Power supply of IT equipment: security or continuity?
Good afternoon friends! Today we will have an article, the purpose of which is to share experience and show the key features and frequent errors arising in the design and organization of the power supply subsystems of the IT infrastructure and the data center as a whole. But I would like to expand the audience a bit and devote several sections to the basic elements of electrical safety and protection of equipment and people. For those who understand what an automaton and RCDs are for, what they are needed for, what they protect against and what are they protected from - go to the section Do you need RCDs for IT equipment, server room, data center? In addition, we will look into the question of in what cases the power outages the operating system is guaranteed to work without failures. So…
Autumn, the rain gushes almost continuously. There is a rapid construction of a cottage settlement near Moscow. The commandant of the village, bypassing the territory under his control, sees the glaring fact of “abuse” of the temporary air line 380V.
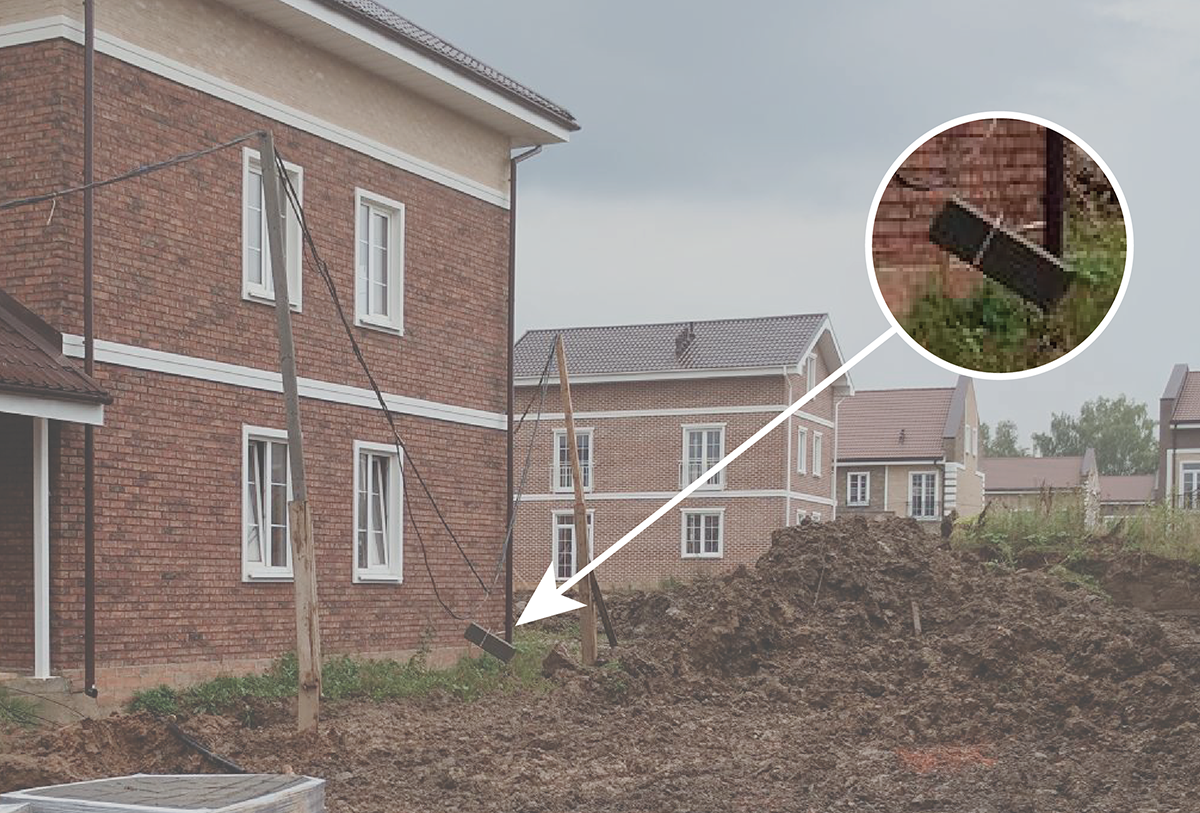

Unable to contain emotions, he turns to the brigadier of the local construction brigade:
')
- Vadim, are you in your mind? Are your hard workers suicide? What is this curb block hanging on an electrical cable?
- Kohl, if you remove it, then around the corner of the house will not pass the excavator!
Behind Vadim, you can see a road worker, who found a bare wire in the dirt that goes somewhere in the bowels of the earth, and happily runs after a colleague, “scaring” him with electricity.
In the meantime, at the substation of the village, the tired guards, burning, for the tenth time, try to turn on a terribly hot automatic switch, which for some reason knocks out every half hour.
Why does a circuit breaker knock out and what other protection options are there for electrical equipment? What to look at first when planning electrical safety in servers and other IT equipment? In order to understand these issues we read both parts of the article in more detail.
Since the regulations provide for a whole range of measures to protect power grids from certain accidents, we will focus on the most common household and industrial sector.

