Tesla Tower. What happens in and near the skyscraper when lightning strikes?
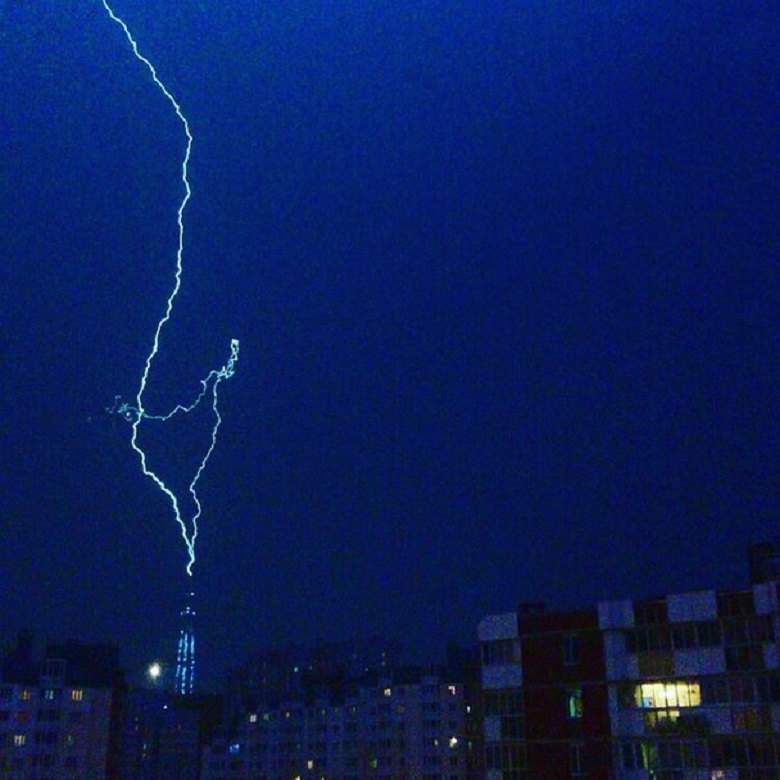
When, in September, lightning struck the Lakhta Center tower, our chief engineer Sergey Nikiforov reassured everyone, saying that the tower had a “classic lightning protection system” and there was nothing to fear. What is this "classic"? Something ancient Greek comes to mind ... Why not? After all, we use to this day such results of ancient thought as a wheel, lock, calendar or paper. Maybe the lightning protection in the tower is well forgotten old? Then - can so old things help so new?
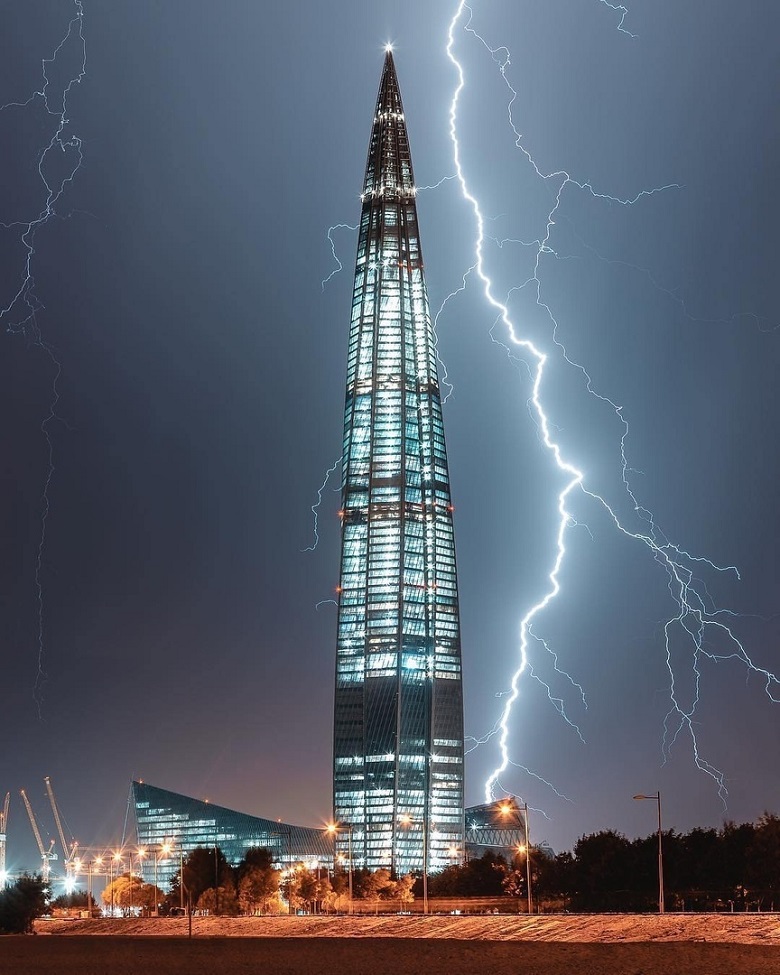

Photo ch0col8te
We will understand!
On the Internet there is a bike about ancient navigators.
')

Photo of the trireme from here
Allegedly, even then the Greek sailors really knew how to ward off the Thunderer’s anger in an ingenious way. A sword was tied vertically to the mast; a cable was attached to it; the ends — into the water. It sounds doubtful. In order to come up with something similar, you need to understand the nature of lightning. The Greeks understood that on Olympus, another family quarrel, save yourself who can, why the sword?

