Kubernetes 1.13: a review of major innovations

At the beginning of this week , the next release of Kubernetes, which was dubbed “Angelic”, took place - 1.13 . This name is associated with the number 113, which is considered “angelic” and, according to the Kubernetes developers, it symbolizes “new beginnings, transformation and the end of one chapter before the opening of new ones”. Without going into further analysis of the symbolism of what is happening, according to the tradition already established for our blog, we will tell about the key changes in the new version of Kubernetes for the seventh time, which are intended to please DevOps- / SRE engineers working with this product.
We used data from the Kubernetes enhancements tracking , CHANGELOG-1.13 table and related issues, pull requests, Kubernetes Enhancement Proposals (KEP) as sources of information.
')
GA for kubeadm
One of the main events of the release of Kubernetes 1.13 was the announcement of the stable status (General Availability, GA) for the console utility kubeadm . The K8s blog has even been dedicated to this. As many know, kubeadm is a tool for creating Kubernetes clusters according to the best practices of the project, as well as their further minimal maintenance. A distinctive feature is that developers strive to keep it compact and independent from the supplier / infrastructure, not including in it such issues as infrastructure provisioning, third-party network solutions, add-ons (monitoring, logging, etc.), specific integration with cloud providers.
GA status marked kubeadm maturity in the following issues:
- a stable console interface that follows the Kubernetes obsolescence policy: the commands and flags presented in the GA release must be maintained for at least a year after being declared obsolete;
- stable implementation “under the hood” due to the fact that the cluster is created by methods that will not change in the near future: the control plane runs as a set of static pods, for
kubeadm joinbootstrap tokens are used , and for setting up kubelet ComponentConfig is used; - the configuration scheme with the new API (v1beta1), which allows declaratively describe almost all cluster components (GitOps becomes possible for clusters created from kubeadm) - an upgrade to version v1 is planned with no or minimal changes;
- the so-called phases (or toolbox interface) in kubeadm (
kubeadm init phase), allowing you to choose which initialization procedures will be performed; - The
kubeadm upgradecommand ensures cluster updates between releases 1.10.x, 1.11.x, 1.12.x and 1.13.x (updates etcd, API Server, Controller Manager and Scheduler); - secure installation of etcd by default (uses TLS everywhere) with the option to expand to an HA cluster if necessary.
You can also note that kubeadm now correctly recognizes Docker 18.09.0 and its newer versions. Finally, the developers ask kubeadm users to go through a small online survey where they can express their wishes for using and developing the project.
CoreDNS default
CoreDNS, which received a stable status in the Kubernetes 1.11 release, went even further and became the default DNS server in K8s (instead of the kube-dns used so far). It was planned that this would happen as early as 1.12, however, developers were faced with the need for additional optimizations in scalability and memory consumption, which were completed only for the current release.

Support for kube-dns will continue “at least for the next release,” but developers are talking about the need to start migrating to the actual solution now.
Of the changes related to the CoreDNS theme in Kubernetes 1.13, you can also note the appearance of the NodeLocal DNS Cache plugin, designed to improve DNS performance. Improvement is achieved by running on the cluster nodes the agent for the DNS cache, which will be directly accessed by the pods of this node. By default, the function is disabled, and for its activation it is necessary to set
KUBE_ENABLE_NODELOCAL_DNS=true .Storage
Much attention in recent releases of Kubernetes is paid to working with the Container Storage Interface (CSI), which began with the alpha version of CSI in K8s 1.9 , continued with the beta version at 1.10 ... However, we already wrote about it more than once . A new milestone has been reached in K8s 1.13: CSI support has been declared stable (GA).
