

In general, this cooling option is not the only one , as there is another - water cooling , which often comes with a beautiful backlight.
Just look at this :
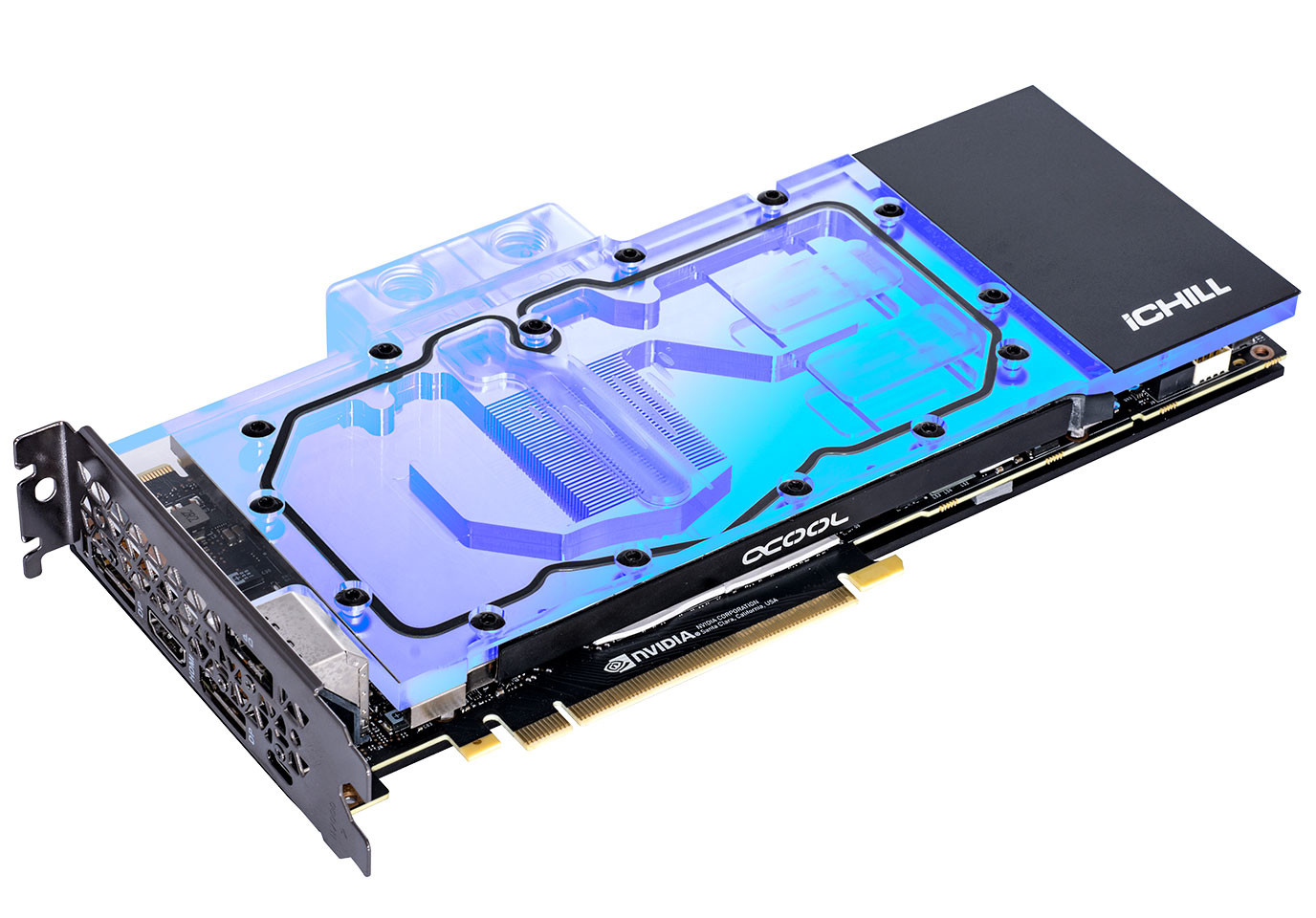
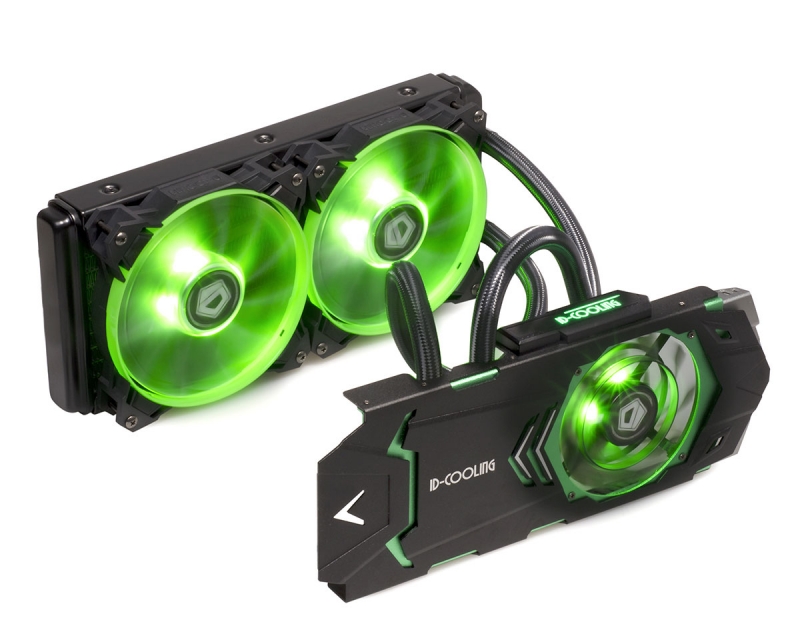
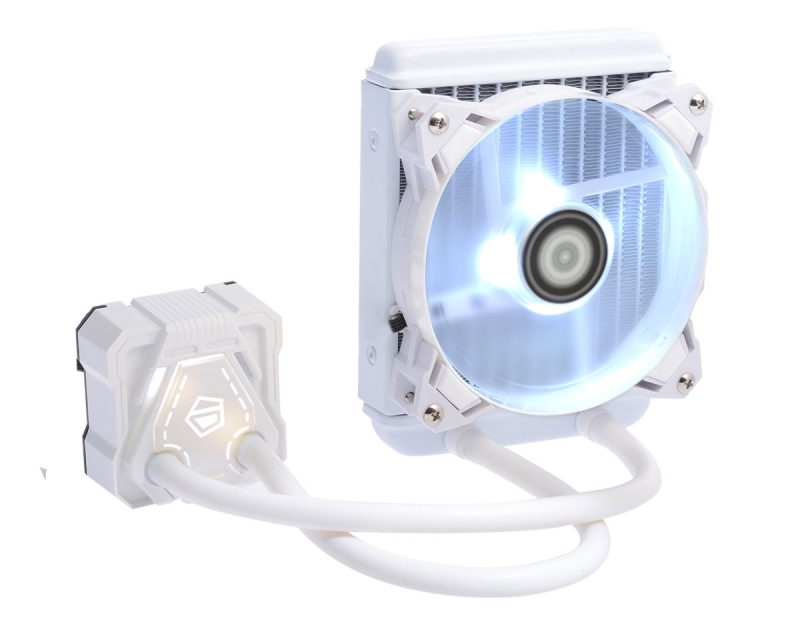




