How to organize long-term archival storage of electronic documents
Recently, in the journal " Inside " we talked about the long-term archival storage of electronic documents (ED), certified by electronic signature (ED). The article was devoted to the review of various points of view on the organization of this process and approaches to the prolongation of the properties of the legal significance of ED. In it, we focused on the approach, which provides for the formation of receipts of the document. They are metadata containing the results of the checks performed, as well as all the necessary attributes confirming the legal significance of the document at the time of the check.
This article describes in more detail another approach to long-term archival storage (DAH) - the formation of an improved electronic signature (CEC), namely, electronic signature in CAdES-A and XAdES-A archive formats.

Let us try to understand in more detail how and why archival ES can extend the life cycle of electronic documents with ES. Let's start with a small theoretical educational program on the types and formats of electronic signature, and then consider in practice the procedure for the formation of archive electronic signature products developed by Gazinformservice.
')
CAdES type electronic signature
CMS Advanced Electronic Signatures (CAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS) standard. The main document describing this standard is ETSI TS 101 733 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); CMS Advanced Electronic Signature (CAdES) ".
CAdES became the development of CMS, in which the main shortcomings of the predecessor were corrected, such as the absence of a stamp of the trusted time of creating an EP, the absence of an EP content type, and the absence of the possibility of long-term preservation of the legal significance of an EP.
The standard defines several CAdES formats, each of which includes the previous one (in accordance with the sequence presented below) and extends it:
The CAdES-A archive archive form consists of the following elements:
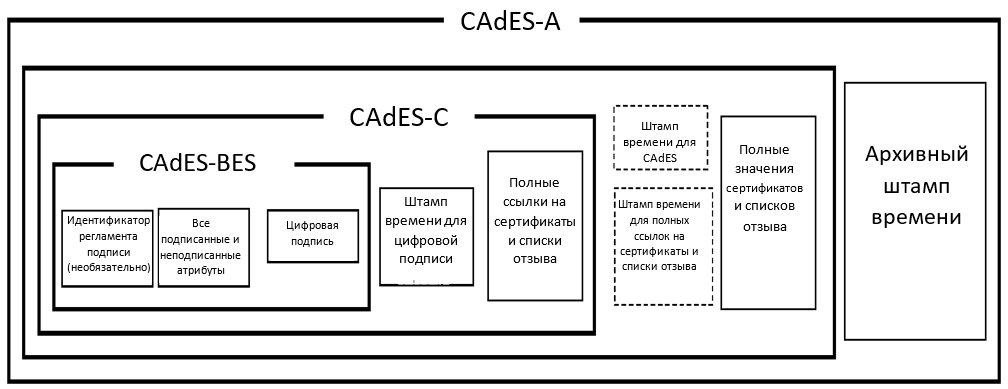
Figure 1 - Scheme of formation of electronic signature in the format CAdES-A
The organization of the DAH is associated not only with the limited validity of the user certificate established by Russian legislation at 1 year 3 months, but also with modifications of cryptographic algorithms, which in turn is caused by the deterioration of their robustness properties due to the development of cryptanalysis methods and computing industry.
An additional time stamp may be imposed on top of the EA in the CAdES-A format, which will protect its contents when identifying vulnerabilities of the cryptographic hash functions used, when hacking the cryptographic algorithms used and when the keys are compromised. It should not be forgotten that the sequence of time stamps can provide protection against ES falsification, provided that these stamps were applied before the time stamp service key was compromised. Thus, the EA in the CAdES-A format allows to preserve its authenticity for very long periods of time, and the periodic installation of archive stamps will provide the possibility of checking the EA when updating cryptographic standards.
It is also important to note that the additional data needed to create the above-described forms of an archived EP are transmitted as unsigned attributes associated with a separate EP by placing the SignerInfo structure in the unsignedeAttrs field. Thus, all attributes of the archived EDS are unsigned due to which its mathematical correctness is not impaired.
Imagine all that was described above, in a more visual table:
Comparative analysis of formats for CA type CAdES
XAdES Electronic Signature
XML Advanced Electronic Signatures (XAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the XML Digital Signature Standard (XMLDSig). The main document describing this standard is ETSI EN 319 132-1 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); XAdES digital signatures.
Similar to the CAdES type EP, several formats are defined for the XAdES type EP, each of which includes the previous one (according to the sequence below) and expands it:
We will not describe in detail the differences of each subsequent format in the list from the previous one, since it exactly repeats the description for CAdES, assuming that the signed structure is “enriched” with similar fields and attributes. The main differences are summarized immediately in tabular form:
Comparative analysis of formats of electronic signature type XAdES