And even if by some accidents, after thousands of triumphs flooded by Zeus, it was possible to reach an understanding that lightning was perfectly caught by the copies and xyphos, then the chain was interrupted. Steel cables from the ancient Greeks was not, and those that were - flax, have a relatively high resistivity. Use this as a guide - and the further journey by swimming is almost guaranteed. If time jump from a burning vessel, of course. If you are really lucky, you will sail to the shore and tell you how wrongly to threaten Zeus with a sword from the mast.

Painting "Odyssey and Navsikaya", Rosa Salvator, Museum of Art of Los Angeles, ca. 1655 Source
Of course, maybe it was not the cables that were there, but the chain or the winding wire, or the cable, was soaked well before putting it into operation. And in general, they were versed in the properties of electricity, conductors and dielectrics ... But for some reason this very useful knowledge further sunk into oblivion, having emerged centuries later. But there was definitely another tool, which even the police had to struggle with.

In the Middle Ages, the scientific paradigm turned upside down - Jupiter and Thor went into oblivion, and in a thunderstorm saw the machinations of the devil.

Destruction of the Catholic Church. Engraving by Mathias Gerung, Germany, 1547. Source
The climatic weapon of the epoch is the bell ringing, because, as is well known , “the first strike of the bell leads the impure force to numbness, on the second strike, it rushes in dismay in all directions;
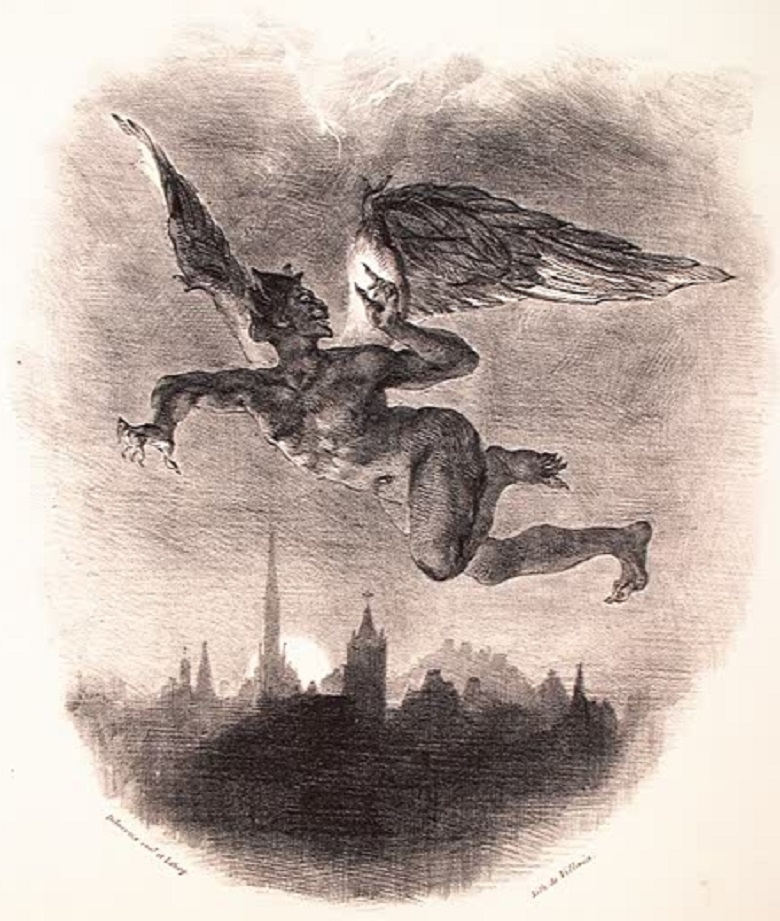

Sinister Mephistopheles flies over Wittenberg. Lithograph of Eugene Delacroix, 1828
How many belfries burned down and the obscurantists fell in this struggle, for centuries they did not count. But later entries are evidence of a deadly risk:
Or, from the notes of the Paris Academy of Sciences:
In general, at least in France, it has been forbidden to ring the bells during a thunderstorm for 30 years by official order of the police. With other medieval ways to prevent weather trouble, for example, by showing some parts of the body through the window, I think, it’s also finished. After all, they finally found - safe and working tools.