By the way, air cooling also has a backlight :
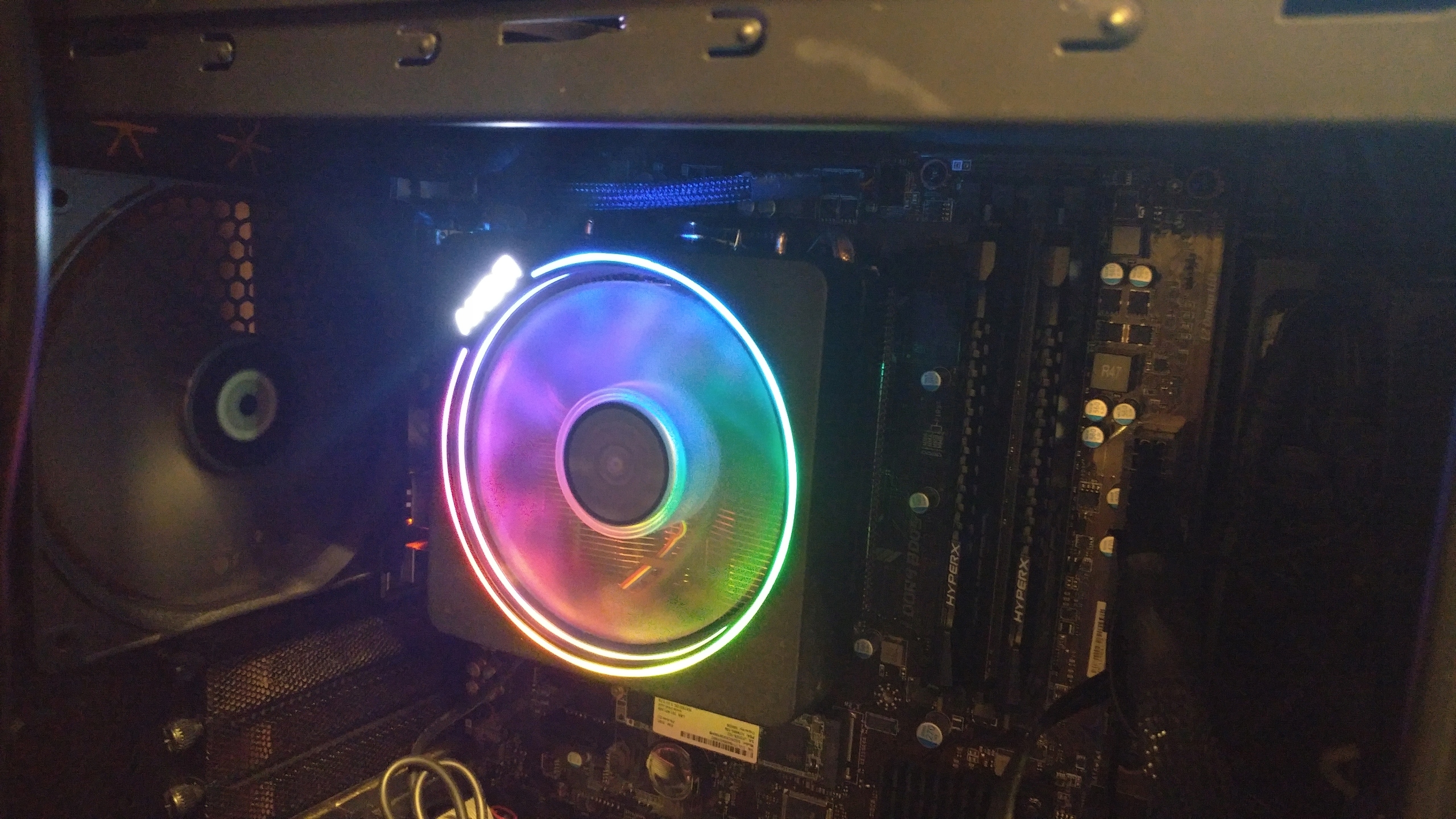

