Connecting Multipath LUN storage to VMware ESXi and Debian GNU / Linux
Friends and colleagues!
One of our customers, who purchased HP servers and blades, and now bought HP MSA 2040, recently had a question:
Why does the server see the moons presented to it as 4 separate disks of the same size (Linux OS)?
')

The answer is simple:
Connection to the server in this case occurs on 4 independent channels and each of these disks is a separate channel.
In order to finally get one disk, you need to use the multipath IO service.
Multipath LUN storage to VMware ESXi
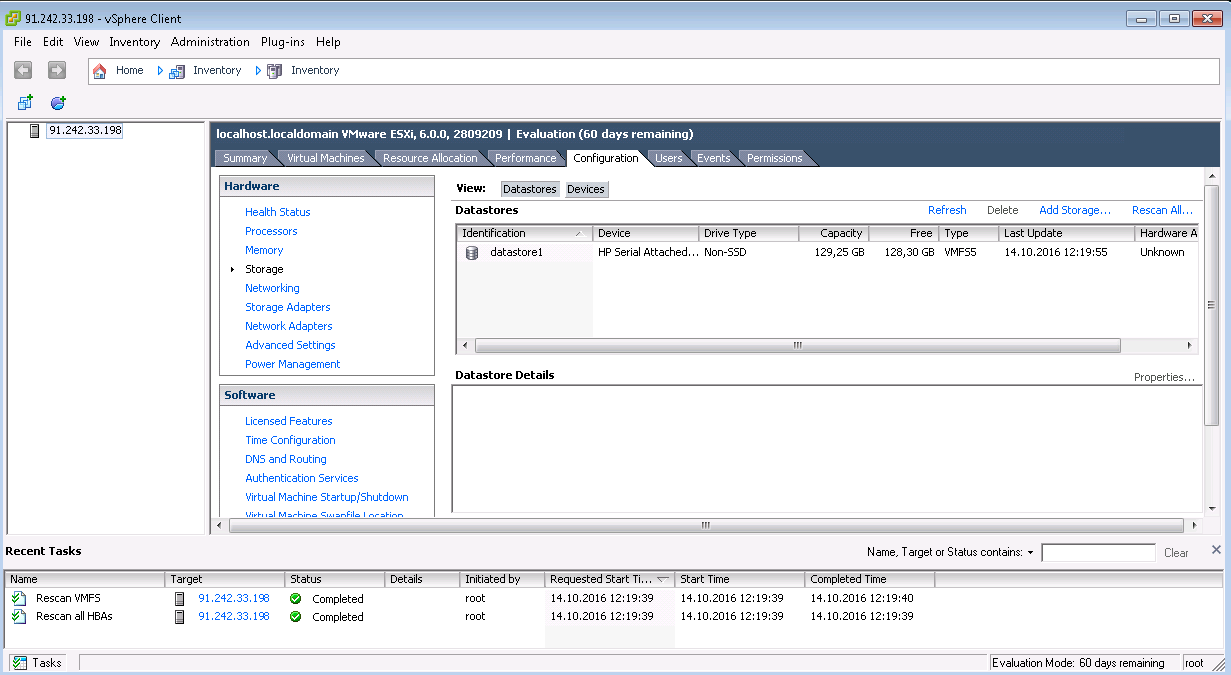
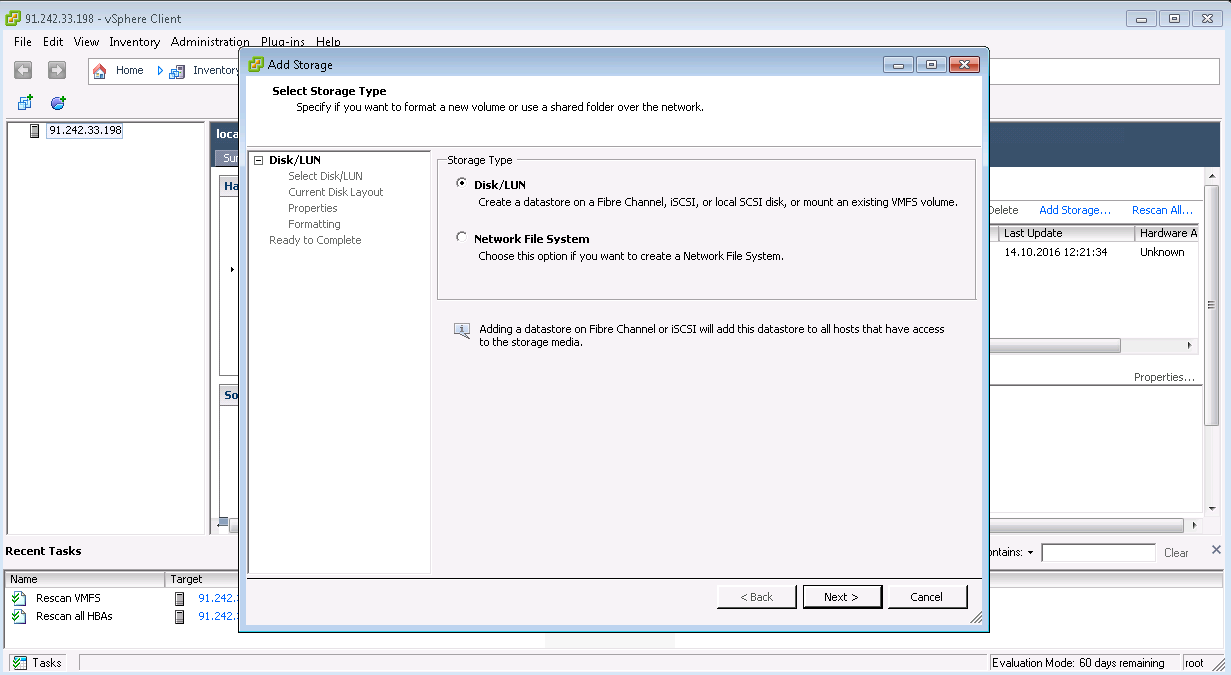
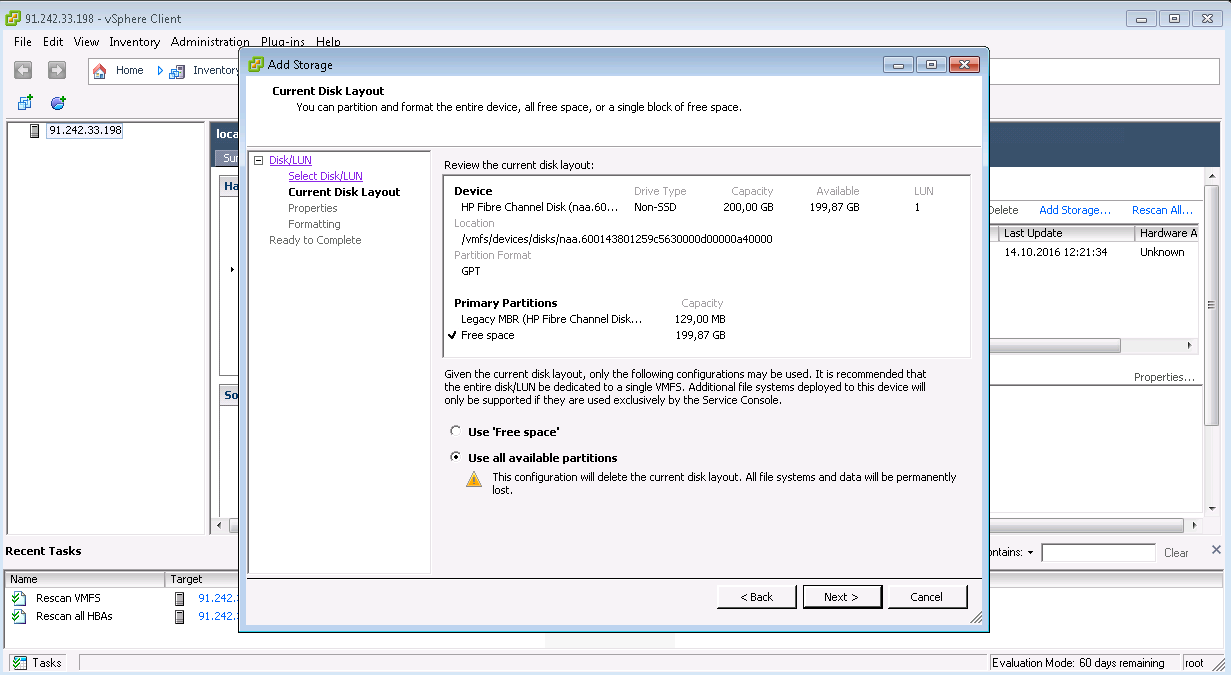
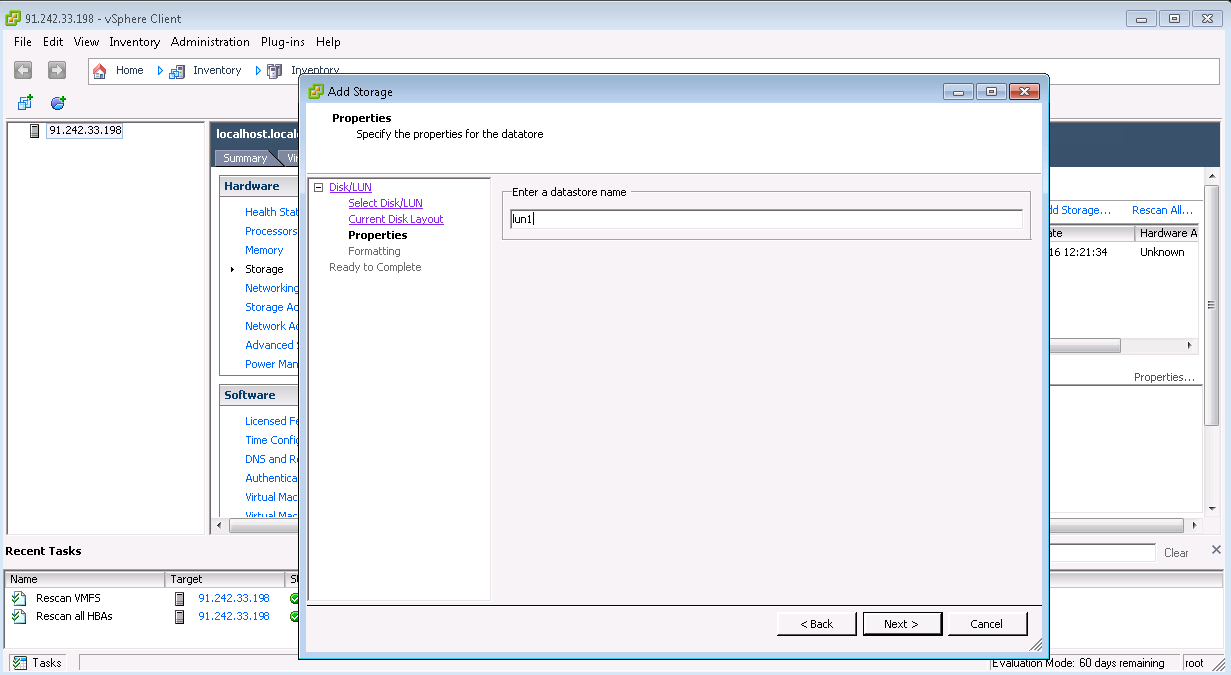
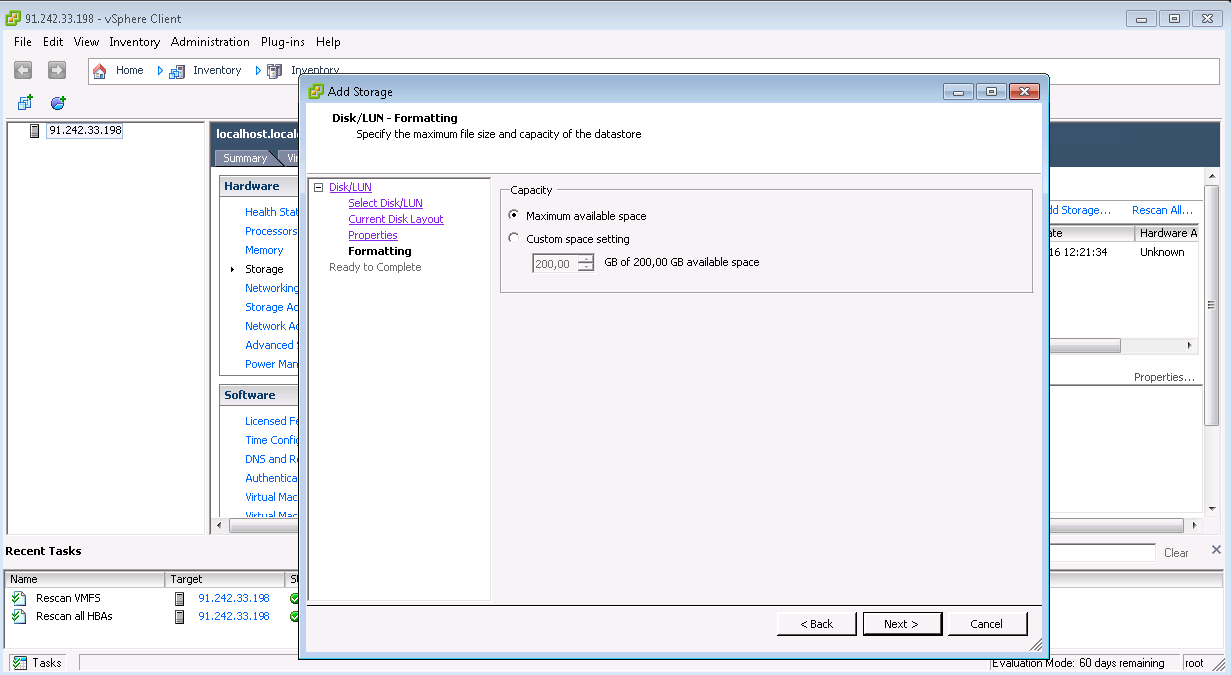
