Where does creativity come from: analysis of alpha brain wave activity during RAT tests

Many of us were looking for work at a certain stage of our life. And during the search we plunged into the Internet, reading a variety of ads from employers that contain many requirements: knowledge of PHP, knowledge of English, higher education, 534 years of experience, the ability to create a hadron collider from wire, two potatoes and chewing gum, standing on one leg on the back of an elephant dancing tap dance. Joking as a joke, but one of the most common requirements, in addition to communicability, responsibility, hard work, etc., can be called creativity. And have you ever wondered - what is creativity from the point of view of neuroscience? Not? Don't worry, I didn't ask either. But today's heroes of ours, scientists from the UK, decided to find out whether it is possible to measure creativity and express it as a certain specific value or indicator, like blood sugar levels. How our brain works when we show creativity; Is this “skill” universal? if we measure it, we will seek answers to these questions in the report of the researchers. Go.
The basis of the study
')
As we know, our brain is the most important organ. Yes, without a heart or lungs, we will not survive. Yes, all organs are important, all organs are needed (except for the appendix, probably, considering how many of us go around the world without it). However, the brain is our PCO, our headquarters, giving orders to everyone and everything in the body. Disruption of the brain does not always mean the end of the life of the organism, but it can change it very much and not for the better.

Not Santa Claus, but similar.
It is also worth noting that even intangible and immeasurable phenomena, such as love, kindness, hatred, or greed, can be directly linked to the activity of certain parts of the brain. I immediately recall the words of one gray-bearded grandfather in a white suit, no, I'm not talking about Santa Claus, but about the Architect from the Matrix: “I already see the beginning of the reactions. Chemical reactions. They will lead to a sharpening of feelings, which always suppress the voice of logic and reason. The feelings that prevent you from seeing the simple and obvious truth: it will die, and you can not prevent it. Love. The quintessence of human illusions. The life-giving source of your great strength and your great weakness. ”
Accordingly, if we can bind love to the work of the brain, then why not bind and creativity. The question remains - what parts of the brain are responsible for it, what processes take place in our central nervous system during the manifestation of creativity, and how is it all measured? And here, scientists who undertake a series of independent experiments on different groups of people whose brain (or rather, certain of its departments) were electrostimulated are taken to work. After analyzing the test results, the scientists came to a quite clear and intelligible conclusion, which I will not mention to you now, because it will be a spoiler, and no one likes spoilers :)
Semantic associative network (an example from the Internet).
Scientists explain the basic principles of creativity as follows: the basis of any creative (creative) process is the ability to create distant and least expected semantic associations. When a word appears in front of us, you start looking for concepts related to it, starting with the strongest semantic association. For example: toy - child - mother - family - people - earthlings. That is, we do not jump from "toy" to "earthlings" immediately. In the creative process, this concept looks different - we begin to consider even the most distant possible semantic links. In other words: the “ordinary” thinking process has a clear vector, while the creative has several vectors at once. This is a rough comparison, nonetheless.
At the same time, it remains unclear exactly what neural processes take place in the human brain at the time of creative thinking. That is, how creative people choose “the distant paths” rather than the “path of least resistance” in the process of thinking. The researchers note that their predecessors expressed a theory about reduced cognitive activity, when the brain begins to look for alternative (more creative) ways to solve a problem or problem.
And now let us proceed directly to this study and to those experiments on humans (sounds frightening, really), which were conducted by scientists from Britain.
Preparing for the experiments
A total of 4 different experiments were carried out, the results of which we will consider a bit later. A common goal for all experiments was to study the alpha rhythm of the brain during convergent and divergent thinking, and also to connect these two opposite processes.
Alpha rhythm * - important in this study that decreases during thought processes and with increasing attention.
Convergent thinking * - straightforward thinking, in the process of which a person, following a certain "algorithm", gradually performs some task or solves a problem.
Divergent thinking * - creative thinking, in the process of which a person does not limit himself in one way of solving a problem or task, but searches for alternative methods.
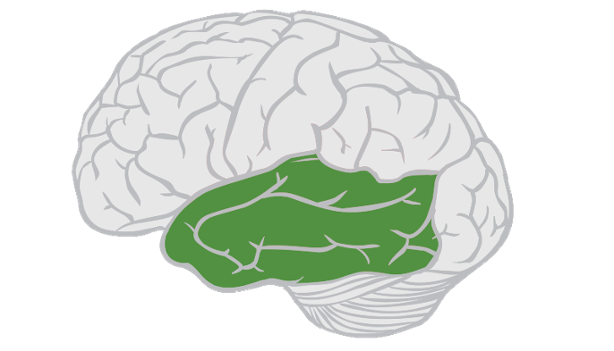
Temporal lobe of the brain.
