A step closer to the HIV vaccine: a study of titers of serum neutralizing antibodies in monkeys

Newcomers from far space, killer robots, nightmare monsters, demons and other evil spirits - these characters often cause the destruction (well, or attempts) of humanity in movies and literature. However, this is all fantastic. Real monsters are diseases that are very, very much. And to fight each of them, we need, as a rule, a unique weapon. One of the most terrible "monsters" among ills can rightly be called HIV - the human immunodeficiency virus, which received the status of the plague of the twentieth century for a reason. For many years, scientists around the world have been looking for ways to combat the virus and ways to protect against it. And now a little ray of hope appeared on the horizon. Namely, a study that confirmed the production of immunity to one of the strains of HIV in primates. How did the scientists achieve this, what results did the experiments show, and how soon do we wait for the HIV vaccine? The source of the answers to these questions will be the report of the research group. Go.
Earlier, I already touched on the topic of HIV in an article describing a study of the new method for diagnosing this virus ( Analysis of the speed of molecular micromotors for HIV diagnosis ).
')
A brief theoretical digression (hid under a spoiler, so as not to repeat, because this text was in the above article):
Talking about illnesses is unpleasant, but necessary. The more we know about them, the better we can protect ourselves and our loved ones from their impact.
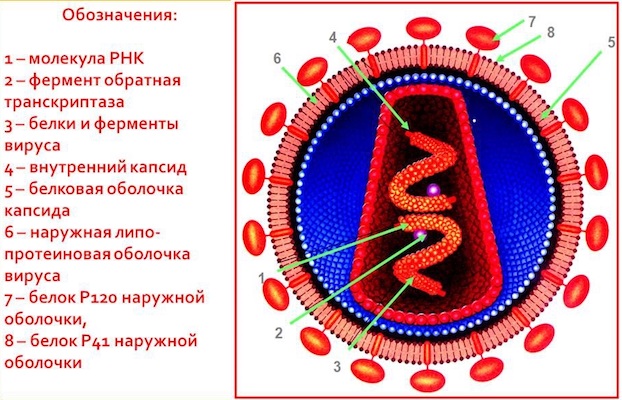
HIV - the human immunodeficiency virus first showed its terrible grimace in the early 80s of the last century. Then no one knew what it was, and the virus itself did not even have a name. Further research has shown that HIV is a retrovirus that infects the cells of the human immune system, one of the most important systems. The result of the work of the virus is the suppression of the immune defense and the development of AIDS, an acquired immune deficiency syndrome. In this state, the body remains defenseless, and any, even the lightest, infection (as well as cancer cells) can have a dramatic effect on it. In essence, HIV destroys our defenses and enemies in the face of infections quietly seize the body.
HIV has a contact mechanism of transmission. Infection can occur through contact with blood, semen, breast milk, pre-seminal fluid, or vaginal secretions. In other words, unprotected sexual intercourse, infected medical instruments, even non-disinfected needles in tattoo parlors are a great way for the virus to spread. During the period of the emergence of HIV, when panic among the population was spreading faster than reliable information about what HIV is and how it spreads, it was believed that you could get infected with a simple handshake. This is a myth, because the virus does not spread through a simple touch with an infected person. However, this type of infection is also possible, but only in the case of open wounds in the hands of an infected and possible victim of infection. I’m not even talking about the fact that some people considered mosquitoes to be carriers of HIV (the mosquito drinks the patient’s blood and, having bitten a healthy person, can infect it) is also a myth.
