Selective bypass blocking on routers with Padavan and Keenetic OS firmware
There are a huge number of instructions with different options for bypassing Internet resource locks. But the topic does not lose relevance. Even more often, there are initiatives at the legislative level to block articles on methods of circumventing locks. And there were rumors that Roskomnadzor would receive another wad of taxpayers' money for “better” locks. Experienced users will not learn anything new and useful from the article. But others will get ready step-by-step instructions for simple and effective selective bypass of locks on popular routers with Padavan and Keenetic firmware.

For about two years I used the option of bypassing locks from Zolg . Many online instructions are based on it. Including mine.
Everything was good, but "the best is always the enemy of the good." First, some new programs have become too “smart” and rezolvyat domains by their own methods, bypassing the router's DNS server. This does not allow dnsmasq on the router to add an address to the ipset to unlock and leads to a natural result - the resource remains locked. In Android 9, full support for DNS-over-TLS appeared, i.e. this lock bypass method stops working (if the other device has not previously accessed dnsmasq). Secondly, updating the entire list of domains from antizapret leads to unpredictable results every time. The list may include domains that are not blocked in reality, and whose operation is important through the main channel. You need to constantly be alert and edit the generated files with your hands. Thirdly, I got tired of “dragging along” a huge list of domains with tens of thousands of casinos and the like, which are simply not needed. Over time, I realized that I needed only a small specific list of blocked resources.
')
So, I have been using the slightly modified unlocking method for a year, which I am completely satisfied with:
It is important to note that my option is not intended for the case when you need to unlock hundreds and thousands of domains. Because at the start of the router, a rezolving of each domain from the specified list occurs. The more domains in the list, the longer will be the initialization of the set ipset to unlock.
The basis of the lock bypass is the same - the Tor network. Its use is due to two simple factors — free of charge, and the likelihood that Tor will be blocked in Russia is close to zero, unlike any VPN service. Tor is the foundation of drug traffic in Russia from the middle to the bottom. Blocking Tor will lead to a search for new tools for the market and a decrease in the level of anonymity, which will lead to the successful revitalization of the work of local law enforcement agencies. In the end, this, like a virus, will begin to negatively affect the upper link. Given the latest amazing news about the links of top state officials with global drug traffic to Russia, blocking Tor in Russia is just a taboo, even though it is trivial. Neither Roskomnadzor, no matter what billions were allocated to this department, no court in Russia has the permission “from above” to block Tor. And it does not even surprise and frighten anyone, even though Russia is simply buried in drugs (every schoolchild knows what “daknet” is, and after 30 minutes has the actual opportunity in any city with a population of 10 thousand people to get any drugs without hindrance. in any quantities - such an evil truth of life). In the current mode, the probability of blocking the Tor network is lower than the probability of blocking the Hermitage museum site.
These instructions are easy to adapt for routers with OpenWrt. Also, minor changes can easily replace Tor with OpenVPN.
Everything is very simple. You have the file /opt/etc/unblock.txt - a simple list to unlock. You can unblock a domain, IP address, address range or CIDR. One line - one element. Blank lines are allowed, and you can use the # character at the beginning of a line to ignore.
After editing this file, you simply execute the command to apply the new configuration:
All resources from unblock.txt are unlocked without the need to restart the router.
You must have a router with Padavan firmware installed and an Entware package manager already configured. On Windows, you can use the PuTTY client to connect to the router via SSH.
Make sure you use Entware, and not outdated Entware-ng. Look at the contents of the / opt / var / opkg-lists folder. There will be an entware or entware-ng file. In the second case, you need to upgrade your router's Padavan firmware to the latest version and reinstall the Entware package manager. Only after that proceed step by step instructions.
As reviews have shown, mostly problems arise for those who have Entware configured incorrectly initially (ie, scripts from init.d are not loaded) in the internal memory of the router. If you have Xiaomi Mi Router 3 or 3G, and you are not sure that Entware in your internal memory is working correctly (automatic start), then just set everything up again. Take PROMETHEUS. Updates the script (1). Update source code (2). Collect and flash the most current firmware (4). Reset the firmware settings (NVRAM and file storage) - More> Administration> Settings. Configure Internet access on the router and enable SSH. Perform in PROMETHEUS Firmware> Format RWFS. Choose Advanced> Administration> Settings> Mount file system in R / W section> UBIFS. Reboot the router. All actual Entware startup scripts from the internal memory will be registered automatically, and everything will work like a clock.
For the tests, I used the popular Xiaomi Mi Router 3G (Entware is installed in the internal memory) with the latest firmware - 32a93db. Everything will work even on the legendary baby WT3020 AD / F / H for $ 10.

mc is the Midnight Commander file manager. It is needed only because of the convenient editor mcedit. If you are used to using another text editor, then you can not install mc.
tor - Tor service.
tor-geoip is a geo-IP base for Tor.
bind-dig is a DNS client (similar to nslookup and host).
cron - task scheduler.
Connect the necessary modules and create an empty set of addresses named unblock when booting the router. To do this, open the /etc/storage/start_script.sh file in the editor:
Add at the end:
To paste from the buffer, use Shift + Insert, save - F2, exit - F10.
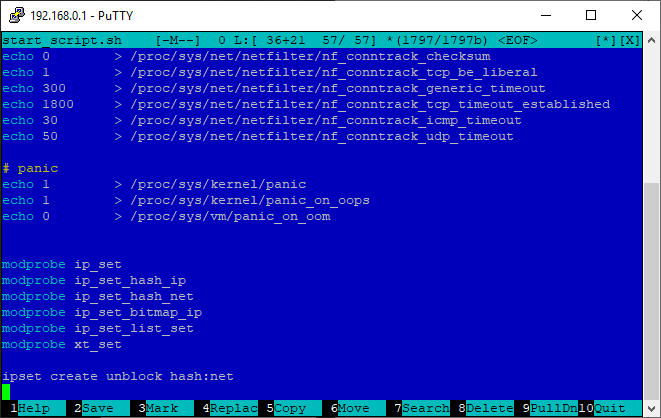
If you wish, you can edit the start_script.sh file through the web interface of the router - “Advanced”> “Personalization”> “Scripts”> “Run before router initialization”. After editing, click "Apply".

