Cooling systems in data centers Selectel
Competitive prices for services have always been the “king of arguments” for customers when choosing a data center. And what are these prices? The first to come to mind are the costs of IT equipment and electricity, but a significant proportion of the price structure is the cost of cooling servers, storage systems (DSS) and network devices. For example, a server with multiple processors emits up to 600 watts and more heat, which must be effectively removed, and cold air is fed to the entrance of the server ventilation openings.
In this article, we will introduce you to the technology of climate systems in the Selectel data centers and tell you how new products in this area reduce the operating costs of data centers, and indirectly, the amounts in our customers' accounts.
')
3 service markets - 3 cooling requirements
In the data center services market, - if roughly estimated - there are three main segments. This is, firstly, colocation, then IaaS infrastructure - dedicated servers plus cloud storage, and the third segment - cloud servers (VPC, VPS, VMware Cloud), including public, private and hybrid clouds.

No matter how surprising it may seem, but the clients of each of the segments have different requirements for climate systems. The most demanding customers are placing their own equipment (collocation) in the data center. Among them are many IT executives with many years of practice and a conservative idea of what temperature should be in the server rooms. 10-15 years ago, the requirement to provide + 18 ° C in the cold corridor was really crucial. But modern servers and storage systems work stably up to + 27 ° C.
By the way, the specific air temperature range for the server rooms of the data center is rather strictly regulated by the recommendations of ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers), which guide all over the world, including Russia. The recommended temperature range changes over time, somewhere in the early 2000s it really was 16-20 ° C, then 18-22 ° C, and today the recommended air temperature for cooling servers is already 20-27 ° C.
 “In its data centers, Selectel strives to maintain the air temperature at the lower limit of the recommended range for ASHRAE, on average about 23 ° C,” noted Kirill Malevanov, technical director of Selectel, for the article.
“In its data centers, Selectel strives to maintain the air temperature at the lower limit of the recommended range for ASHRAE, on average about 23 ° C,” noted Kirill Malevanov, technical director of Selectel, for the article.What can be concluded from this for a data center business? Use of expensive cooling with the help of air conditioners should be mainly for server rooms allocated for the service of collocation. Accordingly, for server rooms for IaaS services, and even more so for cloud servers, you can use equipment that maximally uses cooling due to the environment - up to a simple blowing of the servers with outboard air.
Moreover, since Selectel owns several data centers, and in different regions, freedom of maneuver appears. In other words, it is possible even at the design stage, the construction of a data center and the choice of climate equipment to take into account the cooling requirements in the selected service segment. And later in the process of operation, to carry out modernization of climate systems, taking into account the reduction of TCO in the provision of these services.
What is PUE
The main indicator of data center performance is the energy efficiency ratio (Power usage effectiveness, PUE) used in the data center industry since 2007. What is this coefficient:

In other words, the closer PUE is to 1, the more advanced the data center is. However, the value of 1.0 is in principle impossible to achieve, since this corresponds to the level of energy efficiency of the perpetual motion machine. By the way, the full definition of the term PUE can be found in the document PUE, A Comprehensive Examination of the Metric (PDF) .
In practice, PUE values that are at the level of 1.10 - 1.15 are considered excellent. For example, according to publications, for Google data centers, the PUE value averaged over all data centers in different regions and at different times of the year is 1.12.
Next, let's take a closer look at the cooling systems in separate Selectel data centers.
"Flower 1" - freon
The first data center "Flower 1" was launched in 2008, when the colocation service was dominant in the market. In addition, it is the center of St. Petersburg - with the free areas, the situation was then somewhat constrained. Accordingly, in the data center "Flower 1" were installed classic industrial air conditioners for the data center on the freon, which work to date.
The principle of operation of such an air conditioner is based on the transition of freon to various state of aggregation. Cold air under the raised floor is supplied to the so-called “cold corridors” with computing equipment, and the heated air goes to the server room (to the “hot corridors”), from where it is again sucked into the air-conditioner heat exchanger, is cooled and again supplied to the servers and the storage system.
