The world through the eyes of the car. How do drones see it?

Progress in the field of unmanned vehicles in recent years has accelerated rapidly. As of December 1, 2018, drones will be able to move freely along public roads in Moscow and Tatarstan. It seems a little more and we will be able to get into the car and go about our business while our transport takes over the management of the entire driving process. Dreams are dreams, but what is such a car really capable of and will it crowd out a person?
On the road to full autonomy
The international community of automotive engineers (SAE International) has developed a six-level classification of automobile autonomy. This system demonstrates the path that cars have managed to go over the past decades, and describes the difficulties that have yet to be resolved in order to create a truly unmanned vehicle.
Level 0 - no autonomy. All machines that do not interfere with the management process can be attributed to this level. Without a man, such a car will not move and cannot avoid an accident. ABS or parking sensors - that's all that can be expected from zero level cars.
')
Level 1 - minimal help. It includes machines that can control the steering or acceleration / deceleration with constant monitoring by the driver. This also includes parking assistance systems, when the steering wheel is driven by a car, and the driver takes care of the pedals.
Level 2 - help with the attention of the driver. At the second level, there is full automation of simple processes that require simultaneous automatic control of taxiing and driving. It also includes modern advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
Level 3 - limited autopilot. The frontier level, at which one can already speak of full-fledged autopilot, operating under separate scenarios. Unlike cars of the second level, cars of the third do not require constant attention from the driver - a person can go about his business, not grabbing the wheel every half minute.
Level 4 - autopilot in cities. The fourth-level cars differ from the absolute autopilot (5th level) in that they need 3D maps of the terrain, with which the car will be checked during driving, scanning the terrain. If the car of the fourth level is in the area, which is absent on such maps, the autopilot will switch to the third level mode or will be switched off altogether.
Level 5 - full autopilot. The same spherical autopilot in vacuum, able to move in any weather and in any part of the planet: whether it will be a broken road without a marking, a forest glade, a snow-covered mountain pass, a loaded metropolis - the autopilot of the fifth level will go everywhere, analyzing the situation on the go. He does not need prepared 3D maps - an autonomous car of the fifth level with his skills corresponds to a live driver.
How do real autonomous cars work?
Camera + image processor
When developing the first full-fledged unmanned cars, cameras were the main way to perceive the space around the car. They made it possible to quickly obtain images in the visible range with a wide viewing angle. However, one picture from the camera is not enough for the successful functioning of an autonomous car; the drone needs an electronic analogue of the human brain, that is, a specialized image processing processor.
The development of such processors is handled by both large experienced companies and startups, say, Mobileye, which has become part of Intel, NVIDIA. Toshiba has similar developments. The Toshiba Visconti processor family processes the image from four cameras, evaluating the images at once by a variety of criteria: marking, moving and parked cars, traffic lights and signs, headlights, pedestrians and cyclists. After identifying and classifying objects into video, the processor transmits information to the “brain” of the machine, whose autopilot already decides on optimal behavior. This is how the advanced driver assistance system ADAS works, preventing collisions and pedestrian attacks (second-level autonomy criterion).
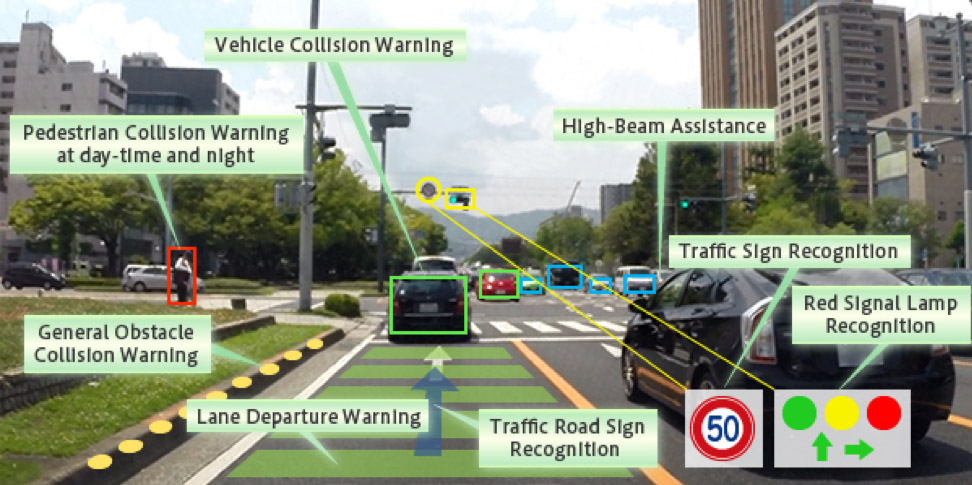
A bunch of camera and processor Toshiba Visconti monitors the traffic situation better and more attentive than a person. Source: Toshiba
The full cycle of Toshiba Visconti of past generations, from receiving an image to issuing information with recognition results, took up to 100 ms. In Visconti 4, the cycle was reduced to 50 ms. At best, the driver response time is 500 ms. During this time, the car traveling at 80 km / h will cover 11 meters - a long distance in case of a dangerous situation on the road.