Delete the contents of the Tor configuration file:
Open the Tor configuration file:
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN). A brief description of the configuration:
unblock.txt - a simple list to unlock. You can unblock a domain, IP address, range or CIDR. One line - one element. Blank lines (including spaces and tabs) are ignored. You can use the # character at the beginning of a line to ignore.
Create the /opt/etc/unblock.txt file:
Each line can contain a domain name, IP address, range or CIDR. You can use the # symbol to comment lines.
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
The script is quite simple, this is the essence of its work ... We are waiting for the rezolving of the google.com domain to work (if this is not done, then the unblock set will not be filled when the router is loaded, because the router will still be in the process of initialization). We read lines in the unblock.txt file. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with a # character. We are looking for the CIDR line. If CIDR is found, then add it to unblock. We search for a range in the string. If it is found, then add it to unblock. We are looking for an IP address in the line. If the IP is found, then add it to unblock. Solve the string via dig. All result IP addresses are added to unblock.
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
The script is quite simple, here is the essence of his work ... We consistently read lines from /opt/etc/unblock.txt. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with #. We skip lines that contain an IP address (IP, range, CIDR), i.e. we are only interested in strings with domain names. In the /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq file we add the lines “ipset = / domain_name / unblock”. This means that after determining the IP addresses of a specific domain, they will be automatically added to the unblock set.
Be sure to run the script to generate the unblock.dnsmasq file:
Check that the unblock.dnsmasq file is created:
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
Create a script /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
Open the /etc/storage/post_iptables_script.sh file in the editor:
Add at the end:
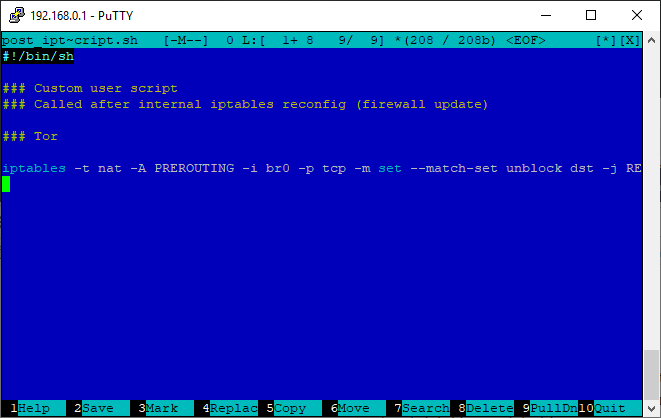
If you wish, you can edit the post_iptables_script.sh file via the web interface of the router - “Advanced”> “Personalization”> “Scripts”> “Run after restarting the firewall rules”. After editing, click "Apply".

In the same file you can add (this is optional) redirect all requests to external port 53 to yourself. This is necessary so that clients on the local network do not use third-party DNS services. Requests will go through a regular DNS server.
If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN).
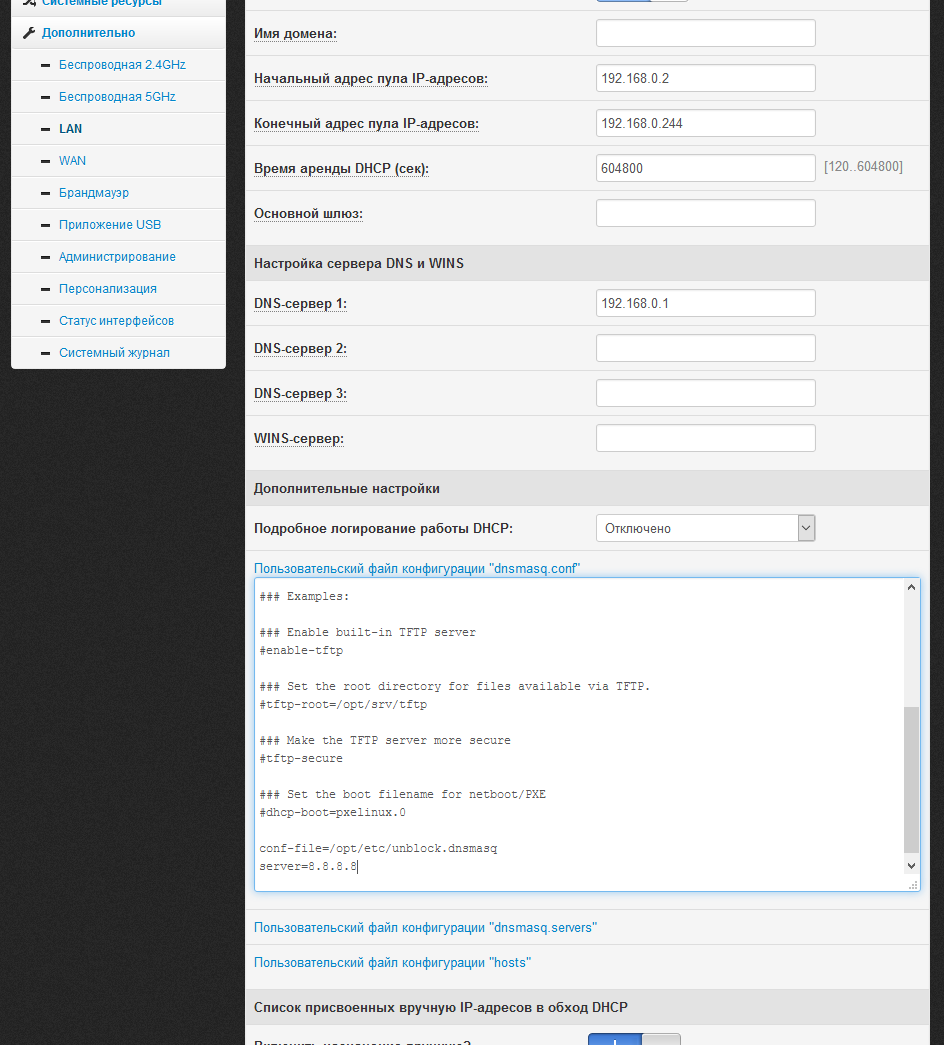
We need to connect the created unblock.dnsmasq file to dnsmasq. To do this, open the /etc/storage/dnsmasq/dnsmasq.conf file in the editor:
Add at the end:
If you wish (this is optional), you can add an additional server for resolving and reliability:
If you wish, you can edit the dnsmasq.conf file through the web interface of the router — Advanced> LAN> DHCP Server> Custom configuration file dnsmasq.conf. After editing, click "Apply".
This is an additional insurance in case programs / devices use their own method of resolving, and the IP address of the domain has changed. All you need to do is run the script unblock_ipset.sh with the desired frequency. For example, we will run every day at 6 am.
Replace the root name in the cron configuration file with admin:
Open the / opt / etc / crontab file in the editor:
Add at the end:
If you wish, you can comment out all the other template tasks. Here is what your crontab will look like:

Run the command:
After the reboot, open the check.torproject.org site in the browser (it should be added to unblock.txt). If you did everything right, then you will see the inscription “Congratulations. This browser is configured to use Tor. ”:

You must have a Keenetic / Zyxel router with an Entware package manager (OPKG) already configured. For example, here is a list of some routers that support Entware: Keenetic II, Keenetic III, Extra, Extra II, Giga II, Giga III, Omni, Omni II, Viva, Ultra, Ultra II, Omni (KN-1410), Extra (KN -1710), Giga (KN-1010), Ultra (KN-1810), Viva (KN-1910), DSL (KN-2010), Duo (KN-2110). Instructions for setting up Entware can be found here (up to 10 points).
If earlier (with firmware earlier than 2.07) you have already added support for Entware, then make sure that you are using non-outdated Entware-ng .
Be sure to enable the “Netfilter Subsystem Kernel Modules” - General Settings> Change Component Set. If it is not in the list of available, then try installing IPv6 Protocol component first. If after that does not appear, then try without it, but there is a high probability that you will not have unlock range and CIDR working (since there will be no support for many hash: net).

