Power supply of IT equipment: security or continuity? part 2
We continue the article, the purpose of which is to share experience and show the key features and frequent errors arising in the design and organization of power supply subsystems of the IT infrastructure and the data center as a whole. But I would like to expand the audience a bit and devote several sections to the basic elements of electrical safety and protection of equipment and people.
Those who missed the first part or want to remember the first part can be passed here .
For those who understand what an automaton and RCDs are for, what they are needed for, what they protect against and what are they protected from - go to the section Do you need RCDs for IT equipment, server room, data center? .
')
Let's see what is the relationship between energy and the end IT equipment, we will understand the question of in what cases the power outages the operating system is guaranteed to work without failures.

Switching to a backup power supply
Power supply of information equipment is organized with redundancy. Consider the organization of power supply in terms of SCHBP-BRP-BP (uninterruptible power supply shield-power distribution unit-power supply). Backup types are of the following types:
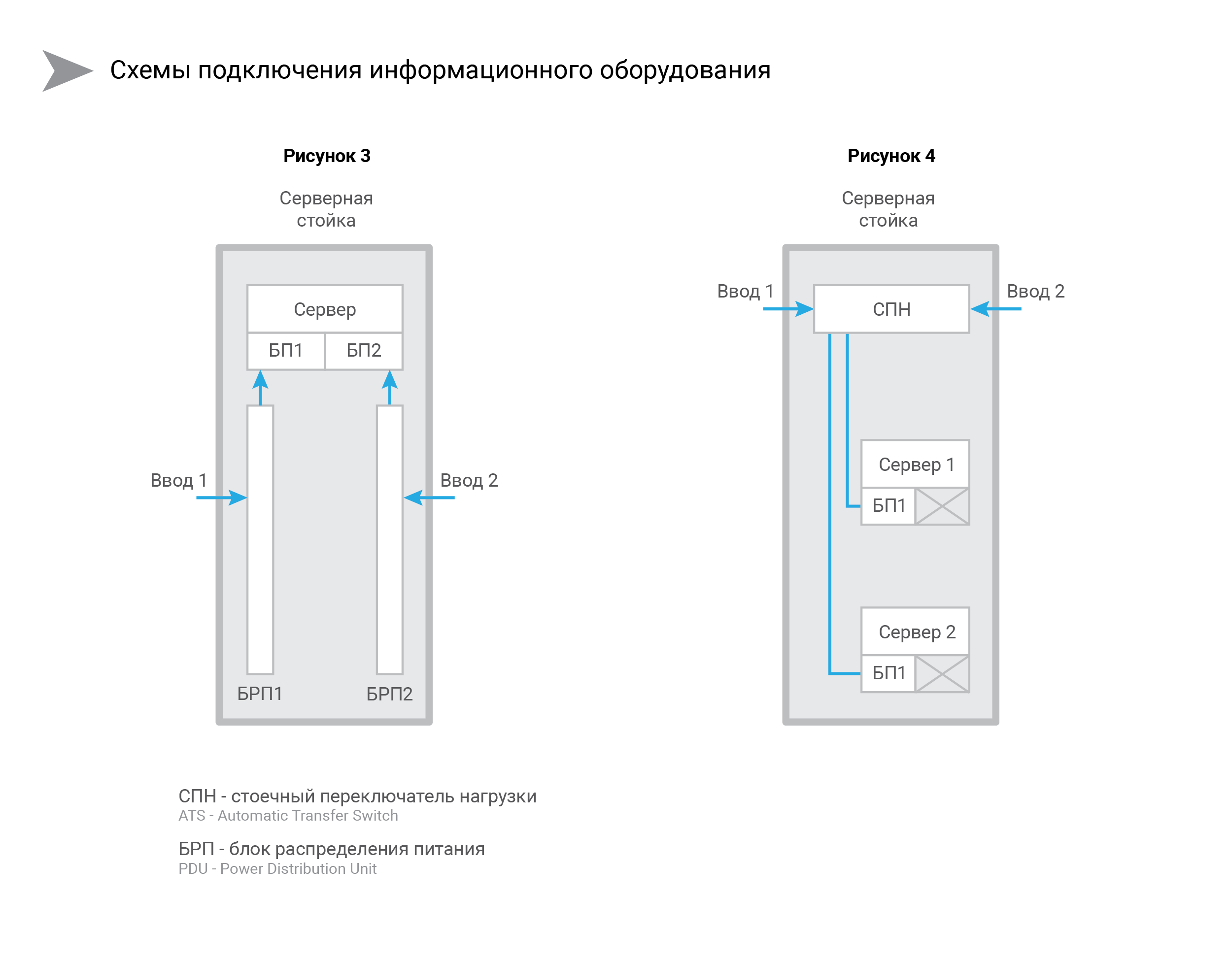
Redundancy at the power supply level directly in the server, switch, IT device (Fig. 3)
Redundancy using rack-mounted load switch, rack-mounted ATS (SPN, also known as ATS) (Fig.4)
To switch between primary and backup inputs can be used:
As we quoted above for IT equipment, “a break in power supply is not allowed.” And what is hidden under this phrase? What is the "break" in the power supply of information equipment? Now let's look at a live example.
