How to scale down databases in Yandex. Cloud without downtime. Three hosts example
The post was prepared by members of the Yandex.Oblaka team: Ivan Vettsov - architect, Leonid Klyuev - editor
 Recently, we talked about the architecture of Yandex . Oblaka . Now let's move from theory to practice. There are several services in the Cloud for automated DBMS control: Managed Service for ClickHouse, Managed Service for PostgreSQL and Managed Service for MongoDB. All of them are platform-based and allow you to focus on the task of storing data, and not on administering the infrastructure. But sometimes it is important to control the cluster virtual machines as well. For example, a scaling problem may arise in response to an increase or decrease in load. Usually this scenario is one of the most time consuming from a practical point of view. Today, we’ll tell you how Yandex.Oblako allows you to automate complex scaling tasks, and make sure that the database remains available during the cluster resizing process.
Recently, we talked about the architecture of Yandex . Oblaka . Now let's move from theory to practice. There are several services in the Cloud for automated DBMS control: Managed Service for ClickHouse, Managed Service for PostgreSQL and Managed Service for MongoDB. All of them are platform-based and allow you to focus on the task of storing data, and not on administering the infrastructure. But sometimes it is important to control the cluster virtual machines as well. For example, a scaling problem may arise in response to an increase or decrease in load. Usually this scenario is one of the most time consuming from a practical point of view. Today, we’ll tell you how Yandex.Oblako allows you to automate complex scaling tasks, and make sure that the database remains available during the cluster resizing process.
Formulation of the problem
When creating a cluster of each service, the user can determine the number of cluster hosts and the availability zone (availability zone, AZ), which corresponds to the physical data center. Yandex.Oblako currently uses three Yandex data centers located in the central region of Russia. Therefore, the recommended configuration is a cluster of a DBMS with three hosts - as the most consistent with the principles of building a fault-tolerant and disaster-resistant architecture.
So, let us imagine a situation where the load on the database cluster has exceeded the capabilities of the base and it is time to add computing resources. This can be done both horizontally - by adding hosts to the cluster, and vertically - by adding resources to each cluster machine. Consider the second option, as the most time-consuming and at risk of errors. Why is this option laborious? Because in the general case, the procedure for adding resources will look something like this: switching the role of the host; if necessary, stop the DBMS; turn off the virtual machine; change its configuration; we start; change the parameters of the DBMS; run the DBMS; waiting for the synchronization of accumulated data changes. And so for all three hosts in turn. Many steps - the risk of a mistake is high. You can automate this process - only before starting the selected automation solution must be tested. Usually, there is not enough time for testing, but in Yandex. Cloud it runs quickly and without unnecessary actions on your part. Let's get started
Preliminary steps and testing process
For preparation we will need:
- Access to the platform. Now, anyone can set up a trial period on the site on Yandex . Obscure .
- The cloud network (I will call it testvpc in my example) and three subnets located in different AZ. The address ranges of subnets are not important in this case.
- Bastion host. Despite the fact that in Yandex. Oblak you can open external access to the database through a public IP, publishing a publicly accessible database is not the right solution. Therefore, we will add to the scheme a bastion host, from which we will open connections to the hosts. As such a host, you can use a machine with a partial (5 percent) use of the kernel. On the virtual machine, you must install clickhouse-client . In addition, according to the instructions for connecting to the service, you need to download an SSL certificate.
- CLI. We will work with Yandex. Oblakom not via the console, but through the command line utility, which must also be installed and initiated according to the documentation .
The test script will be simple: we open three sessions connecting the bastion host to each host of the database cluster, run a SQL query in a loop with a period of, say, 1 second, after which we send the command to scale the cluster and look at the behavior of the system.
Moment of truth
Choose a DBMS to demonstrate scaling. In PostgreSQL, hosts are assigned roles, but the service does not yet have their transparent switching when scaling - this functionality is in our plans. For the rest, the mechanics of cluster expansion and reduction are about the same in the case of all three DBMSs, for example, let's take ClickHouse.
Let's create an experiment object - a cluster consisting of three hosts located in different virtual subnets. To do this, enter the commandyc managed-clickhouse cluster create with the necessary arguments. The order of the arguments corresponds to their listing in the output of “yc --help”. The essence of the command is simple: we create a ch-to-resize cluster in a production environment with a testvpc virtual network, set a name and password, 10 gigabytes of disk space and a minimum class of s1.nano. The following characteristics correspond to this class: 1 CPU, 4 GB RAM. In the future, for scaling, we move on to the class s1.micro so that the number of CPU and RAM doubled. To find out what other classes of hosts you can assign, just enter the commandyc managed-clickhouse resource-preset list .
