Why credit institutions data science
The author of the material on the example of India considers what benefits for credit institutions are the digital revolution, the democratization of data and the analysis of the digital footprint of users.

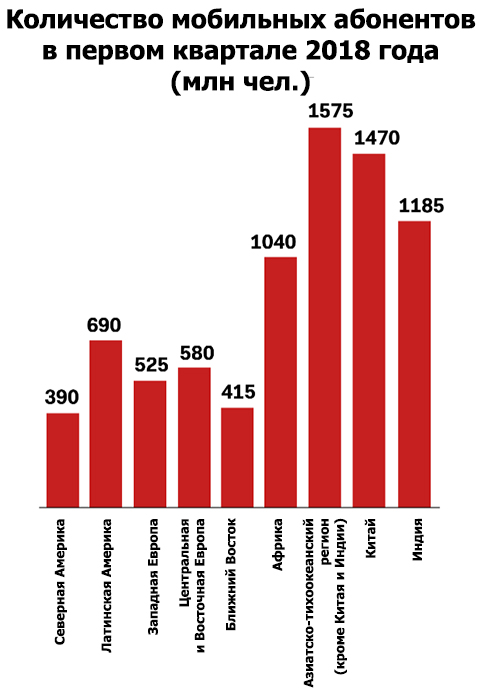
Access to the World Wide Web allows people to learn about new products, services, opportunities and content from anywhere in the world. So, India has become the most active consumer of the mobile Internet.
Large corporations are forced to reckon with such changes. They transfer their business online or provide their presence there. The volume of online retail sales this year rose to $ 50 billion , compared with $ 19.7 billion in 2015. And last year's statistics show that 82% of requests related to e-commerce were sent from mobile devices.
')
Personal computers and tablets in India are classified as expensive devices that are inaccessible to the general population. And smartphones with 4G support cost an average of $ 7. This led to the widespread use of 4G smartphones in the country: their number increased from 47 million in 2015 to 218 million in 2017. According to forecasts, the number of mobile Internet users will also increase dramatically from 240 million in 2016 to 520 million in 2020. The average annual growth rate will be 21%.
The launch of 4G made high-speed Internet accessible to the masses. Reducing the cost of data exchange by 93% - from 3.7 dollars per 1 GB to 0.26 dollars - greatly influenced the behavior of consumers who were addicted to the Internet. According to statistics , Indians today spend at the smartphone about 3 hours a day.
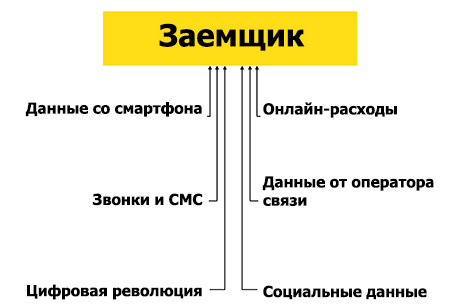
The expansion of geographic coverage and an increase in speed, together with a sharp influx of new users of 4G smartphones, made India a wealth of information about consumers' digital footprints. The democratization of these data may trigger the emergence of completely new approaches to their use in various industries.
Now in all spheres of human activity, we are seriously considering options for using data analysis to increase the coverage and scale of business operations. And this will entail large-scale social, economic and technological consequences. One of them is the use of the fruits of the information revolution to improve the process of granting loans in retail lending.
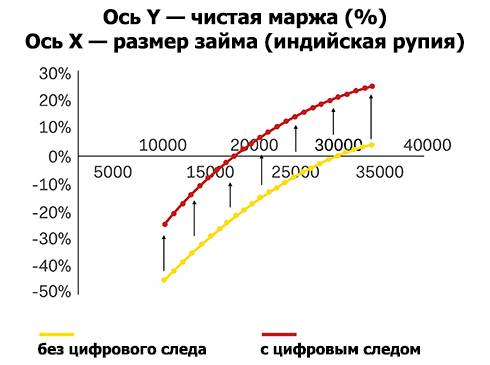
The use of user digital trace analysis leads to an increase in net interest margin due to increased risk management efficiency and lower operating expenses.
