Autumn aggravation: how RTM hackers staged a massive attack on banks and businesses on behalf of state institutions

This fall, Group-IB recorded a massive malicious mailing to financial institutions and enterprises. The attackers sent more than 11,000 letters from the fake mailing addresses of Russian state institutions - all of them contained an RTM Trojan designed to steal money from remote banking services (RB) and payment systems. On average, one successful theft of this type brings about 1.1 million rubles to attackers.
Text: Semen Rogachev, Group-IB Malicious Code Analyst
Since September 11, the Group-IB Threat Intelligence system (cyber intelligence) recorded mass mailings to Russian banks, industrial and transport companies: 3210 letters were sent in September, 2311 - in October, 4768 - in November, and 784 - in December. Mailings went “waves”, the peak fell on September 24 and 27 - 729 and 620 letters, respectively. In total, from September to early December, hackers sent 11,073 letters from 2,900 different e-mail addresses forged by government agencies. Found about 900 different domains associated with the addresses of senders.
')
In the mailing list, among the addresses of senders, are the following domain names associated with state and municipal organizations:
- 14.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Sakha Republic
- 22.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Altai Territory
- 33.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Vladimir Region
- 37.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Ivanovo Region
- 38.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Irkutsk Region
- 39.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Kaliningrad Region
- 42.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Kemerovo Region
- 47.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Leningrad Region
- 89.fsin.su - UFSIN of Russia in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District
- engels-edu.ru - Education Committee of the Administration of Engelsky Municipal District
- enis.gosnadzor.ru - Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Atomic Supervision ROSTEKHNADZOR Yenisei Department
- fbuz29.rospotrebnadzor.ru - Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Arkhangelsk Region
- fcao.ru - Federal Center for Analysis and Evaluation of Technogenic Impact
- fguz-volgograd.ru - center of hygiene and epidemiology in the Volgograd region
- gov39.local - Government of the Kaliningrad region
- mcx-samara.ru - ROSSELKHOZNADZOR Department of the Samara region
- minsoc-buryatia.ru - Ministry of Social Protection of the Republic of Buryatia
- minsoc26.ru - Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Population of the Stavropol Territory
- minzdravsakhalin.ru - Ministry of Health of the Sakhalin Region
- mosoblsud.ru - Moscow Regional Court
- prokuratura.omsk.ru - The Prosecutor's Office of the Omsk Region
- rcro.tomsk.ru - Regional Center for Education Development, Tomsk (Regional State Institution)
- rostrud.ru - Federal Service for Labor and Employment ROSTRUD.
- rpn.gov.ru - Rosprirodnadzor - Federal Service for Supervision of Natural Resources.
- zdrav.spb.ru - Official site of the Committee on Healthcare of St. Petersburg.
- zsib.gosnadzor.ru - Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision ROSTEKHNADZOR.
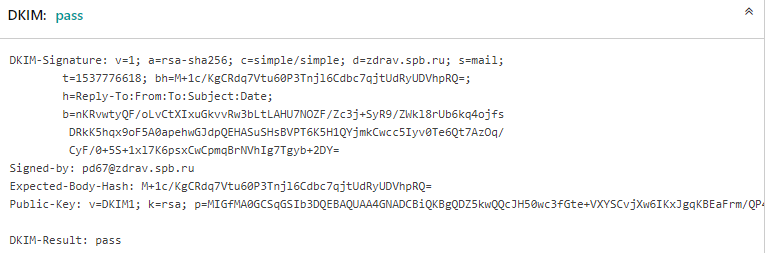
Some letters include the headers of "Domain Key Identifier Mail" ("DKIM"). “DKIM” is an email message authentication method that protects senders from tampering with email and confirms the fact of sending a letter from a stated domain. For example:

The result of the test "DKIM":
How the circuit worked
Letters from the newsletter are disguised as important documents (for example, “Submission on Thursday”, “Service Note”, “Payment August-September”, “Copies of documents”, etc.) are indicated as the subject of the letter. The text of the letter corresponds to the topic, for example:

Or:

A characteristic feature is the discrepancy between the sender's address and the return address of the letter. The return address of the letter is registered on public domains.
For example:

Or

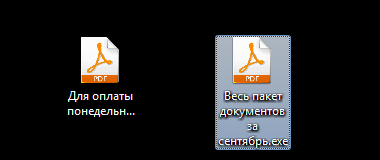
Each letter is attached attachment, which is an archive containing the executable file. Unpacked files have “PDF” icons - files, which further misleads the user. After running the unpacked file, the computer is infected.
RTM Trojan appeared in late 2015 - early 2016. It is aimed at working with RBS and payment systems. RTM is modular, its modules substitute details, read keyboard presses, replace DNS servers and security certificates, take screenshots, etc.
Infection process
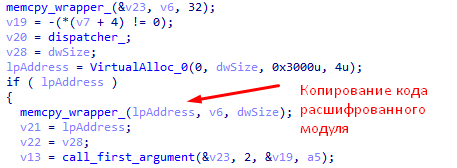
- After launch, RTM unpacks the “DLL” library and stores it in the “% TEMP%” folder, and then loads it into the address space of the current process.
- After unpacking, it copies the unpacked contents of the “.tmp” file into “% ProgramData% \ random_folder \ random_name”.
- Creates a task with the name “Windows Update” to launch the file copied in the previous step through “rundll32.exe”.
- If the creation of the task did not succeed, add the “Windows Update” key with the value “rundll32.exe% ProgramData% \ random_folder \ random_name DllGetClassObject host” to the “HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Run \” registry key. This allows the file from the "% ProgramData%" directory to be launched each time a user logs on to the system.
Description and functionality
- The strings in "RTM" are encrypted with a modified "RC4" algorithm and decrypted before use.
- After launch, it checks the presence of the files “Cckoo”, “fake_drive”, “strawberry”, “tsl”, “targets.xls”, “perl”, “wget.exe”, “* python *” on the “C” disk , "Myapp.exe", "self.exe", "vboxservice.exe", "python.exe". In the case of finding, completes the work.
- Checks for the presence of antivirus "ESET". If it is installed, it fills its license file with zeros, and then deletes it.
- Starts tracking keystrokes on the keyboard. If the active window was created by the browser “Mozilla Firefox” or “Internet Explorer”, the “URL” of the page is added to the data received from the keyboard.
- Tracks and saves data that falls into the clipboard. The name of the window from which the information was copied and the time are added to them.
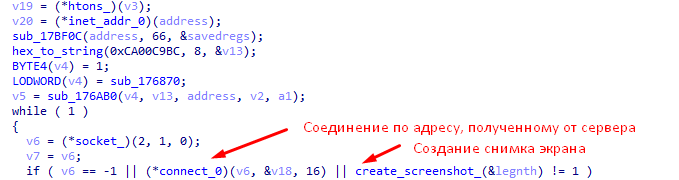
- Keeps track of pressing the left mouse button on items whose class name matches “tpanel” and “obj_button”. When you click on these items, it takes a screenshot and sends it to a remote server.
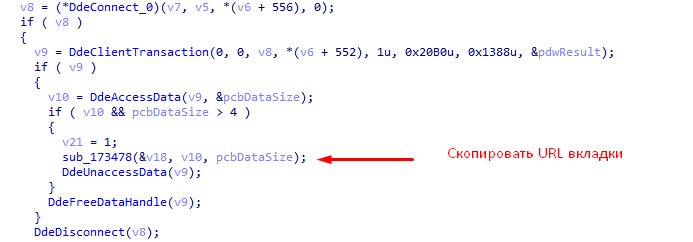
- Checks the addresses of the open tabs of the Internet Explorer and Mozilla Firefox browsers to collect information on interaction with banks, retrieving the current URL of the tab and comparing it with the values from Table 1. In case of a match, the corresponding information is sent to the C & C server .
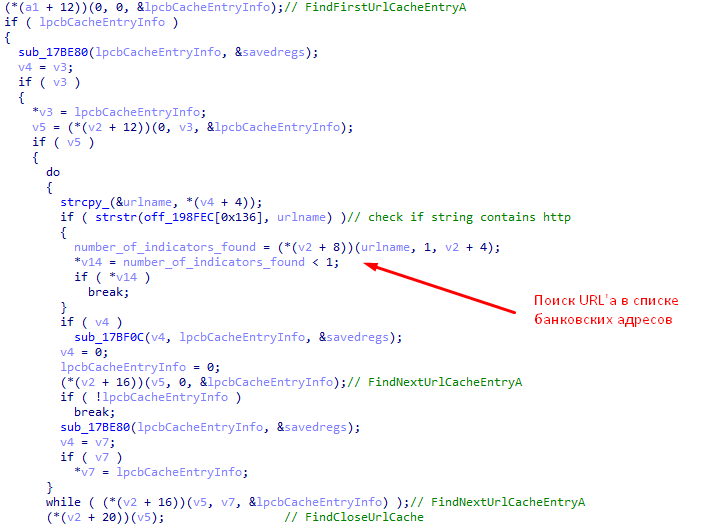
- Looks through the browsing history of Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome browsers and look for information on visiting bank sites in it. In case of coincidence of the received data with the data from Table 1, sends a corresponding message to the “C & C” server.