Thus, the team to create a cluster should be as follows:
yc managed-clickhouse cluster create --name ch-to-resize --environment production --network-name testvpc --host zone-id=ru-central1-a,subnet-id=e9bfnjacigdo9p6j7j2s,assign-public-ip=false,type=clickhouse --host zone-id=ru-central1-b,subnet-id=e2l8iamol3b9mrtskb8q,assign-public-ip=false,type=clickhouse --host zone-id=ru-central1-c,subnet-id=b0c6qit7u9e8r0egedvj,assign-public-ip=false,type=clickhouse --user name=test,password=test123123 --database name=testdb --clickhouse-disk-size 10 --clickhouse-resource-preset s1.nano --clickhouse-disk-type network-nvme –async In response, we get the cluster ID and the list of hostnames of its hosts:
yc managed-clickhouse cluster list +----------------------+--------------+-----------------------------+--------+---------+ | ID | NAME | CREATED AT | HEALTH | STATUS | +----------------------+--------------+-----------------------------+--------+---------+ | c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p | ch-to-resize | 2018-12-10T08:59:09.100272Z | ALIVE | RUNNING | +----------------------+--------------+-----------------------------+--------+---------+ yc managed-clickhouse host list --cluster-id c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p +-------------------------------------------+----------------------+---------+---------------+ | NAME | CLUSTER ID | HEALTH | ZONE ID | +-------------------------------------------+----------------------+---------+---------------+ | rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net | c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p | ALIVE | ru-central1-a | | rc1a-sgxazra54xv6lhni.mdb.yandexcloud.net | c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p | UNKNOWN | ru-central1-a | | rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net | c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p | ALIVE | ru-central1-b | | rc1b-j1rtvsuz6t8x6ev2.mdb.yandexcloud.net | c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p | UNKNOWN | ru-central1-b | | rc1c-emo0f2990povj7ie.mdb.yandexcloud.net | c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p | UNKNOWN | ru-central1-c | | rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net | c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p | ALIVE | ru-central1-c | +-------------------------------------------+----------------------+---------+---------------+ Open a connection to each host and run a query to the database:
clickhouse-client --host rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net --secure --user test --password test123123 --database testdb --port 9440 -q "select concat(host_name, ' is alive\!') from system.clusters where replica_num = 1" clickhouse-client --host rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net --secure --user test --password test123123 --database testdb --port 9440 -q "select concat(host_name, ' is alive!') from system.clusters where replica_num = 2" clickhouse-client --host rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net --secure --user test --password test123123 --database testdb --port 9440 -q "select concat(host_name, ' is alive\!') from system.clusters where replica_num = 3" Finally, send a request to increase the cluster:
yc managed-clickhouse cluster update --id c9q7cr4ji2fe462qej8p --clickhouse-resource-preset s1.micro -–async If we want to reduce rather than increase the amount of resources, then we need to specify a smaller class, referring to the conclusionyc managed-clickhouse resource-preset list — for example, s1.nano. In this case, the structure of the team itself remains the same.
I redirected requests to the file. Here is an abbreviated listing:
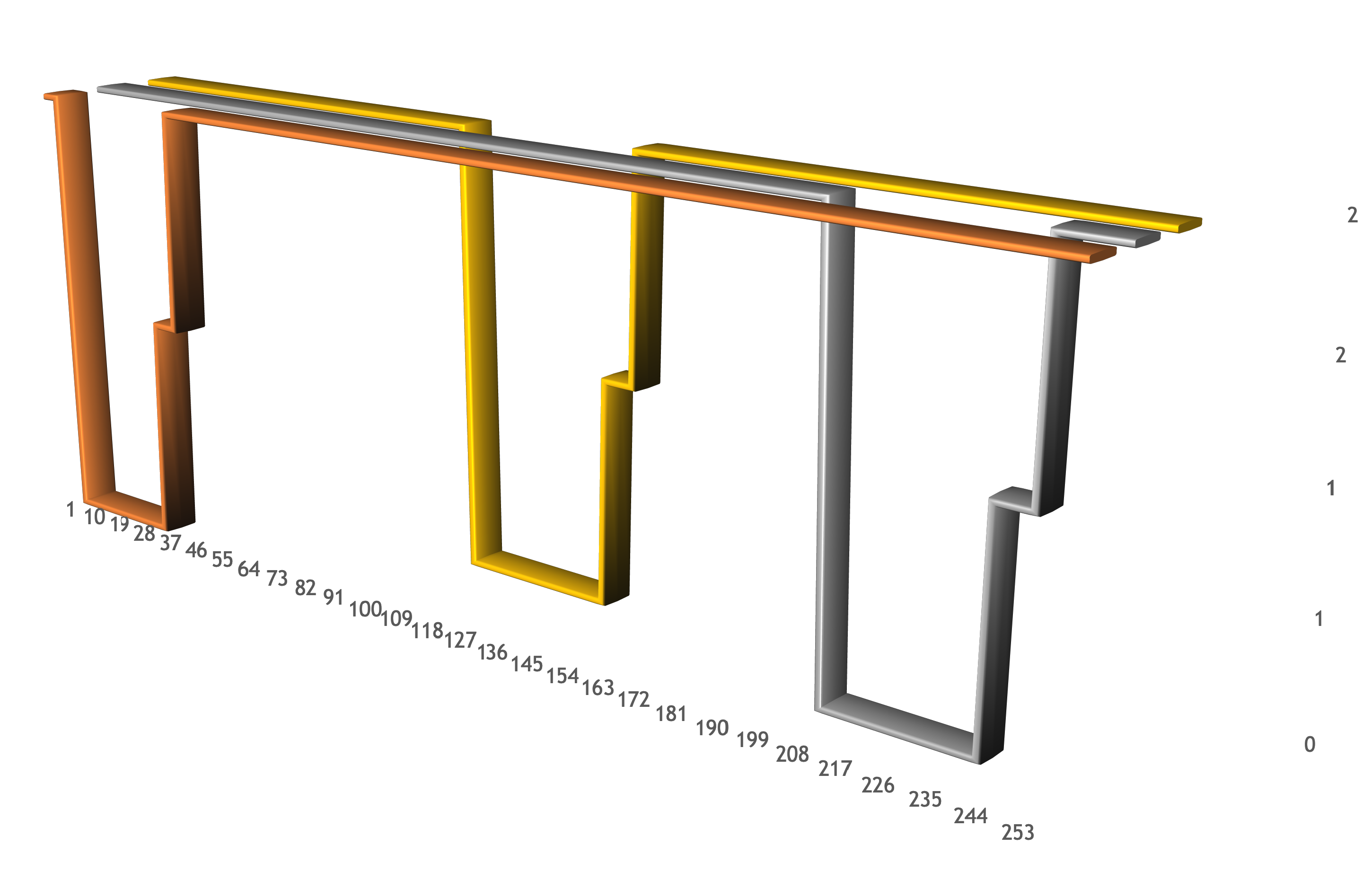
rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net Mon Dec 10 12:47:35 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:47:36 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:47:37 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:47:38 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:47:39 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:47:40 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.7:9440: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:47:51 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.7:9440: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:02 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.7:9440: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:11 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:12 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:13 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:14 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:15 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:16 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:17 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.7) Mon Dec 10 12:48:18 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:48:19 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:48:20 UTC 2018 rc1c-wcxq53lq096m0o6h.