What do we want and can protect against in the first place?
Of course, from electric shock. Secondarily, protect equipment and cables from damage by short-circuit currents, as well as from fire and fire.
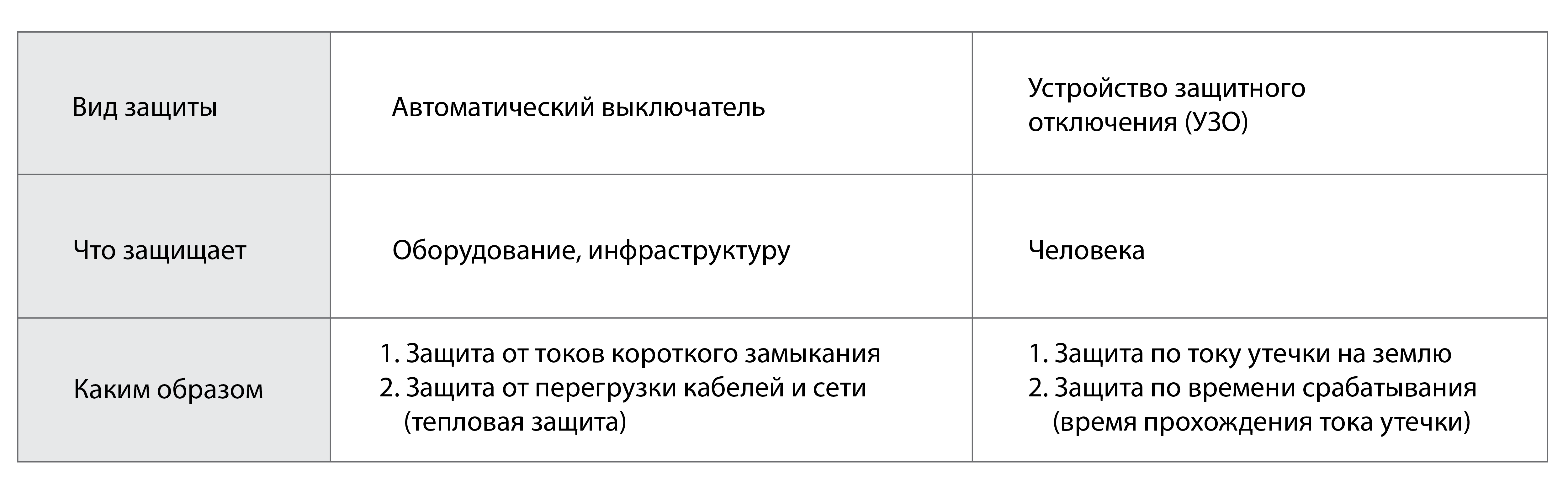
A circuit breaker (circuit breaker) is the most common means of protecting electrical networks. Of course, there are also fuses (fuses), but they are used much less due to their “disposability” and a number of technical differences compared to the automatic.
And bigger? photo is clickable
"Automatic section"
1. short circuit
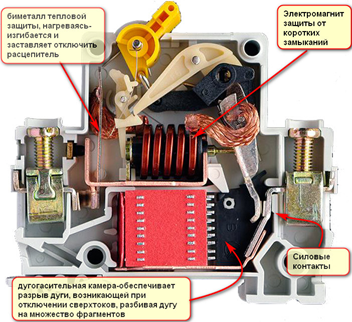
Short circuit (short-circuit) is when the phase of the insulation closes to zero or to ground when the insulation is damaged, from which the current in the circuit increases sharply (5-15 times) and turns off the machine in no more than 0.4 seconds (for a group network according to the rules electrical installation devices). If our automaton is faulty or the network operation modes do not ensure its reliable operation, then the equipment connected to this group, which itself may be a source of short circuit, suffers first. CZ also has negative effects on wires and cables. As a rule, in cases of failure of the automaton in the switchboard, local heating of the short circuit site occurs, an arc appears and the conductive parts are burned off with a firework of molten copper microparticles. And this development of events seems quite favorable, since in this case the accident stops by itself. In some cases, “welding” of current-carrying parts occurs at the short circuit site, and a so-called “metallic” short circuit is formed, which is much more dangerous, since it does not stop by itself, and must be turned off automatically. After that, the specialist must find the place of damage and only then try to turn on the device. But the defense may not work for various reasons, then (God forbid) it can happen
In addition, modern automata perform the function of current limiting in case of an accident, that is, they do not allow currents in the circuit to reach dangerous values.
2. From network overload
Network overload is when insulation damage (or an increased load on the network) causes a prolonged increase in the currents in the circuit beyond the calculated parameters (by 110-300% or 110-500%), which leads to the automatic disconnection from a few minutes to an hour and a half depending on the situation and the type of machine. In this case, protection against overheating, destruction of insulation and fire of elements of the group circuit is provided. That is, the machine must heat up and disconnect before the critical heating of wires, cables, contacts, sockets, switches occurs. For example, the most common automaton of characteristic C, and with a rating of 16A, will reliably protect against network overload at currents from 20.8A (1.3 nominal) and will work in approximately 60 minutes, and in the case of an overload current of 48A (3 nominal) the shutdown will occur from 5 seconds to 20-30 seconds. During this time, the temperature of the insulation of cables, wires, power consumers should not exceed the critical temperature. To do this, sometimes it is required to perform cable calculations for non-flammability at short-circuit currents and to justify
The most common insulating material in the era of "developed socialism" was carbolite. Everyone remembers the black smooth plastic from which almost all electrical devices in the USSR were made? This includes sockets, terminal blocks, automatic machines, and household electrical appliances, electric plugs, etc. So, this material has a heat resistance of up to 150 degrees, which is much better than the characteristics of modern PVC insulation. However, when the temperature reaches above 100 degrees, this material begins to degrade and release hazardous toxic substances.