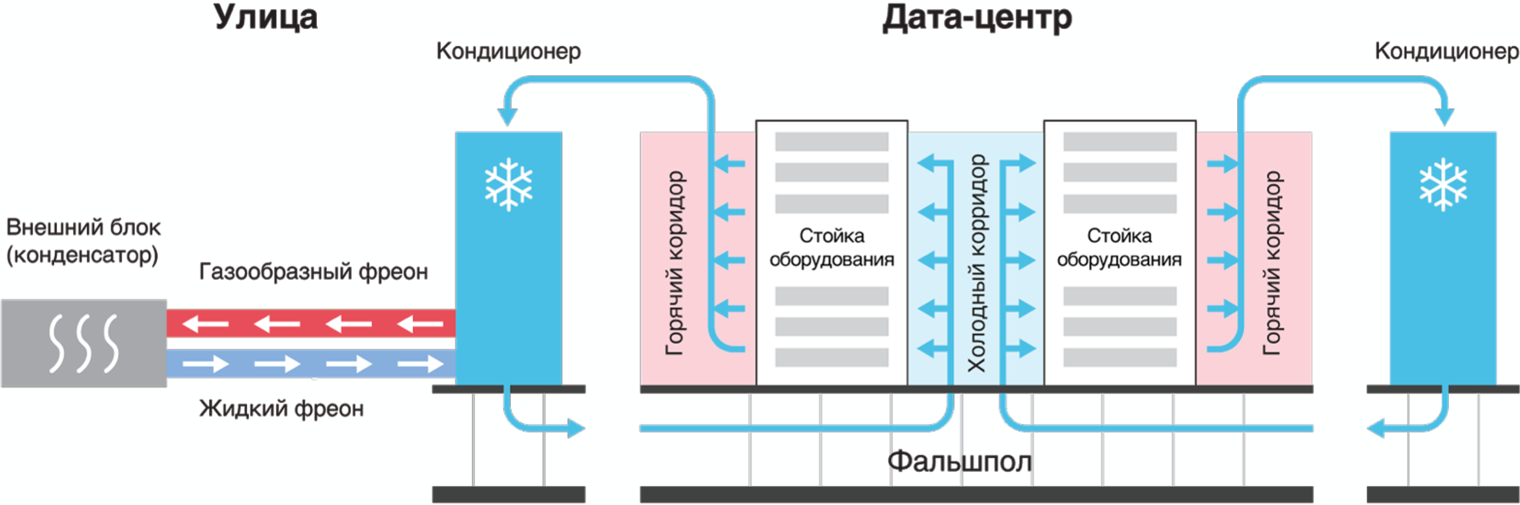
Cooling the data center with air conditioners
The efficiency of a classic air conditioner leaves much to be desired, and therefore the energy efficiency ratio for the data center “Flower 1” is quite high by modern standards, PUE = 1.7. But given that colocation services are provided here, it is quite possible to put up with such a situation until the cardinal modernization of the entire data center.

Inspection of air conditioners in the data center "Flower 1"
“Dubrovka 1”, “Berzarina 1”, “Flower 2” - chillers
The following cooling technology at Selectel was tested in 2010, when the data center "Dubrovka 1" was built in the village of Dubrovka, Leningrad Region. In it, for the first time in the practice of the company, a chiller cooling system was used.
The difference between the chiller system and the freon air conditioners is that an ice-free glycol solution circulates between the internal and external units in the pipelines, which remains liquid all the time and does not go into a gaseous state. The solution is pumped through the air conditioner in the server room, where it heats up from the hot radiator of the air conditioner and from where it is pumped into a remote outdoor heat exchanger called a chiller.
In the chiller, the glycol solution is cooled with the help of outside air and an additional condensing unit. Then, the cooled glycol solution is again supplied to the air conditioner inside the server room of the data center. At the same time, the computing equipment is cooled according to the traditional scheme - cold air is supplied from below through the raised floor to the “cold corridors”, and the hot air goes to the common room and then to the heat exchanger.