The main, one might say so, the hero of the experiments was the right temporal lobe of the subjects' brain, since it is this region that is responsible for the semantic processes, the integration of related information and the recognition of these very connections between different concepts.
The first experiment was aimed at understanding the relationship between alpha waves of the right temporal lobe (10 Hz) during transcranial brain stimulation with alternating current (tACS). The subjects performed certain tasks from the category of “remote association task” (remote associates task or RAT). In this experiment, scientists assumed that stimulation of the right temporal lobe would lead to an improvement in the results of RAT tests containing common, but incorrect semantic associations, since performing such tasks requires searching for remote associations.
In the second experiment, the scientists analyzed the EEG (electroencephalography) indices of the subjects in response to RAT tests with common incorrect semantic associations and in response to RAT tests without associations. So say, comparative analysis.
In the third experiment, an individual alpha frequency (IAF) of the right temporal lobe was stimulated by tACS before, during, and after the “alternative use” test, during which subjects should name as many of the application options as possible.
Finally, in the fourth experiment, peaks of IAF were investigated during the “alternative use” test.
RAT test
This type of testing was first demonstrated by Sarnoff Mednik back in 1959. In this test, there are three words in front of the subjects (example of researchers: walker / main / sweeper, solution - street - streetwalker / main street / street sweeper). The subjects must find a word that will be compared to each of the three and form a new word. For example: laptop (laptop) consists of two words “lap” (knees) and “top” (above), that is, “laptop” can be translated as “on the knees”.

Sarnoff Mednick
As a rule, subjects during the search for word-solutions pay attention to the word-problems, trying to find a semantic connection between them. In this way of thinking, the trick is hidden - if two words from a task have a very close semantic association, which is not the right answer, then this may prevent us from finding the right solution to the problem.
For example, researchers quote the words ear and tone from the task ear / tone / finger. The first two words suggest an incorrect association with sound, which should lead to the correct “ring” answer. In other words, the first 2 words of the task have a common association, and the third remains on the sidelines.
In contrast, scientists give another example - high / teacher / mate, where there is no common association for any of the combinations of words. The solution to this problem is the word "school".
Thus, the ability to avoid the most obvious solution to the problem, paying attention to false associations, helps to solve these very tasks correctly. Creative people show better results in the process of performing such tests, but this has not been confirmed at the neurobiological level.
And now, in order and in more detail about each of the experiments.
Experiment I
The researchers note that manipulating alpha waves through external stimulation of tACS in laboratory (controlled) conditions is a great way to understand how much they influence the creative thinking processes during the execution of RAT tests and how they manifest themselves in the process of erroneous associations.
Some of the RAT tests had a common erroneous association for two of the three words in the problem, which was not the right solution.
In the experiment, 30 subjects took part, and there were only 3 stages: stimulation of the right temporal lobe, stimulation of the left temporal lobe and placebo stimulation (when the subjects thought that there was stimulation, but it was not).

Image number 1
As can be seen from graph 1A , stimulation of the temporal lobes played a large role in the experiment. We also see that the theory indicating the importance of the right temporal lobe in solving problems with an erroneous association is confirmed in practice. At the same time, if there were no erroneous associations in the test, then both the right and left lobes showed approximately the same result.
To determine the degree of importance of stimulation, scientists carried out calculations of the efficiency coefficient, such as the difference between the proportion of correct answers for one condition (stimulation of the right temporal lobe) and the average value of the proportion of correct answers for the other two conditions (stimulation of the left lobe and placebo).
The results of these calculations are shown in graph 1B . As we can see, stimulation of the right lobe shows a significantly higher efficiency ratio for solving tests. Also, scientists note that such a comparative analysis of only placebo and stimulation of the left temporal lobe did not show any striking differences, which once again extols the importance of the right temporal lobe.
Graph 1C shows a comparison of efficiency factors for all types of stimulations (left, right and placebo) with and without an erroneous association in the test task.
Graph 1D shows how effective the stimulation of the right lobe was in comparison with the left. When the right lobe was stimulated, the subjects coped better with tasks with a false association. But when the left temporal lobe was stimulated, the subjects coped with the same tasks worse than even without stimulation. Thus, stimulation of the left temporal lobe had a negative effect.