The customer implements the local server along with the IT infrastructure of two floors under the company's office. At the discussion stage of the power supply system, he has a desire to put all the information equipment with one power supply (PSU), and leave the second slot for the server BPs free, and mount a single ATS rack-mount version for the entire rack. (Fig.4, scheme).
The appearance of the back side of the server with duplicated power supplies
How the customer argued his desire :
We took time out, studied in detail the desire of the Customer from various points of view, the reliability of services in general during the warranty and post-warranty period, as well as:
And that's what turned out:
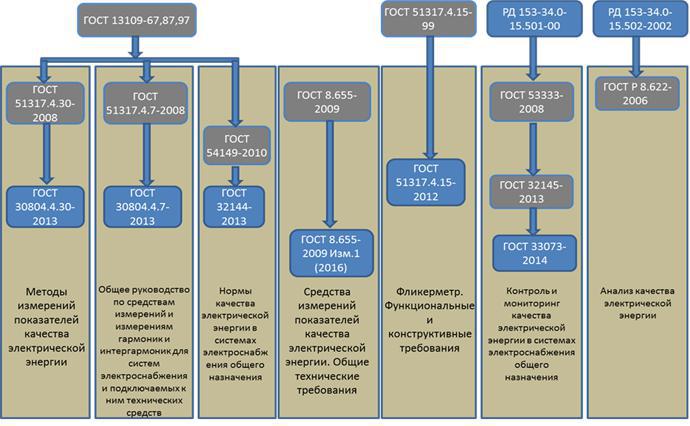
According to the regulatory framework GOST 32144-2013 (Electrical Energy. Electromagnetic Compatibility of Technical Means. Power Quality Standards in General-Purpose Networks. Introduction Date - July 1, 2014), the main cause of failures in the work of information equipment can be voltage dips
We read further:
By the way, it is worth noting that at the moment there are contradictions in the current regulatory framework of the Russian Federation in terms of measuring values related to the quality of electricity, you can read more in the article of our company's technical director Viktor Cherdak (source digitalsubstation.com )
But how fast? How to determine that time in milliseconds, during which the service (and server) of the customer will not fall, and the operating system will not go into the "critical error"?

