We treat the problem of FHRP asymmetric routing
What is “FHRP asymmetric routing”?
Routing state where traffic within one session leaves through one FHRP router (VRRP / HSRP) master, and returns through the second one.
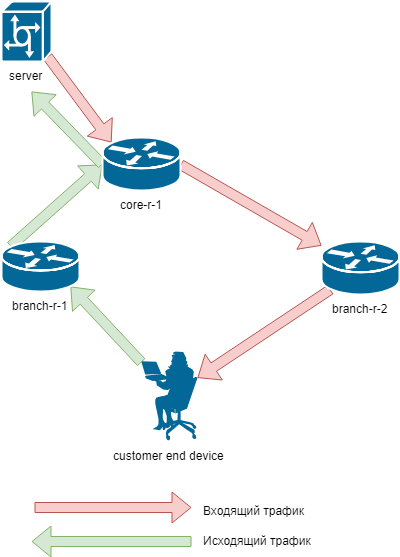
What's bad about it?
If all routers are within the same LAN, then most likely nothing.
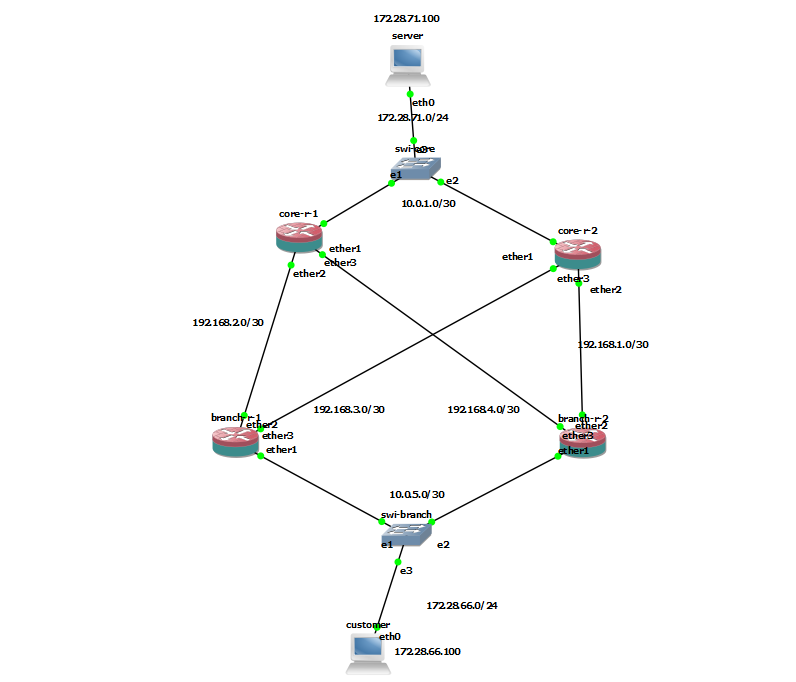
Problems begin if the network topology looks like this:
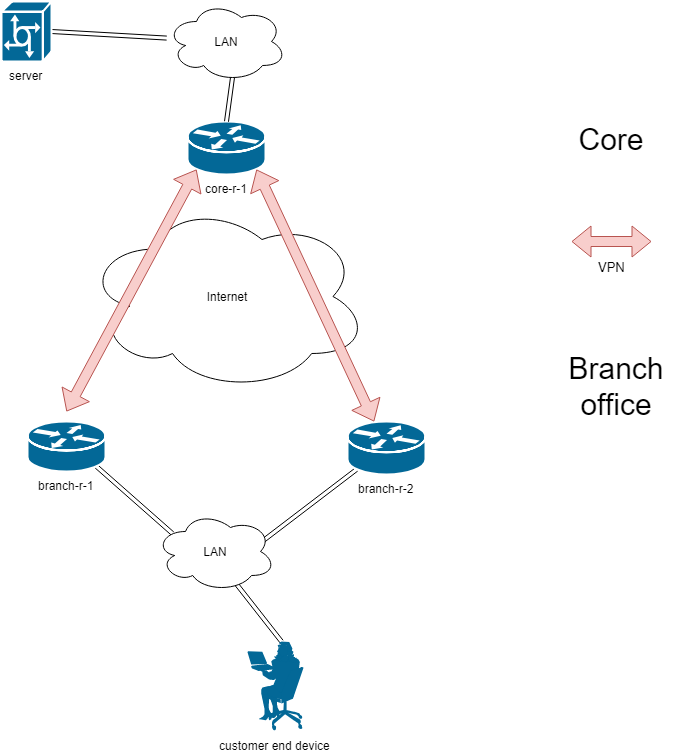
1. MTU discovery - the case of the MTU discovery pathway. For example, the VPN tunnel will not be any MTU. ping will work consistently.