For the tests, I used Keenetic Ultra (KN-1810) with the latest firmware - 2.14.C.0.0-4.
Important note. You will have to disable the regular DNS server in the system, we will use dnsmasq instead. You will lose the ability to assign DNS services (Yandex.DNS / SkyDNS / AdGuard DNS) individually for clients, but you can easily use them globally through the dnsmasq settings if necessary.
mc is the Midnight Commander file manager. It is needed only because of the convenient editor mcedit. If you are used to using another text editor, then you can not install mc.
tor - Tor service.
tor-geoip is a geo-IP base for Tor.
bind-dig is a DNS client (similar to nslookup and host).
cron - task scheduler.
dnsmasq-full - DNS server.
ipset and iptables are console utilities ipset and iptables (perhaps they are already in the system and are not needed, I added them for backup).
Check that your router’s system has support for many hash: net (as it turned out, not all Keenetic routers have it):
If the team has not issued any errors and messages, then there is support, and just follow the instructions further. Otherwise (there is an error) in the following script you need to replace hash: net with hash: ip . At the same time, you will lose the ability to unlock by range and CIDR.
Create an empty set of addresses named unblock when booting the router. To do this, create the file /opt/etc/ndm/fs.d/100-ipset.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
To paste from the buffer, use Shift + Insert, save - F2, exit - F10.
Give execution rights:
Delete the contents of the Tor configuration file:
Open the Tor configuration file:
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN). A brief description of the configuration:
unblock.txt - a simple list to unlock. You can unblock a domain, IP address, range or CIDR. One line - one element. Blank lines (including spaces and tabs) are ignored. You can use the # character at the beginning of a line to ignore.
Create the /opt/etc/unblock.txt file:
Each line can contain a domain name, IP address, range or CIDR. You can use the # symbol to comment lines.
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
The script is quite simple, this is the essence of its work ... We are waiting for the rezolving of the google.com domain to work (if this is not done, the unblock will not be filled when the router is loaded, because the router will be still in the process of initialization). We read lines in the unblock.txt file. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with a # character. We are looking for the CIDR line. If CIDR is found, then add it to unblock. We are looking for a range in the string. If it is found, then add it to unblock. We are looking for an IP address in the line. If the IP is found, then add it to unblock. Solve the string via dig. All result IP addresses are added to unblock.
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
The script is quite simple. We consistently read lines from /opt/etc/unblock.txt. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with #. We skip lines that contain an IP address (IP or CIDR), i.e. we are only interested in strings with domain names. In the /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq file we add the lines “ipset = / domain_name / unblock”. This means that after determining the IP addresses of a specific domain, they will be automatically added to the unblock set.
Be sure to run the script to generate the unblock.dnsmasq file:
Check that the unblock.dnsmasq file is created:
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
Create a script /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
Give execution rights:
To do this, create the file /opt/etc/ndm/netfilter.d/100-redirect.sh :
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
If you used hash: ip instead of hash: net in step 2 , replace hash: net with hash: ip. In fact, we additionally duplicate the function of creating the unblock set of 2 steps. This is needed for security, if the scripts from fs.d have not yet started to run, and the scripts of netfilter.d are already running. It's okay if unblock has already been created earlier, the command will simply be ignored.
In the same file you can add (this is optional) redirect all requests to external port 53 to yourself. This is necessary so that clients on the local network do not use third-party DNS services. Requests will go through a regular DNS server. Before the last exit, add:
If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN).
Give execution rights:
Delete the contents of the dnsmasq configuration file:
Open the dnsmasq configuration file:
Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN).
This is an additional insurance in case programs / devices use their own method of resolving, and the IP address of the domain has changed. All you need to do is run the script unblock_ipset.sh with the desired frequency. For example, we will run every day at 6 am.
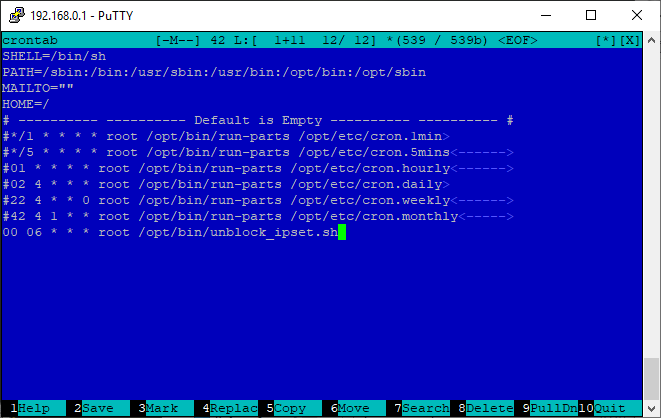
Open the / opt / etc / crontab file in the editor :
Add at the end:
If you wish, you can comment out all the other template tasks. Here is what your crontab will look like:
Connect to the Keenetic router CLI (port 23 for Telnet and 22 for SSH if the SSH Server component is added to the system).
Run the command:
The built-in DNS server will be turned off, and dnsmasq from Entware will be used instead. The router checks when the opt folder is mounted (if there is a flash drive / disk with Entware). If there is, then the regular DNS server is not used. If not, it is used. Those.removing the flash drive and rebooting the router, everything will work for you, as before (before setting up).
After the reboot, open the check.torproject.org site in the browser (it should be added to unblock.txt). If you did everything right, then you will see the inscription “Congratulations. This browser is configured to use Tor. ”:

If the check with the site check.torproject.org (it should be added to unblock.txt) passes, but for other resources the stub from the provider continues to open (or does not open), most likely the provider interferes with the DNS traffic, replacing the answers - you need to do an additional filtering bypass DNS queries.
If, after setting up, something does not work as it should, use simple commands to identify the problem phase.
Display the contents of the unblock set:
If the system reports that there is no such set, then the error in step 2 or you did not include the Netfilter module in the system (in the case of Keenetic).
If the set is empty, then the unblock_ipset.sh script, which in turn must be started with the S99unblock startup script, did not work. Run this unblock_ipset.sh script manually. If the set is full, then the error is at step 8. If the script cannot be executed (most likely it is expecting google.com to be resolved), then the error is somewhere on the side of the DNS server, possibly at step 10 or 6.
Check for a redirect in iptables :
If not, then the error in step 9.
If at all all the sites do not work, i.e. DNS does not work, an error somewhere in step 6 or 10. Perhaps in step 9.
If all sites from unblock.txt do not work (waiting time is exceeded), but all others work, then the problem is somewhere on the Tor side, an error in step 3.
If a provider intervenes in DNS traffic, replacing responses for blocked resources, it is very easy to get around. For this we will use dnscrypt-proxy. With desire and experience, you can easily replace dnscrypt with stubby (DNS over TLS).
dnscrypt will be used only for those domains listed in unblock.txt. All other requests will go through regular DNS servers.
If you are sure that your provider does not filter DNS queries, then this additional configuration is not necessary.
You should already have configured the lock bypass described above. The following settings are identical for Padavan and Keenetic OS.
Install additional software on the router:
Open the dnscrypt-proxy configuration file:
Find the parameters listen_addresses, fallback_resolver, cache and change them:
77.88.8.8:1253 is the address of the Yandex DNS server with a non-standard port. It is a backup in case dnscrypt-proxy encounters any problems.
Run dnscrypt-proxy:
Make sure dnscrypt-proxy is working (you should see a list of IP addresses in response):
Open the /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh script in the editor :
Replace content with:
We made a small change - now dig for resolving uses not a regular DNS server, but dnscrypt-proxy with port 9153.
Open the /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh script in the editor :
Replace content with:
We made a small change - now when generating the unblock.dnsmasq file, additional strings are added of the form "server = / domain_name / 127.0.0.1 # 9153". This means that rezolving of domains from the list will occur through dnscrypt-proxy.
Run unblock_update.sh:
Is done.All complex settings behind. Now you will only edit the unblock.txt list if necessary, adding or removing domains or IP addresses to unlock from it, and using the unblock_update.sh command activate the changes made.
For example, they unblocked torrent trackers and calmly watch torrents directly on your favorite Android box:
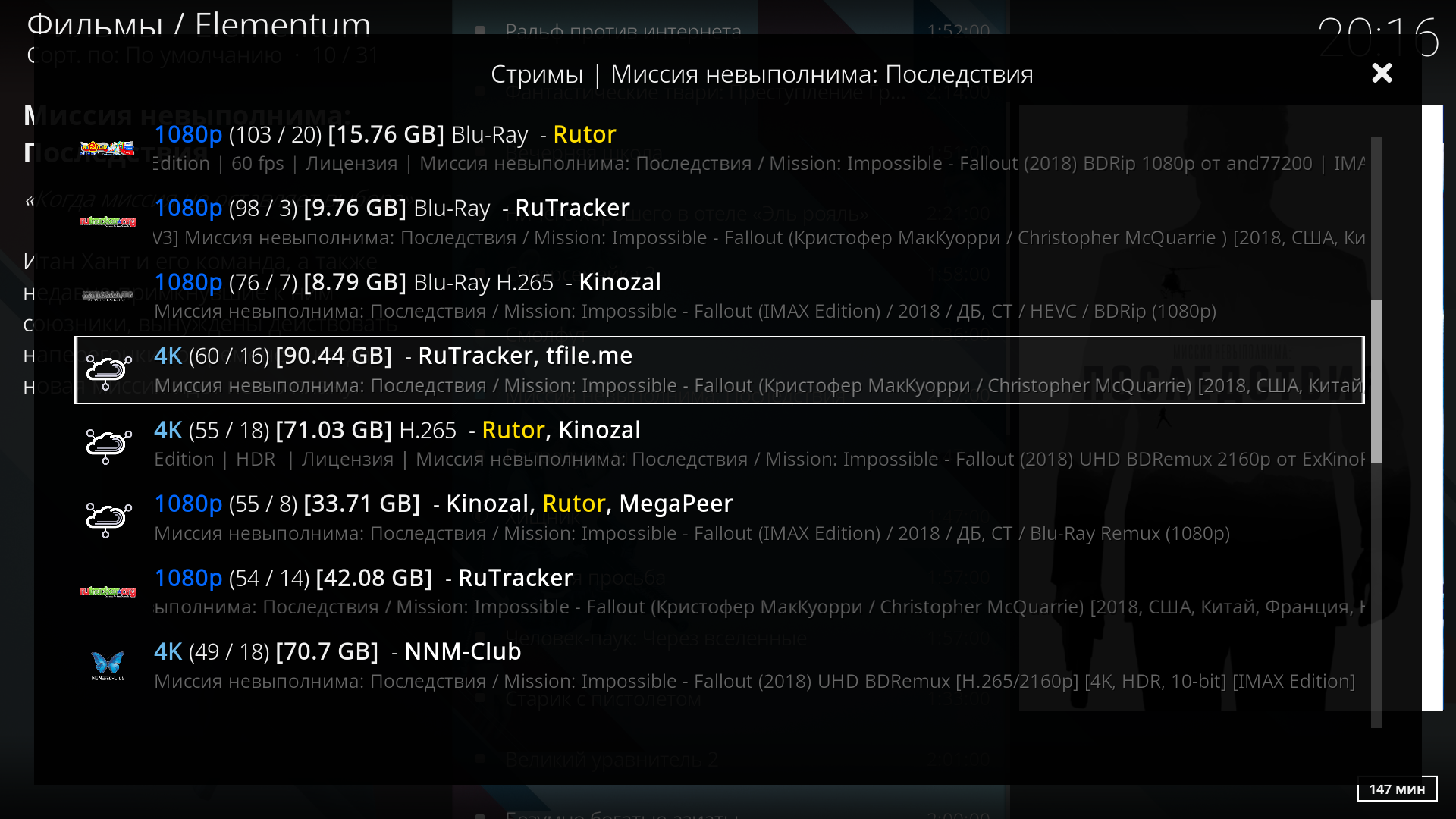
Additional information for those who want to block advertising domains on the router, in this comment. For those who want to use dnscrypt as the main resolver for all domains, in this comment.