Visconti also solves the problem of monocular vision - the processor is able to build a three-dimensional reconstruction of the space, analyzing the sequence of frames when moving. It works for both moving and stationary objects on the roadway and beyond.
Radar
Cameras are not able to recognize distant objects and build detailed maps, moreover, their functionality directly depends on weather conditions. These deficiencies can be compensated by radars emitting radio signals with a frequency of tens of gigahertz. They perfectly define obstacles in space. Radars with a radiation frequency of 24 GHz and 77 GHz are already used in expensive ADAS systems for early braking when detecting the intersection of traffic with a pedestrian or other car. Unlike cameras, radar has a very narrow angle of action, inversely proportional to the desired range. In addition, the radar has a high cost (at the level of $ 1,000), which immediately limits the range of its use only representative and premium cars.
Radars do an excellent job of localizing objects, but without defining their shape and only in a narrow range.
Lidar
Lidars are considered the most effective, but at the same time the most ambiguous sensor for autonomous cars. They build a detailed picture of the world around themselves with the help of laser beams, which are reflected from obstacles and come back. Moreover, the lidars do it with inaccessible to other sensors accuracy. With the help of a lidar, a car creates its own 3D map for tens of meters around, recognizing cars, people and any obstacles.
So the world sees the car with lidar
However, there are more disadvantages to lidar than advantages. First, lidars become helpless under heavy rain or during a snowfall - laser beams are reflected from water droplets and snow flakes. Secondly, the lidar should have a full circle view, which means that it creates a "hump" on the roof of the car. Thirdly, the lidars are not just expensive, but very expensive: the early samples of production Velodyne cost 75 thousand dollars, the modern development of Waymo costs 7500 dollars.
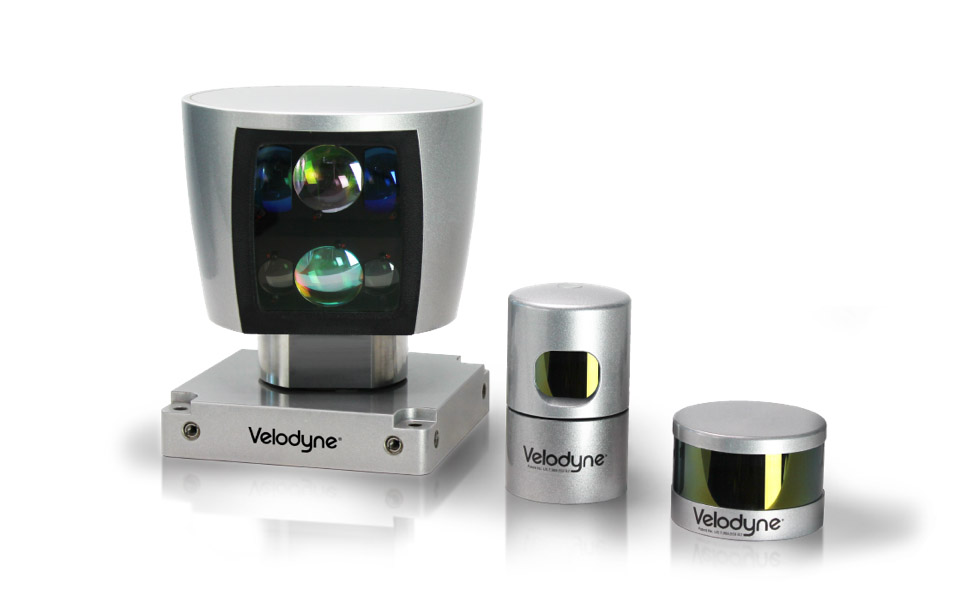

Line of lidar Velodyne. Source: Velodyne
The appearance of “solid-state” lidars without moving parts should reduce the cost of devices by orders of magnitude in the coming years. Velodyne claims to have made a breakthrough that will reduce the price of lidars to $ 50.
Toshiba, in turn, is working to improve the efficiency of lidars. So, this year a new chip was introduced, combining circuits for analyzing data at long and short distances. This allowed the effective range of lidars to be doubled to 200 m, as well as to get rid of the problem of glare that affected the quality of reflections.
How it works for ...
... Tesla
For the implementation of autopilot in Tesla cars, a system of eight cameras with different angles and range of view, 12 ultrasonic sensors in a circle and long-range frontal radar are installed. Ultrasonic sensors are responsible for recognizing machines in adjacent rows and obstacles when driving at low speeds. Cameras are responsible for finding pedestrians, cars, markings and signs. Helps them in this radar. For the route, GPS is used, and the sensors ensure that the car goes strictly along the lanes and avoids accidents. On the one hand, it allows using Tesla autopilot in any cities. On the other hand, the autopilot still requires the attention of the driver to operate.
In Tesla, the lidar is deliberately not used, Ilon Musk openly opposes the lidars, justifying this with their price and problematic work in bad weather. It's hard not to agree with him - an additional 7-10 thousand dollars to the price and a “hump” on the roof would not add Tesla to its attractiveness.