The “Litoria Desktop 2” software package (PC) is a development by Gazinformservice, which provides the user with the option of completely abandoning paper workflow and switching to electronic legally significant and confidential interaction. Formation and verification of CEC in CAdES-A format are already available to users of the software package, starting with release 2.2.3. The same format ES verifies receipts, and also performs their verification of the PC of the Trusted Third Party Service "Litoria DVCS" in release 5.2.2.
Consider the process of forming archived CEC based on product data.
1. With the help of “Litoria Desktop 2” we will form the UEP on an electronic document, which we will transmit to “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”to generate a receipt:
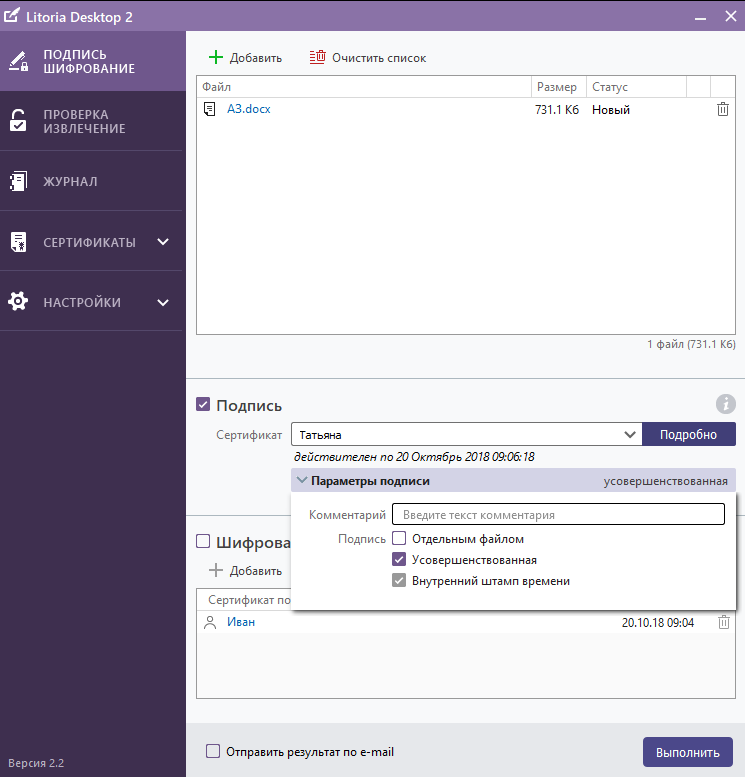
Figure 1 - Formation of CEC with the help of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2"
Detailed information on the formed UEP can be viewed through the tab “Check and extraction”. We see that the signer’s certificate is valid until October 20, 2018 (Figure 2), and the certificate of the TSP server, which actually added a time stamp to the signature and made it improved (Figure 3), until December 22, 2032.
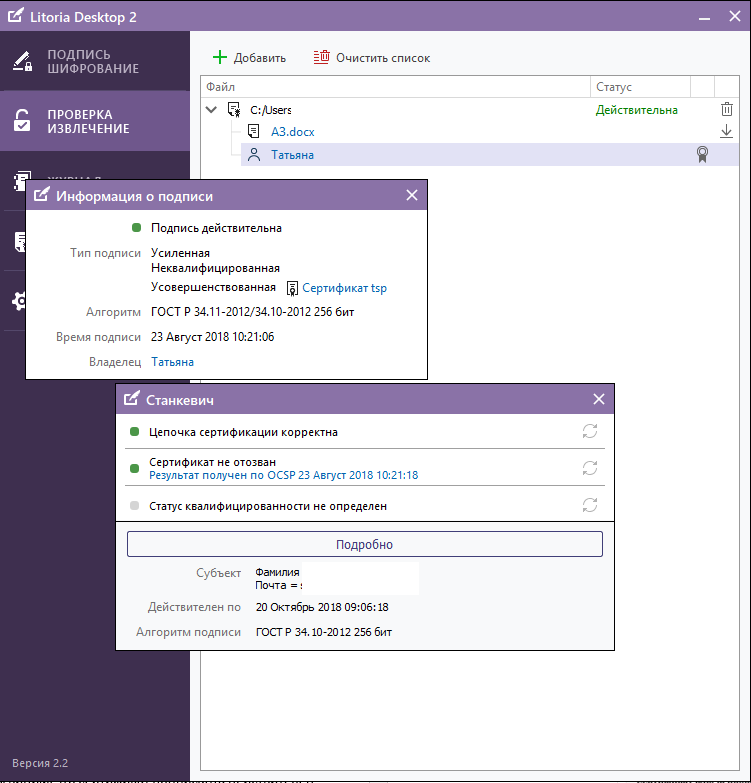
