Solar JSOC research: cybercriminals are becoming more professional
At Solar JSOC, we continuously collect data on information security events and incidents in customer infrastructures. On the basis of this information, we do analytics every six months, which demonstrates how attacks on Russian organizations change. Today we have collected for you the most interesting trends of the first half of 2018.

The average daily flow of information security events processed by SIEM systems and used to provide Solar JSOC services amounted to 28 billion. In total, in the first half of 2018, Solar JSOC specialists recorded more than 357 thousand cyber attacks. This is about two times more than in the first half of 2017. (We believe that it is correct to compare the first half of the year with the first, the second with the second, since there is a stable trend towards an increase in the number of attacks by the end of the year).
It is interesting that from year to year not only the number of attacks increases, but also the growth rate. In the first half of 2017, the number of attacks increased by 40% compared to the same period of 2016, and this year by more than 100%.
')
Approximately one and a half times the number of cyber attacks increased, aimed at gaining control over the organization’s infrastructure. Attackers are increasingly seeking a long-term and imperceptible presence in it with the aim of detailed research and gaining the fullest possible access to information and technological systems.
The number of attacks whose purpose is to directly withdraw money from organizations has increased by 10%, but the success of such attacks is decreasing. At the same time, there is a strong trend towards a decrease in the number of “hooligan” cyber attacks, such as deface or compromise of public sites, corruption and destruction of data. Their number decreased by 45% compared to the first half of 2017.
Separately, researchers note that the tools of the attackers are developing rapidly. Solar JSOC analysts record weekly the emergence of 5-6 new hacking tools, more and more often used to develop legitimate elements of the operating environment, popular tools for remote administration or management of operating systems.
Approximately one in five incidents was classified as critical - that is, potentially leading to financial losses of more than 1 million rubles, compromising confidential information or stopping critical business systems. In the first half of 2018, the share of critical incidents was 18.7%, in the first half of 2017, 17.2% were recognized as critical, in the first half of 2016 - 10.9%. Thus, if in 2016 every ninth incident was critical, now it is already every fifth. This is a record mark for the last four years. It is assumed that such dynamics is associated with a general increase in the intensity of mass and targeted attacks on organizations.
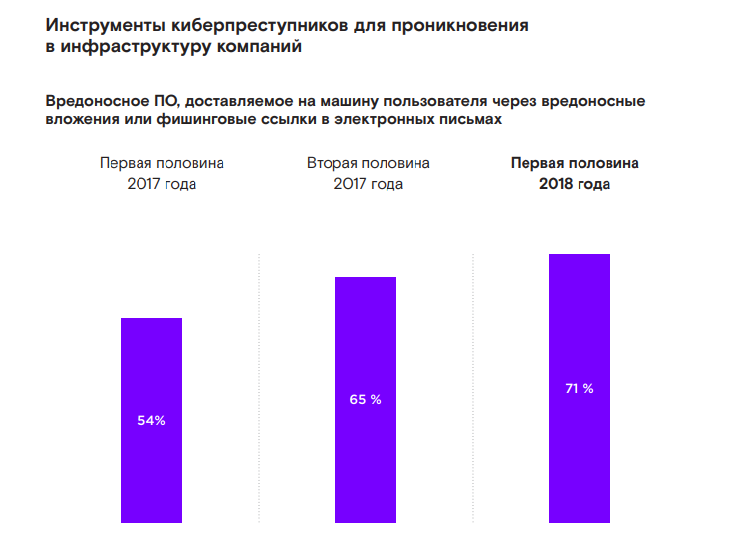
In the first half of 2018, complex external cyber attacks even more often than before (71% vs. 62% in the first half of 2017) began with the introduction of malware into the company's infrastructure through social engineering: users opened malicious attachments and passed through phishing links. Without exaggeration, phishing attacks are currently one of the key threats to the information security of organizations.
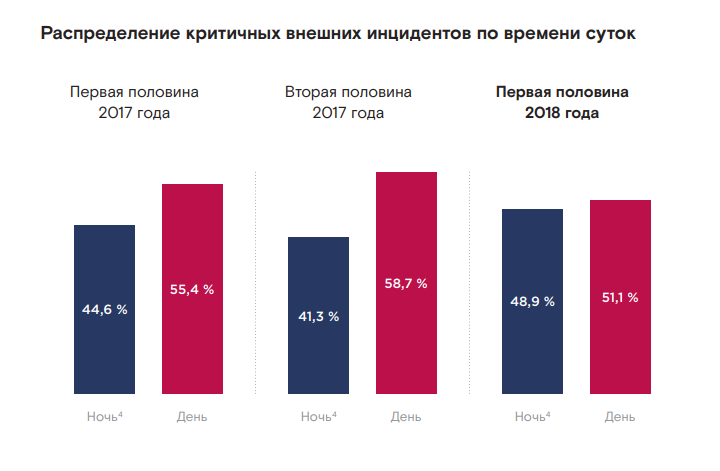
Most of the incidents (88.5%) occurred during the day, but if we talk about critical external attacks, in almost half of the cases (48.9%) they occurred at night. This is the highest since the beginning of 2014.
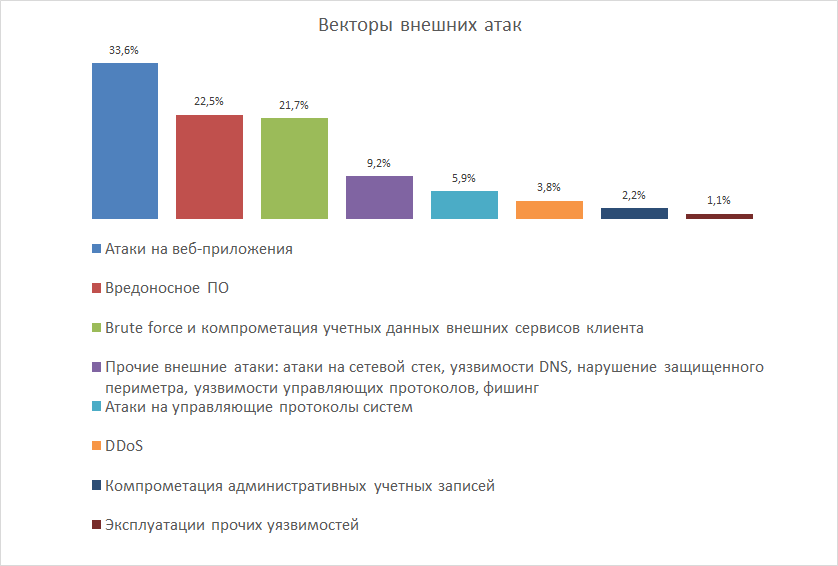
During the attack, cybercriminals most often try to hack the web applications of organizations (33.6%), infect users' servers and workstations with malware (22.5%) or pick passwords for accounts on the company's external services, that is, personal accounts on sites or file exchange systems with counterparties (21.7%).
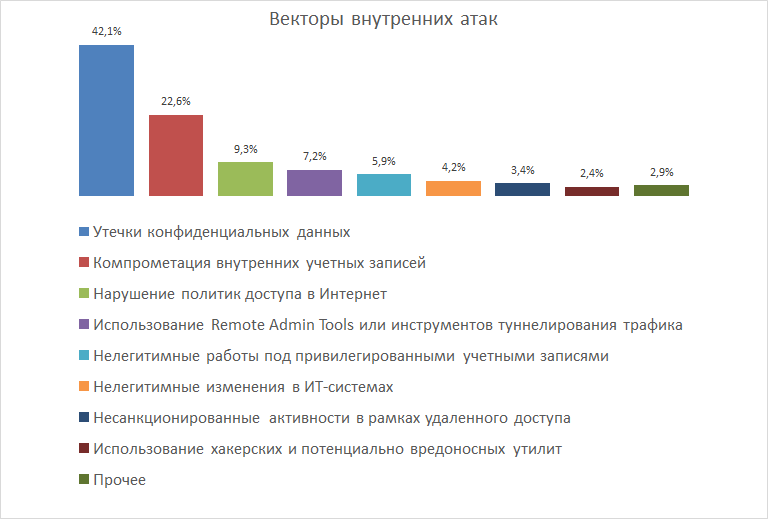
If the company was attacked from within, in 42.1% of cases it faced leaks of confidential data, and in 22.6% of internal accounts were compromised.
The culprits of internal incidents were usually ordinary employees (60.5%) or IT system administrators (28%), in 11.9% of cases the incident was caused by counterparties or contractors of companies.
The full version of the report can be viewed here .