The appearance of the branch clamp with carbolite sheath

The appearance of the branch clamp on the air line after passing a lightning pulse. Phase shrink just exploded, and in the photo, zero shrink, charred by the thermal impulse of supercurrents (Fig. 1).
Cable insulation temperature should not exceed 70-80 degrees Celsius in any type of network failure. In the case of a short circuit, the insulation heats up rapidly; in the event of an overload, the process is relatively extended in time. So what happened at the village substation while the concrete block hung on the electrical cable?
The melting of PVC insulation of the power cable as a result of line overload and constant attempts to turn on the machine without eliminating the cause of the accident (Fig. 2).

Clickable
At the substation, the machine felt a constant overload on the line through one of the phases as a result of poor insulation. It was heating up, and it turned off due to thermal protection. After some time the guard came, and turned on the machine again. Of course, it is almost always possible to turn on the machine immediately after the operation of the thermal protection is not possible: it just “bounces off” when you try to turn it on. But behind the guard were the builders, who demanded to turn on the line urgently, as the power tool does not work, you can not boil tea and so on and so forth ... The situation repeated throughout the day. Attempts to eliminate phase imbalance did not lead to anything on the line, because after two or three days there was an overload on the other phase ... As you can see, the increased load currents selected the weakest link - the cable coming from the top of the machine (in this case it is a self-supporting insulated wire from aluminum). Insulation floated due to a temperature rise of 100 degrees. And this is at low-plus air temperatures. What would be in this situation on a hot summer day?
Of course, the fire and the failure of the main shield of the substation.
Ask what I am putting it for? Everything is very simple - if your protection has worked, a machine gun has been knocked out, or an RCD, then this is connected with something and for no reason happened. Before you turn on the machine you need to understand the causes of the accident. Especially if the machine at the same time clearly heated. In addition, each machine is designed for a certain number of protection trips, and it is not recommended to turn on the machine for damage to an existing line, this reduces its life.
UZO - devices, first of all, are intended for protection of the person against defeat by electric current. If you do not go deep into the technical details, the device detects a leakage of current from the phase conductor to the ground and turns off the damaged group for up to 30 ms or 0.03 seconds. For protection of the person, the RCD is installed on a leakage current of 30 mA. This figure is due to the safe level of current that can flow through the human body without heart fibrillation, that is, without causing harm to the person.