Figure 2 - Display of information about ES in the interface of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2" (user certificate)
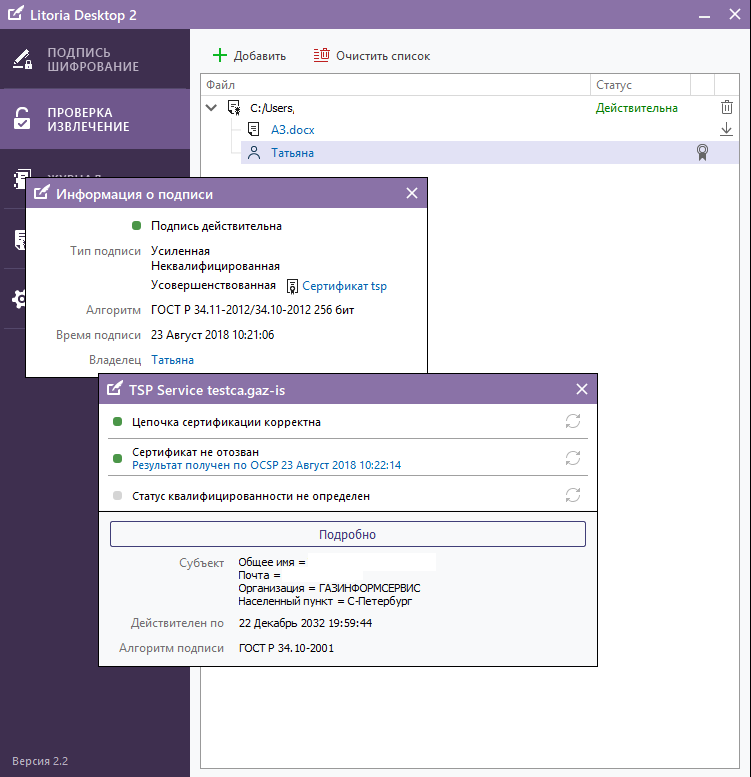
Figure 3 - Display of information about ES in the interface of the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (TSP server certificate)
In turn, the validity of UEP, which is certified by ED, is determined by the validity of the time stamp server certificate. But here you should pay your attention that for the article we used test non-accredited CA and test TSP, for which unqualified certificates were issued. In the Russian reality, the validity period of a qualified time stamp server certificate should not exceed 15 years.
And what should we do when the document should be stored for more than 15 years? Just here the archive format of the electronic signature entered on the receipt comes into play (with the help of the SDTS “Litoria DVCS” PC).
2. Go to the personal account of the user of the PC “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”and send the signed ED to form a receipt for the check (Figures 4, 5).
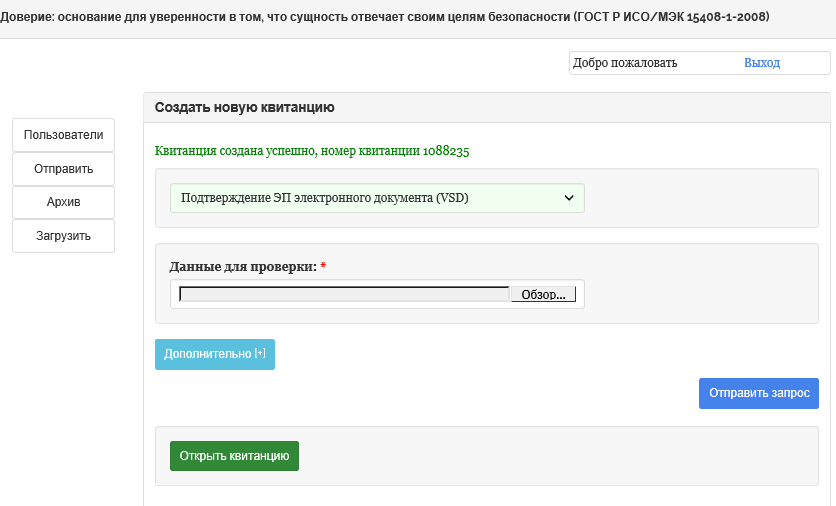
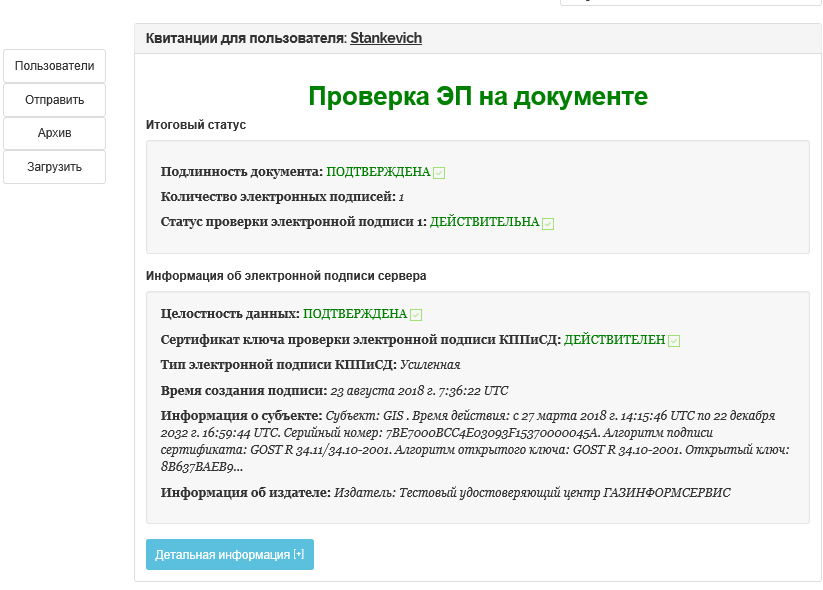
Figure 4 - Formation of a receipt for ED in PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "

Figure 5 - Detailed information on the receipt in the PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "
Checking the ED is completed, the receipt is generated. Now the complex in an automated mode will perform an analysis of the validity of each of the stored receipts, which is determined by the validity of the time stamp service certificate, and upon the occurrence of the event of its expiration, the receipts will be reissued, i.e. a chain of legally relevant documents is formed “source ED - receipt 1 - receipt 2 -…. - n receipt
Let us consider the second, so far mechanized, method of forming an electronic signature in the CAdES-A format using the Litoria Desktop 2 software package.
1. Start the PC "Litoria Desktop 2", form the UEP in a known way
2. Go to the “Archival storage” directory, copy the signed ED to the “edsArch” folder and run the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility (the installation takes place during the installation of the complex in the appropriate directory specified by the user, Figure 6)
Figure 6 - Preparation of ED for the formation of electronic signature in the CAdES format
3. Upon completion of the procedure on the screen, the user in the console will receive a corresponding notification (Figure 7).

Figure 7 - Successful formation of CEC in the format CAdES-A
We emphasize once again that the CAdES-A signature format assumes the addition of unsigned attributes to the source DG, which does not violate the mathematical correctness of the source DG.
4. Now go to the “edsArch” folder and the file generated by the utility’s work is checked in the Litoria Desktop 2 PC (Figures 8, 9, 10).
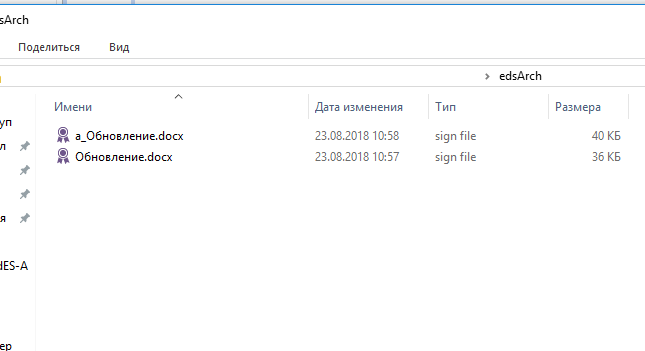
Figure 8 - Archive-signed file generated by the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility
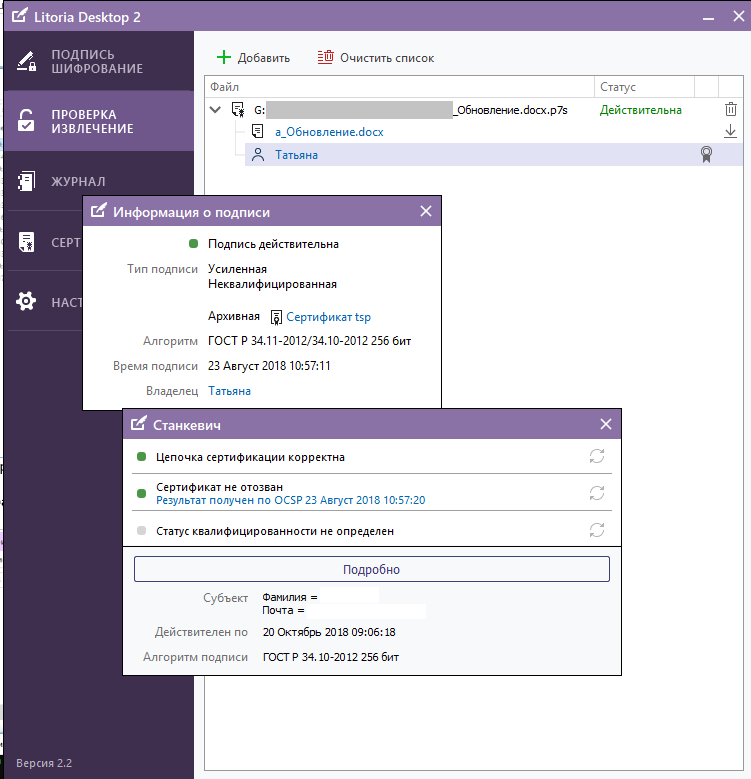
Figure 9 - Results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (user certificate)
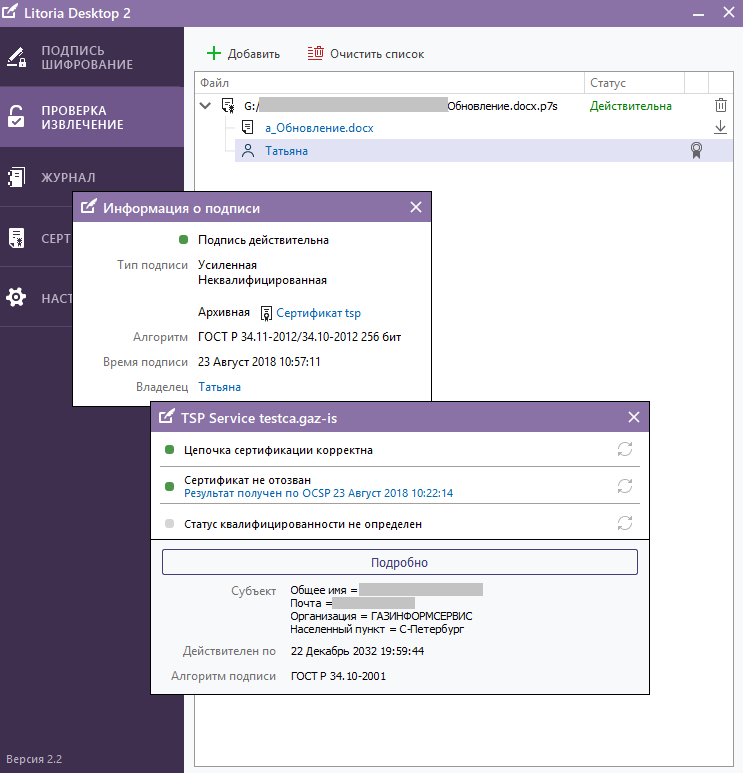
Figure 10 - Results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (TSP service certificate)
And finally - a fragment of the ASN.1 code of the archival time stamp:
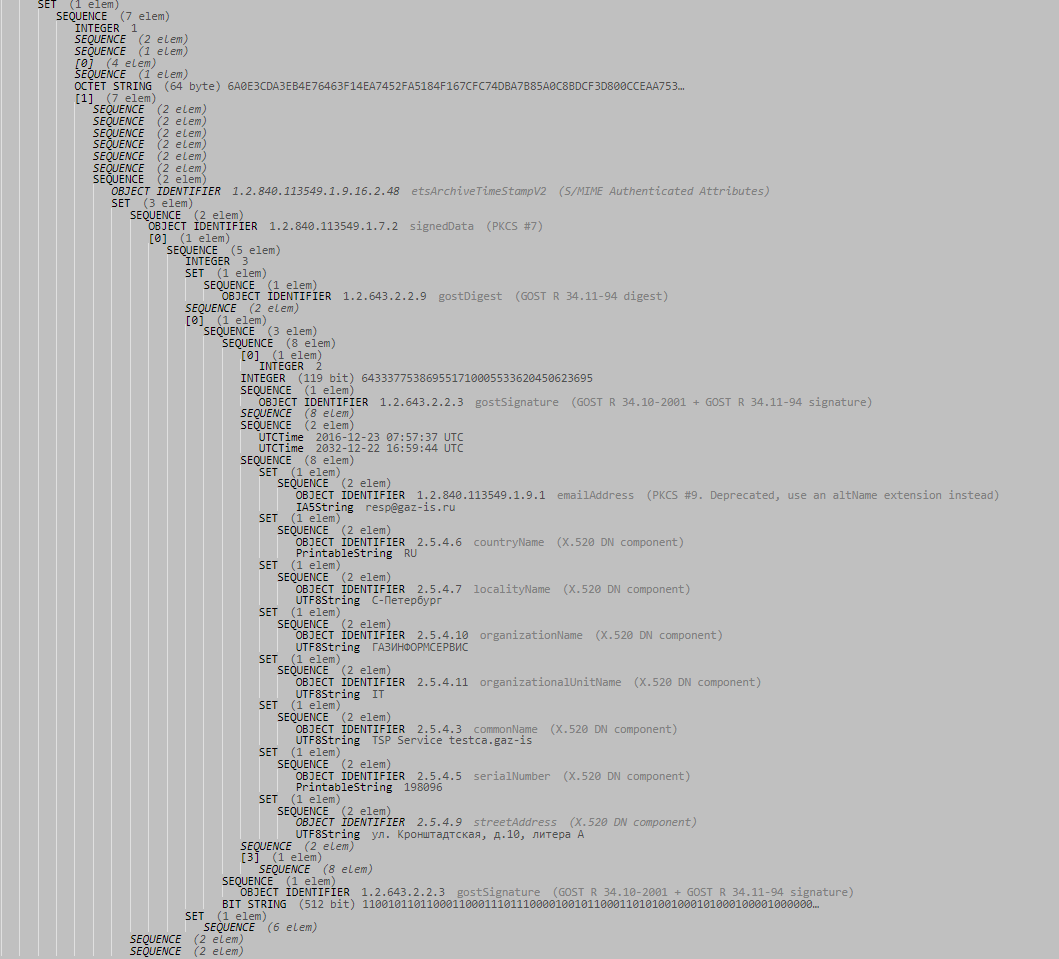
Thus, today there are already viable options for ensuring the full life cycle of electronic legally significant documents requiring long-term storage. For more information about the products designed to solve the designated task, you can find on the website of the developer or by contacting the sales department by phone 8 (812) 677-20-53, email: salespo@gaz-is.ru.
This article describes in more detail another approach to long-term archival storage (DAH) - the formation of an improved electronic signature (CEC), namely, electronic signature in CAdES-A and XAdES-A archive formats.