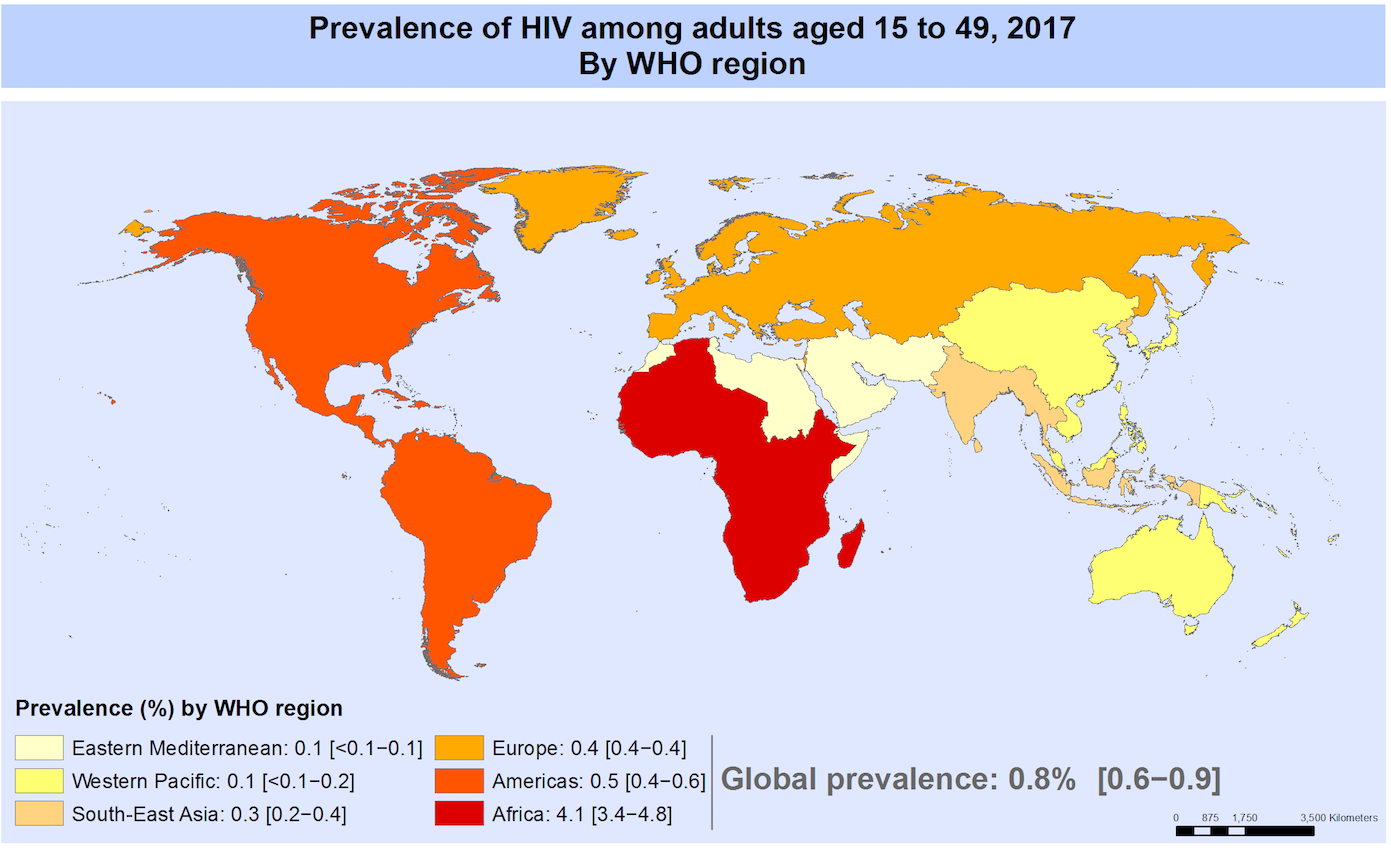
The prevalence of HIV in the world according to the World Health Organization (2017).
I will not describe in detail the virus and the consequences of its development in the body, because we are going to discuss not so much the virus itself, as a new method for its diagnosis. But it is worth noting that HIV is a patient virus that can mutate in the body of an infected over time, which makes it even more resistant to various methods of containment or treatment. This is another reason why it should be discovered as soon as possible. The more time the virus has, the stronger it is, and the weaker the infected person.