There is the CBEMA (Computer and Business Equipment Manufacturers Association) standard, which after some adjustments is now known as the “ITIC curves” (Information Technology Industry Council), and its variants are included in the IEEE 446 ANSI standards. According to these standards, electronic power supply circuits must remain operable for 20 ms (or 0.02 seconds, i.e. a period).

Those same ITIC curves
According to the requirements for the server system and computer systems, the Server System Infrastructure can be said that the Tvout_holdup parameter of the power supply unit during the power supply voltage failure provides the information equipment with a minimum of 21 ms. That is, the full period of the network is the guaranteed time for normal operation of the server or switch. The Tpwok_holdup parameter is specified at least 20ms.
Now let's see how long the switching time is stated by APC, for example, for a rack-mounted load switch of the brand AP7721 . We see that here we usually have 8-12 ms, but 18 ms is the maximum switching time.
We can conclude that the switching time to the backup input for a rack load switch corresponds to the specification of the power supply unit of the server equipment. It turns out that there will be no failures in the operation of information equipment.
Suppose we have three small servers in the rack, into which we can put two power supplies and three devices with non-duplicated power supplies. All are critical and the failure of any device will lead to the failure of the customer’s entire system. Rack load switch we need in any case. It is about 18 thousand rubles.
The customer declares that they do not need a PDU (PDU), which means that only the ATS value will be in the budget - the same 18 thousand rubles. As a replacement for power distribution units (PDUs), the Customer suggests using on-board power distribution of a rack load switch. Also, the Customer plans to buy servers with two slots for power supplies, but in a complete set with one power supply unit for the sake of economy. (picture 4)
The classic version (Figure 3) assumes a set of 2 PDUs - about 32,000 rubles, 3 additional power supplies to servers for $ 500 each for 84 thousand rubles in total. ATS for the same 18 thousand rubles. Having added everything, we understand that the classic solution will cost the customer approximately 134 thousand rubles.
It seems that the customer is right, the money is completely different. But let's look in terms of resiliency and ease of maintenance of both options:
Customer option: Single point of failure - rack load switch. If something happens to him, then we lose the entire rack entirely. So, you need to have a spare parts kit right on the site, which adds 18,000 rubles to the estimate. The power supplies in the servers cost one at a time; they are also points of failure. Therefore, it is desirable to have at least one, and preferably all three power supplies in reserve on the site. Let us assume that we need three power supply units in spare parts and equipment - this is plus 36 thousand rubles. You need to check the power that the rack-mount ATS can switch. Now we assume that 3 kW or 16A will be enough for all the equipment in the rack. If we need ATS for 32A (7kW), then it will be much more expensive (more than 100 thousand rubles). That is, the budget option of the Customer with a detailed review of reliability increases to 160 thousand rubles . In this case, in the case of emergency, despite the fact that spare parts will be on site, you will need down-time to replace the device.
The point of failure is the same ATS. If something happens to him, then we lose the entire rack entirely. We agree that it is necessary to have a spare parts kit right on the site. But in our case, if only ATS refuses, then this can only affect the operation of switches and auxiliary equipment. The servers themselves will continue to work quietly. Power supplies in the ZIP are not needed. Since if one of the duplicated power supplies fails, the server will continue to work on the rest, and, most likely, it will wait for a new power supply from the vendor, regardless of the site distance.
Thus, it is possible to connect all the equipment of the rack to a single ATS, but not rationally, since in this case we get a single point of failure on the power supply. Purchase of servers with duplicated power supply units is preferable in any case, since the fault tolerance at the level of information equipment increases significantly.
The rack-mounted load switch ensures correct and almost instantaneous switching to backup input, the information equipment will not even feel it, software products and operating systems will continue to operate correctly. Rack-mount power distribution units in any case are needed and you do not need to save on them. Visible savings in capital costs for power distribution can lead to unsolvable problems during operation, for example, the need to “extinguish” the entire rack just to move the ATS to another unit or to revise the rack load switch. In any case, duplicate power supplies should have a spare parts kit, but it is not always possible or available.
Appearance of removable server power supply:

