"Hayabusa-2" first touched the asteroid
The first Hayabus probe with honor overcame many problems - the flywheels of the orientation system failed, one after another the engines failed, the miniature landing gear missed, and the device for collecting samples did not work as it should. Nevertheless, one and a half thousand pieces of the Itokawa asteroid were nevertheless delivered to Earth. His follower, Hayabusa-2, who went to Ryuga asteroid, has so far been doing much better. Last week, he first touched an asteroid sampler, fired a tantalum bullet at him, and the contact that was earlier than planned was the biggest trouble.
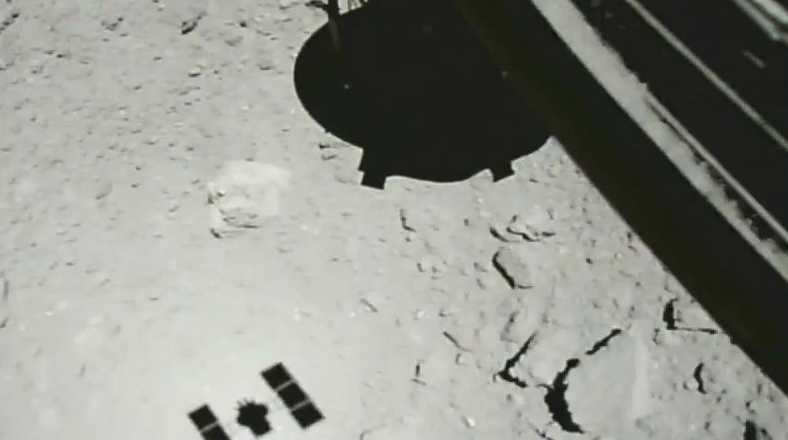

Photos from the training decline in October 2018, height 21 m, photo JAXA
Hayabusa-2 was launched on December 3, 2014, exactly one year later made a gravitational maneuver near the Earth and arrived at the asteroid (162173) Ryugu on July 27, 2018, going into a working orbit of 20 km in height. On September 21, two HIBOU and OWL rovers were successfully dropped to the surface (it would be more correct to call them “jumpers” because they do not ride on the surface, but jump), and on October 3, the MASCOT landing gear. According to the initial plans, the first attempts to collect asteroid samples were planned in the autumn of 2018, but they were transferred to this year. And, after dozens of rehearsals, the probe finally went down on February 21.
Animation of frames from the navigation camera shows the stages of approach to the asteroid from a height of 20 km.
')
Landing on an asteroid is not easy. In order for it to be accurate, the Hayabusa-2 dropped the aiming marker in advance, visible even from a working height of 20 km. Having dropped to a height of 500 m, the device, on command from the Earth, switches to autonomous navigation. At a height of 45 m, the probe freezes, switches between the LIDAR -> LRF laser range finders and waits for the target marker to appear in the field of view of the camera. Capturing the marker, the Hayabusa descends to 4.5 meters, rotates parallel to the surface at the landing site, and touches it with a sampler. Telemetry disappears below 50 meters, and by what happens with the device, you can only monitor the Doppler effect - the decrease and contact of the surface will be noticeable by small changes in the frequency of the signal from the interplanetary station.
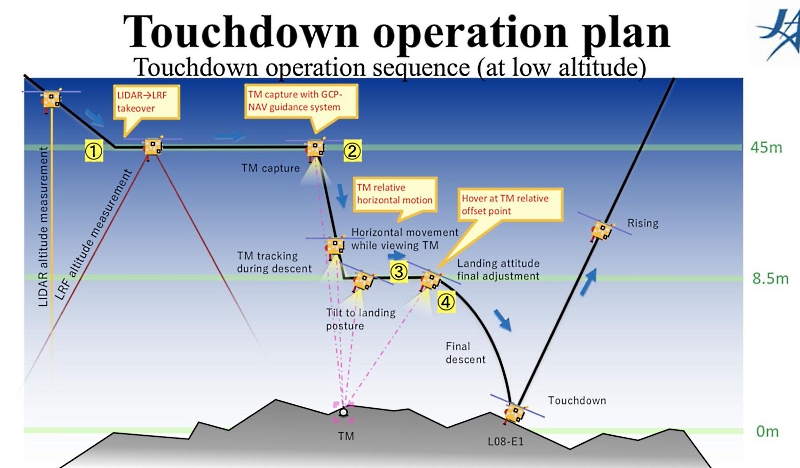
Proximity Diagram, JAXA Image
There are also certain requirements for the landing site. First of all, according to the technical limitations of the orientation of antennas and solar panels, it is not possible for the landing area to be more than 30 °. Further, the slope of the terrain should not exceed 30 °. Stones above 70 cm are unacceptable in the landing area. Finally, the surface temperature cannot exceed 97 ° C, in order not to overheat the instruments. As a result, according to the integral safety assessment, the asteroid had a clearly visible band at the equator, where it was safer to land.