HIV - the human immunodeficiency virus first showed its terrible grimace in the early 80s of the last century. Then no one knew what it was, and the virus itself did not even have a name. Further research has shown that HIV is a retrovirus that infects the cells of the human immune system, one of the most important systems. The result of the work of the virus is the suppression of the immune defense and the development of AIDS, an acquired immune deficiency syndrome. In this state, the body remains defenseless, and any, even the lightest, infection (as well as cancer cells) can have a dramatic effect on it. In essence, HIV destroys our defenses and enemies in the face of infections quietly seize the body.
HIV has a contact mechanism of transmission. Infection can occur through contact with blood, semen, breast milk, pre-seminal fluid, or vaginal secretions. In other words, unprotected sexual intercourse, infected medical instruments, even non-disinfected needles in tattoo parlors are a great way for the virus to spread. During the period of the emergence of HIV, when panic among the population was spreading faster than reliable information about what HIV is and how it spreads, it was believed that you could get infected with a simple handshake. This is a myth, because the virus does not spread through a simple touch with an infected person. However, this type of infection is also possible, but only in the case of open wounds in the hands of an infected and possible victim of infection. I’m not even talking about the fact that some people considered mosquitoes to be carriers of HIV (the mosquito drinks the patient’s blood and, having bitten a healthy person, can infect it) is also a myth.

The prevalence of HIV in the world according to the World Health Organization (2017).
I will not describe in detail the virus and the consequences of its development in the body, because we are going to discuss not so much the virus itself, as a new method for its diagnosis. But it is worth noting that HIV is a patient virus that can mutate in the body of an infected over time, which makes it even more resistant to various methods of containment or treatment. This is another reason why it should be discovered as soon as possible. The more time the virus has, the stronger it is, and the weaker the infected person.
The essence of the study
Researchers note that at the moment a lot of attention is paid to several methods of protection against HIV. Among them, there are studies aimed at searching for cellular and humoral responses, and more specifically at stimulating neutralizing antibodies ( nAbs ) *.
nAbs * - antibodies that protect the cell from the antigen by neutralizing its effects at the biological level.Previously successful studies have been conducted with primates as subjects. As a result, immunization of the organism was achieved through nAbs acting on GP120 (HIV envelope glycoprotein). However, this method is effective only in relation to such types of virus as SHIV Ba-L and SHIV SF162-P4 , which are already quite weak. In other words, this study cannot be representative of those HIV strains that are common among people.
The nAbs-based technique has become extremely popular among researchers because it allowed for complete immunization in monkeys and mice through the use of monoclonal antibodies ( mAbs ) * that neutralize HIV.
mAbs * are antibodies produced by immune cells from a single plasma progenitor cell.nAbs can be an excellent base for creating a vaccine that neutralizes HIV strains with a higher degree of resistance. However, for this it is necessary to combine several techniques together, which the scientists did in this study.
The main tools of scientists in this study were the developments of predecessors, namely SOSIP trimmers * and the artificially recreated infectious SHIV.
Trim er * is a complex molecule, the formation of an oligomer from three molecules.SOSIP trimers are immunogens that work at the level of the envelope glycoproteins (Env) of human immunodeficiency virus.
But to test the effectiveness of these immunogens, an “adversary” in the person of the virus itself is needed. And since the experimental animals in this study were macaques, it was necessary to create a SHIV (monkey / human immunodeficiency virus) with the same Env sequence as the immunizing trimer. This was made possible thanks to previous studies that recreated SHIV on the basis of a Level 2 HIV strain.
Using the above techniques, scientists were able to immunize the SOSIP macaques with trimers based on the Env sequence BG505. After the introduction of BG505-specific nAb level 2, macaques were infected with the neutralization-resistant pathogenic strain SHIV BG505 .
Scientists have found that the protection of the body against the virus directly depends on the level of titers * of serum nAb, while other parameters of antibodies are much less important: antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, T-lymphocyte activity, etc.