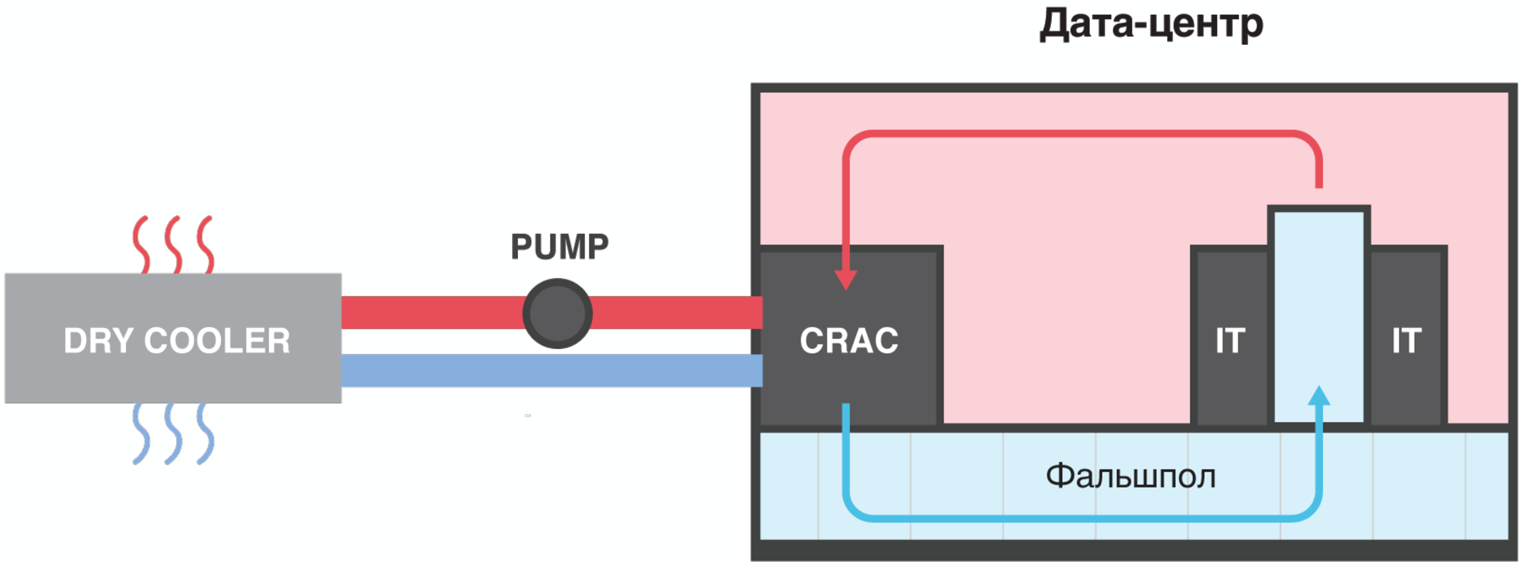
Chillernaya data center cooling system
The scheme with cold and hot corridors provides up to 5% energy savings, so it is so important to isolate cold and hot air pools (corridors and air storage units).
The energy efficiency of the chiller circuit is higher compared to air conditioners, and this is due to the fact that the external chiller condensing unit is activated only at ambient temperatures above + 12 ° C, and the fans of the external unit turn on gradually as the glycol heat transfer temperature rises. This is very similar to how an ordinary car's engine cooling system works.
According to the chiller scheme, Selectel built cooling of three data centers - “Dubrovka 1” (2010), “Berzarina 1” (2011) and “Flower 2” (2015). In the case of the Tsvetochnaya 2 data center, the operating experience gained over the 5 years of operation of the Dubrovka 1 data center in terms of its numerous maintenance features was taken into account. As it turned out, despite the apparent simplicity of the principle of operation, the chiller system is quite capricious in its work and requires careful maintenance and compliance with regulations. More information about the operation of the chiller system in the Berzarina 1 data center can be found in our article in the company's blog .

Cold corridor in the data center "Flower 2"
"Dubrovka 3", "Berzarina 2" - free cooling
The next step in improving the energy efficiency of cooling systems was made at Selectel during the transition to the direct free cooling scheme. The principle of the operation of the classic direct free cooling is the rejection of heat exchangers, and the cooling of the computing equipment occurs due to blowing with the help of outboard air.
Outboard air passes through the filters, where it is cleaned of dust, and then enters the engine room. In winter, as needed, cold air is preliminarily “diluted” with warm air from servers in the mixing chamber in order to maintain a constant equipment blowing temperature.
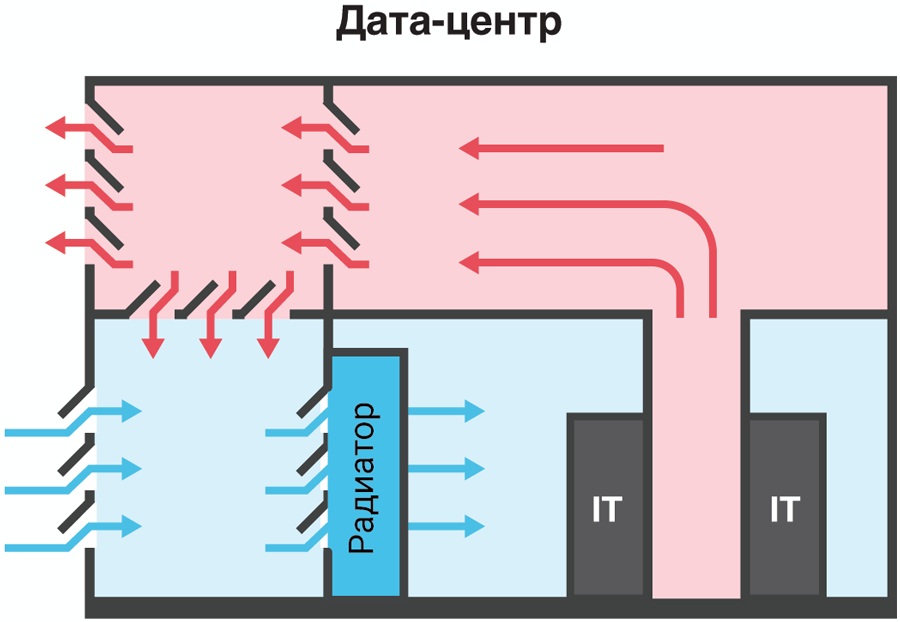
Direct freecooling scheme with cooling without raised floor
As mentioned above, modern servers and storage systems operate reliably at temperatures in cold corridors up to + 27 ° C. Considering the climate of the Leningrad Region, where the multi-year average daily temperature is even at + 20 ° C in July, such a solution seemed quite workable. However, given the temperature record of + 37.8 ° C, recorded in the Leningrad region in 2010, it was impossible to rely only on the mercy of nature. By the way, the “hot summer of 2018” confirmed the correctness of these calculations.