In the 18th century, Benjamin Franklin - the one whose face is well known to many on another occasion, invented a lightning conductor. In 1752, he installed a metal rod on the roof of his own house, connected by the same metal wire to a well in the courtyard.
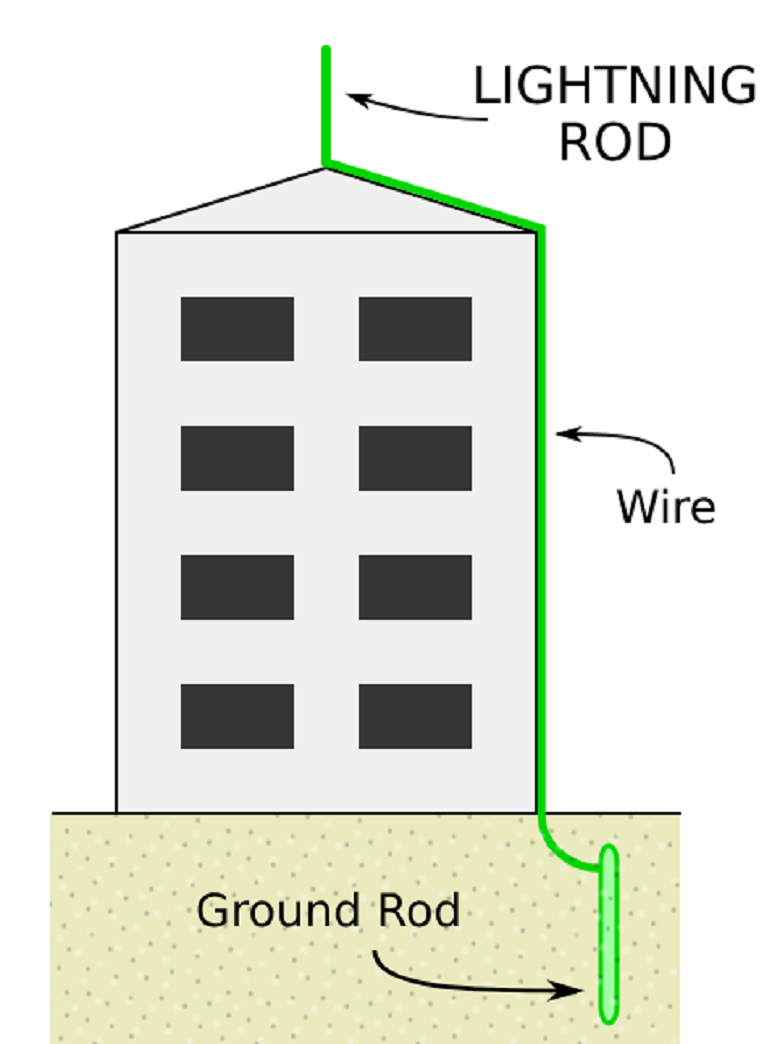
Franklin lightning protection scheme. Figure Wdchk. A source
This lightning conductor repelled the first attack of heavenly electricity 34 years later. Successfully. Perhaps the idea of such a construction was already in the air electrified by the discoveries by that time. In Russia, lightning explores Lomonosov and Richman, and industrialist Akinfiy Demidov builds the Nevyansk tower 57, 5 meters high.

A source
The tower then fell on the coat of arms of the city, a silver coin of the Bank of Russia in 2007, and 5 Ural francs (in 1991 it was like this) - for its “significantness” in history and architecture: the tower deviates from the vertical - 1.85 m.

But on it - the first domestic lightning rod, 25 years before Franklin. The design is similar: metal spire plus grounding.

A source
Since then, mankind has become victorious over lightning. First - in court. Bourgeois Villiers, who installed the novelty on the roof of the house, fought off the claims of his neighbors, who considered the lightning rod a dangerous undertaking. On the defense side - Maximilien Robespierre, on the prosecution side - Jean-Paul Marat - an incredible time! During the 4-year trial, the court sided with Villiers and lightning rods. In Paris, umbrellas and hats with lightning protection are becoming popular.

In the states and without similar stories, the number of lightning rods is in the hundreds. Franklin's circuit - the lightning rod - current lead - grounding, today is considered classic. Nothing better has been thought of yet: the efficiency of a good classical lightning rod approaches 99%. This is what our chief engineer commemorated this stormy September.

Franklin, like Lomonosov, and Richman, came to understand the electrical nature of lightning, and then - to the main thing: you can “pull” electricity from the atmosphere by catching a lightning on a conventional copy. Franklin’s described experience of launching a kite into a thundercloud today is being questioned, but somehow, he arrived at the right conclusions in good health, unlike Richman’s Russian colleague, who paid for his life with science. The properties of the conductors were already open, the rest is a matter of engineering ingenuity and the matter of technology.

From 1860 to 1890, a US dollar vignette with a kite experiment from Franklin’s experiment was only a 10-dollar bill, and only later would he rub the inventor on 100-dollar bills.
The fundamental point in the classical system of lightning protection is one. Provide a continuous circuit from the reception of the discharge to its grounding using a conductor. It can be said that such a system predicts and realizes the intention of the lightning itself. The electric celestial guest wants exactly the same thing - not to break through the thickness of the air insulator, but to bring the multi-polar particles to the connection with the least effort. And people offer her the path of least resistivity.

Photo by Patrick Fisher. A source
So, we need a current collector of metal. The metal spire of the tower fits perfectly - more than 100 meters up the pure conductor!

But - not only him. The profile of the frames of the double-glazed windows of the Supertoll shell is also metallic, the metal is in the elements of the facade service system.