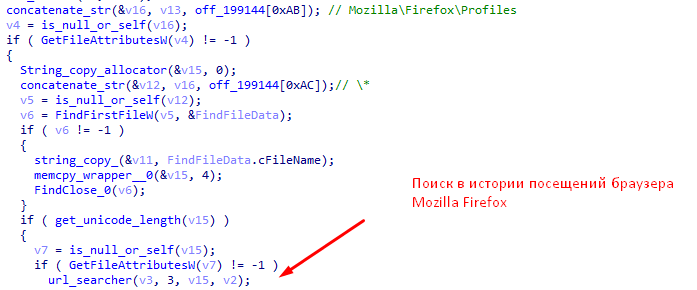
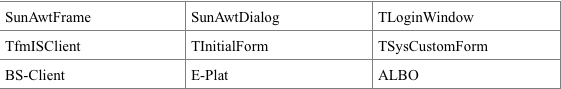
- Checks the names of the classes of running windows for matches with the values from Table 3. In case of a match, it saves the identifiers that will be sent to C & C later as data about interaction with a particular bank.
- Then "RTM" tries to establish a connection with the "C & C" server (the following addresses were found: 188.165.200.156, 185.190.82.182, 5.135.183.146, 151.80.147.153, 109.69.8.34). To obtain the C & C server’s IP address, the site is called “namecha.in”.
- Creates a stream that checks for the presence of connected smart cards.
Further actions depend on the commands received from the "C & C" server.
Received commands are encrypted with a modified RC4 algorithm. In each message received from the “C & C” server, the first 4 bytes are the XOR key. Before decrypting the received data, every 4 bytes of the “S-box” are added with this key modulo two. The "RC4" key itself is stored in the program.
Bytes 4 through 8 are the CRC32 code for the rest of the message. After decryption. The program checks the correctness of the message by comparing the received "CRC-32" code from the message with the actual "CRC-32" code of the message.

The 9th byte of the received message determines the command to be executed.
- If 9 bytes is 0x0, the program continues. Such a response means that the data received by the server is correct.
- If 9 bytes is 0x5, the rest of the message is an optional module that will be loaded into the "RTM" process.