Content
- Introduction
- How will you manage block bypass after setup?
- Principle of operation
- Configuring the router with firmware Padavan
- Configuring a router with Keenetic OS
- Basic methods for diagnosing errors after setup
- Optional bypass filtering DNS requests by the provider
Introduction
For about two years I used the option of bypassing locks from Zolg . Many online instructions are based on it. Including mine.
Everything was good, but "the best is always the enemy of the good." First, some new programs have become too “smart” and rezolvyat domains by their own methods, bypassing the router's DNS server. This does not allow dnsmasq on the router to add an address to the ipset to unlock and leads to a natural result - the resource remains locked. In Android 9, full support for DNS-over-TLS appeared, i.e. this lock bypass method stops working (if the other device has not previously accessed dnsmasq). Secondly, updating the entire list of domains from antizapret leads to unpredictable results every time. The list may include domains that are not blocked in reality, and whose operation is important through the main channel. You need to constantly be alert and edit the generated files with your hands. Thirdly, I got tired of “dragging along” a huge list of domains with tens of thousands of casinos and the like, which are simply not needed. Over time, I realized that I needed only a small specific list of blocked resources.
')
So, I have been using the slightly modified unlocking method for a year, which I am completely satisfied with:
- Simplicity and ease of management (after setting).
- Full control over which resources to unlock.
- Minimum requirements for processor resources and router RAM.
- Wide coverage of nuances when bypassing locks.
It is important to note that my option is not intended for the case when you need to unlock hundreds and thousands of domains. Because at the start of the router, a rezolving of each domain from the specified list occurs. The more domains in the list, the longer will be the initialization of the set ipset to unlock.
The basis of the lock bypass is the same - the Tor network. Its use is due to two simple factors — free of charge, and the likelihood that Tor will be blocked in Russia is close to zero, unlike any VPN service. Tor is the foundation of drug traffic in Russia from the middle to the bottom. Blocking Tor will lead to a search for new tools for the market and a decrease in the level of anonymity, which will lead to the successful revitalization of the work of local law enforcement agencies. In the end, this, like a virus, will begin to negatively affect the upper link. Given the latest amazing news about the links of top state officials with global drug traffic to Russia, blocking Tor in Russia is just a taboo, even though it is trivial. Neither Roskomnadzor, no matter what billions were allocated to this department, no court in Russia has the permission “from above” to block Tor. And it does not even surprise and frighten anyone, even though Russia is simply buried in drugs (every schoolchild knows what “daknet” is, and after 30 minutes has the actual opportunity in any city with a population of 10 thousand people to get any drugs without hindrance. in any quantities - such an evil truth of life). In the current mode, the probability of blocking the Tor network is lower than the probability of blocking the Hermitage museum site.
These instructions are easy to adapt for routers with OpenWrt. Also, minor changes can easily replace Tor with OpenVPN.
How will you manage block bypass after setup?
Everything is very simple. You have the file /opt/etc/unblock.txt - a simple list to unlock. You can unblock a domain, IP address, address range or CIDR. One line - one element. Blank lines are allowed, and you can use the # character at the beginning of a line to ignore.
Here is an example of my personal file.
###- rutracker.org rutor.info rutor.is mega-tor.org kinozal.tv nnm-club.me nnm-club.ws tfile.me tfile-home.org tfile1.cc megapeer.org megapeer.ru tapochek.net tparser.org rustorka.com uniongang.tv fast-torrent.ru ### hdrezka.ag hdrezka.me filmix.co filmix.cc seasonvar.ru ### lib.rus.ec flisland.net flibusta.site ### telegram.org tdesktop.com tdesktop.org tdesktop.info tdesktop.net telesco.pe telegram.dog telegram.me t.me web.telegram.org desktop.telegram.org updates.tdesktop.com venus.web.telegram.org flora.web.telegram.org vesta.web.telegram.org pluto.web.telegram.org aurora.web.telegram.org 149.154.172.0/22 91.108.4.0/22 91.108.8.0/22 91.108.12.0/22 91.108.16.0/22 91.108.56.0/22 149.154.160.0/22 149.154.164.0/22 149.154.168.0/22 ### edem.tv crimerussia.com 4pna.com 2019.vote ### Tor check.torproject.org ### IP ( # ) #195.82.146.214 ### CIDR ( # ) #103.21.244.0/22 ### ( # ) #100.100.100.200-100.100.100.210 After editing this file, you simply execute the command to apply the new configuration:
unblock_update.sh All resources from unblock.txt are unlocked without the need to restart the router.
Principle of operation
- When the router is initialized, an empty IP address set ipset is created with the name unblock.
- A rule is added to the firewall to redirect all packets with unblock destinations to Tor.
- The Tor service starts in transparent proxy mode.
- A special unblock_ipset.sh script runs, which resolves all the domains from unblock.txt and adds their IP addresses to the unblock set. IP addresses, ranges and CIDR from this file are also added to unblock.
- It starts dnsmasq with an additional unblock.dnsmasq configuration file, which specifies the addition of the IP addresses of the domains from unblock.txt to the unblock set during resolving.
- cron runs unblock_ipset.sh at regular intervals to partially compensate for possible cases with nuances.
- If necessary, all domains from unblock.txt (and only they) are resolved via dnscrypt-proxy, if the provider filters DNS.
Configuring the router with firmware Padavan
You must have a router with Padavan firmware installed and an Entware package manager already configured. On Windows, you can use the PuTTY client to connect to the router via SSH.
Make sure you use Entware, and not outdated Entware-ng. Look at the contents of the / opt / var / opkg-lists folder. There will be an entware or entware-ng file. In the second case, you need to upgrade your router's Padavan firmware to the latest version and reinstall the Entware package manager. Only after that proceed step by step instructions.
As reviews have shown, mostly problems arise for those who have Entware configured incorrectly initially (ie, scripts from init.d are not loaded) in the internal memory of the router. If you have Xiaomi Mi Router 3 or 3G, and you are not sure that Entware in your internal memory is working correctly (automatic start), then just set everything up again. Take PROMETHEUS. Updates the script (1). Update source code (2). Collect and flash the most current firmware (4). Reset the firmware settings (NVRAM and file storage) - More> Administration> Settings. Configure Internet access on the router and enable SSH. Perform in PROMETHEUS Firmware> Format RWFS. Choose Advanced> Administration> Settings> Mount file system in R / W section> UBIFS. Reboot the router. All actual Entware startup scripts from the internal memory will be registered automatically, and everything will work like a clock.
For the tests, I used the popular Xiaomi Mi Router 3G (Entware is installed in the internal memory) with the latest firmware - 32a93db. Everything will work even on the legendary baby WT3020 AD / F / H for $ 10.

1. Install the necessary software on the router
opkg update opkg install mc tor tor-geoip bind-dig cron mc is the Midnight Commander file manager. It is needed only because of the convenient editor mcedit. If you are used to using another text editor, then you can not install mc.
tor - Tor service.
tor-geoip is a geo-IP base for Tor.
bind-dig is a DNS client (similar to nslookup and host).
cron - task scheduler.
2. Initialize ipset, create multiple unblock IP addresses (start_script.sh)
Connect the necessary modules and create an empty set of addresses named unblock when booting the router. To do this, open the /etc/storage/start_script.sh file in the editor:
mcedit /etc/storage/start_script.sh Add at the end:
modprobe ip_set modprobe ip_set_hash_ip modprobe ip_set_hash_net modprobe ip_set_bitmap_ip modprobe ip_set_list_set modprobe xt_set ipset create unblock hash:net To paste from the buffer, use Shift + Insert, save - F2, exit - F10.

If you wish, you can edit the start_script.sh file through the web interface of the router - “Advanced”> “Personalization”> “Scripts”> “Run before router initialization”. After editing, click "Apply".