Catch the lightning tower can all the height. This is important - the blow does not always fall on the highest point, and thunderclouds may be below the spire.
After receiving the discharge goes to the current leads. In the steeple, their role is played by steel columns-pipes, below - galvanized steel plates. The plates surround the floor perimeter and are connected to a reliable chain by vertical trunk lanes located in the body of the perimeter columns and the core shell.

The current from the outer shell passes through the flexible conductor (in the red sheath) to the metal plate-current lead around the perimeter of the floor

The vertical highway for the discharge of electrical discharge - through, passes from the top to the bottom of the tower without separating the floors and is the main lightning conductor for the skyscraper. She goes
to minus marks, where the lightning protection circuit of the tower is connected to the ground loop of the Multifunctional building. From there, electrons rush along the reinforcement cage of MFZ piles deep into the earth and, finally, meet with protons, zeroing somewhere in the ancient strata of Precambrian clays.
Of course, lightning temperatures are terrifying. "Leader" - forvad discharge, comes to temperatures of 30 thousand degrees Celsius! Five times hotter than the core of the earth, 30 times hotter than the lava that destroyed Pompeii, Herculaneum and Stabiae in an instant. Yet the tower’s spire withstood three lightning attacks in September and remained unchanged.

Photo by Victor Gusik
All because the lightning flies the way from the current collector to ground at supersonic speeds - more than 1000 kilometers per second! Electric particles complete their route so quickly that the metal simply does not have time to heat up and melt. If there were links with high resistance in the chain or the impulse itself lasted much longer, then the outcome, of course, could have been different.
Inside the tower spire there is a navigation and communication equipment, SOF systems and other electrical equipment. If a lightning strikes the spire, what will happen to it? And in general with the rest of the electrical equipment of a skyscraper?

Such a situation is standard - in all Lahta Center's electrical switchboards there is protection against impulse overvoltages. As for directly placed in the spire, a curious detail is added here. The Lahta Center spire itself is similar in structure to the Faraday cage - the cellular structure of the metal facade, a closed and grounded contour give the effect of shielding an electrical impulse and protect the equipment inside the spire.

Grid of the facades of the spire of the tower Lakhta Center
In September, this issue excited many who had plans to visit the observation deck in the tower of the complex. Do not be afraid. In a thunderstorm it is safe to be absolutely on any habitable level of the Supertoll. The observation deck from the main current operator, the spire, separates the concrete floor at level 88 - it can be considered the roof of a building. All potential paths of lightning current deviation from the line laid for it are reliably blocked: glass is in itself a dielectric, as is concrete, enveloping the cores of the columns and forming the core body.
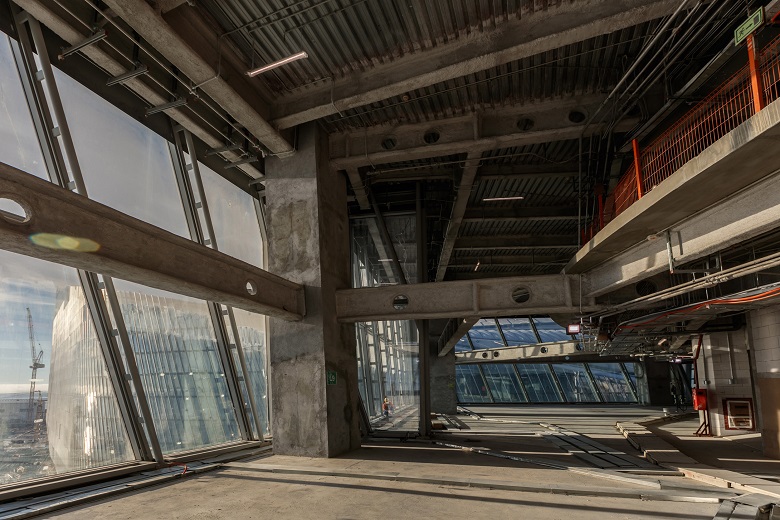

Metal plates-conductors in the body of the column are encased - a thick layer of concrete acts as an insulator
In general, lightning strikes skyscrapers quite often. The old-fashioned gentleman among the super-high "youth", the Empire State Building, receives its annual "light strike" in the amount of from 12 to 100 and so far none of its visitors have already suffered for the nearly century-long history of the building. Like a visitor of any other skyscraper.
Most often, a lightning strike to a skyscraper is a light show for those who are watching from the side, while the inhabitants may not even suspect that around them is a real tesla show. This is exactly what happened during the September thunderstorms with those who worked in those bright moments in the tower of Lakhta Center. About thunderstorms and lightning learned from numerous photos, in response to a request to share experiences - threw up their hands. The whole storm worked, did not look, it's a shame! In general, in a skyscraper in a thunderstorm, not only is safer, but sometimes much more boring - all the most interesting things are opened from the side.
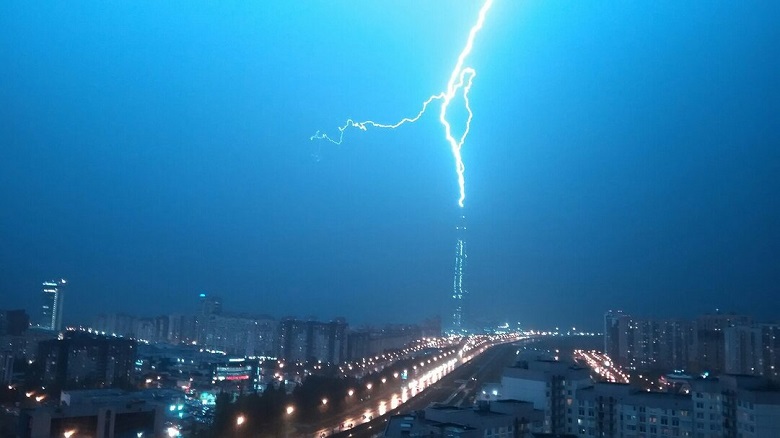