Titre * - the maximum or optimal dilution of antigens, antibodies or complement, which can register a positive reaction between antigens and antibodies or standardize the reaction on one or both components. ("Great Soviet Encyclopedia")The researchers determined the titer threshold for this vaccine in order to experimentally compare its effectiveness with the previous HIV-1 vaccine based on nAb.
Research results
Preliminarily, 78 monkeys were selected. Among them, after 3 procedures of immunization with BG505 Env trimers, a different level of autologous nAb titers of level 2 was observed.
Scientists had to divide the experimental into two main groups (low titer and high) in order to determine the degree of influence of differences between individuals on the formation of protection against the virus. 6 monkeys were selected, which showed the highest level of virus neutralization. Additionally, another 6 individuals were selected, whose nAb titer was extremely low. Representatives of both groups were mixed taking into account gender, age and weight. The control group consisted of 12 individuals.
In order to test how a vaccine works, it is necessary to first determine the optimal "quantity" of the virus, contributing to the infection of the subject from the control unvaccinated group. For this, scientists conducted a separate small study with two groups of 6 individuals each, which were infected with virions * SHIV BG505 S375Y grown in a T-cell Rh CD4 + . The number of virions was either 0.5x10 8 or 1.4x10 7 .
Virion * is a viral particle outside a living cell, which is active only after contact with a carrier cell, forming a virus-cell tandem.As a result, for the main study, the dosage of infection in 1.4x10 7 virions was chosen, since with this amount 4 out of 6 individuals were infected after the first infection, and the remaining two after the second infection.
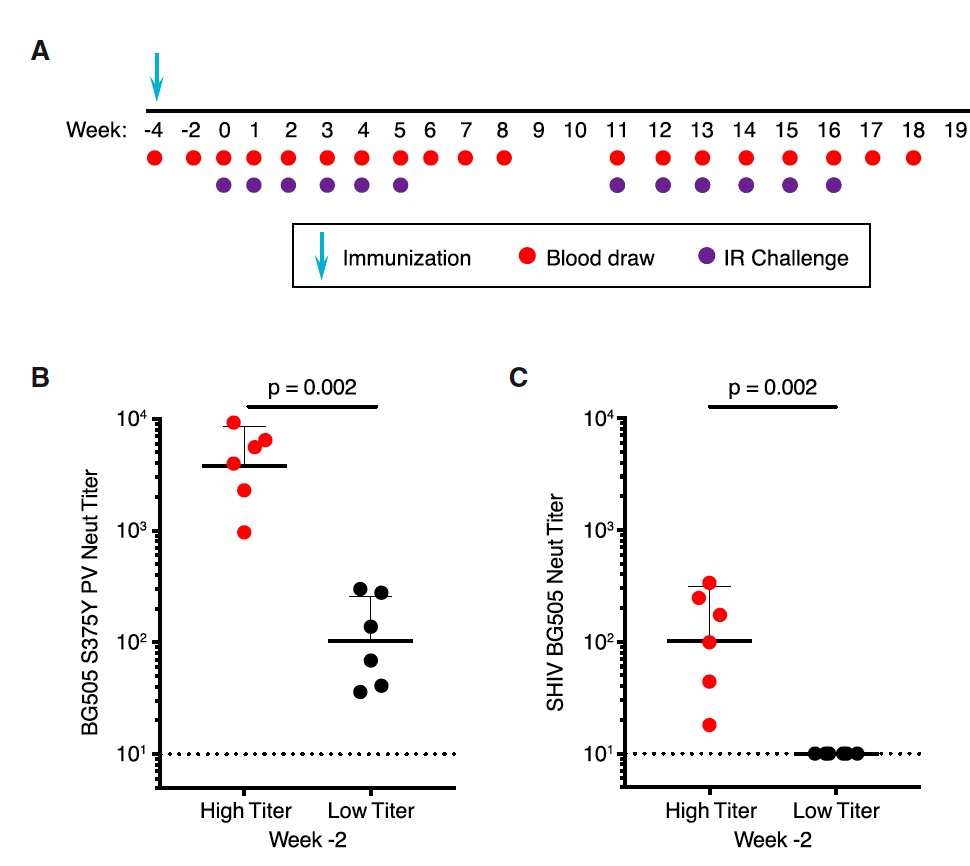
Image number 1
The main groups of subjects (low and high titer nAb) were also prepared by conducting 4 stages of immunization (image 1A ). After 2 weeks, all individuals responded to immunization by increasing the titers of autologous nAb, while the difference between this group was 1: 3790 for the high titer group and 1: 103 for the low group (image 1B ).