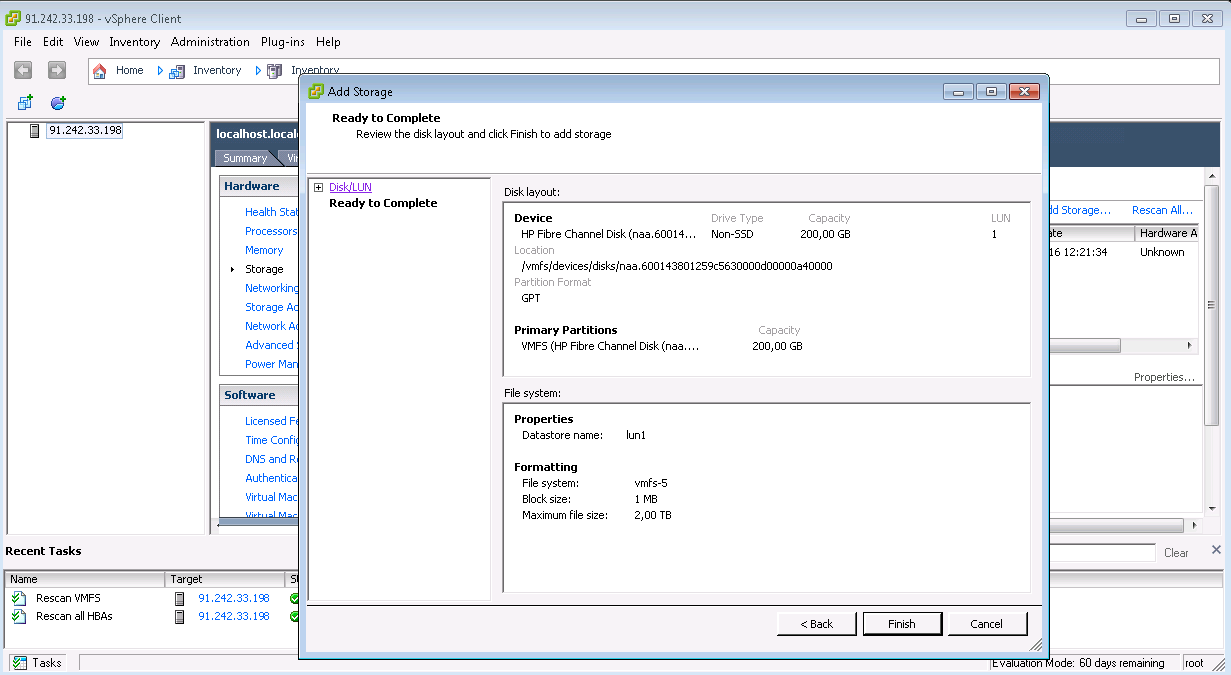
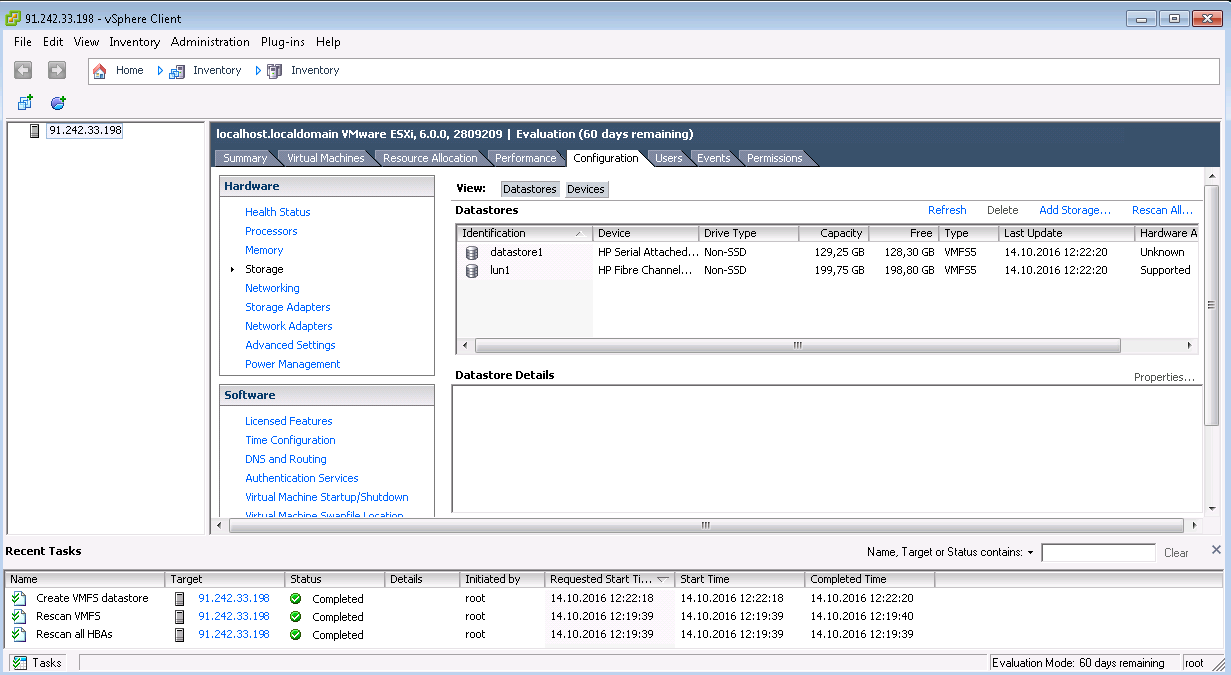
Multipath LUN storage to Debian GNU / Linux
A bit harder:
At the initial stage of installing Debian GNU / Linux, we may encounter the problem of the inability to detect the system firmware ql2400_fw.bin. This is solved simply:
On a working Linux system, download the firmware-qlogic package, unpack it, write it into the image, and mount it via ILO (actions are performed on the HP Proliant server). It looks like this:
We connect qlfw.raw through the menu Virtual Device-> Image File Removable Media. If the installer still cannot find the firmware, you can do it manually by mounting the image in the / lib / firmware directory and reloading the qla2xxx module. Switch to the text console (the following actions are performed in ILO. Keyboard menu-> CTRL-ALT-Fn-> CTRL-ALT-F2):