Here, for example, the photographer Mohhamed Azmi tells how he hunted behind the scenes for two years, where lightning strikes a skyscraper - waiting in bad weather on the roofs of nearby buildings.

All for the sake of this frame
And what can be seen from the observation platform of a skyscraper, being there in a thunderstorm? In some places, the design features allow you to observe the climax scenes of the heavenly drama. For example, such lines can be seen in the material about the sights of the Australian skyscraper Q1:
Those who go to watch the thunderstorm from the Lakhta Center overview, beating in the spire of lightning, unfortunately, cannot be seen - everything will happen beyond the upper ceiling. But the lightning striking below is quite likely to be caught. All you need is a good forecast and a bit of luck.
The September thunderstorms at the Lakhta Center’s tower thundered well in social media and media. So good that there were all sorts of guesses about the nature of an atypical phenomenon.

78 wash
First, such thunderstorms were not seen forever. Secondly - lightning strikes the highest point, and the Lakhta Center tower is known to be the highest in Europe ... Coincidence?

The explanations that lightning occurs under certain weather conditions and no skyscraper can change the climate, even the main weather forecaster of St. Petersburg, Alexander Kolesov, had to give. In our turn, we would be glad if the Lakhta Center could make every summer and autumn in St. Petersburg as warm as the past, but with regret we have to admit that the specialist was right: neither the tower could change the weather, nor even the complex as a whole. .
For very suspicious, there is even a small historical demonstration. Before the tower was completed, tower cranes served as lightning rods.

Despite the fact that these cars were the highest point on the construction site, there was not a single case of lightning entering a crane - summer did not spoil the previous years.
This year abnormally warm September led more than one thunderstorm front. And it is good that the tower was completed - otherwise the lightning could have chosen another target, and it is not known what or who would have become it. On the other hand, one should not rely entirely on such an impressive “lightning rod” - there are not rare cases when the Thunderbird aims the wrong way.
Here is an impressive frame with a thunderstorm, made quite close to the tower. Besides the lightning itself and the skyscraper, the only, but potentially very dangerous situation is also captured here.

There are calculations, according to which up to half of the victims of lightning strikes hid under tall trees. The tower is not a tree, but during a thunderstorm it is imperative to take shelter in the building and absolutely not to aim impressive shots from the amphitheater or from some lawn next to the skyscraper when the playground opens, brushing aside the knowledge that Lakhta Center will in case of something make a lightning rod. Lightning moves in "segments" of several tens of meters and can change direction in any of these areas. On the same frame, one can see how the main blow falls not on the spire, but on the ground or into the bay behind the tower.
And in this video - as lightning changes direction in different segments.
Schoolchildren know most about lightning, and scientists least of all. For the former - a paragraph in the textbook, for the latter - a real terra incognita. The scientific community discusses dark, invisible lightning - very rare and powerful, sprites, jets and elves - phenomena during a thunderstorm in the upper atmosphere and inside a thunder cloud, positive lightning - from earth to sky, ball lightning, their cosmic origin ...

The first color image of the sprite, taken in the near-Earth atmosphere. Photo source
There are a lot of secrets. With their clue, one problem - catching a lightning explorer is incredibly difficult. No one knows where he will hit next time, and the flash itself will last a moment. This year, a special complex was sent to the ISS that will study light phenomena in the upper atmosphere. With the bottom - in the old fashioned way. We need to look for places where the probability of catching lightning is highest. One of these places at one time was the Empire State Building . General Electric engineers equipped a laboratory on the 102nd floor of the tower - from there they made slow-motion flashes, the results were used in a project to study voltage surges in electrical networks during thunderstorms. Here is the contribution of skyscrapers to the scientific business.

Photos - Museum of Innovation and Science Schenectady
Generally, lightning can be very helpful. They can send Marty home and charge light bulbs for free.

We hope that sometime with the lightning not only armed neutrality will be established, but also true friendship. Then we will get the batteries, put them on the tower and become even more environmentally friendly and energy efficient than they are now. Yes, by the way, we can be congratulated - the other day Lakhta Center became the first Russian skyscraper to receive the highest Platinum level in the international LEED green certification system.