Experiment II
In the second experiment, the scientists decided to check how strongly manipulations with the alpha rhythm affect the occurrence of erroneous associations in the subjects (a new group of people) during the tests.
On the basis of the first experiment, 45 RAT tests were selected, which had erroneous semantic associations. And another 45 who did not have them.
Scientists conducted an EEG analysis, comparing the IAF scores in response to RAT tests with or without an erroneous association. The frequency and spatial differences of these two conditions were also compared.
The main theoretical basis for this experiment was the hypothesis that to solve the RAT test with an erroneous association, participants would have to concentrate more on avoiding this error trick in order to give the correct answer to the test task. That is, they will recognize the trick and try to get around it, and scientists will be able to fix it on the EEG. Scientists have suggested that during such tests, the IAF indices of the right temporal lobe will be significantly higher in comparison with tests without erroneous associations.
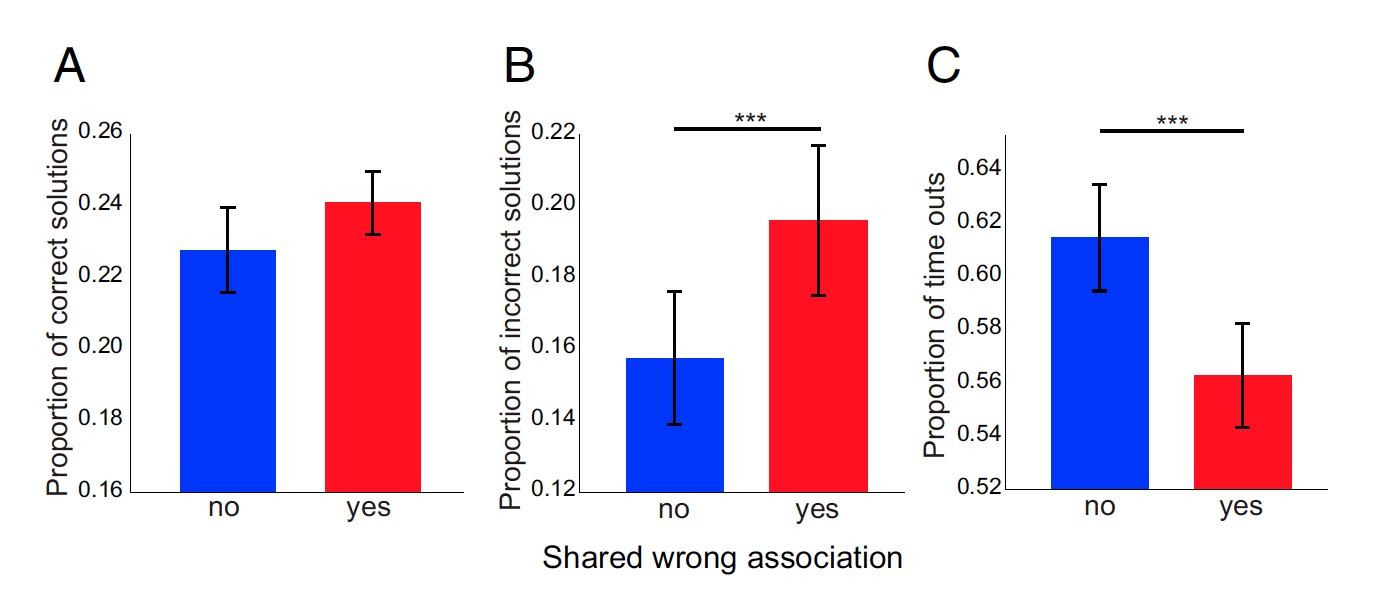
Image number 2
Graph 2A shows the overall results of the correct answers to tests with trick ( yes ) and without trick ( no ). But on the adjacent graph 2B , the proportion of incorrect answers to both versions of tests is already shown. And here we see that the participants made far more mistakes precisely in tests with an erroneous association (ploy), which the scientists supposed.
Graph 2C shows the percentage of tests when subjects did not give an answer at all. The expected peculiarity is also visible here - the subjects responded more confidently to tests with a general association, since many tried an erroneous association (ploy) for the correct answer. In other words, fast but wrong.