The neutralizing titers of rhesus CD4 + T cells of SHIV BG505 S375Y were 30 times lower than the average value when tested on target cells TZM-bl (image 1C ).
After 4 weeks after immunization, all individuals passed the 6-week stage of infection with SHIV strain BG505 .
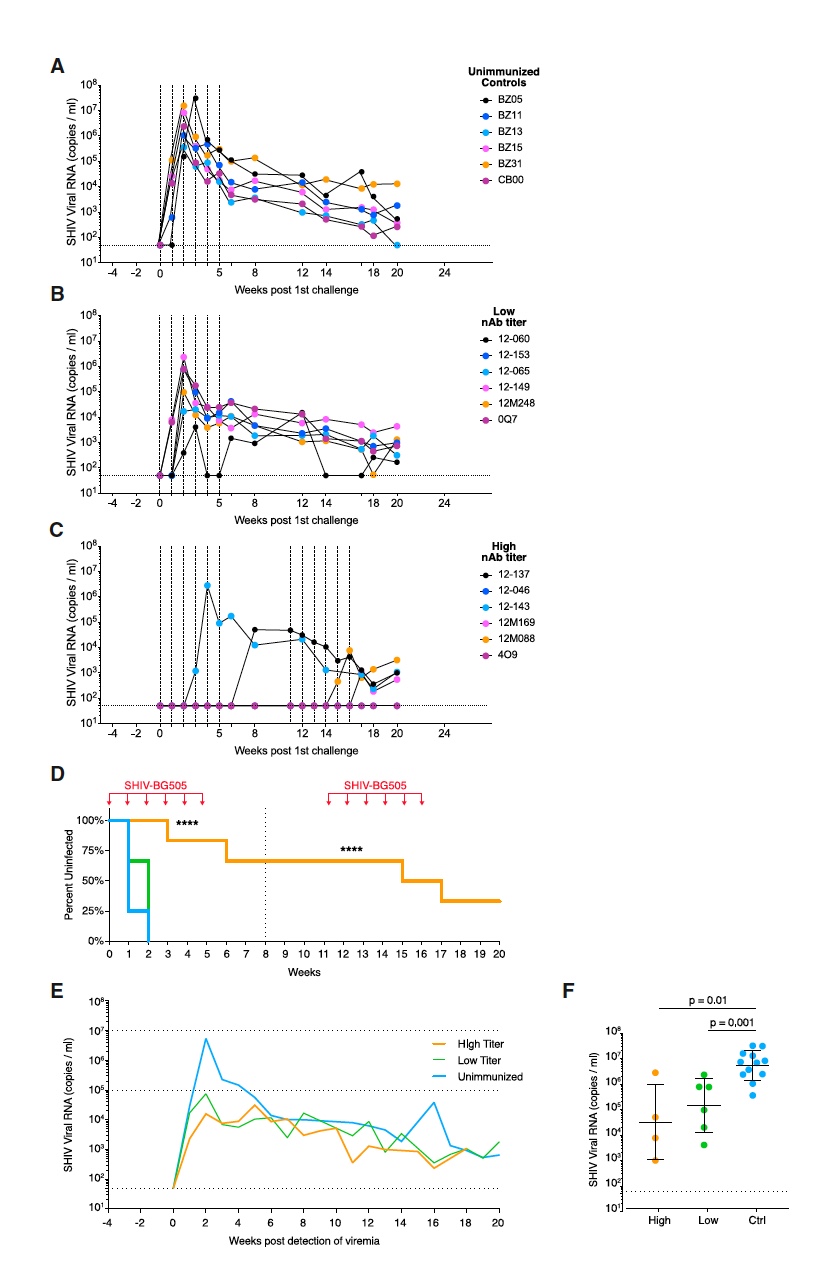
Image number 2
To improve the process of comparing the results of viral loads and time stamps were measured for all individuals on the sixth and twentieth weeks at the same time ( 2A - 2C ).