- If 9 bytes is 0x6, the rest of the message is an executable file. It will be saved and launched.
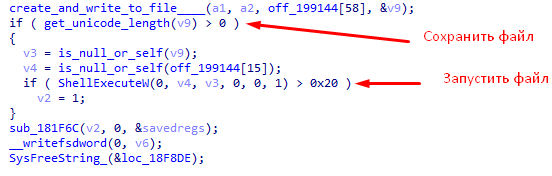
- If 9 bytes is 0x8, the remainder of the message is a “DLL” library. It will be saved and loaded.
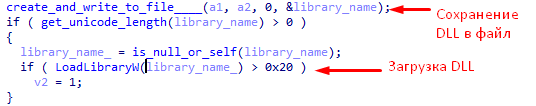
- If 9 bytes is 0x9, the rest of the message is an executable file that will be run without saving.

- If 9 bytes is 0xB, the remainder of the message is a new executable file that will replace the current RTM executable file.
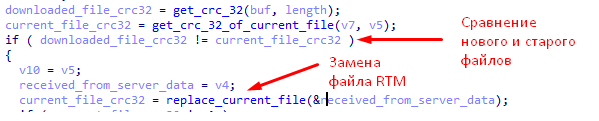
- If 9 bytes is 0xC, the rest of the message will be saved to a file in the "% LocalAppData%" directory.
- If 9 bytes is 0x1, the remainder of the message is a string with one of the following commands:
- “Find_files” - searches for a file with the name received from “C & C”,
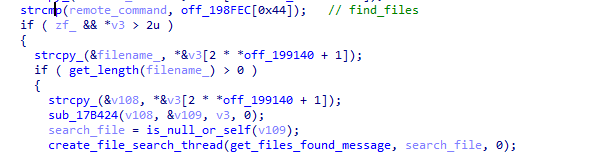
- “Download” - sends to the remote north the contents of the file with the name obtained from the “C & C” server, if it exists.
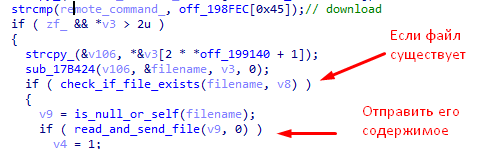
- “Unload” - stops “RTM” operation until the next restart.
- “Uninstall” - RTM removes the current executable file.
- “Uninstall-lock” removes the current executable file and sets the key “Shell” of the registry key “HKLM \ SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Windows NT \ CurrentVersion \ Winlogon \” to “shutdown –s –f –t 0”, which causes the computer to shut down at every login.
- “Auto-elevate” - creates a window, when clicking on the buttons of which the launch of “RTM” on behalf of the administrator occurs through the launch of “rundll32.exe”.
- “Dbo-scan” launches a search for files related to banking services (Table 2).
- “Shutdown” - turns off the computer.
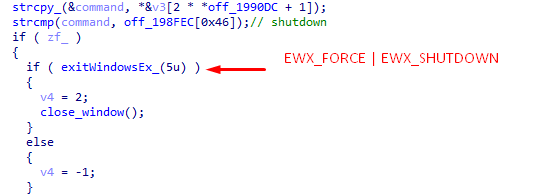
- "Reboot" - reboot the computer
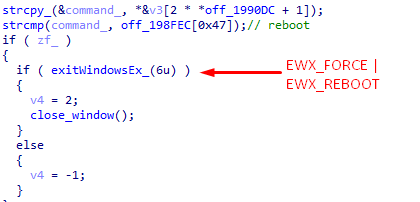
- “Hosts-add” - writes the received data to the “hosts” file and clears the cache of DNS service records by running the “ipconfig.exe / flushdns” command
- “Hosts-clear” - cleans the “hosts” file and clears the cache of DNS service records by running the “ipconfig.exe / flushdns” command
- "Screenshot" - creates a screenshot and sends it to the server.
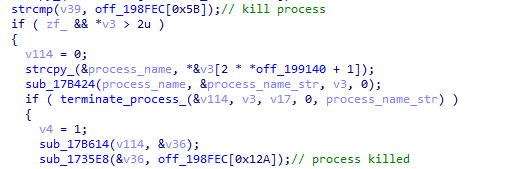
- “Kill-process” - searches for running processes, in the name of which there is a string received from the server, obtains their identifiers and terminates them.