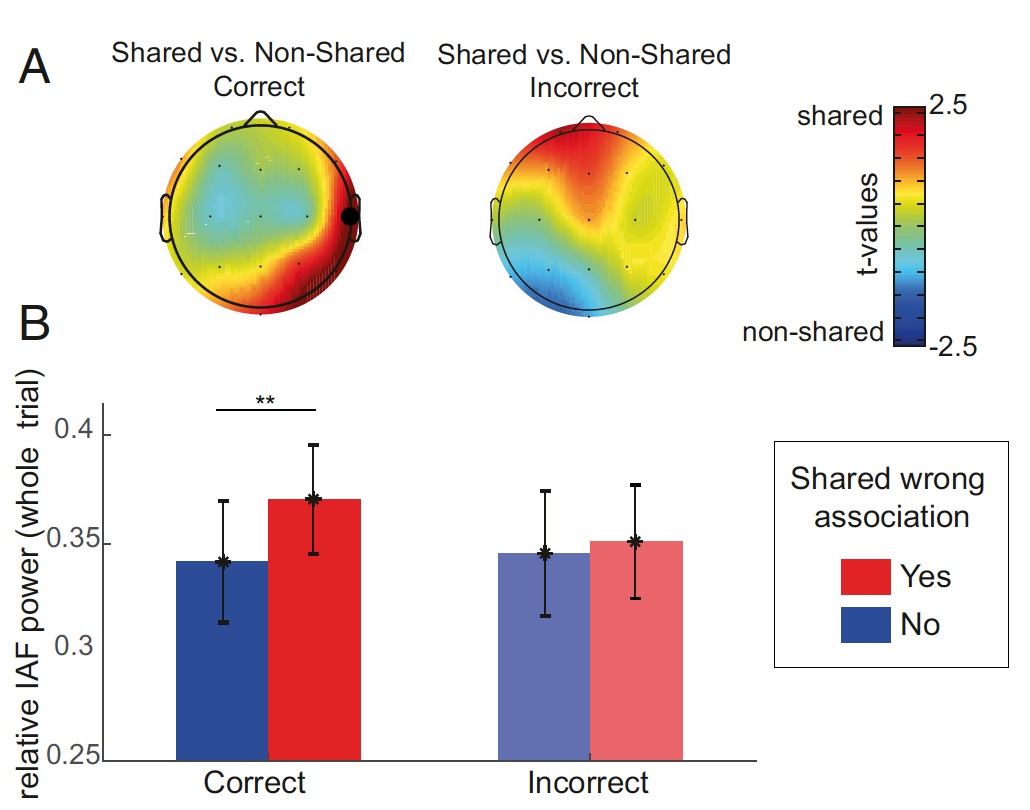
Image number 3
The IAF data underwent triple dispersion analysis taking into account various indicators (variables): erroneous association (yes / no); accuracy of answers (true / false); ROI - area of interest (right frontal lobe, left frontal, right temporal, left temporal, right parietal, left parietal and insular lobe).
Scientists have found that IAF is higher in the case of tests with a trick than without it. However, the rates varied depending on the area of interest (brain lobes).
As can be seen in image 3A , the IAF of the right temporal lobe is quite high with the correct solution of tests with an erroneous association. In the case of an incorrect decision of the tests, a large activity is observed in the frontal lobe of the brain. When the tests do not contain tricks, such IAF jumps are not observed. This confirms that in order to solve the problem in a more creative way, the subjects actively “use” the right temporal lobe of the brain.
Also, the researchers checked whether similar peaks of activity would be observed if manipulated with theta (4–8 Hz), beta (13–30 Hz) and brain gamma rhythm (30–40 Hz), that is, to conduct an experiment outside the alpha rhythm range (8 to 14 Hz). However, as expected, there were no unique and notable changes.
Experiment III
Scientists note that they perfectly understand the importance of the right temporal lobe in forming obvious associations, that is, in the process of convergent thinking. However, they are also confident that this area of the brain plays an equally important role in creative thinking. Therefore, this experiment was conducted, in which the degree of involvement of the right temporal lobe in the process of performing the “alternative use” test, which is the most basic method for determining the degree of divergent thinking in the subject, was determined.
Again, a new group of subjects was selected, who had to write as many alternatives as possible to the use of ordinary everyday objects. In the process, there were again three options for stimulation: left, right and placebo.
The lists (answers) of the subjects were given to three evaluators, who, at their own discretion, evaluated the answers by three parameters:
- creativity (creativity);
- remoteness from the main method of use (option: a pencil is to write this basic purpose, but to rush into the ceiling, like Agent Mulder, this is already a remote assignment);
- ingenuity / cleverness / cleverness.
First, the researchers conducted tests with the subjects before stimulation, the results of which showed that there was no particular difference between the participants in any of the above parameters.