If it is not yet obvious from the photographs, keep in mind that the air cooling system involves only a radiator (made of copper or aluminum, as it has a large heat capacity, as a result, it pulls over most of the heat) and the fan (“blows out” this heat from radiator), in English the term cooler itself is usually divided into 2 parts. So, for example, there are the concepts of heat sink & fan - a radiator and a fan due to this and the board element (s) is cooled ()
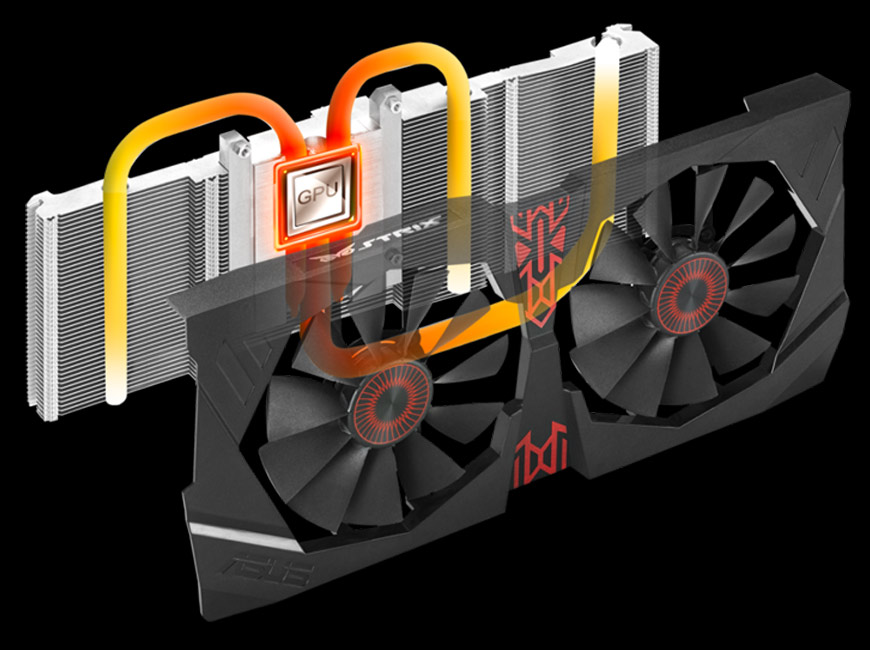
The liquid cooling system is a cooling system, in which a liquid , and not air, acts as a coolant.
Pure water is rarely used as a coolant (due to electrical conductivity and corrosiveness of water), most often it is distilled water (with various anti-corrosion additives), sometimes oil, other special liquids.
The main difference in the use of air and liquid cooling is that in the second case, instead of air, heat is used to transfer heat , which is much larger than air,
heat capacity.
A typical system consists of a water block in which heat is transferred from the processor to the coolant ( heat exchanger ), a pump that pumps water through the closed loop of the system (creates a certain pressure, allowing the fluid to circulate in the system), a radiator where heat is generated from the coolant to the air, the tank ( serves to fill the system with water and other service needs) and connecting hoses , cooler (s) .