3. Configure Tor
Delete the contents of the Tor configuration file:
cat /dev/null > /opt/etc/tor/torrc Open the Tor configuration file:
mcedit /opt/etc/tor/torrc Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
User admin PidFile /opt/var/run/tor.pid ExcludeExitNodes {RU},{UA},{AM},{KG},{BY} StrictNodes 1 TransPort 192.168.0.1:9141 ExitRelay 0 ExitPolicy reject *:* ExitPolicy reject6 *:* GeoIPFile /opt/share/tor/geoip GeoIPv6File /opt/share/tor/geoip6 DataDirectory /opt/var/lib/tor If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN). A brief description of the configuration:
- Exclude weekend nodes: Russia, Ukraine, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan, Belarus.
- Hang the "transparent" proxy to the address 192.168.0.1, port 9141.
- Disallow being an exit point.
4. List of domains (and not only) to bypass the blocking (unblock.txt)
unblock.txt - a simple list to unlock. You can unblock a domain, IP address, range or CIDR. One line - one element. Blank lines (including spaces and tabs) are ignored. You can use the # character at the beginning of a line to ignore.
Create the /opt/etc/unblock.txt file:
mcedit /opt/etc/unblock.txt Each line can contain a domain name, IP address, range or CIDR. You can use the # symbol to comment lines.
Here is an example of my personal file.
###- rutracker.org rutor.info rutor.is mega-tor.org kinozal.tv nnm-club.me nnm-club.ws tfile.me tfile-home.org tfile1.cc megapeer.org megapeer.ru tapochek.net tparser.org rustorka.com uniongang.tv fast-torrent.ru ### hdrezka.ag hdrezka.me filmix.co filmix.cc seasonvar.ru ### lib.rus.ec flisland.net flibusta.site ### telegram.org tdesktop.com tdesktop.org tdesktop.info tdesktop.net telesco.pe telegram.dog telegram.me t.me web.telegram.org desktop.telegram.org updates.tdesktop.com venus.web.telegram.org flora.web.telegram.org vesta.web.telegram.org pluto.web.telegram.org aurora.web.telegram.org 149.154.172.0/22 91.108.4.0/22 91.108.8.0/22 91.108.12.0/22 91.108.16.0/22 91.108.56.0/22 149.154.160.0/22 149.154.164.0/22 149.154.168.0/22 ### edem.tv crimerussia.com 4pna.com 2019.vote ### Tor check.torproject.org ### IP ( # ) #195.82.146.214 ### CIDR ( # ) #103.21.244.0/22 ### ( # ) #100.100.100.200-100.100.100.210 5. Script to populate the set of unblock IP addresses of a given list of domains (unblock_ipset.sh)
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh until ADDRS=$(dig +short google.com @localhost) && [ -n "$ADDRS" ] > /dev/null 2>&1; do sleep 5; done while read line || [ -n "$line" ]; do [ -z "$line" ] && continue [ "${line:0:1}" = "#" ] && continue cidr=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}/[0-9]{1,2}') if [ ! -z "$cidr" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $cidr continue fi range=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}-[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}') if [ ! -z "$range" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $range continue fi addr=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}') if [ ! -z "$addr" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $addr continue fi dig +short $line @localhost | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}' | awk '{system("ipset -exist add unblock "$1)}' done < /opt/etc/unblock.txt Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh The script is quite simple, this is the essence of its work ... We are waiting for the rezolving of the google.com domain to work (if this is not done, then the unblock set will not be filled when the router is loaded, because the router will still be in the process of initialization). We read lines in the unblock.txt file. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with a # character. We are looking for the CIDR line. If CIDR is found, then add it to unblock. We search for a range in the string. If it is found, then add it to unblock. We are looking for an IP address in the line. If the IP is found, then add it to unblock. Solve the string via dig. All result IP addresses are added to unblock.
6. Script for generating the additional dnsmasq configuration file from the specified list of domains (unblock_dnsmasq.sh)
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh cat /dev/null > /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq while read line || [ -n "$line" ]; do [ -z "$line" ] && continue [ "${line:0:1}" = "#" ] && continue echo $line | grep -Eq '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}' && continue echo "ipset=/$line/unblock" >> /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq done < /opt/etc/unblock.txt Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh The script is quite simple, here is the essence of his work ... We consistently read lines from /opt/etc/unblock.txt. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with #. We skip lines that contain an IP address (IP, range, CIDR), i.e. we are only interested in strings with domain names. In the /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq file we add the lines “ipset = / domain_name / unblock”. This means that after determining the IP addresses of a specific domain, they will be automatically added to the unblock set.
Be sure to run the script to generate the unblock.dnsmasq file:
unblock_dnsmasq.sh Check that the unblock.dnsmasq file is created:
cat /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq 7. Script manual forced system update after editing the list of domains (unblock_update.sh)
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh ipset flush unblock /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh restart_dhcpd sleep 3 /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh & Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh 8. Script for automatic filling of unblock sets when booting the router (S99unblock)
Create a script /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock :
mcedit /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh [ "$1" != "start" ] && exit 0 /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh & Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock 9. Redirecting packets from unblock to Tor (post_iptables_script.sh)
Open the /etc/storage/post_iptables_script.sh file in the editor:
mcedit /etc/storage/post_iptables_script.sh Add at the end:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i br0 -p tcp -m set --match-set unblock dst -j REDIRECT --to-port 9141 
If you wish, you can edit the post_iptables_script.sh file via the web interface of the router - “Advanced”> “Personalization”> “Scripts”> “Run after restarting the firewall rules”. After editing, click "Apply".

In the same file you can add (this is optional) redirect all requests to external port 53 to yourself. This is necessary so that clients on the local network do not use third-party DNS services. Requests will go through a regular DNS server.
iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -i br0 -p udp --dport 53 -j DNAT --to 192.168.0.1 iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -i br0 -p tcp --dport 53 -j DNAT --to 192.168.0.1 If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN).
10. Connecting an additional configuration file to dnsmasq
We need to connect the created unblock.dnsmasq file to dnsmasq. To do this, open the /etc/storage/dnsmasq/dnsmasq.conf file in the editor:
mcedit /etc/storage/dnsmasq/dnsmasq.conf Add at the end:
conf-file=/opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq If you wish (this is optional), you can add an additional server for resolving and reliability:
server=8.8.8.8 If you wish, you can edit the dnsmasq.conf file through the web interface of the router — Advanced> LAN> DHCP Server> Custom configuration file dnsmasq.conf. After editing, click "Apply".

11. Adding a task to cron to periodically update the contents of the set unblock
This is an additional insurance in case programs / devices use their own method of resolving, and the IP address of the domain has changed. All you need to do is run the script unblock_ipset.sh with the desired frequency. For example, we will run every day at 6 am.
Replace the root name in the cron configuration file with admin:
sed -i 's/root/admin/g' /opt/etc/crontab Open the / opt / etc / crontab file in the editor:
mcedit /opt/etc/crontab Add at the end:
00 06 * * * admin /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh If you wish, you can comment out all the other template tasks. Here is what your crontab will look like:

12. Reboot the router
Run the command:
reboot After the reboot, open the check.torproject.org site in the browser (it should be added to unblock.txt). If you did everything right, then you will see the inscription “Congratulations. This browser is configured to use Tor. ”:

Configuring a router with Keenetic OS
You must have a Keenetic / Zyxel router with an Entware package manager (OPKG) already configured. For example, here is a list of some routers that support Entware: Keenetic II, Keenetic III, Extra, Extra II, Giga II, Giga III, Omni, Omni II, Viva, Ultra, Ultra II, Omni (KN-1410), Extra (KN -1710), Giga (KN-1010), Ultra (KN-1810), Viva (KN-1910), DSL (KN-2010), Duo (KN-2110). Instructions for setting up Entware can be found here (up to 10 points).
If earlier (with firmware earlier than 2.07) you have already added support for Entware, then make sure that you are using non-outdated Entware-ng .
Be sure to enable the “Netfilter Subsystem Kernel Modules” - General Settings> Change Component Set. If it is not in the list of available, then try installing IPv6 Protocol component first. If after that does not appear, then try without it, but there is a high probability that you will not have unlock range and CIDR working (since there will be no support for many hash: net).