***
For assistance in preparing the material, thanks go to our specialists - Dmitry Matveev, head of the direction of facade and metal structures and Vasily Balakshin, head of the direction of electrical systems of JSC "MFC Lakhta Center"

Photo ch0col8te
We will understand!
Greek rode across the river
On the Internet there is a bike about ancient navigators.
')

Photo of the trireme from here
Allegedly, even then the Greek sailors really knew how to ward off the Thunderer’s anger in an ingenious way. A sword was tied vertically to the mast; a cable was attached to it; the ends — into the water. It sounds doubtful. In order to come up with something similar, you need to understand the nature of lightning. The Greeks understood that on Olympus, another family quarrel, save yourself who can, why the sword?

And even if by some accidents, after thousands of triumphs flooded by Zeus, it was possible to reach an understanding that lightning was perfectly caught by the copies and xyphos, then the chain was interrupted. Steel cables from the ancient Greeks was not, and those that were - flax, have a relatively high resistivity. Use this as a guide - and the further journey by swimming is almost guaranteed. If time jump from a burning vessel, of course. If you are really lucky, you will sail to the shore and tell you how wrongly to threaten Zeus with a sword from the mast.

Painting "Odyssey and Navsikaya", Rosa Salvator, Museum of Art of Los Angeles, ca. 1655 Source
Of course, maybe it was not the cables that were there, but the chain or the winding wire, or the cable, was soaked well before putting it into operation. And in general, they were versed in the properties of electricity, conductors and dielectrics ... But for some reason this very useful knowledge further sunk into oblivion, having emerged centuries later. But there was definitely another tool, which even the police had to struggle with.

Thunder and lightning! Three thousand devils!
In the Middle Ages, the scientific paradigm turned upside down - Jupiter and Thor went into oblivion, and in a thunderstorm saw the machinations of the devil.

Destruction of the Catholic Church. Engraving by Mathias Gerung, Germany, 1547. Source
The climatic weapon of the epoch is the bell ringing, because, as is well known , “the first strike of the bell leads the impure force to numbness, on the second strike, it rushes in dismay in all directions;

Sinister Mephistopheles flies over Wittenberg. Lithograph of Eugene Delacroix, 1828
How many belfries burned down and the obscurantists fell in this struggle, for centuries they did not count. But later entries are evidence of a deadly risk:
“In the Journal de Paris, in August 1807, the parishioner Puzhibe, a more pious than an experienced person, told about Trulsky (near Toulouse), who, hearing thunder, ran to the belfry and began to call with all his might for disgust of thunder. The Trul mayor, who knew physics better than Pujibe, hurried to church to stop the ringing; but it was too late: the miserable Pujibe lay on the floor, struck by thunder. The editor of Journal de Paris says on this occasion: "Here is a new example of the danger of ringing bells during a thunderstorm."
Place of events - Toulouse, photographer Florian Calas (Florian Calas)
Or, from the notes of the Paris Academy of Sciences:
“In 1718, August 15, a strong thunderstorm rose in Lower Brittany; thunder, booming strong, struck at twenty-four churches, located between Landernau and Saint-Paul-de-Leon; in all these churches they called to put off the thunderstorm; in which they did not call, they remained intact ” (This and other cases can be found in the Edinburgh New Philosofical Journal, v. 20, collected by Robert Jameson)
In general, at least in France, it has been forbidden to ring the bells during a thunderstorm for 30 years by official order of the police. With other medieval ways to prevent weather trouble, for example, by showing some parts of the body through the window, I think, it’s also finished. After all, they finally found - safe and working tools.

Classic lightning protection as it is
In the 18th century, Benjamin Franklin - the one whose face is well known to many on another occasion, invented a lightning conductor. In 1752, he installed a metal rod on the roof of his own house, connected by the same metal wire to a well in the courtyard.

Franklin lightning protection scheme. Figure Wdchk. A source
This lightning conductor repelled the first attack of heavenly electricity 34 years later. Successfully. Perhaps the idea of such a construction was already in the air electrified by the discoveries by that time. In Russia, lightning explores Lomonosov and Richman, and industrialist Akinfiy Demidov builds the Nevyansk tower 57, 5 meters high.

A source
The tower then fell on the coat of arms of the city, a silver coin of the Bank of Russia in 2007, and 5 Ural francs (in 1991 it was like this) - for its “significantness” in history and architecture: the tower deviates from the vertical - 1.85 m.

But on it - the first domestic lightning rod, 25 years before Franklin. The design is similar: metal spire plus grounding.

A source
Since then, mankind has become victorious over lightning. First - in court. Bourgeois Villiers, who installed the novelty on the roof of the house, fought off the claims of his neighbors, who considered the lightning rod a dangerous undertaking. On the defense side - Maximilien Robespierre, on the prosecution side - Jean-Paul Marat - an incredible time! During the 4-year trial, the court sided with Villiers and lightning rods. In Paris, umbrellas and hats with lightning protection are becoming popular.