In the second picture is shown, but the hoses are also connected to the pump
Having a liquid cooling system, it usually cools all strongly heating components, and then it looks like this:

But for the video card itself, the cooling is carried out only by the video chip itself:

The principle of operation of the liquid cooling system remotely resembles the cooling system in a car's engines — fluid is pumped through the radiator instead of air, which provides a much better heat sink .
In the radiators of a cooled object, water is heated, after which water from this place circulates to a colder one, i.e. removes heat.
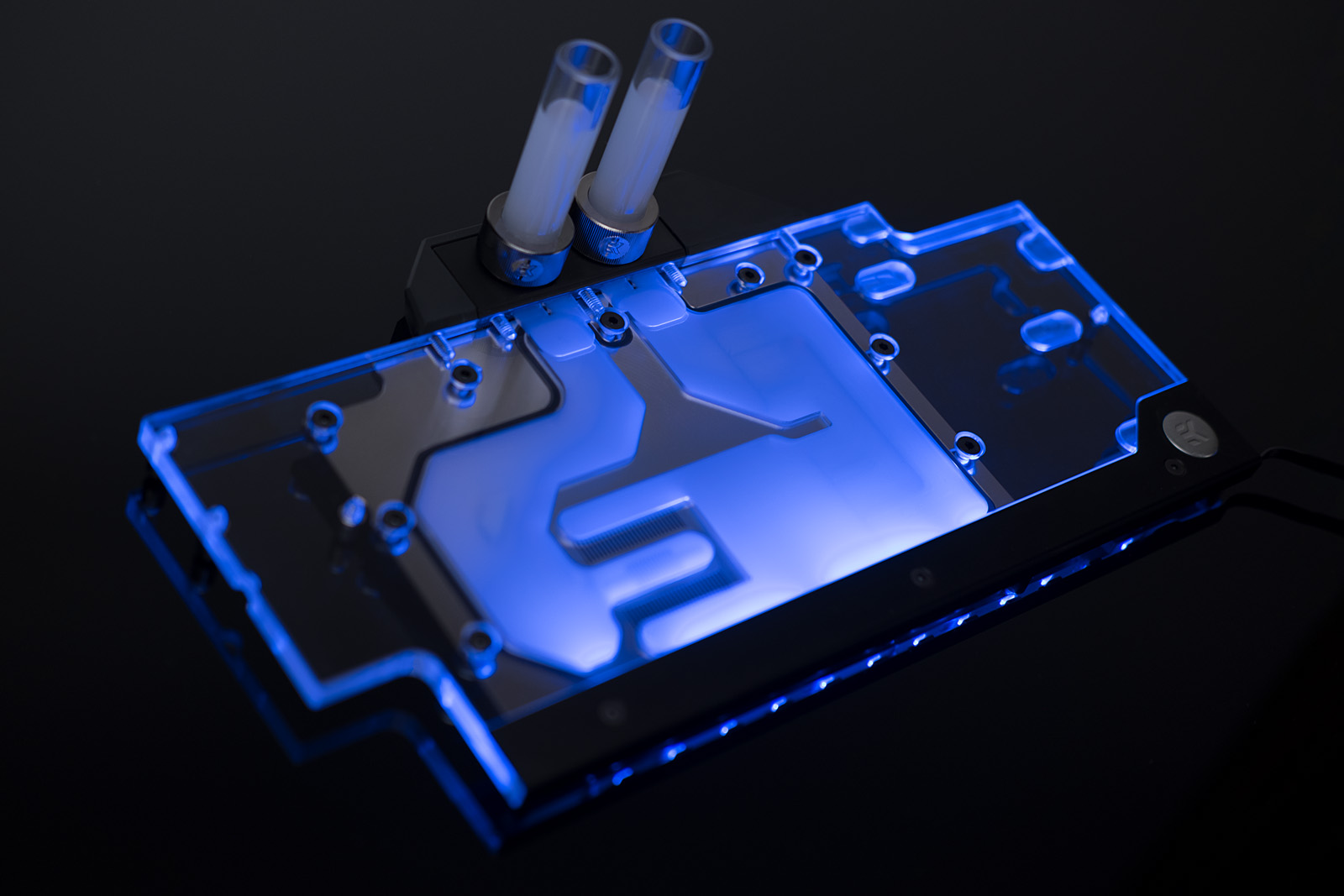
One of the common problems of owners of liquid cooling systems is overheating of the motherboard's near-processor elements, which can get very hot.
This is due to the fact that usually in such systems there is no circulation of cold air.
Just the solution of combining with a cooler that will cool the other basking elements, in many cases saves the situation
When choosing a liquid cooling system, be careful. This approach, although it makes the computer work less noisy and cools better, but nevertheless, sometimes it ends badly, including all the ensuing consequences.

