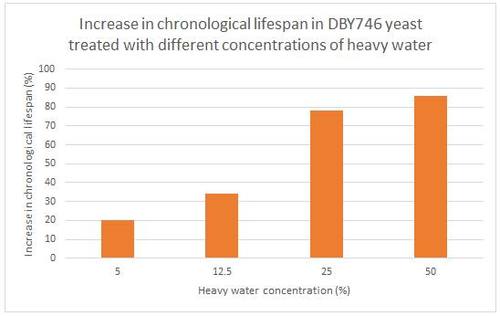
Heavy water (D2O) prolongs yeast life by 80%, fruit flies by 30%, nematodes 10%

Deuterium solution (concentration 25%) and ordinary water
Despite the fact that some combinations of geroprotectors or Yamanaki factors (which turn ordinary cells into pluripotent ones) are capable of prolonging life by more than 50% in mice, with deuterium and other stable isotopes, a precedent is important.
The first who proposed to use the isotope hydrogen deuterium for biological effects is our compatriot Mikhail Schepinov .
')
While we think isotopes exhibit identical chemical behavior, this is not entirely accurate. Isotopes exhibit a subtle difference in chemical bond strength. The heavier the isotope, the stronger the bond. For example, carbon-deuterium bond is 5-10 times stronger than carbon-hydrogen. Deuterium is much heavier than hydrogen compared to carbon-13 (+1 neutron) and carbon (atomic mass 12). Previous studies have shown that the amount of free radicals decreases in isolated rat mitochondria exposed to heavy water.
The experiment was inspired by the fact that in old age the content of heavy isotopes (carbon-13, deuterium, nitrogen-15, oxygen-18, sulfur-34) in amino acids falls. Most likely that in metabolites too.
Shchepinov founded biotechnology firm Retrotope, which is engaged at this stage in clinical research of rt001 rt002 preparations, which are deuterium-modified fatty acids (such as omega 3) for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and Friedreich's Ataxy (mitochondrial disease).
In animals, a heavy water solution was able to normalize high blood pressure caused by a high salt diet in rats, possibly through the suppression of hypertension associated with an increase in calcium absorption. This effect will certainly prolong life.
Deuterium and carbon-13 are also apparently non-toxic. Mice are perfectly normal, even when 60 percent of the carbon atoms in their bodies are carbon-13. Decades of experiments in which animals received heavy water indicate that up to one fifth of the water in your body can be replaced with heavy water without any side effects.
Similar experiments have been performed on humans, albeit with lower levels of deuterium. One recent experiment kept people on a low-level, heavy-water diet for 10 weeks, during which their heavy water levels increased to about 2.5% of body weight without any side effects (Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, vol 1760, p 730) .
Heavy water, however, is not completely safe. In mammals, the toxic effect starts somewhere from the 20% mark, and at a dose of 35% is lethal. This is largely due to the effect of the isotope - every protein in your body has the potential to take a deuterium atom of heavy water instead of hydrogen, and once this radically changes the entire biochemistry. Still, a lot of heavy water is required to suffer from any painful effect - 5 milliliters will not hurt you with anything, but even startups like Retrotrope do not advertise heavy water as the elixir of life.
Mikhail Schepinov speaks about the benefits of the isotope effect at the Belarusian State University

While Retrotope is concentrating on aging, Schepinov says there are other uses for the isotope effect that he would like to explore. One of them protects long-term space travelers from the effects of cosmic rays and other ionizing radiation, which are as damaging as aging.
Another possibility is the production of meat, eggs, or milk, enriched with deuterium or carbon-13, by feeding deuterated water or enriched with isotopes of amino acids for farm animals.
The idea of using chemical isotopes to fight aging can be new, but nature is already acting in this way to protect us from free radical attack, which is considered the main cause of aging. Babies and mice are born with much more carbon-13 isotope in their bodies than their mothers, and women seem to become unusually depleted in carbon-13 during their birth. Both findings suggest an active transfer of carbon-13 from mother to fetus. This will have a good evolutionary meaning, since many of the proteins and DNA molecules formed at an early stage should be with us all our lives. "Every single atom in the brain DNA of a 100-year-old person is the same atom as when he was 15 years old."
Another obstacle Retrotope will have to overcome the cost. At current prices, a liter of heavy water costs you $ 300. “Isotopes are expensive,” says Shchepinov. “But nobody needs them to be cheap. Methods to get them there, but nobody wants them. ” If demand does not increase, there is no incentive to produce them in bulk, and this holds a high price.
Also the proportion of heavy isotopes in metabolites and amino acids can serve as a biomarker of human age.
It would be interesting to discover if a mouse drank a certain concentration of deuterium oxide would also live longer ...
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/428269/
All Articles