Let us try to understand in more detail how and why archival ES can extend the life cycle of electronic documents with ES. Let's start with a small theoretical educational program on the types and formats of electronic signature, and then consider in practice the procedure for the formation of archive electronic signature products developed by Gazinformservice.
')
Some theory
CAdES type electronic signature
CMS Advanced Electronic Signatures (CAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS) standard. The main document describing this standard is ETSI TS 101 733 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); CMS Advanced Electronic Signature (CAdES) ".
CAdES became the development of CMS, in which the main shortcomings of the predecessor were corrected, such as the absence of a stamp of the trusted time of creating an EP, the absence of an EP content type, and the absence of the possibility of long-term preservation of the legal significance of an EP.
The standard defines several CAdES formats, each of which includes the previous one (in accordance with the sequence presented below) and extends it:
Formats standard CAdES
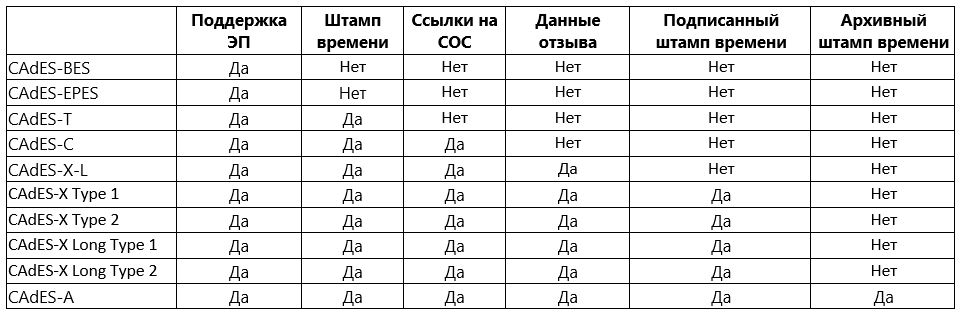
1. CAdES-BES (Basic Electronic Signature) - the basic and simplest format of the standard, provides basic authentication of data and protection of its integrity. It contains the following attributes:
2. CAdES-EPES (Explicit Policy-based Electronic Signature) is a format that contains an explicit indication of the selected EP policy. A signature-policy-identifier attribute is added to CAdES-EPES, which identifies the identifier of the selected ES policy. By signing this identifier, the sender explicitly indicates that he applied a specific policy when creating it. Accordingly, the recipient must verify the ES under the same regulations.
3. CAdES-T (Timestamp) is an electronic format of CAdES type, in which a field for fixing the trusted time is added.
4. CAdES-C (Complete) contains a complete set of verification data. It differs from CAdES-T by adding unsigned attributes to complete-certificate-references and complete-revocation-references.
The first attribute contains the identifiers of all certificates used to verify the ES. The second attribute contains identifiers of certificates from the list of revoked certificates (Certificate Revocation Lists, CRL, SOS) and / or responses received via the protocol for checking the current status of certificates (Online Certificate Status Protocol, OCSP).
The inclusion of these attributes makes it easier to obtain information about the certificates of the ES verification keys, which are necessary for the recipient to verify the ES, since the data on valid and invalid certificates will already be contained in the ES itself.
5. CAdES-X (Extended) is an CA format of the CAdES type, including the following sub-formats included in the CadES-C type:
6. CAdES-X Long Type 1 — This EP format is a combination of the CAdES-X Long and CAdES-X Type 1 formats.
7. CAdES-X Long Type 2 — This EP format is a combination of the CAdES-X Long and CAdES-X Type 2 formats.
8. CAdES-A (Archival) is a CAdES type EP format, formed on the basis of CAdES-X Long Type 1 or Type 2 by adding one or more archive-time-stamp attributes representing archive time stamps (Figure 1). It is this ES format that is used for archiving long-term ES and ensuring DAH, subject to possible verification of the legal significance of the stored ED on a long time period (the so-called “time interoperability”).
- Subscribed user data (sender's ED);
- a set of required signed attributes (attributes are called signed, if the generation of ES occurs from a combination of these attributes and user data);
- ES value calculated for user data and signed attributes;
- set of additional attributes;
- set of optional signed attributes.
2. CAdES-EPES (Explicit Policy-based Electronic Signature) is a format that contains an explicit indication of the selected EP policy. A signature-policy-identifier attribute is added to CAdES-EPES, which identifies the identifier of the selected ES policy. By signing this identifier, the sender explicitly indicates that he applied a specific policy when creating it. Accordingly, the recipient must verify the ES under the same regulations.
3. CAdES-T (Timestamp) is an electronic format of CAdES type, in which a field for fixing the trusted time is added.
4. CAdES-C (Complete) contains a complete set of verification data. It differs from CAdES-T by adding unsigned attributes to complete-certificate-references and complete-revocation-references.
The first attribute contains the identifiers of all certificates used to verify the ES. The second attribute contains identifiers of certificates from the list of revoked certificates (Certificate Revocation Lists, CRL, SOS) and / or responses received via the protocol for checking the current status of certificates (Online Certificate Status Protocol, OCSP).
The inclusion of these attributes makes it easier to obtain information about the certificates of the ES verification keys, which are necessary for the recipient to verify the ES, since the data on valid and invalid certificates will already be contained in the ES itself.
5. CAdES-X (Extended) is an CA format of the CAdES type, including the following sub-formats included in the CadES-C type:
- CAdES-X Long is a long-term extended EA format, which adds the certificate-values and revocation-values attributes. They represent the complete certificate and COC data required to verify the CAdES-C signature, even if their original source is not available and eliminates the possibility of losing this information.
- CAdES-X Type 1 - adds a time-stamp attribute that contains a time stamp on the entire CAdES-C signature. This ensures the integrity and availability of trusted time in all elements of the EA. Thus, this attribute allows you to protect certificates, SOS and responses received via the OCSP protocol, information about which is recorded in the ES (relevant when the certification authority key, SOS publisher key or OCSP service key is compromised).
- CAdES-X Type 2 - adds a time stamp to CAdES-C, but not to the entire ES, but only to full references to certificates and SOS.
6. CAdES-X Long Type 1 — This EP format is a combination of the CAdES-X Long and CAdES-X Type 1 formats.
7. CAdES-X Long Type 2 — This EP format is a combination of the CAdES-X Long and CAdES-X Type 2 formats.
8. CAdES-A (Archival) is a CAdES type EP format, formed on the basis of CAdES-X Long Type 1 or Type 2 by adding one or more archive-time-stamp attributes representing archive time stamps (Figure 1). It is this ES format that is used for archiving long-term ES and ensuring DAH, subject to possible verification of the legal significance of the stored ED on a long time period (the so-called “time interoperability”).
The CAdES-A archive archive form consists of the following elements:
- full set of verification data (CAdES-);
- certificate and COC values (CAdES-X Type 1 or CAdES-X Type 2), if used;
- signed user data and an additional archived time stamp applied to all data.