Well, more precisely, it is, and it is enough, for example, today you can :
- Read about what a video card is.
- Choose a video card
- Compare its characteristics
- Choose one of the sides of the camp
What kind of camps?
Speaking about the camps , I mean, of course, for a long time already competing companies - AMD and NVIDIA - to them, in the course of the story, I will definitely come back
But at the same time, this information is scattered across various sources, and it seems to me that it would not hurt to systematize it a little in just two articles.
In the first part I will try to give basic knowledge, in the second there will be a slightly more in-depth level.
')
I will try to touch on various topics related to video cards, in particular - what it is , why it is needed , what it consists of, characteristics and applications in computing

Part 1 : What is a video card? Why is it needed? What is it made of?
Part 2: Characteristics and application of video cards in computing
PS I will attach the link to part 2 as soon as it is
Go:
What is a video card and why is it needed?
A video card is a device that converts an image stored in a computer's memory into a video signal for a monitor.
A video card in different sources can be named like: graphics accelerator, graphics card, video adapter, 3D accelerator, GPU and other similar terms. All these are different names for the same device, which is very important in a modern computer.
Why a 3D accelerator or why a graphics accelerator ? Why "important in a modern computer" ? Where is this all from? More on this later
And now look - video cards are divided into 3 types:
- Integrated graphics cards (i.e. Embedded Graphics or IGP)
- Discrete video cards
- Hybrid solutions
In order :
Integrated video cards: These are video chips integrated into the processor core (CPU), (reside on a processor chip) or, less commonly, embedded into the motherboard (as a rule, they are on their own, but generally can be located under a chip called the " north bridge ". video cards give poor performance for those who want good graphics performance.
After all, integrated solutions for this are not calculated and are used in, for example, office computers (or laptops), where it is assumed that there will not be strong loads on the video chip.
The problem of integrated video cards is that they do not have their own random access memory (RAM), and they use the computer’s single RAM together with the processor, while the signal transmission goes through the same system bus - both of which, in fact, greatly hinder the operation .
The integrated video card goes instead of with all the other components on the board, since, obviously, it is located on this board
Example 1:

Example 2:

Example 3:

Discrete video cards: This is just an option for those who just need good graphics performance.
Discrete video cards differ in their computing power in comparison with integrated video adapters, since I have my own memory - therefore there is no need to climb and take a couple of computer memory with a processor, although a discrete video card also knows how
The discrete card is not integrated into the motherboard, but is located separately, being independent (wanted-pulled out and carried with itself) and connecting to the system data bus using expansion cards (in other words, slots ), which
View all images
used to connect external devices (aka adapters or controllers of these connected devices)
Speaking of slots , I mean :