The consumer’s digital trace is a clean and unprocessed data source generated by the user. It is an excellent tool for customer profiling, as well as for identifying consumer behavior and preferences. Indian retail lenders who have signed strategic agreements with technology services have already appreciated the benefits of the analysis of digital customer metadata. For example, a year ago, ICICI entered into a partnership with Paytm, which allowed it to offer instant short-term online loans. Capital Float recently acquired Walnut's personal finance management application for $ 30 million.
Behavioral patterns and user trends will help lenders identify potentially trustworthy clients and give them a positive response, even if clients have not yet managed to build a positive credit history. Models using digital traces and alternative data as additional information have already shown their effectiveness in world practice. In many ways, they bypass the traditional models of credit institutions. The FICO study showed that alternative data sources allow better prediction of risks and margins, while transaction data, utility accounts, media and other sources complement the overall predictive power of the models.
In general, the collection, processing and analysis of digital traces of consumers will make financial services more accessible at several levels, described below.
In India, more than 300 million people use smartphones, and by the end of 2018 this figure should increase to 530 million. The projected growth in the number of social network users will be about 64% (371 million people compared to the current 225 million).
Expanding the digital presence of Indians will allow more people in the country to access loans. This view is shared by many professionals who support the idea of introducing alternative data for risk assessment. They believe that this will have a positive impact on the capabilities of clients who previously could not get an assessment of their solvency. According to a PERC study , adding alternative data improved the credit rating of 64% of customers who lacked a credit history, and deterioration was observed only in 1% of cases.
The operating costs of digital lenders are lower than those of traditional lending institutions. Private lending institutions in India work closely with fintech companies, thereby improving the quality of their financing and reducing the cost of its issuance. The size of operating expenses in traditional banks reaches 6% of the amount of outstanding loans, while for alternative creditors this figure does not even reach 2%. Integration of alternative data into credit evaluation processes can further reduce costs and increase profits.
The integration of alternative data into the credit risk assessment process reduces the cost of providing financing and allows a wider circle of clients to qualify for loans. This increases the profitability of small loans.
Experts note that the main advantage of using alternative data sources for credit institutions is an increase in the number of profitable loans with a moderate level of risk. In addition, alternative data allows lenders to draw up a more detailed portrait of the borrower and offer him individual interest rates. This task is still considered difficult for many players in the lending industry.
The growth of profitability will also motivate credit institutions to more actively study and implement such methods.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) also emphasizes the value of alternative data for retail lenders. As RBI notes in its report, the integration of alternative data gives credit organizations new criteria for assessing the financial situation of borrowers, allowing you to make more informed decisions.
Regulatory impulse and the socio-economic need for the introduction of alternative data sources provoked an influx of startups in the field of AI and data analysis, which focused on tools for processing alternative data in order to improve the efficiency of lending.
This will make the integration of alternative data a massive phenomenon and bring to life the desire of the Deputy Head of RBI, Vishal Acharya, to create conditions for the emergence of individual loan products that meet the needs of each borrower in the country.
“Banking services and access to loans in the future will be segmented according to customer needs and will be available to the general population like the consumer goods sector. We want even a small tea shop to borrow 500 rupees at an acceptable percentage for a period of, say, a week, ”says Vishal Acharya, deputy head of the RBI.


Data democratization
Access to the World Wide Web allows people to learn about new products, services, opportunities and content from anywhere in the world. So, India has become the most active consumer of the mobile Internet.
Number of mobile subscribers in Q1 2018
Large corporations are forced to reckon with such changes. They transfer their business online or provide their presence there. The volume of online retail sales this year rose to $ 50 billion , compared with $ 19.7 billion in 2015. And last year's statistics show that 82% of requests related to e-commerce were sent from mobile devices.
')
Prevalence of smartphones
Personal computers and tablets in India are classified as expensive devices that are inaccessible to the general population. And smartphones with 4G support cost an average of $ 7. This led to the widespread use of 4G smartphones in the country: their number increased from 47 million in 2015 to 218 million in 2017. According to forecasts, the number of mobile Internet users will also increase dramatically from 240 million in 2016 to 520 million in 2020. The average annual growth rate will be 21%.
Increase average data consumption
The launch of 4G made high-speed Internet accessible to the masses. Reducing the cost of data exchange by 93% - from 3.7 dollars per 1 GB to 0.26 dollars - greatly influenced the behavior of consumers who were addicted to the Internet. According to statistics , Indians today spend at the smartphone about 3 hours a day.