Figure 1 - Scheme of formation of electronic signature in the format CAdES-A
The organization of the DAH is associated not only with the limited validity of the user certificate established by Russian legislation at 1 year 3 months, but also with modifications of cryptographic algorithms, which in turn is caused by the deterioration of their robustness properties due to the development of cryptanalysis methods and computing industry.
An additional time stamp may be imposed on top of the EA in the CAdES-A format, which will protect its contents when identifying vulnerabilities of the cryptographic hash functions used, when hacking the cryptographic algorithms used and when the keys are compromised. It should not be forgotten that the sequence of time stamps can provide protection against ES falsification, provided that these stamps were applied before the time stamp service key was compromised. Thus, the EA in the CAdES-A format allows to preserve its authenticity for very long periods of time, and the periodic installation of archive stamps will provide the possibility of checking the EA when updating cryptographic standards.
It is also important to note that the additional data needed to create the above-described forms of an archived EP are transmitted as unsigned attributes associated with a separate EP by placing the SignerInfo structure in the unsignedeAttrs field. Thus, all attributes of the archived EDS are unsigned due to which its mathematical correctness is not impaired.
Imagine all that was described above, in a more visual table:
Comparative analysis of formats for CA type CAdES

XAdES Electronic Signature
XML Advanced Electronic Signatures (XAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the XML Digital Signature Standard (XMLDSig). The main document describing this standard is ETSI EN 319 132-1 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); XAdES digital signatures.
Similar to the CAdES type EP, several formats are defined for the XAdES type EP, each of which includes the previous one (according to the sequence below) and expands it:
XAdES Formats
- XAdES-BES (Basic Electronic Signature)
- XAdES-EPES (Explicit policy electronic signatures)
- XAdES-T (Timestamp)
- XAdES-C (Complete)
- XAdES-X (Extended Validation Data)
- XAdES-XL (Extended Long Term)
- XAdES-A (Archival)
We will not describe in detail the differences of each subsequent format in the list from the previous one, since it exactly repeats the description for CAdES, assuming that the signed structure is “enriched” with similar fields and attributes. The main differences are summarized immediately in tabular form:
Comparative analysis of formats of electronic signature type XAdES