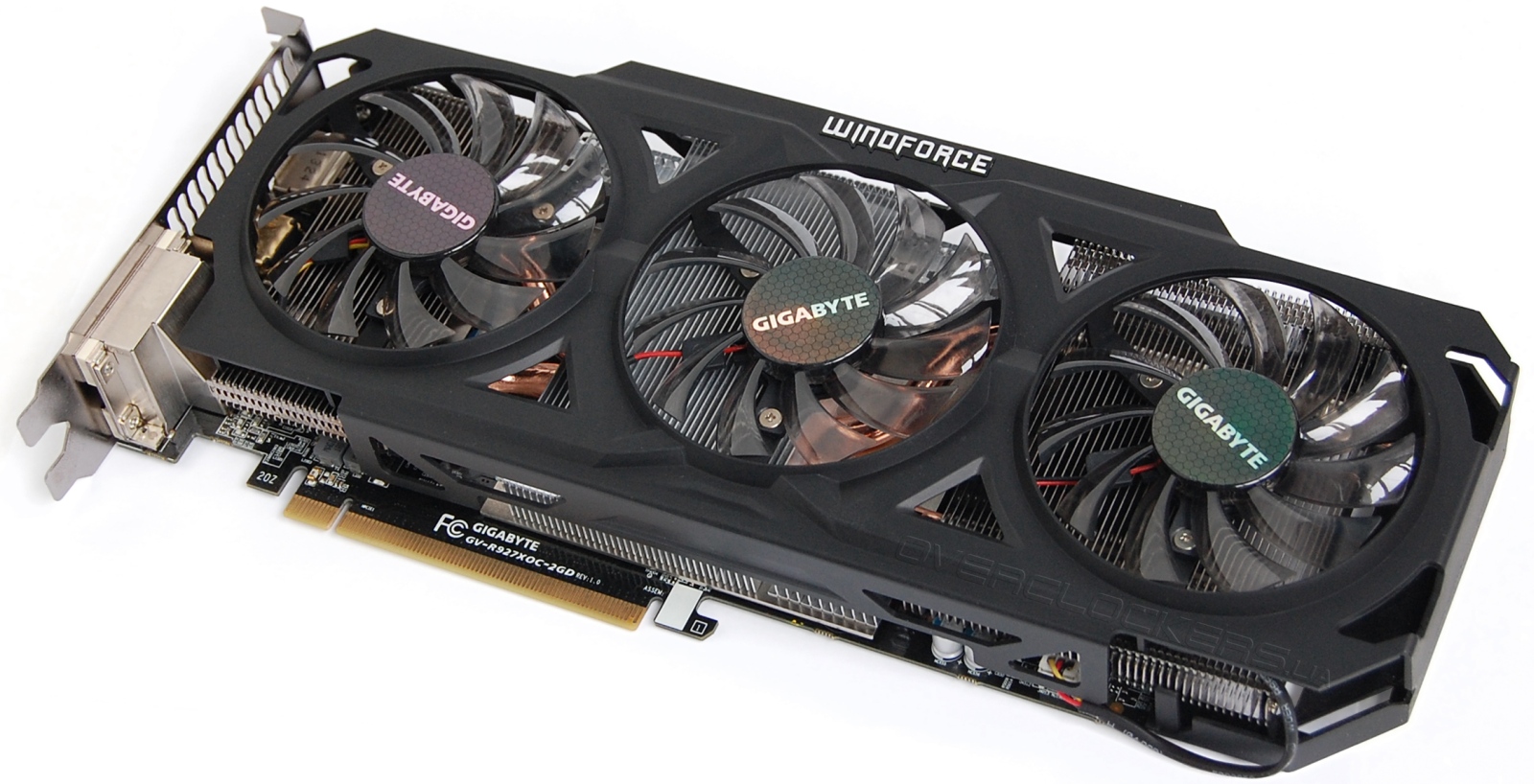
The discrete map is obviously different from the integrated one and looks like this:
Example 1:

Example 2:

Example 3:

Example 4:

As you can see, discrete cards, unlike integrated ones, are not an integral part of the board and are made as a separate chip.
Hybrid solutions: This option (well, or this solution) implies in itself, as, actually, it is clear from the name - the combination of an integrated video card and a discrete one (only the work does not take place simultaneously, but in turn, while resources requiring large computing powers are given discretely, and Smaller - weak, integrated video card (there should be a switch - should )
And in this case, the video card (just usually they mean discrete) can be considered a graphics accelerator, a 3D accelerator, because the speed of work increases noticeably, and with the passage of games there are fewer problems.
It is for its computing power that a discrete card plays the role of a very important component in a modern computer.
Computers can be sold both with a processor containing a video chip inside it , and without it, but in this case it will be a board that includes a discrete video card and is designed for heavy computational actions (for example, go to Witcher 3 for maximum speeds) then things are more serious)
If you do not plan to heavily load your computer (or laptop), for example, you just need to sit on the Internet, run light games, sometimes program, using editors, and maybe even IDE, edit tables - then you can take a computer (or laptop) with an integrated video card - they are cheaper than discrete ones, and, you see, it is reasonable if you do not overpay for opportunities that will not be used.
The disadvantages can be attributed to the fact that if for some reason your video chip fails, it will be painful, since it is already in the processor, which is quite problematic
If you want to get high power from a computer, because you need, for example, to play new games, freely watch videos in the best quality, render videos and a whole lot more that warms up your “machine” well, then you should definitely take a discrete video card, let it cost you more.
In the event of a chip failure on a discrete card, since a discrete card is pulled out as freely as it is inserted - it can be re-soldered or replaced, initially, of course, taking out this video card (you shouldn’t warm it up, I think this is nonsense and then it will only get worse)
What does a video card consist of?
An integrated video card uses the same resources as other components on this board, but with a discrete card, things are more interesting, it has its own components.
Who cares,