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net: Mon Dec 10 12:50:58 UTC 2018 rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:50:59 UTC 2018 rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:51:00 UTC 2018 rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:51:01 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.6:9440: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:12 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.6:9440: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:23 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.6:9440: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:34 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.6:9440: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:35 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:36 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:37 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:38 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:39 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:40 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:41 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:42 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:43 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.6) Mon Dec 10 12:51:44 UTC 2018 rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:51:45 UTC 2018 rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:51:46 UTC 2018 rc1a-qysm9t78x5ybdb78.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net: Mon Dec 10 12:49:15 UTC 2018 rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:49:16 UTC 2018 rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:49:17 UTC 2018 rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:49:18 UTC 2018 rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:49:19 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.8:9440: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:49:30 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.8:9440: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:49:41 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.8:9440: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:49:52 UTC 2018 Code: 209. DB::NetException: Timeout: connect timed out: 192.168.58.8:9440: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:49:56 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:49:57 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:49:58 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:49:59 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:50:00 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:50:01 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:50:03 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:50:04 UTC 2018 Code: 210. DB::NetException: Connection refused: (rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net:9440, 192.168.58.8) Mon Dec 10 12:50:05 UTC 2018 rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:50:06 UTC 2018 rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! Mon Dec 10 12:50:07 UTC 2018 rc1b-2t82xtpscgr4gi6j.mdb.yandexcloud.net is alive! In the listing, you can see the moments of shutdown of each cluster host (when connect time out starts), moments when the host turns on and ClickHouse starts loading (when the connection refused starts), as well as moments when the host returns to the system. The most important thing is the separation of time periods when the hosts were unavailable. As long as the scaling went on, at least two hosts were available for querying. This can be seen on the chart:
Conclusions and best practices
At first glance, the development of projects with databases includes a large amount of routine work. The database needs to be maintained, that is, backed up, adjusted to the process of regularly updating the DBMS, etc. Cloud management services appeared first of all in order to remove these labor-consuming functions from you. However, in a real production-environment, it is useful that the systems are not only manageable from the point of view of maintenance, but also flexible - responsive to the rise and fall of load. We told how to increase the performance of the database in Yandex. If the base is configured correctly, then with the growth of traffic there is an increase in the volume of available resources, and during a decline - a multiple decrease, which also reduces your costs.
What approaches, tools, or technologies on a cloud topic would you like to know? Offer in the comments topic for the following posts Yandeks.Oblaka.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/433814/
All Articles