GPS firewall for data centers - why you need it and how it works
GPS data is needed not only for navigators to build routes, but also data centers for time synchronization. This feature is used by hackers when they attack IT infrastructure. We will explain the essence of such attacks and how the GPS firewall protects them.

/ Wikimedia / NASA / PD
Every year attacks on the IT infrastructure of banks, airports and data centers increase by 20%. The task of such attacks is not the theft of money, but harming the organization’s business processes. Moreover, the final damage to the company may be greater than in the case of the ordinary theft of funds.
')
One of the most famous examples of attacks on IT infrastructure is WannaCry encryption. According to experts , the goal of the viral campaign was not to obtain financial benefits, but to stop the work of specific organizations (including banks).
GPS data centers receive Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC ) data. This information is used to synchronize servers using NTP . Synchronization systems are needed to set time stamps and indicate the beginning and end of any process in the data center network. Failure in the GPS system can complicate troubleshooting: if the error was logged with the wrong time stamp, it complicates the search for its cause.
When intruders are planning to hack data center systems, they can replace the true GPS signal from a satellite in an attempt to hide their malicious activity. This type of attack is called GPS spoofing . The substitution of a signal is possible due to the fact that it is not encrypted and is subject to environmental interference (it is easy to “block” it).
Danger for GPS data center systems also represent jammer devices. They " turn off " the satellite signal, which is why servers, routers and other equipment in the data center can not synchronize their work . The effects of the attack with the GPS jammer were experienced by Equinix. True, it happened by chance - an old GPS-antenna was installed on the roof of the data center, which weakened the signal and seriously interfered with the normal operation of the IT infrastructure.
To protect the data center from spoofing and interference with the positioning system, the American company Microsemi has developed a GPS firewall . The device acts as a buffer between the GPS antenna and the critical infrastructure of the data center.
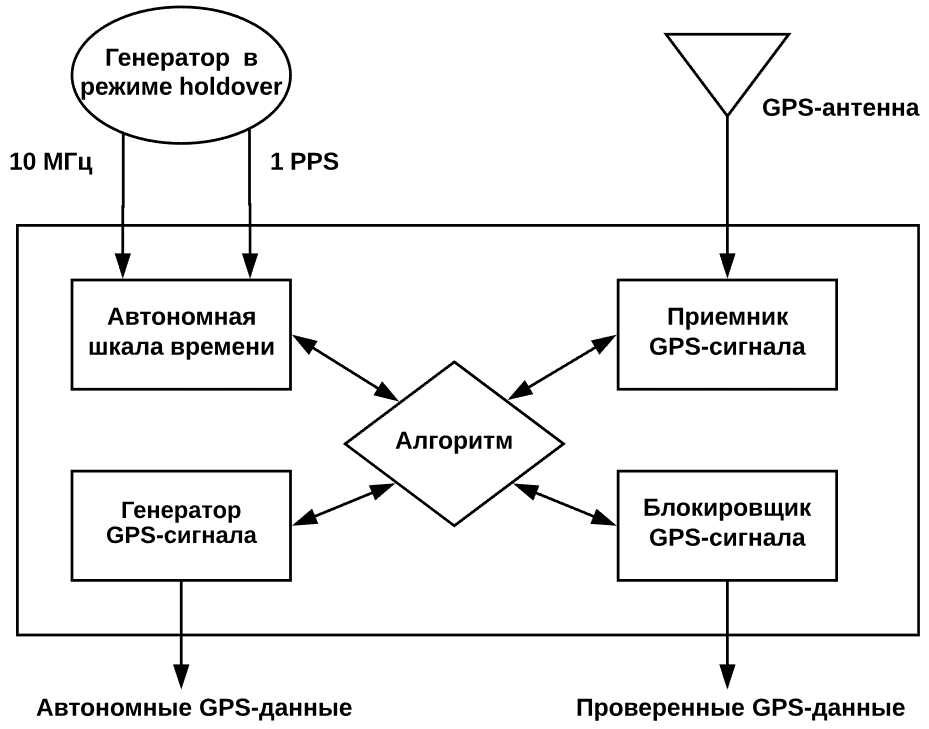
The firewall implements special algorithms that evaluate the characteristics of the GPS signal: radio frequency power, the correctness of geodata and time, and so on. If the system understands that the signal does not match the desired parameters (for example, anomalies in the transmission power are detected), then it is blocked. In this case (or in case of loss of communication with satellites), the firewall starts the generator of the reference time - the rubidium clock (holdover mode). They maintain the performance of all systems until the GPS signal is restored.
Two years ago, an error in the work of the GPS network disrupted the work of receivers developed by Microsemi around the world. Devices could not correctly determine the time and coordinates.
Microsemi says that the atomic clock in the firewall for the data center will help to avoid problems with the synchronization of equipment in the event of a global GPS failure. However, such hours will work only for a couple of months. If during this time the GPS malfunction is not resolved, problems may occur with the timestamp arrangement in the logs, etc.
Algorithms for detecting GPS spoofing have also been developed by researchers from the University of Texas at San Antonio. Their solution compares the time of the incoming GPS signal with previous figures. If a substitution of parameters is detected, the system informs the data center operators about this.
Another option for protecting geolocation systems is encryption. In Russia, to protect GLONASS, it was proposed to use high-precision signals (BT code) instead of standard ones. They are protected by the ever-changing secret codes. However, this solution did not find application, since it is possible to use the BT code only with the permission of the RF Ministry of Defense .
Probably in the future there will be other technologies to protect the systems for determining the time and coordinates in the data centers. Or they will be transferred to fully autonomous solutions, which will be less dependent on external factors.