After that, we return to the installer (menu Keyboard-> CTRL-ALT-Fn-> CTRL-ALT-F5), and reinstall the system in the normal mode.
On the production system, we will need to install the multipath-tools package with all dependencies:
Determine autostart service:
Let's see how the devices are grouped:
Create a file system on the LUN we need:
We will mount and see what happened:
LUN is mounted and ready to use. It remains to add a line in fstab:
In this case, we looked at an example of connecting to VMware ESXi and Debian GNU / Linux.
We also use the system for allocating LUNs to servers on our hosting.
In this case, we use:
1. Blade chassis HP C7000 in the maximum configuration, with two administrative modules.
2. FC switches in C7000 chassis for connecting external storage systems - HP Brocade 8Gb 8 / 24c SAN Switch. External FC Switches - HP StorageWorks 8/40 Base 24, (24) Full Fabric SAN Switch Port.
3. Storage HPE 3PAR StorServ 7400 (4-node), HPE 3PAR StorServ 7450c (4-node), HPE 3PAR StorServ 7400c (2-node) and Storage HPE EVA P6550.
Where do we highlight the moon:
ALLFlash - only SSD
AO - Mixed SSD + SAS
NL - only SAS
In the next article we will look at Connecting Multipath Storage LUN to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2012.
One of our customers, who purchased HP servers and blades, and now bought HP MSA 2040, recently had a question:
Why does the server see the moons presented to it as 4 separate disks of the same size (Linux OS)?
')

The answer is simple:
Connection to the server in this case occurs on 4 independent channels and each of these disks is a separate channel.
In order to finally get one disk, you need to use the multipath IO service.
Multipath LUN storage to VMware ESXi









Multipath LUN storage to Debian GNU / Linux
A bit harder:
At the initial stage of installing Debian GNU / Linux, we may encounter the problem of the inability to detect the system firmware ql2400_fw.bin. This is solved simply:
On a working Linux system, download the firmware-qlogic package, unpack it, write it into the image, and mount it via ILO (actions are performed on the HP Proliant server). It looks like this:
#apt-get --download-only install firmware-qlogic #cp /var/cache/apt/archives/firmware-qlogic_* . #ar x firmware-qlogic* #tar cJpfv data.tar.xz #dd if=/dev/zero of=qlfw.raw bs=1M count=50 #mkdir fw #mount -o loop qlfw.raw fw #cp -r lib/firmware/* fw #umount fw We connect qlfw.raw through the menu Virtual Device-> Image File Removable Media. If the installer still cannot find the firmware, you can do it manually by mounting the image in the / lib / firmware directory and reloading the qla2xxx module. Switch to the text console (the following actions are performed in ILO. Keyboard menu-> CTRL-ALT-Fn-> CTRL-ALT-F2):
#fdisk -l| grep 50 Disk /dev/sdr: 50 MiB, 52428800 bytes, 102400 sectors #mkdir /lib/firmware #mount /dev/sdr /lib/firmware #rmmod qla2xxx #modprobe qla2xxx After that, we return to the installer (menu Keyboard-> CTRL-ALT-Fn-> CTRL-ALT-F5), and reinstall the system in the normal mode.