For the tests, I used Keenetic Ultra (KN-1810) with the latest firmware - 2.14.C.0.0-4.
Important note. You will have to disable the regular DNS server in the system, we will use dnsmasq instead. You will lose the ability to assign DNS services (Yandex.DNS / SkyDNS / AdGuard DNS) individually for clients, but you can easily use them globally through the dnsmasq settings if necessary.
1. Install the necessary software on the router
opkg update opkg install mc tor tor-geoip bind-dig cron dnsmasq-full ipset iptables mc is the Midnight Commander file manager. It is needed only because of the convenient editor mcedit. If you are used to using another text editor, then you can not install mc.
tor - Tor service.
tor-geoip is a geo-IP base for Tor.
bind-dig is a DNS client (similar to nslookup and host).
cron - task scheduler.
dnsmasq-full - DNS server.
ipset and iptables are console utilities ipset and iptables (perhaps they are already in the system and are not needed, I added them for backup).
2. Initialize ipset, create multiple unblock IP addresses (100-ipset.sh)
Check that your router’s system has support for many hash: net (as it turned out, not all Keenetic routers have it):
ipset create test hash:net If the team has not issued any errors and messages, then there is support, and just follow the instructions further. Otherwise (there is an error) in the following script you need to replace hash: net with hash: ip . At the same time, you will lose the ability to unlock by range and CIDR.
Create an empty set of addresses named unblock when booting the router. To do this, create the file /opt/etc/ndm/fs.d/100-ipset.sh :
mcedit /opt/etc/ndm/fs.d/100-ipset.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh [ "$1" != "start" ] && exit 0 ipset create unblock hash:net -exist exit 0 To paste from the buffer, use Shift + Insert, save - F2, exit - F10.
Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/etc/ndm/fs.d/100-ipset.sh 3. Configure Tor
Delete the contents of the Tor configuration file:
cat /dev/null > /opt/etc/tor/torrc Open the Tor configuration file:
mcedit /opt/etc/tor/torrc Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
User root PidFile /opt/var/run/tor.pid ExcludeExitNodes {RU},{UA},{AM},{KG},{BY} StrictNodes 1 TransPort 192.168.0.1:9141 ExitRelay 0 ExitPolicy reject *:* ExitPolicy reject6 *:* GeoIPFile /opt/share/tor/geoip GeoIPv6File /opt/share/tor/geoip6 DataDirectory /opt/var/lib/tor If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN). A brief description of the configuration:
- Exclude weekend nodes: Russia, Ukraine, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan, Belarus.
- Hang the "transparent" proxy to the address 192.168.0.1, port 9141.
- Forbid to be an exit point.
4. List of domains (and not only) to bypass the blocking (unblock.txt)
unblock.txt - a simple list to unlock. You can unblock a domain, IP address, range or CIDR. One line - one element. Blank lines (including spaces and tabs) are ignored. You can use the # character at the beginning of a line to ignore.
Create the /opt/etc/unblock.txt file:
mcedit /opt/etc/unblock.txt Each line can contain a domain name, IP address, range or CIDR. You can use the # symbol to comment lines.
Here is an example of my personal file.
###- rutracker.org rutor.info rutor.is mega-tor.org kinozal.tv nnm-club.me nnm-club.ws tfile.me tfile-home.org tfile1.cc megapeer.org megapeer.ru tapochek.net tparser.org rustorka.com uniongang.tv fast-torrent.ru ### hdrezka.ag hdrezka.me filmix.co filmix.cc seasonvar.ru ### lib.rus.ec flisland.net flibusta.site ### telegram.org tdesktop.com tdesktop.org tdesktop.info tdesktop.net telesco.pe telegram.dog telegram.me t.me web.telegram.org desktop.telegram.org updates.tdesktop.com venus.web.telegram.org flora.web.telegram.org vesta.web.telegram.org pluto.web.telegram.org aurora.web.telegram.org 149.154.172.0/22 91.108.4.0/22 91.108.8.0/22 91.108.12.0/22 91.108.16.0/22 91.108.56.0/22 149.154.160.0/22 149.154.164.0/22 149.154.168.0/22 ### edem.tv crimerussia.com 4pna.com 2019.vote ### Tor check.torproject.org ### IP ( # ) #195.82.146.214 ### CIDR ( # ) #103.21.244.0/22 ### ( # ) #100.100.100.200-100.100.100.210 5. Script to populate the set of unblock IP addresses of a given list of domains (unblock_ipset.sh)
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh until ADDRS=$(dig +short google.com @localhost) && [ -n "$ADDRS" ] > /dev/null 2>&1; do sleep 5; done while read line || [ -n "$line" ]; do [ -z "$line" ] && continue [ "${line:0:1}" = "#" ] && continue cidr=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}/[0-9]{1,2}') if [ ! -z "$cidr" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $cidr continue fi range=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}-[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}') if [ ! -z "$range" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $range continue fi addr=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}') if [ ! -z "$addr" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $addr continue fi dig +short $line @localhost | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}' | awk '{system("ipset -exist add unblock "$1)}' done < /opt/etc/unblock.txt Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh The script is quite simple, this is the essence of its work ... We are waiting for the rezolving of the google.com domain to work (if this is not done, the unblock will not be filled when the router is loaded, because the router will be still in the process of initialization). We read lines in the unblock.txt file. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with a # character. We are looking for the CIDR line. If CIDR is found, then add it to unblock. We are looking for a range in the string. If it is found, then add it to unblock. We are looking for an IP address in the line. If the IP is found, then add it to unblock. Solve the string via dig. All result IP addresses are added to unblock.
6. Script for generating the additional dnsmasq configuration file from the specified list of domains (unblock_dnsmasq.sh)
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh cat /dev/null > /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq while read line || [ -n "$line" ]; do [ -z "$line" ] && continue [ "${line:0:1}" = "#" ] && continue echo $line | grep -Eq '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}' && continue echo "ipset=/$line/unblock" >> /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq done < /opt/etc/unblock.txt Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh The script is quite simple. We consistently read lines from /opt/etc/unblock.txt. Spaces and tabs at the beginning and at the end are automatically removed from the read lines. Skipping blank lines. We skip lines that begin with #. We skip lines that contain an IP address (IP or CIDR), i.e. we are only interested in strings with domain names. In the /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq file we add the lines “ipset = / domain_name / unblock”. This means that after determining the IP addresses of a specific domain, they will be automatically added to the unblock set.
Be sure to run the script to generate the unblock.dnsmasq file:
unblock_dnsmasq.sh Check that the unblock.dnsmasq file is created:
cat /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq 7. Script manual forced system update after editing the list of domains (unblock_update.sh)
Create a script /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh ipset flush unblock /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh /opt/etc/init.d/S56dnsmasq restart /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh & Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/bin/unblock_update.sh 8. Script for automatic filling of unblock sets when booting the router (S99unblock)
Create a script /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock :
mcedit /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh [ "$1" != "start" ] && exit 0 /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh & Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/etc/init.d/S99unblock 9. Redirecting packets from unblock to Tor (100-redirect.sh)
To do this, create the file /opt/etc/ndm/netfilter.d/100-redirect.sh :
mcedit /opt/etc/ndm/netfilter.d/100-redirect.sh Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
#!/bin/sh [ "$type" == "ip6tables" ] && exit 0 if [ -z "$(iptables-save 2>/dev/null | grep unblock)" ]; then ipset create unblock hash:net -exist iptables -w -t nat -A PREROUTING -i br0 -p tcp -m set --match-set unblock dst -j REDIRECT --to-port 9141 fi exit 0 If you used hash: ip instead of hash: net in step 2 , replace hash: net with hash: ip. In fact, we additionally duplicate the function of creating the unblock set of 2 steps. This is needed for security, if the scripts from fs.d have not yet started to run, and the scripts of netfilter.d are already running. It's okay if unblock has already been created earlier, the command will simply be ignored.
In the same file you can add (this is optional) redirect all requests to external port 53 to yourself. This is necessary so that clients on the local network do not use third-party DNS services. Requests will go through a regular DNS server. Before the last exit, add:
if [ -z "$(iptables-save 2>/dev/null | grep "udp \-\-dport 53 \-j DNAT")" ]; then iptables -w -t nat -I PREROUTING -i br0 -p udp --dport 53 -j DNAT --to 192.168.0.1 fi if [ -z "$(iptables-save 2>/dev/null | grep "tcp \-\-dport 53 \-j DNAT")" ]; then iptables -w -t nat -I PREROUTING -i br0 -p tcp --dport 53 -j DNAT --to 192.168.0.1 fi If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN).
Give execution rights:
chmod +x /opt/etc/ndm/netfilter.d/100-redirect.sh 10. Configure dnsmasq and connect an additional configuration file to dnsmasq
Delete the contents of the dnsmasq configuration file:
cat /dev/null > /opt/etc/dnsmasq.conf Open the dnsmasq configuration file:
mcedit /opt/etc/dnsmasq.conf Insert (Shift + Insert) content:
user=nobody bogus-priv no-negcache clear-on-reload bind-dynamic listen-address=192.168.0.1 listen-address=127.0.0.1 min-port=4096 cache-size=1536 expand-hosts log-facility=/dev/null log-async conf-file=/opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq server=8.8.8.8 If necessary, replace 192.168.0.1 with the internal address of your router (LAN).
11. Adding a task to cron to periodically update the contents of the set unblock
This is an additional insurance in case programs / devices use their own method of resolving, and the IP address of the domain has changed. All you need to do is run the script unblock_ipset.sh with the desired frequency. For example, we will run every day at 6 am.
Open the / opt / etc / crontab file in the editor :
mcedit /opt/etc/crontab Add at the end:
00 06 * * * root /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh If you wish, you can comment out all the other template tasks. Here is what your crontab will look like:

12. Disable regular DNS server and reboot the router
Connect to the Keenetic router CLI (port 23 for Telnet and 22 for SSH if the SSH Server component is added to the system).
Run the command:
opkg dns-override system configuration save system reboot The built-in DNS server will be turned off, and dnsmasq from Entware will be used instead. The router checks when the opt folder is mounted (if there is a flash drive / disk with Entware). If there is, then the regular DNS server is not used. If not, it is used. Those.removing the flash drive and rebooting the router, everything will work for you, as before (before setting up).
After the reboot, open the check.torproject.org site in the browser (it should be added to unblock.txt). If you did everything right, then you will see the inscription “Congratulations. This browser is configured to use Tor. ”:

Basic methods for diagnosing errors after setup
If the check with the site check.torproject.org (it should be added to unblock.txt) passes, but for other resources the stub from the provider continues to open (or does not open), most likely the provider interferes with the DNS traffic, replacing the answers - you need to do an additional filtering bypass DNS queries.
If, after setting up, something does not work as it should, use simple commands to identify the problem phase.
Display the contents of the unblock set:
ipset list unblock If the system reports that there is no such set, then the error in step 2 or you did not include the Netfilter module in the system (in the case of Keenetic).
If the set is empty, then the unblock_ipset.sh script, which in turn must be started with the S99unblock startup script, did not work. Run this unblock_ipset.sh script manually. If the set is full, then the error is at step 8. If the script cannot be executed (most likely it is expecting google.com to be resolved), then the error is somewhere on the side of the DNS server, possibly at step 10 or 6.
Check for a redirect in iptables :
iptables-save 2>/dev/null | grep unblock If not, then the error in step 9.
If at all all the sites do not work, i.e. DNS does not work, an error somewhere in step 6 or 10. Perhaps in step 9.
If all sites from unblock.txt do not work (waiting time is exceeded), but all others work, then the problem is somewhere on the Tor side, an error in step 3.
Optional bypass filtering DNS requests by the provider
If a provider intervenes in DNS traffic, replacing responses for blocked resources, it is very easy to get around. For this we will use dnscrypt-proxy. With desire and experience, you can easily replace dnscrypt with stubby (DNS over TLS).
dnscrypt will be used only for those domains listed in unblock.txt. All other requests will go through regular DNS servers.
If you are sure that your provider does not filter DNS queries, then this additional configuration is not necessary.
You should already have configured the lock bypass described above. The following settings are identical for Padavan and Keenetic OS.
Install additional software on the router:
opkg update opkg install dnscrypt-proxy2 Open the dnscrypt-proxy configuration file:
mcedit /opt/etc/dnscrypt-proxy.toml Find the parameters listen_addresses, fallback_resolver, cache and change them:
listen_addresses = ['127.0.0.1:9153'] fallback_resolver = '77.88.8.8:1253' cache = false 77.88.8.8:1253 is the address of the Yandex DNS server with a non-standard port. It is a backup in case dnscrypt-proxy encounters any problems.
Run dnscrypt-proxy:
/opt/etc/init.d/S09dnscrypt-proxy2 start Make sure dnscrypt-proxy is working (you should see a list of IP addresses in response):
dig +short google.com @localhost -p 9153 Open the /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh script in the editor :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_ipset.sh Replace content with:
#!/bin/sh until ADDRS=$(dig +short google.com @localhost -p 9153) && [ -n "$ADDRS" ] > /dev/null 2>&1; do sleep 5; done while read line || [ -n "$line" ]; do [ -z "$line" ] && continue [ "${line:0:1}" = "#" ] && continue cidr=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}/[0-9]{1,2}') if [ ! -z "$cidr" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $cidr continue fi range=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}-[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}') if [ ! -z "$range" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $range continue fi addr=$(echo $line | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}') if [ ! -z "$addr" ]; then ipset -exist add unblock $addr continue fi dig +short $line @localhost -p 9153 | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}' | awk '{system("ipset -exist add unblock "$1)}' done < /opt/etc/unblock.txt We made a small change - now dig for resolving uses not a regular DNS server, but dnscrypt-proxy with port 9153.
Open the /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh script in the editor :
mcedit /opt/bin/unblock_dnsmasq.sh Replace content with:
#!/bin/sh cat /dev/null > /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq while read line || [ -n "$line" ]; do [ -z "$line" ] && continue [ "${line:0:1}" = "#" ] && continue echo $line | grep -Eq '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}' && continue echo "ipset=/$line/unblock" >> /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq echo "server=/$line/127.0.0.1#9153" >> /opt/etc/unblock.dnsmasq done < /opt/etc/unblock.txt We made a small change - now when generating the unblock.dnsmasq file, additional strings are added of the form "server = / domain_name / 127.0.0.1 # 9153". This means that rezolving of domains from the list will occur through dnscrypt-proxy.
Run unblock_update.sh:
unblock_update.sh Is done.All complex settings behind. Now you will only edit the unblock.txt list if necessary, adding or removing domains or IP addresses to unlock from it, and using the unblock_update.sh command activate the changes made.
For example, they unblocked torrent trackers and calmly watch torrents directly on your favorite Android box:

Additional information for those who want to block advertising domains on the router, in this comment. For those who want to use dnscrypt as the main resolver for all domains, in this comment.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/428992/
All Articles