In the states and without similar stories, the number of lightning rods is in the hundreds. Franklin's circuit - the lightning rod - current lead - grounding, today is considered classic. Nothing better has been thought of yet: the efficiency of a good classical lightning rod approaches 99%. This is what our chief engineer commemorated this stormy September.

Why does the Franklin lightning rod work?
Franklin, like Lomonosov, and Richman, came to understand the electrical nature of lightning, and then - to the main thing: you can “pull” electricity from the atmosphere by catching a lightning on a conventional copy. Franklin’s described experience of launching a kite into a thundercloud today is being questioned, but somehow, he arrived at the right conclusions in good health, unlike Richman’s Russian colleague, who paid for his life with science. The properties of the conductors were already open, the rest is a matter of engineering ingenuity and the matter of technology.

From 1860 to 1890, a US dollar vignette with a kite experiment from Franklin’s experiment was only a 10-dollar bill, and only later would he rub the inventor on 100-dollar bills.
The fundamental point in the classical system of lightning protection is one. Provide a continuous circuit from the reception of the discharge to its grounding using a conductor. It can be said that such a system predicts and realizes the intention of the lightning itself. The electric celestial guest wants exactly the same thing - not to break through the thickness of the air insulator, but to bring the multi-polar particles to the connection with the least effort. And people offer her the path of least resistivity.

Photo by Patrick Fisher. A source
What it looks like in the tower of Lakhta Center
So, we need a current collector of metal. The metal spire of the tower fits perfectly - more than 100 meters up the pure conductor!

But - not only him. The profile of the frames of the double-glazed windows of the Supertoll shell is also metallic, the metal is in the elements of the facade service system.

Catch the lightning tower can all the height. This is important - the blow does not always fall on the highest point, and thunderclouds may be below the spire.
After receiving the discharge goes to the current leads. In the steeple, their role is played by steel columns-pipes, below - galvanized steel plates. The plates surround the floor perimeter and are connected to a reliable chain by vertical trunk lanes located in the body of the perimeter columns and the core shell.

The current from the outer shell passes through the flexible conductor (in the red sheath) to the metal plate-current lead around the perimeter of the floor

The vertical highway for the discharge of electrical discharge - through, passes from the top to the bottom of the tower without separating the floors and is the main lightning conductor for the skyscraper. She goes
to minus marks, where the lightning protection circuit of the tower is connected to the ground loop of the Multifunctional building. From there, electrons rush along the reinforcement cage of MFZ piles deep into the earth and, finally, meet with protons, zeroing somewhere in the ancient strata of Precambrian clays.
Can lightning melt the facade or spire of a tower?
Of course, lightning temperatures are terrifying. "Leader" - forvad discharge, comes to temperatures of 30 thousand degrees Celsius! Five times hotter than the core of the earth, 30 times hotter than the lava that destroyed Pompeii, Herculaneum and Stabiae in an instant. Yet the tower’s spire withstood three lightning attacks in September and remained unchanged.

Photo by Victor Gusik
All because the lightning flies the way from the current collector to ground at supersonic speeds - more than 1000 kilometers per second! Electric particles complete their route so quickly that the metal simply does not have time to heat up and melt. If there were links with high resistance in the chain or the impulse itself lasted much longer, then the outcome, of course, could have been different.
Cell protection
Inside the tower spire there is a navigation and communication equipment, SOF systems and other electrical equipment. If a lightning strikes the spire, what will happen to it? And in general with the rest of the electrical equipment of a skyscraper?

Such a situation is standard - in all Lahta Center's electrical switchboards there is protection against impulse overvoltages. As for directly placed in the spire, a curious detail is added here. The Lahta Center spire itself is similar in structure to the Faraday cage - the cellular structure of the metal facade, a closed and grounded contour give the effect of shielding an electrical impulse and protect the equipment inside the spire.

Grid of the facades of the spire of the tower Lakhta Center
Is it dangerous to stay in Lakhta Center during a lightning strike?
In September, this issue excited many who had plans to visit the observation deck in the tower of the complex. Do not be afraid. In a thunderstorm it is safe to be absolutely on any habitable level of the Supertoll. The observation deck from the main current operator, the spire, separates the concrete floor at level 88 - it can be considered the roof of a building. All potential paths of lightning current deviation from the line laid for it are reliably blocked: glass is in itself a dielectric, as is concrete, enveloping the cores of the columns and forming the core body.

Metal plates-conductors in the body of the column are encased - a thick layer of concrete acts as an insulator
In general, lightning strikes skyscrapers quite often. The old-fashioned gentleman among the super-high "youth", the Empire State Building, receives its annual "light strike" in the amount of from 12 to 100 and so far none of its visitors have already suffered for the nearly century-long history of the building. Like a visitor of any other skyscraper.
Impression hunters
Most often, a lightning strike to a skyscraper is a light show for those who are watching from the side, while the inhabitants may not even suspect that around them is a real tesla show. This is exactly what happened during the September thunderstorms with those who worked in those bright moments in the tower of Lakhta Center. About thunderstorms and lightning learned from numerous photos, in response to a request to share experiences - threw up their hands. The whole storm worked, did not look, it's a shame! In general, in a skyscraper in a thunderstorm, not only is safer, but sometimes much more boring - all the most interesting things are opened from the side.