Of the six individuals that did not receive immunization, five were infected immediately after the first stage of infection. The remaining individual was also subjected to infection after the second stage ( 2A ). In other words, 9 out of 12 individuals from the control group became infected with the virus.
Scientists note that the dosage of the virus in 1.4x10 7 per 1 procedure of artificial infection is quite large, that is, it is difficult for the body to fight this amount of virions. Twelve weeks after infection, individuals that did not receive immunization showed peak viremia * . Viremia * is a condition of the body when the virus enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body. Of the six individuals with a low titer of nAb, two individuals became infected after the first stage of infection, and the remaining four after the second ( 2B ). Thus, it was confirmed that subjects with a low titer of nAb, although more resistant to the virus in comparison with subjects without immunization, but the difference is insignificant ( 2D ). However, individuals with low titer nAb still had a distinctive feature - significantly lower viral loads ( 2E ).
More importantly, the results of a group of subjects with high titers. In the eighth week of testing, this group showed a high level of resistance to the virus after the first stage of infection. On the 11th week, a second infection was carried out, the purpose of which was to determine the duration of the protection against the virus and the period at which the level of nAb titers is maintained.
The result of already two stages of infection was the infection of 4 individuals from the group with a high titer of nAb (after 3, 6, 10 and 12 viral "injections", respectively). However, 2 individuals showed complete protection ( 2C ) against the virus.
Despite infection, individuals from this group showed significantly lower peak viremia than individuals from the non-immunized group (2E). Against the background of these observations, scientists have put forward a theory: sub-protective levels of nAb in serum during infection, in conjunction with the activation of B-cells that stimulate the rapid production of nAb, reduce primary viremia, which reduces the viral load on the body.
As a conclusion, individuals with a high titer of nAb even after 11 attempts to infect them remained healthy and maintained the primary level of protection against the virus. While low titers or non-immunized individuals were extremely rapidly infected.
Next, the scientists decided to analyze the changes in the titer of nAb in different groups of subjects during all stages of the study. This made it possible to more clearly understand the relationship between the degree of protection from the virus and the level of nAb titer.
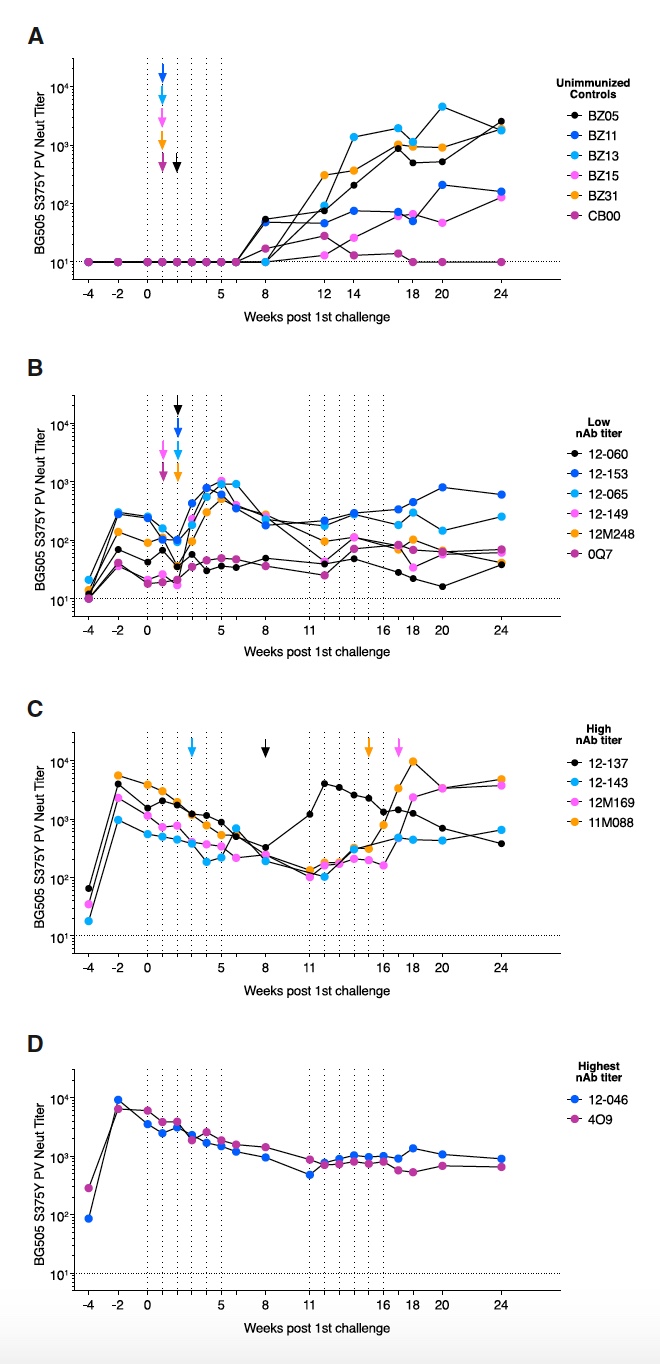
Image number 3