The work of information equipment with two power supplies was well described in the article by Vadim Sinitsky @ dimskiy . As you can see, there are advantages and disadvantages. And the presence of redundant power supplies for information equipment in any case is necessary, especially if the object is outside the zone of fast delivery of the power supply from the vendor. In addition, we want to note that online calculators for calculating the capacity of new servers from vendors can only be used as a guideline for system administrators and customer personnel.
The real possibilities of connecting the new powerful server to the existing rack should be assessed taking into account the initial power supply design, current state and load of the rack, server, UPS, generator .... In terms of connection to the rack, it is also worth considering:
Separate attention should be paid to the reliability of the server power supply system, if it is built on the system shown in Fig. 2 (with two bus systems), the presence of a new powerful server may, in the case of repair work, lead to an overload of the entire power supply system, reduce the battery runtime of the UPS , force the UPS to transfer to the bypass for overload and so on ...
And how is your distribution system built in the rack?
What is the BP resource for IT equipment and the algorithm for their software redundancy?
Which PDU do you prefer to use: basic, monitored? How useful is the “managed PDU / PDU” function in practice and has it ever helped you?
Author: Oleg Kulikov
Lead Design Engineer
Department of integration solutions
"Open Technologies"
okulikov@ot.ru
Registration in the National Register of Specialists "NOPRIZ" P-045870
Those who missed the first part or want to remember the first part can be passed here .
For those who understand what an automaton and RCDs are for, what they are needed for, what they protect against and what are they protected from - go to the section Do you need RCDs for IT equipment, server room, data center? .
')
Part two
Let's see what is the relationship between energy and the end IT equipment, we will understand the question of in what cases the power outages the operating system is guaranteed to work without failures.

Switching to a backup power supply
Power supply of information equipment is organized with redundancy. Consider the organization of power supply in terms of SCHBP-BRP-BP (uninterruptible power supply shield-power distribution unit-power supply). Backup types are of the following types:
- Redundant cabling to the rack, equipment, using separate power distribution units, PDU (Figure 1)
- Redundant power buses in the power supply panel, using separate power distribution units, PDU (Figure 2)
Redundancy at the power supply level directly in the server, switch, IT device (Fig. 3)
Redundancy using rack-mounted load switch, rack-mounted ATS (SPN, also known as ATS) (Fig.4)

To switch between primary and backup inputs can be used:
- in the field of information systems: ABP / STS (Static Transfer Swith) cabinets for high-power systems, for switching to power from a backup UPS at the time of operation of a full-fledged 2N system or combinations of N + 1 systems;
- in the field of power supply systems of various types of circuit breaker circuit (on contactors, on controllers);
- at the server rack level: automatic high-speed rack-mount automatic transfer switch \ ATS (Automatic Transfer Switching);
- at the level of specific information equipment: duplicated power supplies.
As we quoted above for IT equipment, “a break in power supply is not allowed.” And what is hidden under this phrase? What is the "break" in the power supply of information equipment? Now let's look at a live example.
The customer implements the local server along with the IT infrastructure of two floors under the company's office. At the discussion stage of the power supply system, he has a desire to put all the information equipment with one power supply (PSU), and leave the second slot for the server BPs free, and mount a single ATS rack-mount version for the entire rack. (Fig.4, scheme).
The appearance of the back side of the server with duplicated power supplies

How the customer argued his desire :
- Cost savings ($ 500-800 per device per rack)
- You can put two simple PDUs and apply them to power distribution after ATS
- Absolutely similar level of system reliability, compared to the classical distribution method
We took time out, studied in detail the desire of the Customer from various points of view, the reliability of services in general during the warranty and post-warranty period, as well as:
- cost (savings) of capital costs in the implementation (CAPEX)
- the cost of depreciation, maintenance of spare parts, labor costs of client personnel ( OPEX )
- comparison of operation algorithms and switching time to the backup line in both variants, checking for “single points of failure”
- the level of risks of lagging and / or rebooting the operating systems of information equipment, the fall of information services that run on them.
And that's what turned out:
According to the regulatory framework GOST 32144-2013 (Electrical Energy. Electromagnetic Compatibility of Technical Means. Power Quality Standards in General-Purpose Networks. Introduction Date - July 1, 2014), the main cause of failures in the work of information equipment can be voltage dips
usually occur due to faults in electrical networks or electrical installations of consumers, as well as when connecting a powerful load
We read further:
duration of voltage sags can be up to 1 minuteThis phrase tells us that the information equipment should be provided by the UPS and / or high-speed AVR, since voltage dips of similar duration are acceptable and normal in terms of high energy, but will be fatal to IT equipment and services.
By the way, it is worth noting that at the moment there are contradictions in the current regulatory framework of the Russian Federation in terms of measuring values related to the quality of electricity, you can read more in the article of our company's technical director Viktor Cherdak (source digitalsubstation.com )
Some excerpts from the article
 "
"
In recent years, state standards in the field of measuring parameters of electrical energy related to QE have been actively developed and have been repeatedly revised.
 "
"An important change was the replacement of GOST 13109-97 “Electric energy. Electromagnetic compatibility of technical equipment. Quality standards for electrical energy in general-purpose power supply systems ”[16], GOST 32144-2013. These standards define a different range of power quality indicators.
But how fast? How to determine that time in milliseconds, during which the service (and server) of the customer will not fall, and the operating system will not go into the "critical error"?