Hereinafter images JAXA
Of the 17 candidates for the landing site, three were left - the main L08 and two backup L07 and M04.
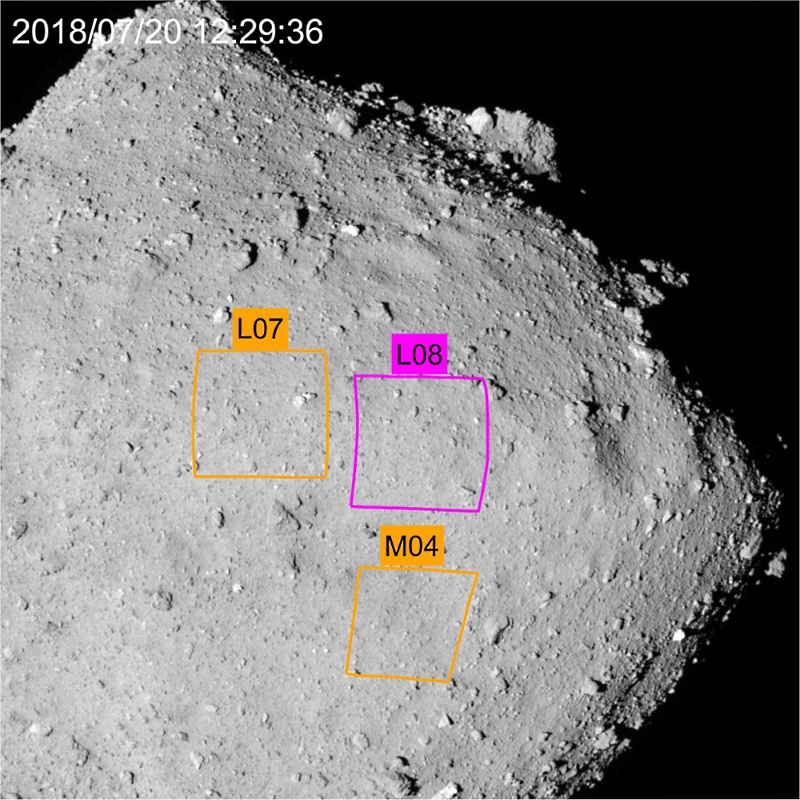
In 3D view. White dot - aiming marker.

For sampling on the "Hayabus" there are three "guns". Two of them are loaded with bullets from tantalum weighing 5 grams. They are fired at a speed of 300 m / s, when the probe touches the surface with a sampler, and emit particles of the asteroid on impact.
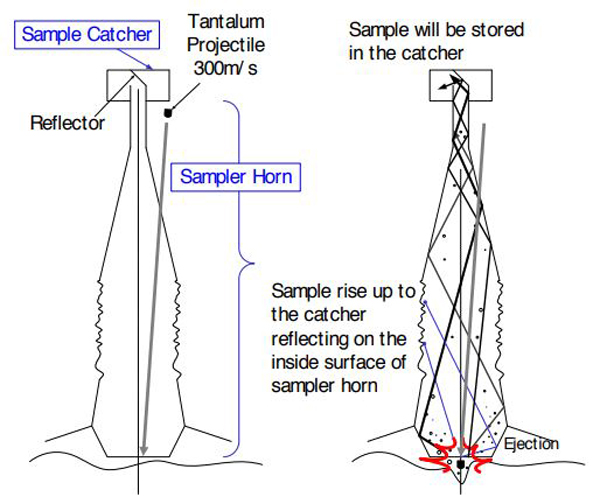
Animation ground test.