On the production system, we will need to install the multipath-tools package with all dependencies:
#apt-get install multipath-tools … … : multipath-tools-boot , : multipath-tools 0, 1 , 0 , 0 . 0 B/185 kB . , 632 kB. multipath-tools. ( … 30895 .) …/multipath-tools_0.5.0-6+deb8u2_amd64.deb … multipath-tools (0.5.0-6+deb8u2) … systemd (215-17+deb8u5) … man-db (2.7.0.2-5) … multipath-tools (0.5.0-6+deb8u2) … libc-bin (2.19-18+deb8u6) … Determine autostart service:
#systemctl enable multipath-tools Synchronizing state for multipath-tools.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d... Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d multipath-tools defaults Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d multipath-tools enable Let's see how the devices are grouped:
# multipath -l 36001438005dea4600001a000000f0000 dm-0 HP,HSV450 size=100G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw |-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=active | |- 0:0:2:1 sdd 8:48 active undef running | |- 0:0:3:1 sde 8:64 active undef running | |- 2:0:0:1 sdj 8:144 active undef running | `- 2:0:1:1 sdk 8:160 active undef running `-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=enabled |- 0:0:0:1 sdb 8:16 active undef running |- 0:0:1:1 sdc 8:32 active undef running |- 2:0:2:1 sdl 8:176 active undef running `- 2:0:3:1 sdm 8:192 active undef running 3600143801259c5630000d00000a40000 dm-1 HP,HSV360 size=200G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw |-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=active | |- 0:0:4:1 sdf 8:80 active undef running | |- 0:0:5:1 sdg 8:96 active undef running | |- 2:0:4:1 sdn 8:208 active undef running | `- 2:0:5:1 sdo 8:224 active undef running `-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=enabled |- 0:0:6:1 sdh 8:112 active undef running |- 0:0:7:1 sdi 8:128 active undef running |- 2:0:6:1 sdp 8:240 active undef running `- 2:0:7:1 sdq 65:0 active undef running Create a file system on the LUN we need:
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/dm-0 mke2fs 1.42.12 (29-Aug-2014) Creating filesystem with 26214400 4k blocks and 6553600 inodes Filesystem UUID: ae98a176-55d4-484a-b637-6a57a9212d3c Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208, 4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (32768 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done We will mount and see what happened:
# mount /dev/dm-0 /mnt/ # df -h /mnt % C /dev/mapper/36001438005dea4600001a000000f0000 99G 60M 94G 1% /mnt LUN is mounted and ready to use. It remains to add a line in fstab:
#echo '/dev/dm-0 /mnt/ext4 defaults 0 0'>>/etc/fstab In this case, we looked at an example of connecting to VMware ESXi and Debian GNU / Linux.
We also use the system for allocating LUNs to servers on our hosting.
In this case, we use:
1. Blade chassis HP C7000 in the maximum configuration, with two administrative modules.
2. FC switches in C7000 chassis for connecting external storage systems - HP Brocade 8Gb 8 / 24c SAN Switch. External FC Switches - HP StorageWorks 8/40 Base 24, (24) Full Fabric SAN Switch Port.
3. Storage HPE 3PAR StorServ 7400 (4-node), HPE 3PAR StorServ 7450c (4-node), HPE 3PAR StorServ 7400c (2-node) and Storage HPE EVA P6550.
Where do we highlight the moon:
ALLFlash - only SSD
AO - Mixed SSD + SAS
NL - only SAS
In the next article we will look at Connecting Multipath Storage LUN to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2012.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/428059/
All Articles