There is the CBEMA (Computer and Business Equipment Manufacturers Association) standard, which after some adjustments is now known as the “ITIC curves” (Information Technology Industry Council), and its variants are included in the IEEE 446 ANSI standards. According to these standards, electronic power supply circuits must remain operable for 20 ms (or 0.02 seconds, i.e. a period).

Those same ITIC curves
According to the requirements for the server system and computer systems, the Server System Infrastructure can be said that the Tvout_holdup parameter of the power supply unit during the power supply voltage failure provides the information equipment with a minimum of 21 ms. That is, the full period of the network is the guaranteed time for normal operation of the server or switch. The Tpwok_holdup parameter is specified at least 20ms.
Some details on the SSI parameters can be found here.
Reference: Hold-up time is the time period during which the power supply unit can maintain the output voltages within certain limits after the input voltage is lost at its input. In most computer power supplies, the Hold-up time also characterizes the power good signal (PWR_OK) after which the time will tell the system that the voltages produced by the power supply are unstable (for computer power supplies, this parameter is usually more than 16 ms).

Here is one of the tables from the document.

And this is a diagram (time-line) with regulated BP operation algorithms.

Here is one of the tables from the document.

And this is a diagram (time-line) with regulated BP operation algorithms.
Now let's see how long the switching time is stated by APC, for example, for a rack-mounted load switch of the brand AP7721 . We see that here we usually have 8-12 ms, but 18 ms is the maximum switching time.
We can conclude that the switching time to the backup input for a rack load switch corresponds to the specification of the power supply unit of the server equipment. It turns out that there will be no failures in the operation of information equipment.
Summary of the timings of the elements of the system