Accordingly, in the data center "Dubrovka 3", commissioned in 2013, direct free cooling with an additional cooling unit (ABCM, absorption refrigerating machine) in case of summer heat is used. Outboard air passes through the filters and then passes through the heat exchanger ABHM. In the cold corridors of the server room, air is supplied under the raised floor.
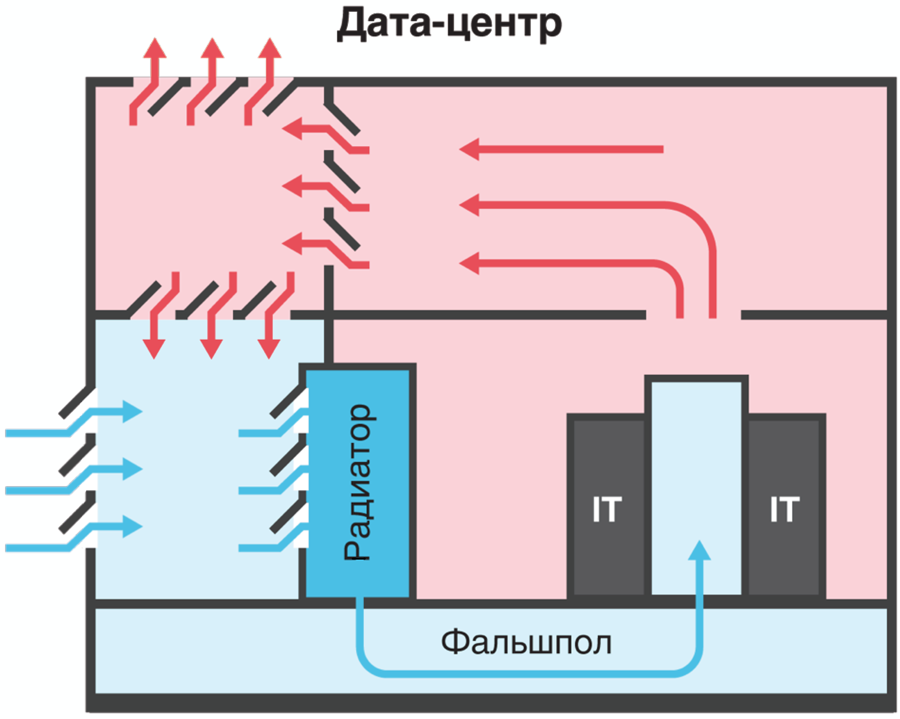
Cooling a data center with a free-cooling scheme with a raised floor
As experience has shown, this solution works without switching on ABCM to an ambient temperature of + 21 ° C, which practically means that ABCM functions only during the summer months. Thus, it is a fairly energy efficient solution with PUE ~ 1.25.
An important advantage of ABKHM is environmental safety, as it works on ordinary water without the use of freon. Among the drawbacks of ABChM are giant external heat exchangers, but given the location of the Dubrovka 3 data center in almost open field, this does not play a special role in terms of the size of the areas for ABCM equipment.

The cooling system of the data center "Dubrovka 3" with ABKHM
Since 2013, the direct cooling free-cooling scheme has shown its high efficiency and will be re-implemented in the Berzarina 2 data center under construction in Moscow. However, due to limited space, the aftercooling unit will be implemented using an adiabatic system.