/ Wikimedia / NASA / PD
Infrastructure attacks are gaining momentum
Every year attacks on the IT infrastructure of banks, airports and data centers increase by 20%. The task of such attacks is not the theft of money, but harming the organization’s business processes. Moreover, the final damage to the company may be greater than in the case of the ordinary theft of funds.
')
One of the most famous examples of attacks on IT infrastructure is WannaCry encryption. According to experts , the goal of the viral campaign was not to obtain financial benefits, but to stop the work of specific organizations (including banks).
Types of GPS attacks
GPS data centers receive Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC ) data. This information is used to synchronize servers using NTP . Synchronization systems are needed to set time stamps and indicate the beginning and end of any process in the data center network. Failure in the GPS system can complicate troubleshooting: if the error was logged with the wrong time stamp, it complicates the search for its cause.
When intruders are planning to hack data center systems, they can replace the true GPS signal from a satellite in an attempt to hide their malicious activity. This type of attack is called GPS spoofing . The substitution of a signal is possible due to the fact that it is not encrypted and is subject to environmental interference (it is easy to “block” it).
Danger for GPS data center systems also represent jammer devices. They " turn off " the satellite signal, which is why servers, routers and other equipment in the data center can not synchronize their work . The effects of the attack with the GPS jammer were experienced by Equinix. True, it happened by chance - an old GPS-antenna was installed on the roof of the data center, which weakened the signal and seriously interfered with the normal operation of the IT infrastructure.
How to protect against attacks: GPS-firewall
To protect the data center from spoofing and interference with the positioning system, the American company Microsemi has developed a GPS firewall . The device acts as a buffer between the GPS antenna and the critical infrastructure of the data center.

The firewall implements special algorithms that evaluate the characteristics of the GPS signal: radio frequency power, the correctness of geodata and time, and so on. If the system understands that the signal does not match the desired parameters (for example, anomalies in the transmission power are detected), then it is blocked. In this case (or in case of loss of communication with satellites), the firewall starts the generator of the reference time - the rubidium clock (holdover mode). They maintain the performance of all systems until the GPS signal is restored.
Two years ago, an error in the work of the GPS network disrupted the work of receivers developed by Microsemi around the world. Devices could not correctly determine the time and coordinates.
Microsemi says that the atomic clock in the firewall for the data center will help to avoid problems with the synchronization of equipment in the event of a global GPS failure. However, such hours will work only for a couple of months. If during this time the GPS malfunction is not resolved, problems may occur with the timestamp arrangement in the logs, etc.
“The GPS firewall will protect against spoofing and jamming signals, but it is important to understand that such attacks are often used by hackers as a screen. So they disguise their malicious activities on the network, so it’s important not to forget about ordinary firewalls, ”says Sergey Belkin, head of the IaaS service development department at 1cloud.ru . - IaaS-providers who place their equipment in data centers, just offer such a service. For example, our customers can connect to a firewall that will protect the infrastructure at the network level . In the near future, the feature will be available at the server level . The system closes attack vectors such as MITM or IP spoofing . ”
About other ways to protect
Algorithms for detecting GPS spoofing have also been developed by researchers from the University of Texas at San Antonio. Their solution compares the time of the incoming GPS signal with previous figures. If a substitution of parameters is detected, the system informs the data center operators about this.
Another option for protecting geolocation systems is encryption. In Russia, to protect GLONASS, it was proposed to use high-precision signals (BT code) instead of standard ones. They are protected by the ever-changing secret codes. However, this solution did not find application, since it is possible to use the BT code only with the permission of the RF Ministry of Defense .
Probably in the future there will be other technologies to protect the systems for determining the time and coordinates in the data centers. Or they will be transferred to fully autonomous solutions, which will be less dependent on external factors.
Other posts from our corporate blog:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/428774/
All Articles