The average daily flow of information security events processed by SIEM systems and used to provide Solar JSOC services amounted to 28 billion. In total, in the first half of 2018, Solar JSOC specialists recorded more than 357 thousand cyber attacks. This is about two times more than in the first half of 2017. (We believe that it is correct to compare the first half of the year with the first, the second with the second, since there is a stable trend towards an increase in the number of attacks by the end of the year).
It is interesting that from year to year not only the number of attacks increases, but also the growth rate. In the first half of 2017, the number of attacks increased by 40% compared to the same period of 2016, and this year by more than 100%.
')
Approximately one and a half times the number of cyber attacks increased, aimed at gaining control over the organization’s infrastructure. Attackers are increasingly seeking a long-term and imperceptible presence in it with the aim of detailed research and gaining the fullest possible access to information and technological systems.
The number of attacks whose purpose is to directly withdraw money from organizations has increased by 10%, but the success of such attacks is decreasing. At the same time, there is a strong trend towards a decrease in the number of “hooligan” cyber attacks, such as deface or compromise of public sites, corruption and destruction of data. Their number decreased by 45% compared to the first half of 2017.
Separately, researchers note that the tools of the attackers are developing rapidly. Solar JSOC analysts record weekly the emergence of 5-6 new hacking tools, more and more often used to develop legitimate elements of the operating environment, popular tools for remote administration or management of operating systems.
Approximately one in five incidents was classified as critical - that is, potentially leading to financial losses of more than 1 million rubles, compromising confidential information or stopping critical business systems. In the first half of 2018, the share of critical incidents was 18.7%, in the first half of 2017, 17.2% were recognized as critical, in the first half of 2016 - 10.9%. Thus, if in 2016 every ninth incident was critical, now it is already every fifth. This is a record mark for the last four years. It is assumed that such dynamics is associated with a general increase in the intensity of mass and targeted attacks on organizations.
In the first half of 2018, complex external cyber attacks even more often than before (71% vs. 62% in the first half of 2017) began with the introduction of malware into the company's infrastructure through social engineering: users opened malicious attachments and passed through phishing links. Without exaggeration, phishing attacks are currently one of the key threats to the information security of organizations.

Most of the incidents (88.5%) occurred during the day, but if we talk about critical external attacks, in almost half of the cases (48.9%) they occurred at night. This is the highest since the beginning of 2014.

During the attack, cybercriminals most often try to hack the web applications of organizations (33.6%), infect users' servers and workstations with malware (22.5%) or pick passwords for accounts on the company's external services, that is, personal accounts on sites or file exchange systems with counterparties (21.7%).

If the company was attacked from within, in 42.1% of cases it faced leaks of confidential data, and in 22.6% of internal accounts were compromised.

The culprits of internal incidents were usually ordinary employees (60.5%) or IT system administrators (28%), in 11.9% of cases the incident was caused by counterparties or contractors of companies.
The full version of the report can be viewed here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/431164/
All Articles