Let's look at the external (discrete) card again:

Modern discrete graphics card consists of the following parts:
1. Graphic processor
The graphics processor (well, or the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) - a graphics processor unit) is engaged in the calculations of the displayed image , relieving the central processor of this responsibility, and makes calculations for processing 3D graphics commands. It is the basis of the graphics card , it depends on it the speed and capabilities of the entire device.
Modern graphics processors are not inferior in complexity to the central processor of a computer, and often surpass it in computing power , thanks to a large number of universal computing units (more cores)
Looks like a GPU, for example, like this :


We ’ll talk about its architecture and, in principle, the differences between CPU and GPU, after I have reviewed all the components
Going further :
2.Video controller
The video controller is responsible for the image formation in the video memory, it sends commands to the digital-to-analog converter (RAMDAC) and processes the CPU commands

If we talk about a discrete card, it uses VRAM (video memory)
Modern graphics adapters (video cards) - for example, AMD, NVidia - usually have at least two video controllers operating independently of each other and controlling simultaneously one or several displays each.
Pictures :





3.Video ROM
Video ROM — do not confuse with video memory — a permanent memory device (ROM) in which video cards BIOS, screen fonts, service tables, etc. are written to the ROM. The video controller is not used by the video controller directly — it is accessed only by the central processor



4.Video memory (VRAM) is an internal memory allocated for storing data used to form an image on a monitor screen.
Video memory serves as a frame buffer, which stores the image created and constantly changed by the graphics processor until it is displayed on the monitor (or multiple monitors).
Intermediate, invisible on the screen elements of the image and other data are also stored in the video memory.




These black chips located around the GPU are the video memory.
Here is another example:

Video memory is of several types, differing in access speed and operating frequency, we'll talk about it later when I touch on the characteristics of video cards
5. Digital to analog converter (D / A converter)
The video controller generates an image, but it needs to be converted into a necessary signal with certain color levels.
This process performs the DAC.
Read more
The DAC is built in the form of four blocks, three of which are responsible for the RGB conversion (red, green, and blue), and the fourth block, the last block, stores information about the upcoming brightness and gamma correction (called SRAM).
One channel operates at 256 levels of brightness for individual colors, and in total, the DAC displays 16.7 million colors (and due to gamma correction, it is possible to display the original 16.7 million colors in a much larger color space).
Some DACs have a 10-bit bit depth for each channel (1024 brightness levels), which allows you to immediately display more than 1 billion colors, but this feature is hardly used.
To support a second monitor , a second DAC is often installed.
One channel operates at 256 levels of brightness for individual colors, and in total, the DAC displays 16.7 million colors (and due to gamma correction, it is possible to display the original 16.7 million colors in a much larger color space).
Some DACs have a 10-bit bit depth for each channel (1024 brightness levels), which allows you to immediately display more than 1 billion colors, but this feature is hardly used.
To support a second monitor , a second DAC is often installed.
There is also TMDS:
TMDS - briefly: differential signal transmission with minimization of level differences - a digital signal transmitter with no DAC conversions (no need to convert a signal from analog to digital).
Used with DVI-D, HDMI, DisplayPort connections.
The fact is that with the proliferation of liquid crystal monitors and plasma panels, the need to transmit this very analog signal disappeared - unlike cathode ray tubes, they no longer have an analog component and work inside with digital data right away .
More information about TMDS here
If anyone is not familiar with cathode ray tubes, they look like
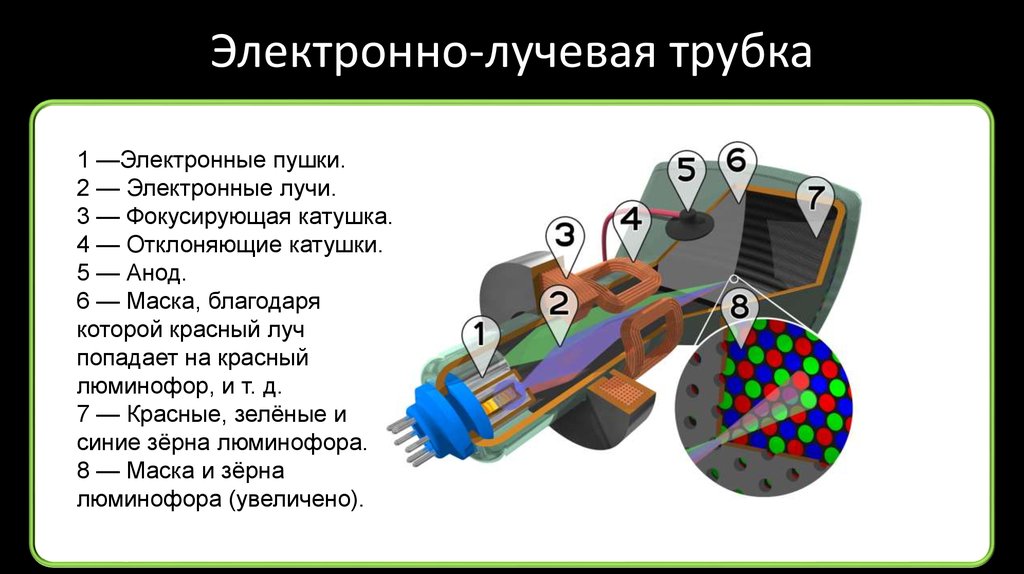