2. If there is a path, it’s not broken. It is not necessary to make sure that you’ve been on the track.
Why is this so?
The upstream router (core-r-1) does not have information about the roles of downstream routers in the FHRP.
The decision to choose a route is made autonomously, based on the dynamic routing protocol or PBR metrics.
How to fix it?
In terms of traffic: the traffic must go and return through the same router and VPN tunnel
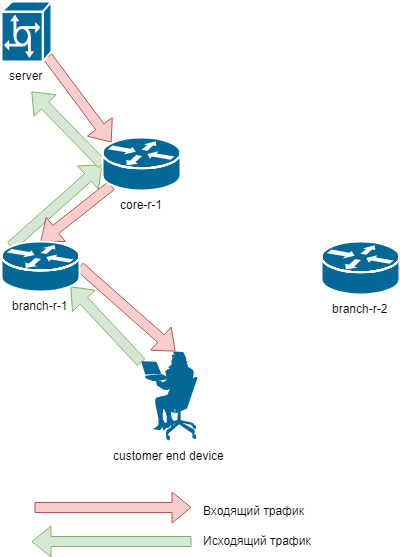
In terms of routing:
Upstream routers should receive FHRP status information.
For example, a route to a subnet with end devices during normal events should be announced only by the FHRP master.
How it works?
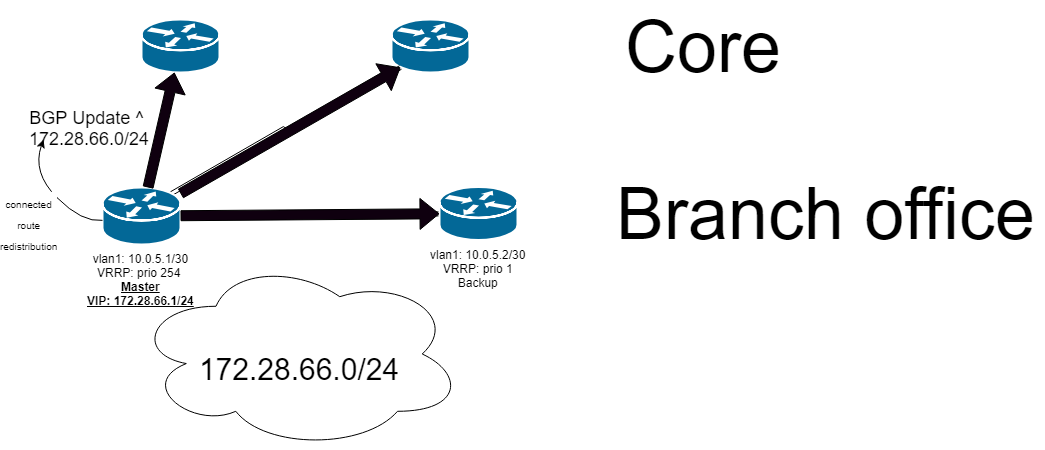
Test bench (GNS3, MikroTik, BGP, VRRP).
- Download link
- Router credentials:
A. Login: admin
B. Pass: no
Bonus for those who read to the end
In fact, it is not necessary to use 100,500 dedicated / 30 IPv4 subnets.
Dynamic IPv6 link-local addresses can be used to solve the problem, which greatly simplifies the initial deployment.
The solution (in the implementation for MikroTik RouterOS) is as follows: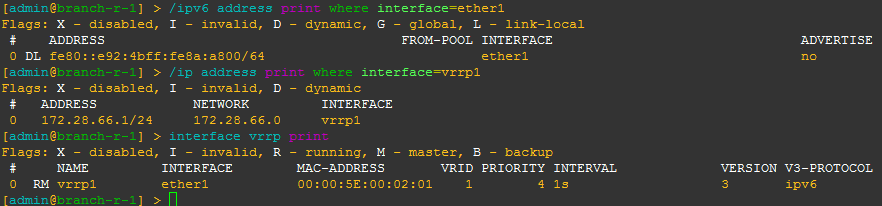
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/427939/
All Articles