Residual current device
As you know, the danger to humans is not voltage, but current. For example, you can kill a person with 1 volt voltage, and it is important what current passes through the person, along which path, and in what time. So, the RCD is designed to protect a person when touched to parts under dangerous voltage. This may be the case of household appliances, industrial equipment, any metal parts. As a rule, the RCD disconnects the damaged line in advance, and not at that moment when touched by a person. But there are cases when dangerous potential on the equipment may appear at the moment of the person working with him.
The first safety shut-off device was patented in 1928 by the German company RWE (Rheinisch - Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk AG).
In 1937, the firm Schutzapparategesellschaft Paris & Co. manufactured the first operating device based on a differential transformer and a polarized relay, which had a sensitivity of 0.01 A and a speed of 0.1 s. In the same year, with the help of a volunteer (an employee of the company), an RCD test was conducted. The experiment ended well, the device worked clearly, the volunteer experienced only a weak electric shock, although he refused to participate in further experiments.
At the moment there are RCDs with a leakage current of 300 mA. They are designed to protect against fire and perform the function of additional protection with thermal protection of the machine.
What is the difference between the RCD and the thermal protection available in the circuit breaker? After all, in fact, the overload of the line can be due to leakage of current to the ground.
First , the response time of thermal protection is measured in seconds and hours, RCD - in milliseconds (usually up to 25 ms, or 0.025 seconds).
Secondly , thermal protection is designed to protect equipment, but not to protect people. If there is no RCD in the dashboard when a person touches the equipment case, the network mode will go into a short circuit stage, the current will increase dramatically, the short circuit protection in the machine will work and turn off the line relatively quickly. But this time may be enough for a person to get an electric shock incompatible with life.
Thirdly , UZO is an additional measure of protection and is established, as a rule, for hazardous premises and for household outlets, while automatic machines are the main measure of protection and are used everywhere and always.
Fourthly, the use of RCDs without automatic switches is excluded, but automatic machines without RCDs are quite common.
The question is ambiguous and, as a rule, remains at the discretion of the Customer.
On the one hand, the safety of personnel must prevail over other considerations. Human life is a priority. On the other hand, the equipment of information systems often itself refers to the life support systems of other people, services can “spin” on them, and their work should be uninterrupted. For example, medical institutions, emergency services, emergency services and other life support organizations. And the server rooms themselves are classified, as a rule, as rooms without a permanent stay of people, without permanent jobs.
That is, quite often the information equipment can be attributed to the first category of electrical receivers in terms of power supply reliability ( .1.2.18), along with fire-fighting systems and emergency lighting. For this group, a break in electricity supply is unacceptable , as it can lead to significant material losses and be a threat to the life and health of people. If you examine the current standards more deeply, you can find indications that it is permissible for vital consumers to install protection only against short circuits, without thermal protection.
For example, fire pumps must operate in fire conditions until cable insulation finally burns out and does not happen.
For example, in clause 7.1.81 of the Rules for the Electrical Installations () it is stated: “the installation of a UZO is prohibited for electrical receivers, the disconnection of which can lead to situations dangerous for consumers”.For information equipment today, as a rule, standard automatic switches are used, but RCDs are not used to prevent false alarms and sudden shutdown of important servers and services. There are special types of RCDs that take into account the specifics of switching power supplies of servers and other IT equipment, but they are rarely available, are difficult to select, and lead to an increase in the cost of the project as a whole. For server and data centers, it is assumed that these rooms, as a rule, are equipped with individual gas fire extinguishing systems, and the presence of personnel is minimal in time.
As an additional level of protection for server and data center personnel, it is imperative to organize reliable earthing of metal parts of server racks, pipelines, of any accessible metal parts in the room, including a metal fire door (s). With the proper organization of the Additional Capacity Adjustment System (DPMS) in the server room, the data center will ensure an adequate level of personnel and information equipment safety, despite the absence of RCDs in the power distribution circuits.
For technological needs, several sockets are installed within the server rooms, which are provided with protective disconnect devices. To these sockets (and only to them) any portable power tool and / or equipment that is not related to the direct goals of our server should be connected.
Continued in the second part of the article , where we understand the question of network interference can lead to a fall in operating systems? why not all UPS, AVR and ATS are good? and go through the chain of the grid-server rack-power supply-electronics IT equipment-operating system
Author: Oleg Kulikov
Leading Design Engineer
Department of Integrated Solutions "Open Technologies"
okulikov@ot.ru
Registration in the National Register of Specialists "NOPRIZ" P-045870
Part one
Autumn, the rain gushes almost continuously. There is a rapid construction of a cottage settlement near Moscow. The commandant of the village, bypassing the territory under his control, sees the glaring fact of “abuse” of the temporary air line 380V.

Unable to contain emotions, he turns to the brigadier of the local construction brigade:
')
- Vadim, are you in your mind? Are your hard workers suicide? What is this curb block hanging on an electrical cable?
- Kohl, if you remove it, then around the corner of the house will not pass the excavator!
Behind Vadim, you can see a road worker, who found a bare wire in the dirt that goes somewhere in the bowels of the earth, and happily runs after a colleague, “scaring” him with electricity.
In the meantime, at the substation of the village, the tired guards, burning, for the tenth time, try to turn on a terribly hot automatic switch, which for some reason knocks out every half hour.
Why does a circuit breaker knock out and what other protection options are there for electrical equipment? What to look at first when planning electrical safety in servers and other IT equipment? In order to understand these issues we read both parts of the article in more detail.
Since the regulations provide for a whole range of measures to protect power grids from certain accidents, we will focus on the most common household and industrial sector.