But the third shot is harder. This is a complete projectile with 4.5 kg of explosives and a shell of 2 kg of copper. The “gun” will separate from the “Hayabusy” with another mini-satellite with a camera and shoot at the asteroid, creating a funnel with a depth of about 2 meters.
The first cannon with a 5-gram projectile fired on February 21, the second and third shots are expected in March and April.
It seems that in the plan published by JAXA the last nominally possible time of contact of the asteroid was indicated. Because in reality, the probe did not wait, but went to a decrease almost without delay and touched the surface earlier than planned. In standalone mode, without telemetry, he successfully touched the surface (noticeably due to frequency shift due to the Doppler effect).

Broadcast frame
Then the probe successfully shot out at the asteroid - the temperature rise in the barrel of the first gun indicates a successful shot.
Telemetry returned at an altitude of about 1200 m. A subsequent analysis showed that the shot and the sequence of sampling operations were successful, and the device returned to a working height of 20 km. After the first touch, the traces of the engines on the asteroid are barely noticeable, and the most spectacular third shot is expected in April.

Photos from the training decline in October 2018, height 21 m, photo JAXA
Prehistory
Hayabusa-2 was launched on December 3, 2014, exactly one year later made a gravitational maneuver near the Earth and arrived at the asteroid (162173) Ryugu on July 27, 2018, going into a working orbit of 20 km in height. On September 21, two HIBOU and OWL rovers were successfully dropped to the surface (it would be more correct to call them “jumpers” because they do not ride on the surface, but jump), and on October 3, the MASCOT landing gear. According to the initial plans, the first attempts to collect asteroid samples were planned in the autumn of 2018, but they were transferred to this year. And, after dozens of rehearsals, the probe finally went down on February 21.
Animation of frames from the navigation camera shows the stages of approach to the asteroid from a height of 20 km.
')
Algorithm and landing site
Landing on an asteroid is not easy. In order for it to be accurate, the Hayabusa-2 dropped the aiming marker in advance, visible even from a working height of 20 km. Having dropped to a height of 500 m, the device, on command from the Earth, switches to autonomous navigation. At a height of 45 m, the probe freezes, switches between the LIDAR -> LRF laser range finders and waits for the target marker to appear in the field of view of the camera. Capturing the marker, the Hayabusa descends to 4.5 meters, rotates parallel to the surface at the landing site, and touches it with a sampler. Telemetry disappears below 50 meters, and by what happens with the device, you can only monitor the Doppler effect - the decrease and contact of the surface will be noticeable by small changes in the frequency of the signal from the interplanetary station.

Proximity Diagram, JAXA Image
There are also certain requirements for the landing site. First of all, according to the technical limitations of the orientation of antennas and solar panels, it is not possible for the landing area to be more than 30 °. Further, the slope of the terrain should not exceed 30 °. Stones above 70 cm are unacceptable in the landing area. Finally, the surface temperature cannot exceed 97 ° C, in order not to overheat the instruments. As a result, according to the integral safety assessment, the asteroid had a clearly visible band at the equator, where it was safer to land.

Hereinafter images JAXA
Of the 17 candidates for the landing site, three were left - the main L08 and two backup L07 and M04.

In 3D view. White dot - aiming marker.

Peace Guns
For sampling on the "Hayabus" there are three "guns". Two of them are loaded with bullets from tantalum weighing 5 grams. They are fired at a speed of 300 m / s, when the probe touches the surface with a sampler, and emit particles of the asteroid on impact.

Animation ground test.

But the third shot is harder. This is a complete projectile with 4.5 kg of explosives and a shell of 2 kg of copper. The “gun” will separate from the “Hayabusy” with another mini-satellite with a camera and shoot at the asteroid, creating a funnel with a depth of about 2 meters.
The first cannon with a 5-gram projectile fired on February 21, the second and third shots are expected in March and April.
First went
It seems that in the plan published by JAXA the last nominally possible time of contact of the asteroid was indicated. Because in reality, the probe did not wait, but went to a decrease almost without delay and touched the surface earlier than planned. In standalone mode, without telemetry, he successfully touched the surface (noticeably due to frequency shift due to the Doppler effect).

Broadcast frame
Then the probe successfully shot out at the asteroid - the temperature rise in the barrel of the first gun indicates a successful shot.

Telemetry returned at an altitude of about 1200 m. A subsequent analysis showed that the shot and the sequence of sampling operations were successful, and the device returned to a working height of 20 km. After the first touch, the traces of the engines on the asteroid are barely noticeable, and the most spectacular third shot is expected in April.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/441546/
All Articles