Actually, DAC:




6.Video connectors
Video cards have the ability to transfer images to other output devices by connecting, via interfaces (outputs):
VGA (Video Graphics Adapter) is used to output an analog signal

Connector for called VGA or D-Sub 15 (15-pin connector)
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) interface for high-definition multimedia, allowing you to transfer high-resolution digital video data and copy-protected multi-channel digital audio signals



DVI (Digital Visual Interface) - a digital interface that is used to connect a video card to LCD monitors, televisions, projectors, and plasma panels



S-Video (or S-VHS)
S-Video (or S-VHS) is an analog connector that is used to output images to televisions and video equipment.


DisplayPort - a fundamentally new type of digital interface for connecting video cards with display devices


RCA (Radio Corporation of America) aka “Tulip” or “Bell” connector.
Normal output, which can be found on televisions and video equipment


More about connectors
7. Cooling system
These are the fans that you saw on the discrete cards above - this is the main cooling system (air), the component itself is called a cooler , translated from English ( English cooler) means cooler
The cooling system is designed to preserve the temperature mode of the video processor and (often) the video memory within acceptable limits - obviously

In general, this cooling option is not the only one , as there is another - water cooling , which often comes with a beautiful backlight.
Just look at this :




By the way, air cooling also has a backlight :
If it is not yet obvious from the photographs, keep in mind that the air cooling system involves only a radiator (made of copper or aluminum, as it has a large heat capacity, as a result, it pulls over most of the heat) and the fan (“blows out” this heat from radiator), in English the term cooler itself is usually divided into 2 parts. So, for example, there are the concepts of heat sink & fan - a radiator and a fan due to this and the board element (s) is cooled ()


The liquid cooling system is a cooling system, in which a liquid , and not air, acts as a coolant.
Pure water is rarely used as a coolant (due to electrical conductivity and corrosiveness of water), most often it is distilled water (with various anti-corrosion additives), sometimes oil, other special liquids.
The main difference in the use of air and liquid cooling is that in the second case, instead of air, heat is used to transfer heat , which is much larger than air,
heat capacity.
A typical system consists of a water block in which heat is transferred from the processor to the coolant ( heat exchanger ), a pump that pumps water through the closed loop of the system (creates a certain pressure, allowing the fluid to circulate in the system), a radiator where heat is generated from the coolant to the air, the tank ( serves to fill the system with water and other service needs) and connecting hoses , cooler (s) .


In the second picture is shown, but the hoses are also connected to the pump
Having a liquid cooling system, it usually cools all strongly heating components, and then it looks like this:
But for the video card itself, the cooling is carried out only by the video chip itself:

The principle of operation of the liquid cooling system remotely resembles the cooling system in a car's engines — fluid is pumped through the radiator instead of air, which provides a much better heat sink .
In the radiators of a cooled object, water is heated, after which water from this place circulates to a colder one, i.e. removes heat.

One of the common problems of owners of liquid cooling systems is overheating of the motherboard's near-processor elements, which can get very hot.
This is due to the fact that usually in such systems there is no circulation of cold air.
Just the solution of combining with a cooler that will cool the other basking elements, in many cases saves the situation
When choosing a liquid cooling system, be careful. This approach, although it makes the computer work less noisy and cools better, but nevertheless, sometimes it ends badly, including all the ensuing consequences.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/441866/
All Articles