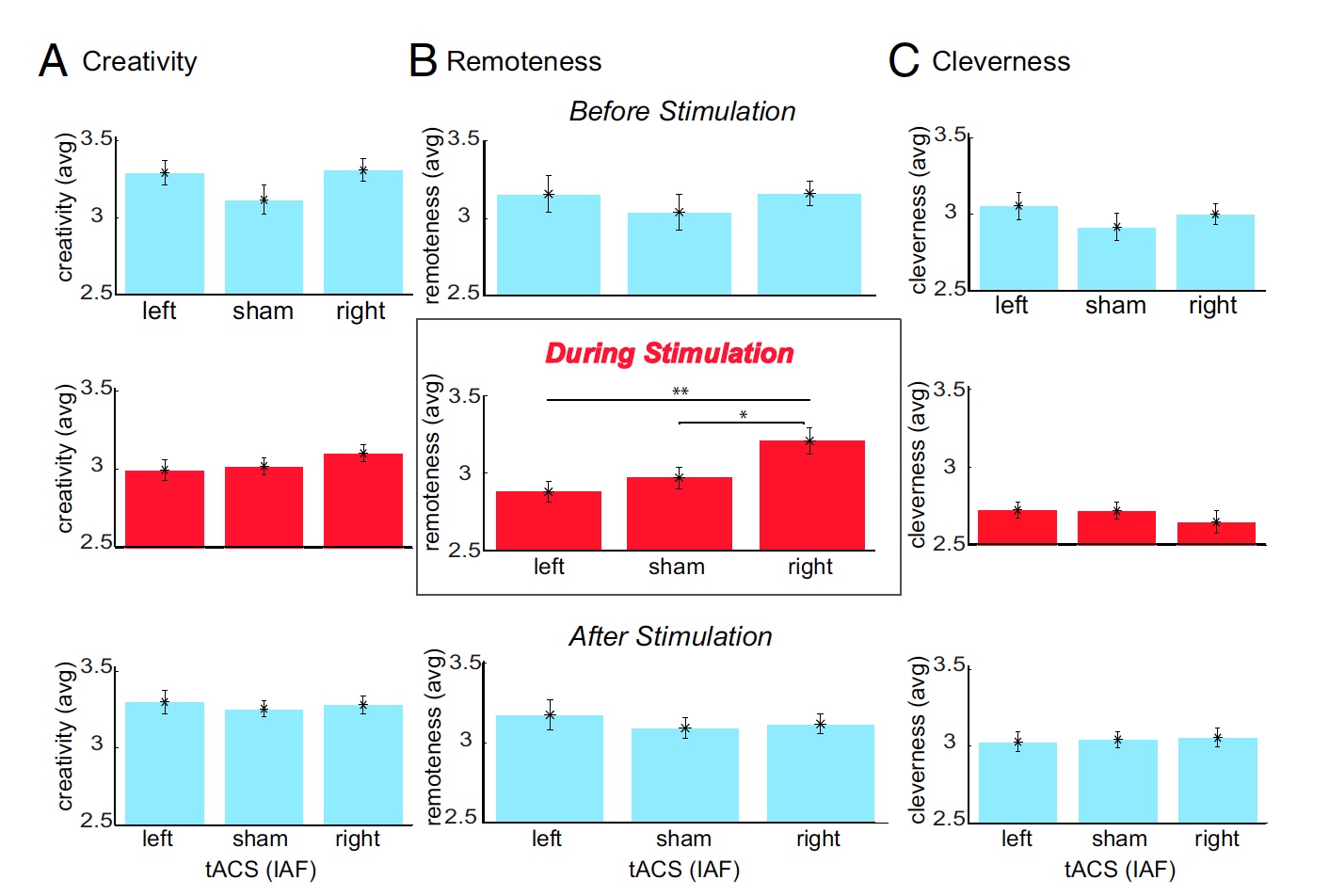
Image number 4
Already during the actual experiment, the researchers noted that the effect of stimulation was clearly pronounced, this was especially noticeable in terms of changes in distance indicators. But while the other two indicators (creativity and ingenuity) have changed slightly. There was also noticeable activity in the right temporal lobe (graph in the center of image 4B ).
Also, scientists conducted an analysis of the activity after testing, which showed its decline to the usual level. Thus, it becomes obvious that certain parts of the brain, which are necessary for solving problems in a creative way, are activated at the moment of solving these problems, and stimulation enhances their effect. If it is very exaggerated and roughly rephrase - creative skills are activated when it is necessary for a person.