A few words about reservations
Traditionally, cooling systems in data centers of the Tier III level are reserved according to the scheme not lower than N + 1. This means that there must always be at least one cooling installation in the supply, which is put into effect in the event of an accident or repair (scheduled maintenance) of one of the systems involved. So, in the data center "Dubrovka 1" 4 ventilation free-cooling machines are used with the need for 3, and in the data center "Dubrovka 3" there are three ABChM machines, of which one machine is turned off and in reserve, prepared for launch.
By the way, Selectel, in its data centers, seeks, whenever possible, to tighten the N + 1 redundancy requirement, and to keep in reserve not one, but two backup cooling systems. For example, in the data center "Flower 1" and "Flower 2" there are 2 reserve air conditioners and a chiller, respectively.

Air conditioners in the server room of the data center "Flower 1" (center)
"Berzarina 2" - soon in the ranks
In November 2018, the new Berzarina 2 data center in Moscow was put into operation, where for the first time in the company's practice a free cooling scheme with additional cooling with an adiabatic system will be applied. If the outside air is too warm - and the temperature in Moscow in summertime often exceeds 23 ° C - then the adiabatic cooling system is turned on.
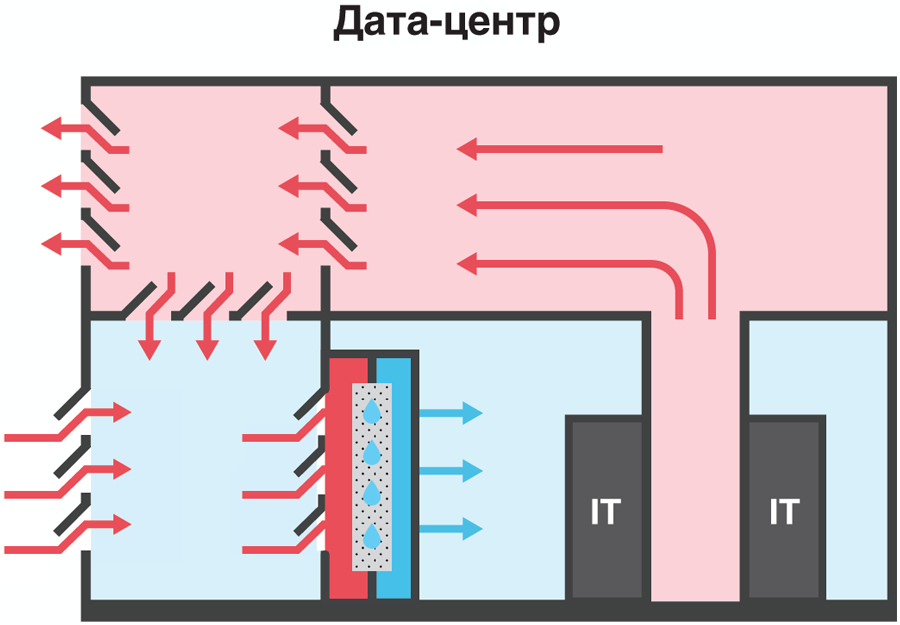
Freecooling with additional cooling with an adiabatic system in the Berzarina 2 data center
Adiabatic cooling technology is based on spraying water in the form of the smallest droplets in the path of the air flow, which allows you to cool the air by evaporating water. When using spray-type humidifiers, the electricity costs for the cooling process itself are small compared with other cooling systems. The complex cellular structure of the wetted barrier in the path of the supplied air does not allow the microcaps of water to get further into the air ducts of the data center. At the same time, the level of humidity remains within the limits of permissible values for IT equipment.
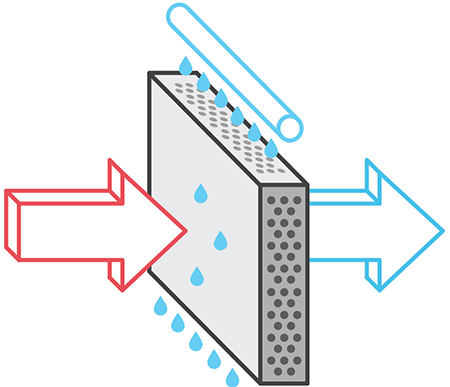
The scheme of the adiabatic system
“There are many interesting solutions for cooling systems in the world, which allow to save electricity. However, it is impossible to try all the new ones - you need to get funding, carry out the design, then complete the purchase of equipment, preparation and commissioning of equipment. The stages of delivery, installation, adjustment and running-in are all very lengthy procedures. Therefore, the climate systems after launch have been working for at least a decade and rarely are being drastically modernized during the operation of an already built data center. And interesting news is coming to the new data center, in which they will serve their 10-15 years, ”concluded Kirill Malevanov, technical director of Selectel.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/428413/
All Articles