What do we want and can protect against in the first place?
Of course, from electric shock. Secondarily, protect equipment and cables from damage by short-circuit currents, as well as from fire and fire.

A circuit breaker (circuit breaker) is the most common means of protecting electrical networks. Of course, there are also fuses (fuses), but they are used much less due to their “disposability” and a number of technical differences compared to the automatic.

And bigger? photo is clickable
"Automatic section"
In the classic case, the circuit breaker protects:
1. short circuit
Short circuit (short-circuit) is when the phase of the insulation closes to zero or to ground when the insulation is damaged, from which the current in the circuit increases sharply (5-15 times) and turns off the machine in no more than 0.4 seconds (for a group network according to the rules electrical installation devices). If our automaton is faulty or the network operation modes do not ensure its reliable operation, then the equipment connected to this group, which itself may be a source of short circuit, suffers first. CZ also has negative effects on wires and cables. As a rule, in cases of failure of the automaton in the switchboard, local heating of the short circuit site occurs, an arc appears and the conductive parts are burned off with a firework of molten copper microparticles. And this development of events seems quite favorable, since in this case the accident stops by itself. In some cases, “welding” of current-carrying parts occurs at the short circuit site, and a so-called “metallic” short circuit is formed, which is much more dangerous, since it does not stop by itself, and must be turned off automatically. After that, the specialist must find the place of damage and only then try to turn on the device. But the defense may not work for various reasons, then (God forbid) it can happen
fire of the New Year tree, just a few seconds and oxygen remains only at the very floor
In addition, modern automata perform the function of current limiting in case of an accident, that is, they do not allow currents in the circuit to reach dangerous values.
A little more about current limiting
With the increase in the power of networks in the global sense, single-phase short-circuit currents can reach large values, up to tens of thousands of Amperes, especially if our consumer, equipment or outlet is installed close enough to the substation. And in such modes there is the concept of "electrodynamic action of short-circuit currents". Again a difficult term, you will say. And no. In plain language, this term can be explained as attempts of copper busbars in shields, cables and other stuffing to move from the place under the action of large currents, to bend, especially if the installers simply threw the cables into the tray and fixed it as necessary: with improvised means, remnants of wire, etc. . And in this situation, the development of an accident can be even more deplorable - interfacial short circuit, destruction of equipment and so on ... Thus, a properly selected machine is the key to proper operation of the equipment, and if it is knocked out for some reason, then you should not try to turn it on. while resenting that he instantly turns off again.
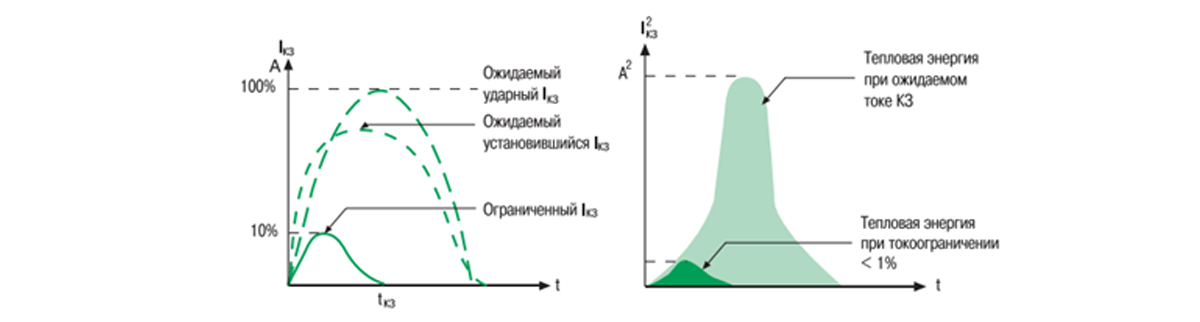
Schedule of current limitation and reduction of thermal energy
What does current limiting mean and how dangerous are high short circuit currents?
With the increase in the power of networks in the global sense, single-phase short-circuit currents can reach large values, up to tens of thousands of Amperes, especially if our consumer, equipment or outlet is installed close enough to the substation. And in such modes there is the concept of "electrodynamic action of short-circuit currents". Again a difficult term, you will say. And no. In plain language, this term can be explained as attempts of copper busbars in shields, cables and other stuffing to move from the place under the action of large currents, to bend, especially if the installers simply threw the cables into the tray and fixed it as necessary: with improvised means, remnants of wire, etc. . And in this situation, the development of an accident can be even more deplorable - interfacial short circuit, destruction of equipment and so on ... Thus, a properly selected machine is the key to proper operation of the equipment, and if it is knocked out for some reason, then you should not try to turn it on. while resenting that he instantly turns off again.