Individuals without immunization began to produce BG505 S375Y pseudo-viral ID 50 nAb titers 8-12 weeks after infection in response to SHIV BG505 S375Y ( 3A ). The low titer group had a reverse process — the nAb titer began to decline after infection, and only after 1-2 weeks it began to rise ( 3B ).
Infected individuals from the high titer group of nAb showed an increase in BG505 S375Y nAb titers 1-4 weeks after infection ( 3C ).
It is important to note that different individuals showed different results. The most significant were 2 individuals, which showed complete protection against the virus. They began to decrease the titer at the beginning of the test, but at the 10th week it began to grow and reached the level of 1: 800. After he remained at this level steadily until the very end of the test ( 3D ).
No less important, scientists believe and understanding of what other factors influenced the formation of protection against the virus, in addition to nAb titers. In short, analyzing the data of all subjects from the very beginning of the experiments to their completion, the scientists assure that the formation of the defense mechanism was not affected by either antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, or T-lymphocyte activity, or gp120 antibody. However, this statement requires clarification, since there may be other factors that in one way or another influenced the process of immunization of the test specimens.
For more detailed acquaintance with the nuances of the study I recommend reading the report of scientists, available here .
Epilogue
At the moment there are many studies aimed at finding methods for creating protection against HIV. This virus is very dangerous and cunning, considering its latent period. In the fight against it, everything is important: both treatment and diagnosis.
Perhaps the use of animals in scientific research and seem to someone a manifestation of cruelty, but it is worth a look from the perspective of these studies. Such experiences bring their results, opening up new ways to combat HIV, which affects millions of people. And it would be extremely cruel to argue that they deserve it.
Similar studies have already been done before, although they did show excellent results, but they were not applicable to humans, since the vaccines obtained worked exclusively on monkeys and could only cope with a certain strain of HIV, which is considered the weakest. Yes, the second type of HIV is not the most common, but finding a way to effectively deal with it or defend against it, scientists will be able to apply new knowledge in research related to HIV-1.
In any case, this study can not be called useless. Any knowledge, especially concerning diseases, is very important in the fight against them.
Thank you for your attention, remain curious, do not forget about your health and the health of others. Have a great weekend, friends.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps until January 1 for free if you pay for a period of six months, you can order here .
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/433630/
All Articles