Digital trace

The expansion of geographic coverage and an increase in speed, together with a sharp influx of new users of 4G smartphones, made India a wealth of information about consumers' digital footprints. The democratization of these data may trigger the emergence of completely new approaches to their use in various industries.
Now in all spheres of human activity, we are seriously considering options for using data analysis to increase the coverage and scale of business operations. And this will entail large-scale social, economic and technological consequences. One of them is the use of the fruits of the information revolution to improve the process of granting loans in retail lending.
Digital footprint as a means of improving lending efficiency

The use of user digital trace analysis leads to an increase in net interest margin due to increased risk management efficiency and lower operating expenses.
The consumer’s digital trace is a clean and unprocessed data source generated by the user. It is an excellent tool for customer profiling, as well as for identifying consumer behavior and preferences. Indian retail lenders who have signed strategic agreements with technology services have already appreciated the benefits of the analysis of digital customer metadata. For example, a year ago, ICICI entered into a partnership with Paytm, which allowed it to offer instant short-term online loans. Capital Float recently acquired Walnut's personal finance management application for $ 30 million.
Behavioral patterns and user trends will help lenders identify potentially trustworthy clients and give them a positive response, even if clients have not yet managed to build a positive credit history. Models using digital traces and alternative data as additional information have already shown their effectiveness in world practice. In many ways, they bypass the traditional models of credit institutions. The FICO study showed that alternative data sources allow better prediction of risks and margins, while transaction data, utility accounts, media and other sources complement the overall predictive power of the models.
In general, the collection, processing and analysis of digital traces of consumers will make financial services more accessible at several levels, described below.
Level 1: Expanded audience coverage with new methods for analyzing alternative data
In India, more than 300 million people use smartphones, and by the end of 2018 this figure should increase to 530 million. The projected growth in the number of social network users will be about 64% (371 million people compared to the current 225 million).
Expanding the digital presence of Indians will allow more people in the country to access loans. This view is shared by many professionals who support the idea of introducing alternative data for risk assessment. They believe that this will have a positive impact on the capabilities of clients who previously could not get an assessment of their solvency. According to a PERC study , adding alternative data improved the credit rating of 64% of customers who lacked a credit history, and deterioration was observed only in 1% of cases.
Level 2: Cost Reduction
The operating costs of digital lenders are lower than those of traditional lending institutions. Private lending institutions in India work closely with fintech companies, thereby improving the quality of their financing and reducing the cost of its issuance. The size of operating expenses in traditional banks reaches 6% of the amount of outstanding loans, while for alternative creditors this figure does not even reach 2%. Integration of alternative data into credit evaluation processes can further reduce costs and increase profits.
Level 3: Profitability of small loans
The integration of alternative data into the credit risk assessment process reduces the cost of providing financing and allows a wider circle of clients to qualify for loans. This increases the profitability of small loans.
Experts note that the main advantage of using alternative data sources for credit institutions is an increase in the number of profitable loans with a moderate level of risk. In addition, alternative data allows lenders to draw up a more detailed portrait of the borrower and offer him individual interest rates. This task is still considered difficult for many players in the lending industry.
The growth of profitability will also motivate credit institutions to more actively study and implement such methods.
Conclusion
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) also emphasizes the value of alternative data for retail lenders. As RBI notes in its report, the integration of alternative data gives credit organizations new criteria for assessing the financial situation of borrowers, allowing you to make more informed decisions.
Regulatory impulse and the socio-economic need for the introduction of alternative data sources provoked an influx of startups in the field of AI and data analysis, which focused on tools for processing alternative data in order to improve the efficiency of lending.
This will make the integration of alternative data a massive phenomenon and bring to life the desire of the Deputy Head of RBI, Vishal Acharya, to create conditions for the emergence of individual loan products that meet the needs of each borrower in the country.
“Banking services and access to loans in the future will be segmented according to customer needs and will be available to the general population like the consumer goods sector. We want even a small tea shop to borrow 500 rupees at an acceptable percentage for a period of, say, a week, ”says Vishal Acharya, deputy head of the RBI.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/427781/
All Articles