Schedule of current limitation and reduction of thermal energy
2. From network overload
Network overload is when insulation damage (or an increased load on the network) causes a prolonged increase in the currents in the circuit beyond the calculated parameters (by 110-300% or 110-500%), which leads to the automatic disconnection from a few minutes to an hour and a half depending on the situation and the type of machine. In this case, protection against overheating, destruction of insulation and fire of elements of the group circuit is provided. That is, the machine must heat up and disconnect before the critical heating of wires, cables, contacts, sockets, switches occurs. For example, the most common automaton of characteristic C, and with a rating of 16A, will reliably protect against network overload at currents from 20.8A (1.3 nominal) and will work in approximately 60 minutes, and in the case of an overload current of 48A (3 nominal) the shutdown will occur from 5 seconds to 20-30 seconds. During this time, the temperature of the insulation of cables, wires, power consumers should not exceed the critical temperature. To do this, sometimes it is required to perform cable calculations for non-flammability at short-circuit currents and to justify
suitability for further use
... to further exploitation. This topic relates more to high-voltage cables, however, sometimes the Customer, using RAO UES circulars and departmental standards, also requires calculations for 0.4 kV cables (and small sections!) In two ways: checking that the cable is not flammable in short-circuit mode and checking the cable suitability further operation in the postemergency mode. In the latter case, this means to check the fact of the "survivability" of the insulation after the passage of a short circuit current, the fact that the insulation did not have time to heat up to the degradation temperatures of the insulation materials.


The most common insulating material in the era of "developed socialism" was carbolite. Everyone remembers the black smooth plastic from which almost all electrical devices in the USSR were made? This includes sockets, terminal blocks, automatic machines, and household electrical appliances, electric plugs, etc. So, this material has a heat resistance of up to 150 degrees, which is much better than the characteristics of modern PVC insulation. However, when the temperature reaches above 100 degrees, this material begins to degrade and release hazardous toxic substances.

The appearance of the branch clamp with carbolite sheath

The appearance of the branch clamp on the air line after passing a lightning pulse. Phase shrink just exploded, and in the photo, zero shrink, charred by the thermal impulse of supercurrents (Fig. 1).
Cable insulation temperature should not exceed 70-80 degrees Celsius in any type of network failure. In the case of a short circuit, the insulation heats up rapidly; in the event of an overload, the process is relatively extended in time. So what happened at the village substation while the concrete block hung on the electrical cable?
The melting of PVC insulation of the power cable as a result of line overload and constant attempts to turn on the machine without eliminating the cause of the accident (Fig. 2).

Clickable
At the substation, the machine felt a constant overload on the line through one of the phases as a result of poor insulation. It was heating up, and it turned off due to thermal protection. After some time the guard came, and turned on the machine again. Of course, it is almost always possible to turn on the machine immediately after the operation of the thermal protection is not possible: it just “bounces off” when you try to turn it on. But behind the guard were the builders, who demanded to turn on the line urgently, as the power tool does not work, you can not boil tea and so on and so forth ... The situation repeated throughout the day. Attempts to eliminate phase imbalance did not lead to anything on the line, because after two or three days there was an overload on the other phase ... As you can see, the increased load currents selected the weakest link - the cable coming from the top of the machine (in this case it is a self-supporting insulated wire from aluminum). Insulation floated due to a temperature rise of 100 degrees. And this is at low-plus air temperatures. What would be in this situation on a hot summer day?
Of course, the fire and the failure of the main shield of the substation.
Ask what I am putting it for? Everything is very simple - if your protection has worked, a machine gun has been knocked out, or an RCD, then this is connected with something and for no reason happened. Before you turn on the machine you need to understand the causes of the accident. Especially if the machine at the same time clearly heated. In addition, each machine is designed for a certain number of protection trips, and it is not recommended to turn on the machine for damage to an existing line, this reduces its life.
Now consider the RCD
UZO - devices, first of all, are intended for protection of the person against defeat by electric current. If you do not go deep into the technical details, the device detects a leakage of current from the phase conductor to the ground and turns off the damaged group for up to 30 ms or 0.03 seconds. For protection of the person, the RCD is installed on a leakage current of 30 mA. This figure is due to the safe level of current that can flow through the human body without heart fibrillation, that is, without causing harm to the person.

