Using DeviceLock DLP and Citrix Xen to control email on mobile devices
The professional community is seriously concerned about the risks of leakage of limited access information through corporate and personal mail from mobile BYOD devices. Practically at every data leakage conference, the question of controlling corporate mail on mobile devices running the most common Android and iOS platforms arises for most participants.
Let's try to deal with this issue.
Of course, the active use of personal mobile devices for business purposes, and above all for operational communications via e-mail, greatly simplifies the practical use of corporate data in production processes, increases employee productivity, mobility and efficiency.
As a solution to this problem, the application wrapper class solutions are most often offered on the market, in which technologies of insulating containers for mobile applications allow protecting information when a mobile device is lost, and all email communications of corporate applications are redirected via a VPN tunnel to an office DLP gateway is used to control the content of “container” mail. Another option that is applicable in a limited segment of critical ICs is expensive “secure phones”, which, in fact, are specialized software and hardware MDM solutions based on the reduced version of Android. There are also attempts to create a DLP-like agent for Android mobile devices, where traffic control really comes down to redirecting it to a VPN tunnel. Common to all of these corporate email protection options is the use of a DLP gateway or server monitoring email traffic received from mobile devices via VPN tunnels.
An important factor affecting the architecture of solutions to prevent data leaks from mobile personal devices is that, for various reasons, modern mobile operating systems do not ensure reliable operation of DLP agents. The iOS platform does not allow applications access to the OS kernel, whereas Android, on the contrary, is an open platform, which means that any user can get full administrative access to his Android device and remove the application — in this case, a hypothetical DLP agent, the most disabling control of transmitted data and prevent leakage of valuable information. Finally, we must not forget that personal devices always remain personal, even if they are provided by the organization - there are a lot of limitations of both organizational and technical nature. The complexity of access, the impossibility of automated centralized deployment, the lack of administrative control of a personal device by the IT service, etc. should be taken into account.
The network-centric DLP solutions behind corporate gateways and VPN tunnels are limited in many domestic products to the monitoring of email communications, and proprietary encryption in these protocols is fundamentally impossible for the MAPI and Lotus protocols - they fundamentally exclude the ability to analyze the contents of email messages after they are sent. In the case of MAPI and Lotus, content analysis is possible only up to the moment of sending, which requires the use of an agent-based DLP architecture and interception of messages by introducing its own code into the address space of the mail client processes.
Another dynamically developing direction of information security is the provision of access to information assets of the company through a remote connection to a sterile work environment created using virtualization solutions for work environments and applications. With regard to the prevention of leaks in mail communications on Android and iOS devices, this is achieved by providing remote access to corporate servers in general and service mail in particular through terminal sessions. At the same time, mail communications of each terminal session are monitored by a DLP agent running on a terminal server. In this model, an email client for working with corporate email is published as a virtualized application: for example, in Citrix XenApp, a user can work with an email client from any device - including Android and iOS mobile devices, and DLP control is implemented directly in the corporate virtualization environment on the terminal. server. To do this, a terminal client (for example, Citrix Receiver) is installed on the personal device by the user or the IT department of the organization, or any web browser that supports HTML5 can be used instead.
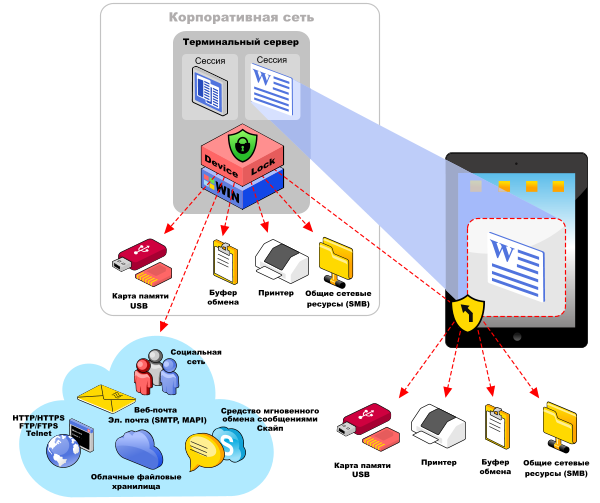
On the user side, in the organizational plan, the access model to the mail client through the terminal session is implemented quite simply - Citrix Receiver is available in the App Store and in the Play Market and without any difficulty is installed on any version of iOS and Android, and instructions for connecting to corporate mail client as a virtualized application will be quite compact.

The last, most important part of the model described is the DLP system that controls email communications in a virtualization environment. An agent of the DeviceLock DLP software complex, installed on the terminal server, provides context control and content filtering of network communications for each session of the virtual corporate environment. DeviceLock Virtual DLP technology allows you to intercept email messages directly from an email client application that is available in Citrix XenApp, which is accessed by the user through a terminal session, and in real time check the message context (attachments, email identifiers) and content (content a) messages and attachments for their compliance with the DLP policies set for this user. If a violation is detected, the restricted access data transmission is blocked in order to prevent their leakage, a corresponding log entry and a shadow copy of the transmitted message with attachments are created, and an alarm alert is generated for processing as part of the IS incident management procedure.