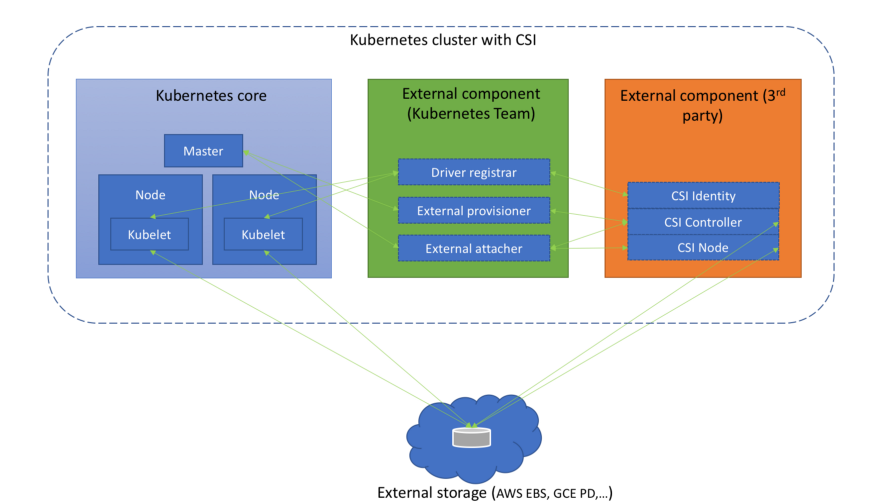
(Scheme from the article "We understand the Container Storage Interface ")
At the same time, support for the CSI version v1.0.0 specification appeared and support for older versions of the standard (0.3 and earlier) was recognized as obsolete. This means that older CSI drivers for Kubernetes 1.15 and older versions will need to be updated to CSI 1.0 (and moved to the new Kubelet plug-in registration directory). By the way, from the drivers themselves it is worth noting the appearance of the alpha version of the CSI interface for managing the life cycle of AWS EBS (Elastic Block Store) volumes.
The new addon manager now automatically installs CRD from CSI if at least one of the two feature gates is activated:
CSIDriverRegistry and CSINodeInfo . It has the status of an alpha version, and in fact is only a temporary solution of the problem, described in detail as a CRD installation mechanism .Volume planning with topology ( Topology Aware Volume Scheduling ), which we described in the context of the release of Kubernetes 1.10, has become stable . In short, with him the scheduler in his work takes into account the limitations of the topology of the pod volume (for example, its zone and node).
The possibility of using block raw devices (not networked), presented in Kubernetes 1.9, as Persistent Volumes has been transferred to the beta version and is now enabled by default.
We conclude the repository topic in that the support for GCERegionalPersistentDisk is declared stable.
Cluster nodes
Introduced alpha-version support for third-party plug-ins for monitoring devices . The idea behind this initiative is to bring out device-specific out-of-tree knowledge from Kubelet. Cluster administrators will receive metrics reported by device plug-ins at the container level, and manufacturers will be able to create these metrics without having to make changes to the Kubernetes core. Details of the implementation can be found in the proposal, called Kubelet Metadata API .
Declared stable Kubelet Plugin Watcher (also called Kubelet Device Plugin Registration) , which allows node-level plug-ins (device plug-ins, CSI and CNI) to report and interact with Kubelet about themselves.
New feature in alpha version status - NodeLease . If earlier the “heartbeat” of a node was determined by NodeStatus, then with a new feature, each node will have an associated
Lease object (in the kube-node-lease namespace), which is periodically updated by the node. "Pulse" now set both parameters: the old NodeStatus, which is communicated to the master only in case of changes or at a fixed timeout (by default, this is once a minute), and a new object (it is updated frequently). Since this object is quite small, it will greatly improve scalability and performance. The authors took up the creation of a new “pulse” after testing clusters with a size of more than 2000 nodes, which during their work could rest on the limits etcd, see KEP-0009 for more details. type Lease struct { metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"` // Standard object's metadata. // More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#metadata // +optional ObjectMeta metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"` // Specification of the Lease. // More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status // +optional Spec LeaseSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"` } type LeaseSpec struct { HolderIdentity string `json:"holderIdentity"` LeaseDurationSeconds int32 `json:"leaseDurationSeconds"` AcquireTime metav1.MicroTime `json:"acquireTime"` RenewTime metav1.MicroTime `json:"renewTime"` LeaseTransitions int32 `json:"leaseTransitions"` } (Compact specification of a new object for representing the “pulse” of a node -
Lease - is identical to LeaderElectionRecord )Security
The alpha version of Dynamic Audit Control follows the ideas of Dynamic Admission Control and provides dynamic configuration of advanced audit capabilities — for this you can now register (dynamically) the webhook that will receive the event flow. The need for this feature is due to the fact that the audit at Kubernetes offers very powerful features, but they are difficult to configure, and each configuration change still required an apiserver reboot.