Residual current device
As you know, the danger to humans is not voltage, but current. For example, you can kill a person with 1 volt voltage, and it is important what current passes through the person, along which path, and in what time. So, the RCD is designed to protect a person when touched to parts under dangerous voltage. This may be the case of household appliances, industrial equipment, any metal parts. As a rule, the RCD disconnects the damaged line in advance, and not at that moment when touched by a person. But there are cases when dangerous potential on the equipment may appear at the moment of the person working with him.
History reference:
The first safety shut-off device was patented in 1928 by the German company RWE (Rheinisch - Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk AG).
In 1937, the firm Schutzapparategesellschaft Paris & Co. manufactured the first operating device based on a differential transformer and a polarized relay, which had a sensitivity of 0.01 A and a speed of 0.1 s. In the same year, with the help of a volunteer (an employee of the company), an RCD test was conducted. The experiment ended well, the device worked clearly, the volunteer experienced only a weak electric shock, although he refused to participate in further experiments.
At the moment there are RCDs with a leakage current of 300 mA. They are designed to protect against fire and perform the function of additional protection with thermal protection of the machine.
What is the difference between the RCD and the thermal protection available in the circuit breaker? After all, in fact, the overload of the line can be due to leakage of current to the ground.
First , the response time of thermal protection is measured in seconds and hours, RCD - in milliseconds (usually up to 25 ms, or 0.025 seconds).
Secondly , thermal protection is designed to protect equipment, but not to protect people. If there is no RCD in the dashboard when a person touches the equipment case, the network mode will go into a short circuit stage, the current will increase dramatically, the short circuit protection in the machine will work and turn off the line relatively quickly. But this time may be enough for a person to get an electric shock incompatible with life.
Thirdly , UZO is an additional measure of protection and is established, as a rule, for hazardous premises and for household outlets, while automatic machines are the main measure of protection and are used everywhere and always.
Fourthly, the use of RCDs without automatic switches is excluded, but automatic machines without RCDs are quite common.
Why should the RCD application be paired with a gun?
Since the main protection is provided by a circuit breaker, it also protects the residual current device. For correct operation of the circuit, the nominal value of the contacts of the RCD is selected one step higher than that of the automaton. For example, the machine is set to 16A, and the RCD is set to 25A. In this case, the RCD will safely pass through a short-circuit current to the machine, which will provide protection. For its part, the RCD will provide additional protection for a person in case of leakage to the body (ground). There are combined devices "automatic + UZO" in a single package, the so-called difavtomaty. I will not consider them, anyone can study the Wiki question about the UZO , the wiki about difavtomats (or AVDT) . Let me just say that difavtomaty save space in the shield, as they occupy less modules on DIN-rail.
In the industrial sector, RCDs are typically used in denominations of 100 and 300 milliamperes as a means of protection against fire on the lines of street lamps, street equipment, etc.
In the industrial sector, RCDs are typically used in denominations of 100 and 300 milliamperes as a means of protection against fire on the lines of street lamps, street equipment, etc.
Do RCDs for IT equipment, server, data center?
The question is ambiguous and, as a rule, remains at the discretion of the Customer.
On the one hand, the safety of personnel must prevail over other considerations. Human life is a priority. On the other hand, the equipment of information systems often itself refers to the life support systems of other people, services can “spin” on them, and their work should be uninterrupted. For example, medical institutions, emergency services, emergency services and other life support organizations. And the server rooms themselves are classified, as a rule, as rooms without a permanent stay of people, without permanent jobs.
That is, quite often the information equipment can be attributed to the first category of electrical receivers in terms of power supply reliability ( .1.2.18), along with fire-fighting systems and emergency lighting. For this group, a break in electricity supply is unacceptable , as it can lead to significant material losses and be a threat to the life and health of people. If you examine the current standards more deeply, you can find indications that it is permissible for vital consumers to install protection only against short circuits, without thermal protection.
For example, fire pumps must operate in fire conditions until cable insulation finally burns out and does not happen.
metal short circuit
A metallic, or deaf short circuit is the welding of conductors (for example, phase and zero) at the point of insulation breakdown. A closed short circuit is formed, and in this case, the operation of the protection apparatus must be ensured. In most cases, a dead short circuit does not occur, but the probability of it exists. For fire-fighting systems, in particular fire extinguishing systems, the basic idea set forth in the regulations, in the case of emergency situations, fire-prevention systems must work in spite of everything and ensure the safety of people even in case of damage to the cable insulation. The operating time of fire protection systems is determined by the time required to evacuate people and personnel.
To power the responsible electrical receivers, they use fire-resistant cables with the FRLS brand, which have the properties to withstand the heat of the insulation without ignition and reflow. As part of the insulation of such cables, mica is used, which gives extra time for normal line operation without short circuits in fire conditions.
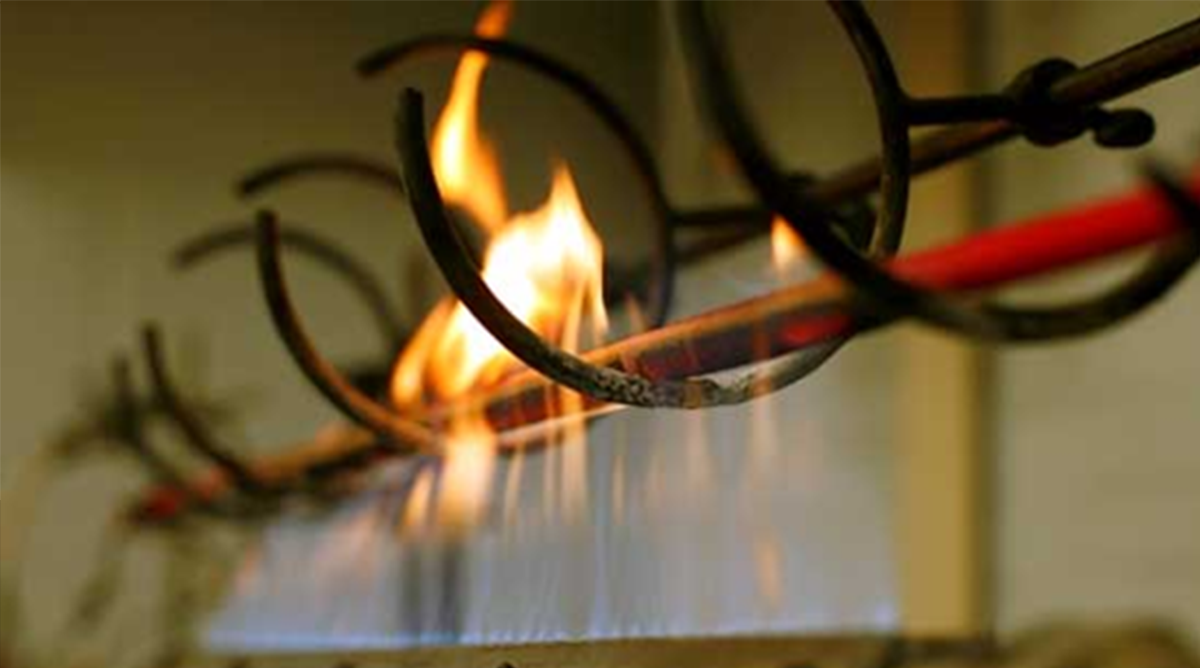