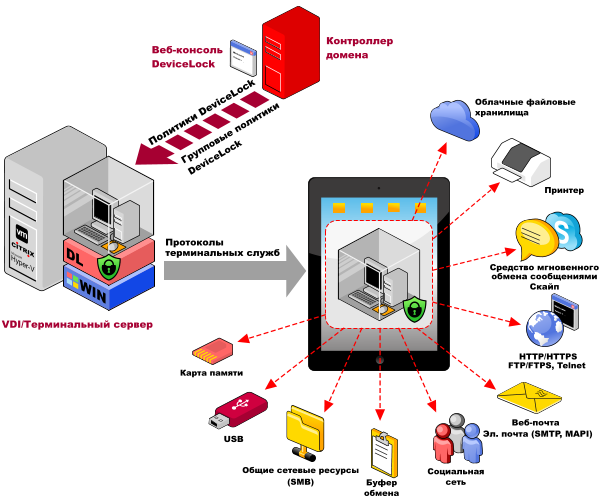
Virtual DLP differs from the solutions described above for c task redirection of traffic to the VPN tunnel and analysis of mail communications at the DLP server level primarily because the user does not have access to the data in the mail clients as such, but to their graphical representation in the terminal session. In addition, Virtual DLP uses an agent-based control option for network communications, when control functions are performed directly at the point of origin of the traffic. Only in such an architecture is it possible to intercept data before encrypting it with proprietary protocols both in mail, such as MAPI and messengers (for example, Private Conversations in Skype). In addition, real-time verification of the contents of data transmitted via the clipboard and removable drives redirected from a personal device to a terminal session of the desktop or application is ensured, which is equally important for protecting from corporate data leakage from BYOD devices than controlling mail .
It is worth noting that DeviceLock DLP allows you to control all common mail protocols - SMTP / SMTP over SSL, MAPI and IBM / Lotus Notes, and users need to install and configure only the application for terminal access on their mobile device. Moreover, due to the use of DeviceLock Virtual DLP technology, full control of various options for using personal mobile devices in various models of using virtualization solutions (BYOD, “home office”, thin clients), built on virtualization platforms and terminal access from Microsoft, Citrix, VMware and other manufacturers - companies can fully control not only email communications, but also corporate virtualization environments in general, transmitted to any personal devices udnikov, including mobile, as well as any other remote device on all operating systems.
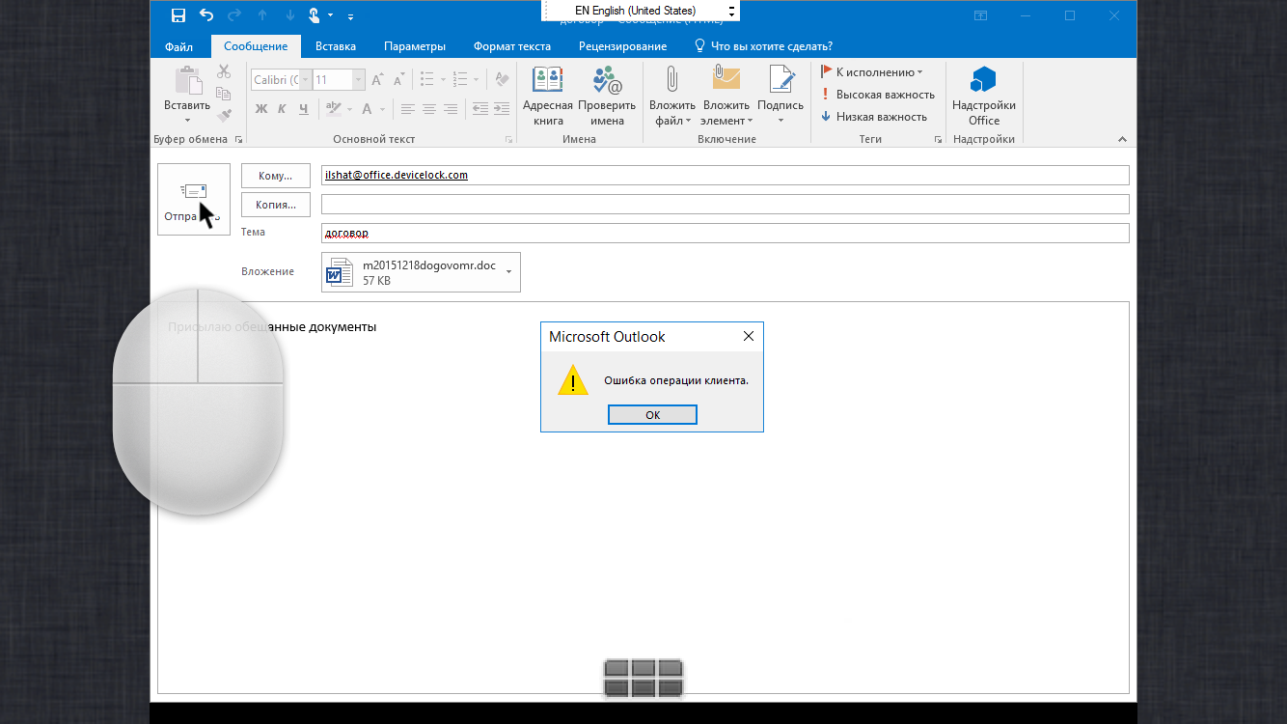
Nota bene: Of course, it should be borne in mind that working with a full-fledged email client on a smartphone with a tiny screen will be completely impossible, and talking seriously about using Outlook, especially older versions, on 4-inch screens at 800x480 resolution is not serious. But if we take as a virtualized email client a more “compact” application in terms of saturation with different interface elements, equip a device with a quality screen of a larger diagonal - the situation changes dramatically. Again, you shouldn’t forget the organizational and technical aspect - if an employee needs mobile access to email communications by occupation, why not provide him with a tablet or a light ultrabook?
On the tablet screen, even a full-fledged Outlook becomes really usable, as can be seen in this figure.

In the next article, we plan to describe in more detail how the control of data flows in terminal sessions in Virtual DLP technology is arranged. Stay in touch!
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/432642/
All Articles