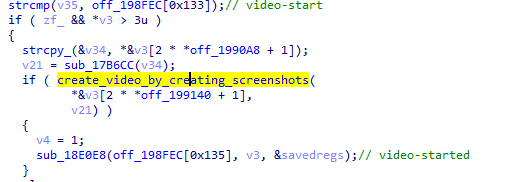
- “Video-start” - creates a stream, creating a screenshot every 2 seconds and transmitting it to a remote address received from the C & C server.
- “Video-stop” - stops the stream creating screenshots.
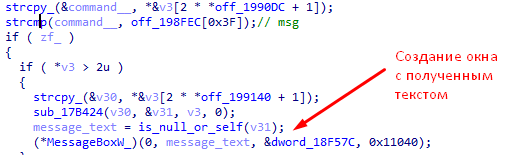
- “Msg” - creates a pop-up window with text received from C & C
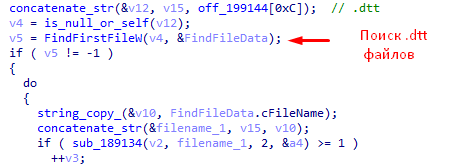
- It is assumed that "RTM" has the ability to load additional modules with the extension ".dtt".
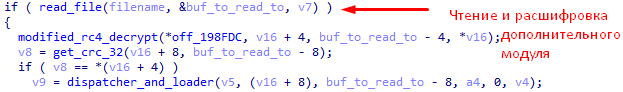
- It is assumed that after receiving the “del-module” command, execution stops and deletes the code of the loaded module.

Table 1 - List of "URLs" indicating interaction with banks
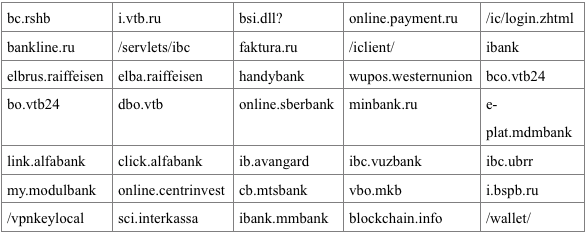
Table 2 - List of files indicating interaction with banks
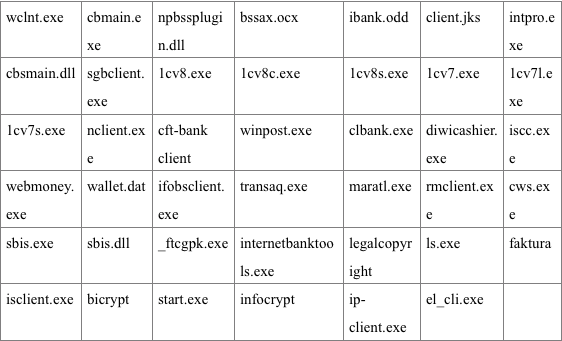
Table 3 - List of class names
Theft scheme
RTM with the help of screenshots and keylogger learns the username and password of the user, downloads and launches tools for remote computer control, after which either a payment order is created and sent to the RBS system via remote control on the infected computer, or the authentication data and secret key used in the RBS system is stolen , and sending the order occurs from the attacker's computer. According to Group-IB, in the event of successful theft, on average, hackers “earn” on such attacks about 1,100,000 rubles from one legal entity.
In general, in the fall - from September to November - the RTM criminal group launched several large-scale attacks on large Russian banks and enterprises. The malicious activity was detected and blocked using the Threat Detection System Polygon (TDS) cyber attack early warning system, which allows you to “unpack” suspicious emails in a safe environment isolated from the bank’s main network, check them for malicious attachments and make a verdict on the degree of danger of the detected object .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/432256/
All Articles