New features of Litoria products to ensure DAH
The “Litoria Desktop 2” software package (PC) is a development by Gazinformservice, which provides the user with the option of completely abandoning paper workflow and switching to electronic legally significant and confidential interaction. Formation and verification of CEC in CAdES-A format are already available to users of the software package, starting with release 2.2.3. The same format ES verifies receipts, and also performs their verification of the PC of the Trusted Third Party Service "Litoria DVCS" in release 5.2.2.
Consider the process of forming archived CEC based on product data.
1. With the help of “Litoria Desktop 2” we will form the UEP on an electronic document, which we will transmit to “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”to generate a receipt:

Figure 1 - Formation of CEC with the help of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2"
Detailed information on the formed UEP can be viewed through the tab “Check and extraction”. We see that the signer’s certificate is valid until October 20, 2018 (Figure 2), and the certificate of the TSP server, which actually added a time stamp to the signature and made it improved (Figure 3), until December 22, 2032.

Figure 2 - Display of information about ES in the interface of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2" (user certificate)

Figure 3 - Display of information about ES in the interface of the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (TSP server certificate)
In turn, the validity of UEP, which is certified by ED, is determined by the validity of the time stamp server certificate. But here you should pay your attention that for the article we used test non-accredited CA and test TSP, for which unqualified certificates were issued. In the Russian reality, the validity period of a qualified time stamp server certificate should not exceed 15 years.
And what should we do when the document should be stored for more than 15 years? Just here the archive format of the electronic signature entered on the receipt comes into play (with the help of the SDTS “Litoria DVCS” PC).
2. Go to the personal account of the user of the PC “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”and send the signed ED to form a receipt for the check (Figures 4, 5).


Figure 4 - Formation of a receipt for ED in PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "

Figure 5 - Detailed information on the receipt in the PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "
Checking the ED is completed, the receipt is generated. Now the complex in an automated mode will perform an analysis of the validity of each of the stored receipts, which is determined by the validity of the time stamp service certificate, and upon the occurrence of the event of its expiration, the receipts will be reissued, i.e. a chain of legally relevant documents is formed “source ED - receipt 1 - receipt 2 -…. - n receipt
Signed in CAdES-A format using the Litoria Desktop 2 PC
Let us consider the second, so far mechanized, method of forming an electronic signature in the CAdES-A format using the Litoria Desktop 2 software package.
1. Start the PC "Litoria Desktop 2", form the UEP in a known way
2. Go to the “Archival storage” directory, copy the signed ED to the “edsArch” folder and run the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility (the installation takes place during the installation of the complex in the appropriate directory specified by the user, Figure 6)

Figure 6 - Preparation of ED for the formation of electronic signature in the CAdES format
3. Upon completion of the procedure on the screen, the user in the console will receive a corresponding notification (Figure 7).

Figure 7 - Successful formation of CEC in the format CAdES-A
We emphasize once again that the CAdES-A signature format assumes the addition of unsigned attributes to the source DG, which does not violate the mathematical correctness of the source DG.
4. Now go to the “edsArch” folder and the file generated by the utility’s work is checked in the Litoria Desktop 2 PC (Figures 8, 9, 10).

Figure 8 - Archive-signed file generated by the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility

Figure 9 - Results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (user certificate)

Figure 10 - Results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (TSP service certificate)
And finally - a fragment of the ASN.1 code of the archival time stamp:

Thus, today there are already viable options for ensuring the full life cycle of electronic legally significant documents requiring long-term storage. For more information about the products designed to solve the designated task, you can find on the website of the developer or by contacting the sales department by phone 8 (812) 677-20-53, email: salespo@gaz-is.ru.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/426081/
All Articles