Here, for example, the photographer Mohhamed Azmi tells how he hunted behind the scenes for two years, where lightning strikes a skyscraper - waiting in bad weather on the roofs of nearby buildings.

All for the sake of this frame
And what can be seen from the observation platform of a skyscraper, being there in a thunderstorm? In some places, the design features allow you to observe the climax scenes of the heavenly drama. For example, such lines can be seen in the material about the sights of the Australian skyscraper Q1:
“... In addition to surfing, theme parks and balloon flights, visitors to Australia’s popular Gold Coast can add another attraction to their list of thrills: head to Surfers Paradise suburb and watch the lightning strike the Q1 landmark - while it's cozy inside. him ... According to one source, visitors like to lie on the floor during a thunderstorm to see how lightning strikes an impressive 97.7-meter spire Q1. Judging by this incredible image, it must be a damn interesting experience, and certainly not for the faint of heart! ”
Photo by Ann VB
Those who go to watch the thunderstorm from the Lakhta Center overview, beating in the spire of lightning, unfortunately, cannot be seen - everything will happen beyond the upper ceiling. But the lightning striking below is quite likely to be caught. All you need is a good forecast and a bit of luck.
Does the tower draw lightning?
The September thunderstorms at the Lakhta Center’s tower thundered well in social media and media. So good that there were all sorts of guesses about the nature of an atypical phenomenon.

78 wash
First, such thunderstorms were not seen forever. Secondly - lightning strikes the highest point, and the Lakhta Center tower is known to be the highest in Europe ... Coincidence?

The explanations that lightning occurs under certain weather conditions and no skyscraper can change the climate, even the main weather forecaster of St. Petersburg, Alexander Kolesov, had to give. In our turn, we would be glad if the Lakhta Center could make every summer and autumn in St. Petersburg as warm as the past, but with regret we have to admit that the specialist was right: neither the tower could change the weather, nor even the complex as a whole. .

For very suspicious, there is even a small historical demonstration. Before the tower was completed, tower cranes served as lightning rods.

Despite the fact that these cars were the highest point on the construction site, there was not a single case of lightning entering a crane - summer did not spoil the previous years.
This year abnormally warm September led more than one thunderstorm front. And it is good that the tower was completed - otherwise the lightning could have chosen another target, and it is not known what or who would have become it. On the other hand, one should not rely entirely on such an impressive “lightning rod” - there are not rare cases when the Thunderbird aims the wrong way.
When a skyscraper in a thunderstorm is dangerous
Here is an impressive frame with a thunderstorm, made quite close to the tower. Besides the lightning itself and the skyscraper, the only, but potentially very dangerous situation is also captured here.

There are calculations, according to which up to half of the victims of lightning strikes hid under tall trees. The tower is not a tree, but during a thunderstorm it is imperative to take shelter in the building and absolutely not to aim impressive shots from the amphitheater or from some lawn next to the skyscraper when the playground opens, brushing aside the knowledge that Lakhta Center will in case of something make a lightning rod. Lightning moves in "segments" of several tens of meters and can change direction in any of these areas. On the same frame, one can see how the main blow falls not on the spire, but on the ground or into the bay behind the tower.
And in this video - as lightning changes direction in different segments.
Someday marty will go home
Schoolchildren know most about lightning, and scientists least of all. For the former - a paragraph in the textbook, for the latter - a real terra incognita. The scientific community discusses dark, invisible lightning - very rare and powerful, sprites, jets and elves - phenomena during a thunderstorm in the upper atmosphere and inside a thunder cloud, positive lightning - from earth to sky, ball lightning, their cosmic origin ...

The first color image of the sprite, taken in the near-Earth atmosphere. Photo source
There are a lot of secrets. With their clue, one problem - catching a lightning explorer is incredibly difficult. No one knows where he will hit next time, and the flash itself will last a moment. This year, a special complex was sent to the ISS that will study light phenomena in the upper atmosphere. With the bottom - in the old fashioned way. We need to look for places where the probability of catching lightning is highest. One of these places at one time was the Empire State Building . General Electric engineers equipped a laboratory on the 102nd floor of the tower - from there they made slow-motion flashes, the results were used in a project to study voltage surges in electrical networks during thunderstorms. Here is the contribution of skyscrapers to the scientific business.

Photos - Museum of Innovation and Science Schenectady
Generally, lightning can be very helpful. They can send Marty home and charge light bulbs for free.

We hope that sometime with the lightning not only armed neutrality will be established, but also true friendship. Then we will get the batteries, put them on the tower and become even more environmentally friendly and energy efficient than they are now. Yes, by the way, we can be congratulated - the other day Lakhta Center became the first Russian skyscraper to receive the highest Platinum level in the international LEED green certification system.

***
For assistance in preparing the material, thanks go to our specialists - Dmitry Matveev, head of the direction of facade and metal structures and Vasily Balakshin, head of the direction of electrical systems of JSC "MFC Lakhta Center"
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/434212/
All Articles