Data encryption in etcd (see official documentation ) has been transferred from experimental status to beta version.
kind: EncryptionConfiguration apiVersion: apiserver.config.k8s.io/v1 resources: - resources: - secrets providers: - identity: {} - aesgcm: keys: - name: key1 secret: c2VjcmV0IGlzIHNlY3VyZQ== - name: key2 secret: dGhpcyBpcyBwYXNzd29yZA== - aescbc: keys: - name: key1 secret: c2VjcmV0IGlzIHNlY3VyZQ== - name: key2 secret: dGhpcyBpcyBwYXNzd29yZA== - secretbox: keys: - name: key1 secret: YWJjZGVmZ2hpamtsbW5vcHFyc3R1dnd4eXoxMjM0NTY= (An example of a configuration with encrypted data is taken from the documentation .)
Among the less significant innovations in this category:
- Now apiserver can be configured to refuse requests that can not get into the audit-logs.
- The
PodSecurityPolicyobjectsPodSecurityPolicyadded support for theMayRunAsrule for thefsGroupandsupplementalGroupsoptions, which allow defining the range of allowed group identifiers (GIDs) for pods / containers without forcing the default GID. In addition, withPodSecurityPolicy, the RunAsGroup strategy is now possible in the pod specification, i.e. You can control the main GID for containers. - For kube-scheduler, they replaced the old insecure port (10251) with a new secure (10259) port and enabled it by default. If no additional flags are specified, then self-signed certificates are created for it in memory when loaded.
CLI
The
kubectl diff , which shows the difference between the local configuration and the actual description of the working object (works and recursively for directories with configurations), received the status of a beta version.In fact,
diff “predicts” the changes that will be made with the execution of the kubectl apply , and another new feature is used for this - APIServer DryRun . Its essence - idle launch - should be clear from the title, and a more detailed description is available in the Kubernetes documentation . By the way, in release 1.13, the DryRun feature was also “upgraded” to the beta version and enabled by default.And another advancement to beta in the console world of Kubernetes has touched upon a new plugin mechanism . Along the way, the order of displaying plug-ins (
kubectl plugin list ) was corrected in it, removing the additional sorting from there.In addition, in
kubectl describe node added the output of the ephemeral-storage resources used, and in kubectl describe pod volumes of projected type.Other changes
The Taint Based Eviction scheduler feature has been converted to beta status and enabled by default after a long lull in development. Its purpose is to automatically add taints to nodes (using a NodeController or kubelet) when certain conditions occur, such as, for example,
node.kubernetes.io/not-ready , which corresponds to the NodeCondition value in Ready=False .Annotation critical for the operation of the cluster of pods -
critical-pod - has been declared obsolete. Instead, it is proposed to use priorities (in beta with Kubernetes 1.11) .For the first time, AWS (within the framework of alpha versions) became available:
- AWS ALB (Application Load Balancer) integration with Kubernetes Ingress - aws-alb-ingress-controller resources (the project was originally created by Ticketmaster and CoreOS to migrate first to the AWS cloud);
- AWS's external CCM (Cloud Controller Manager), cloud-provider-aws , is responsible for running controllers with cloud-specific provider (AWS) functionality.
SIG Azure implemented additional support for Azure Disk (Ultra SSD, Standard SSD and Premium Azure Files) and advanced Cross resource group nodes to the beta version. In addition, in CNI-plug-ins for Windows , the ability to configure DNS in the container.
Compatibility
- Version etcd - 3.2.24 (not changed from Kubernetes 1.12).
- Checked Docker versions - 1.11.1, 1.12.1, 1.13.1, 17.03, 17.06, 17.09, 18.06 (also have not changed).
- Go version - 1.11.2, coincides with the minimum supported.
- CNI version is 0.6.0.
- The CSI version is 1.0.0.
- CoreDNS version - 1.2.6.
PS
Read also in our blog:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/432208/
All Articles