Tests of fire-resistant cables of the Spetskabel plant for fire alarm systems
To power the responsible electrical receivers, they use fire-resistant cables with the FRLS brand, which have the properties to withstand the heat of the insulation without ignition and reflow. As part of the insulation of such cables, mica is used, which gives extra time for normal line operation without short circuits in fire conditions.

Tests of fire-resistant cables of the Spetskabel plant for fire alarm systems
For example, in clause 7.1.81 of the Rules for the Electrical Installations () it is stated: “the installation of a UZO is prohibited for electrical receivers, the disconnection of which can lead to situations dangerous for consumers”.For information equipment today, as a rule, standard automatic switches are used, but RCDs are not used to prevent false alarms and sudden shutdown of important servers and services. There are special types of RCDs that take into account the specifics of switching power supplies of servers and other IT equipment, but they are rarely available, are difficult to select, and lead to an increase in the cost of the project as a whole. For server and data centers, it is assumed that these rooms, as a rule, are equipped with individual gas fire extinguishing systems, and the presence of personnel is minimal in time.
As an additional level of protection for server and data center personnel, it is imperative to organize reliable earthing of metal parts of server racks, pipelines, of any accessible metal parts in the room, including a metal fire door (s). With the proper organization of the Additional Capacity Adjustment System (DPMS) in the server room, the data center will ensure an adequate level of personnel and information equipment safety, despite the absence of RCDs in the power distribution circuits.
For technological needs, several sockets are installed within the server rooms, which are provided with protective disconnect devices. To these sockets (and only to them) any portable power tool and / or equipment that is not related to the direct goals of our server should be connected.
Continued in the second part of the article , where we understand the question of network interference can lead to a fall in operating systems? why not all UPS, AVR and ATS are good? and go through the chain of the grid-server rack-power supply-electronics IT equipment-operating system
Author: Oleg Kulikov
Leading Design Engineer
Department of Integrated Solutions "Open Technologies"
okulikov@ot.ru
Registration in the National Register of Specialists "NOPRIZ" P-045870
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/422459/
All Articles