And what about the economic component and which of the options is more profitable and fault tolerant?
Suppose we have three small servers in the rack, into which we can put two power supplies and three devices with non-duplicated power supplies. All are critical and the failure of any device will lead to the failure of the customer’s entire system. Rack load switch we need in any case. It is about 18 thousand rubles.
The customer declares that they do not need a PDU (PDU), which means that only the ATS value will be in the budget - the same 18 thousand rubles. As a replacement for power distribution units (PDUs), the Customer suggests using on-board power distribution of a rack load switch. Also, the Customer plans to buy servers with two slots for power supplies, but in a complete set with one power supply unit for the sake of economy. (picture 4)
The classic version (Figure 3) assumes a set of 2 PDUs - about 32,000 rubles, 3 additional power supplies to servers for $ 500 each for 84 thousand rubles in total. ATS for the same 18 thousand rubles. Having added everything, we understand that the classic solution will cost the customer approximately 134 thousand rubles.
It seems that the customer is right, the money is completely different. But let's look in terms of resiliency and ease of maintenance of both options:
Customer option: Single point of failure - rack load switch. If something happens to him, then we lose the entire rack entirely. So, you need to have a spare parts kit right on the site, which adds 18,000 rubles to the estimate. The power supplies in the servers cost one at a time; they are also points of failure. Therefore, it is desirable to have at least one, and preferably all three power supplies in reserve on the site. Let us assume that we need three power supply units in spare parts and equipment - this is plus 36 thousand rubles. You need to check the power that the rack-mount ATS can switch. Now we assume that 3 kW or 16A will be enough for all the equipment in the rack. If we need ATS for 32A (7kW), then it will be much more expensive (more than 100 thousand rubles). That is, the budget option of the Customer with a detailed review of reliability increases to 160 thousand rubles . In this case, in the case of emergency, despite the fact that spare parts will be on site, you will need down-time to replace the device.
Single Point Of Failure (SPOF, Single Point Of Failure) —a node, link, or data accessibility system object, the failure of which can disable the entire system or cause data unavailabilityOpen Technology Option : As per Figure 3 , but if necessary, add ATS for small network equipment with a single power supply.
The point of failure is the same ATS. If something happens to him, then we lose the entire rack entirely. We agree that it is necessary to have a spare parts kit right on the site. But in our case, if only ATS refuses, then this can only affect the operation of switches and auxiliary equipment. The servers themselves will continue to work quietly. Power supplies in the ZIP are not needed. Since if one of the duplicated power supplies fails, the server will continue to work on the rest, and, most likely, it will wait for a new power supply from the vendor, regardless of the site distance.
Interpretation of the term SPOF as applied to IT systems
Single Point Of Failure (SPOF, Single Point Of Failure) is a node, device, or circuit point whose failure can disable the entire system and cause unavailability of data and services. Considered when developing and designing any critical systems. The complete absence of single points of failure leads to a significant increase in capital costs during implementation, so the criticality of a particular system, service is determined at the design stage based on the project budget, as well as the wishes and requirements of the Customer. We always find the perfect solution for each customer, defining several options for the project, and offering them to the customer. As a result, at the stage of project delivery, the customer receives exactly the solution he wanted to see in terms of price / quality / reliability.
Thus, it is possible to connect all the equipment of the rack to a single ATS, but not rationally, since in this case we get a single point of failure on the power supply. Purchase of servers with duplicated power supply units is preferable in any case, since the fault tolerance at the level of information equipment increases significantly.
The rack-mounted load switch ensures correct and almost instantaneous switching to backup input, the information equipment will not even feel it, software products and operating systems will continue to operate correctly. Rack-mount power distribution units in any case are needed and you do not need to save on them. Visible savings in capital costs for power distribution can lead to unsolvable problems during operation, for example, the need to “extinguish” the entire rack just to move the ATS to another unit or to revise the rack load switch. In any case, duplicate power supplies should have a spare parts kit, but it is not always possible or available.
Appearance of removable server power supply:

The use of rack-mount AVR has its own characteristics
For example, the power of such AVR is limited, and it can switch the complex relatively weak in terms of power consumption loads. Have questions about the number of output power connectors. For example, the aforementioned ATS AP7721 is equipped with C14 connectors at the input, which means a maximum switching power of 2.5 kW. For a large load power, there is a 2U model AP7724 , which is equipped with a 32 A plug at the input, that is, the maximum power of the equipment can be up to 7 kW. This means that a typical rack with equipment can be connected to this automatic transfer switch in full. However, the price of such a decision will be more than 100 thousand rubles.
The work of information equipment with two power supplies was well described in the article by Vadim Sinitsky @ dimskiy . As you can see, there are advantages and disadvantages. And the presence of redundant power supplies for information equipment in any case is necessary, especially if the object is outside the zone of fast delivery of the power supply from the vendor. In addition, we want to note that online calculators for calculating the capacity of new servers from vendors can only be used as a guideline for system administrators and customer personnel.
The real possibilities of connecting the new powerful server to the existing rack should be assessed taking into account the initial power supply design, current state and load of the rack, server, UPS, generator .... In terms of connection to the rack, it is also worth considering:
- current PDU capabilities, such as loose connectors in them
- ratings of automata in the boards and the cross section and the phase of the cable line to the rack.
Separate attention should be paid to the reliability of the server power supply system, if it is built on the system shown in Fig. 2 (with two bus systems), the presence of a new powerful server may, in the case of repair work, lead to an overload of the entire power supply system, reduce the battery runtime of the UPS , force the UPS to transfer to the bypass for overload and so on ...
And how is your distribution system built in the rack?
What is the BP resource for IT equipment and the algorithm for their software redundancy?
Which PDU do you prefer to use: basic, monitored? How useful is the “managed PDU / PDU” function in practice and has it ever helped you?
Author: Oleg Kulikov
Lead Design Engineer
Department of integration solutions
"Open Technologies"
okulikov@ot.ru
Registration in the National Register of Specialists "NOPRIZ" P-045870
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/423801/
All Articles