Experiment IV
And finally, the final stage number 4 was aimed at a specific dimension of the IAF. More precisely, the new group of test subjects again passed the test with unusual ways of using quite ordinary objects, and scientists measured the strength of the IAF when they created each of the options separately, and not as a whole. In addition to observing brain activity by scientists, test results were analyzed by independent evaluators who were not familiar with the details of the experiment.
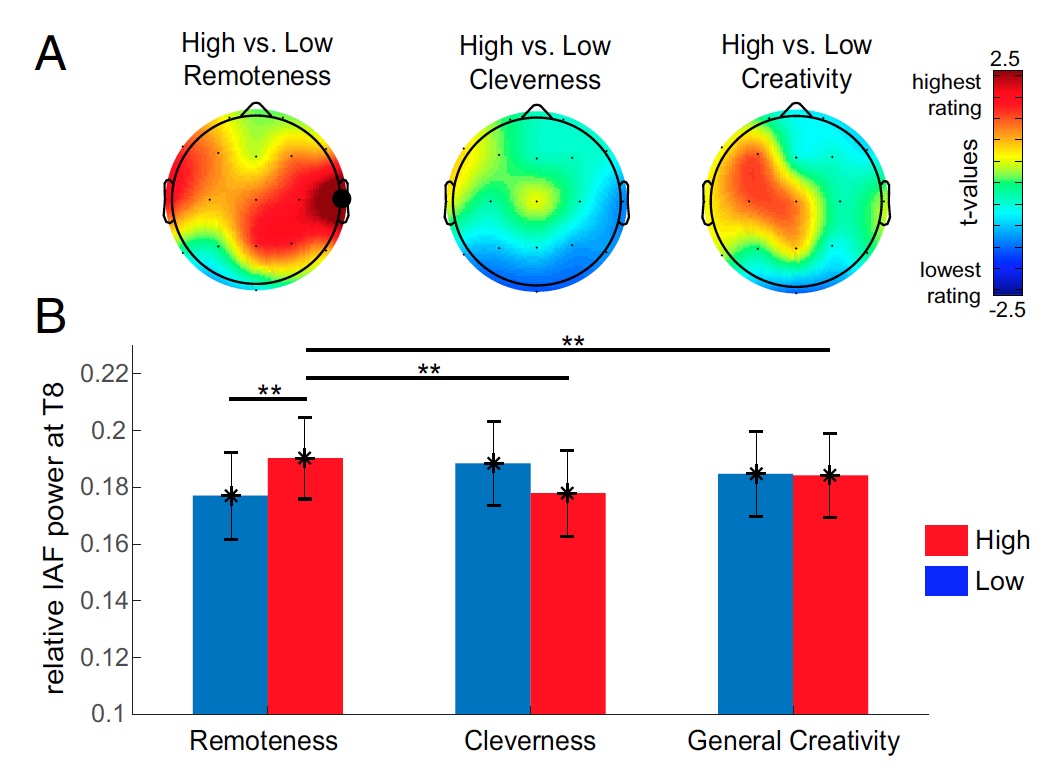
Image number 5
Scientists compared their observations and estimates of independent appraisers, highlighting a certain average value. The images and graphs above show results that either exceed this average level or are lower than it (image No. 5).
Figure 5A shows the brain activity topology (color corresponds to the level of test results, from low to high). And here we again receive confirmation that it is the right temporal lobe (these phrases I now type faster than my name) plays the most important role in creating the most “remote” answers. As for creativity and intellectuality, for these indicators the activity of the right lobe is not so clearly expressed.
For more detailed acquaintance with the aspects of the study (methods, calculations, etc.) I recommend to look into the report of scientists and additional materials to it.
Epilogue
Well, if we can still argue with the ancient Greeks and their belief that the human soul is in the liver, then the fact that the creative principle of man is in the right temporal lobe is no longer there. This study has expanded our knowledge of our most important organ, the brain.
The study of the human brain is easy to compare with the study of the expanses of the universe or the depths of the oceans, so mysterious and complex it is. We use this body constantly, without a break for lunch and weekends, but we still do not know all of its properties, characteristics, nuances.
Someone can show that we, people, do not need such knowledge. Well, the body works, let it work. But understanding how any mechanism works, especially as complicated as the brain, we can create new ways to diagnose breakdowns and new tools to eliminate them. In addition, no new knowledge, bearing the benefit, can not be called unimportant.
Thank you for your attention, remain curious, and have a good work week, friends.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps until January 1 for free if you pay for a period of six months, you can order here .
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/433428/
All Articles