No matter how good the bundle of cameras, radar and ultrasonic sensors looks, and they have failures. In 2018, the Tesla Model S crashed into a road divider in autopilot mode, causing the driver to die. As the investigation showed by the owners of the electric car, the Tesla autopilot could not correctly read the erased markings, and the cameras and radars, in turn, did not see the danger in the rapidly approaching steel barrier.
... Waymo
The Waymo system uses a lidar, five radars, eight cameras and GPS, and Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid cars (currently 600, 62 thousand units are planned) and Jaguar I-PACE (with 20 thousand units planned) are chosen as serial commercial carriers.
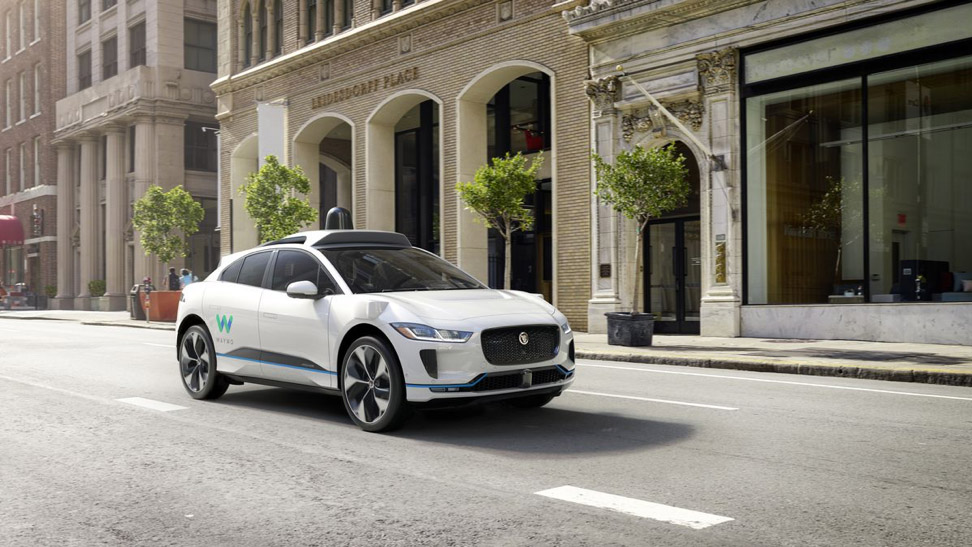

Electric Waymo Jaguar I-PACE is not as utilitarian as the spacious Chrysler Pacifica, but it looks amazing - even the lidar on the roof does not spoil the view. Copyright: Waymo
When moving, the Waymo system uses Google Street View data, checking it with its sensors. Due to this, complete autonomy is achieved - unlike Tesla, Waymo cars really do not require driver intervention, but simply carry passengers. Unlike Tesla, Waymo does not sell cars, but the transportation service, that is, robotaxi.
Panoramic video of Waymo helps you understand how a stand-alone car recognizes the surrounding space.
The main disadvantage of Waymo is the extremely limited list of cities where the drones operate - for the correct functioning of the autopilot the urban environment should be shot in 3D, and this is a long and complicated procedure, therefore, while Waymo operates in only two dozen American cities. However, the expansion of the road network is only a matter of time. Big time.
... Yandex
Yandex presented its draft unmanned vehicle just a year ago. The Toyota Prius was equipped with a block of lidar, cameras, radar, GPS and IMU, that is typical for autonomous car components. From Yandex, the drone got a software platform that showed itself well when driving along the cramped streets of Moscow’s Khamovniki district, and on a long journey from Moscow to Kazan.
The car of Yandex that reached Tatarstan remained there, becoming the first unmanned taxi in Russia. He now works in the city of Innopolis, carrying passengers between the five main points. And in October, a similar taxi appeared on the territory of Skolkovo. In the company's distant plans to bring unmanned taxis to the streets of cities on a commercial basis.
... of KAMAZ
In 2016, the state institute NAMI showed an unmanned “minibus” of the SHUTTLE, which was then no more than an experimental concept car. Two years later, KAMAZ-1221 ShATL was announced as a future serial project, which will be put on the conveyor in 2022. The mini-electric bus with lidars, cameras and ultrasonic sensors is still gently moving at a speed of 10 km / h, but as the software platform improves, they promise to tighten the speed to 110 km / h.
What will the drones change?
The exclusion of the human factor will allow to increase the marginal conditions of car operation - to increase the maximum speed, reduce the width of lanes, reduce the distance between cars in the stream. As a result, the throughput of roads will significantly increase, the average speed will increase and the number of jams will decrease.
According to the American Highway Capacity Manual, one lane of the highway per hour passes about 2,200 cars running by people. Various studies show that switching to autonomous cars will increase this figure to 7200-12000 cars per hour. Such an impressive leap in road use efficiency is achieved by increasing the safe speed and reducing the distance between cars on the lane from 40-50 meters to 6-7 meters - for cars that send each other information about their speed and intended maneuvers, this distance will be enough for safe movement.
However, we are still far from such an unmanned future. Serial cars of famous automakers have just adapted the second level of autonomy, the best and most expensive models are preparing to step over to the third level. But in the next decade, it is not worth even dreaming about the fifth-level autonomous drones - a person will be the main thing on the road for a long time.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/431388/
All Articles