Hackers: Russia and China
According to Kaspersky Lab , in the world of cybercrime, three of the largest “mafias” are leading now: Chinese, Russian (Russian-speaking) and Latin American. A distinctive feature of the “Russian hackers” has always been the invention of new technologies, specialization in creating networks of infected computers, major thefts of money from banks and their clients, spamming and DDoS attacks. Chinese cybercriminals focused on attacks against users of online games, data theft and intellectual property, experts say. But if the topic of “Russian hackers” has long been the order of the world media, then their Chinese counterparts are written less frequently.

Many countries are actively attracting highly qualified specialists in the field of information security, and a lot of news is also devoted to this every day: from the operations of the “hacker army” of China to the attacks of the “Russian cyber-saboteurs” on the power system of Ukraine. What is it: fake or new reality? Hackers of which country - Russia or China - are more dangerous, more numerous, use the most sophisticated attack methods?
In the Western press, it is often possible to find references to the activities of Russian pro-government hacker groups, which are said to lead large-scale economic and political espionage. The activities of such groups, according to Western experts, are planned as a single center, but Russian hackers, unlike their Chinese counterparts, work very carefully.
')
After Russia's alleged attempts to influence the US presidential election in 2016, hacker activity at the state level became a particularly “hot” topic, although in this particular case of email leakage, it seemed to be based on simple password phishing. According to the CIA, hackers from Russia (Fancy Bears group) were involved in hacking into the systems of the US Democratic Party, as a result of which correspondence by the head of the election headquarters Hillary Clinton got into the network.
Interestingly, this story continues. So, recently in the Microsoft company declared that hackers tried to attack three candidates in congressmen. The cybercriminals allegedly wanted to take possession of their personal data using a fake webpage that looked like a copy of the Microsoft website. The company stressed that a similar method was used when intervening in the US presidential election in 2016.
Chinese hackers pursue more than political, but purely economic goals. According to foreign media reports , they have been engaged in hacking security systems of American (and other) companies for more than a dozen years. A number of computer security experts believe that China today can thus obtain any intellectual property it needs. They also believe that the tight control of the Chinese government over the Chinese segment of the Internet gives reason to believe that Chinese hackers are breaking into networks in the United States either by direct order or by tacit consent of the authorities. However, there has been a decline in China’s hacker activity against the United States after President Obama and the Chinese leaders signed an agreement to combat hacking . Observers record a decrease in the number of “Chinese invasions”, in particular, APT (advanced persistent threat) attacks.
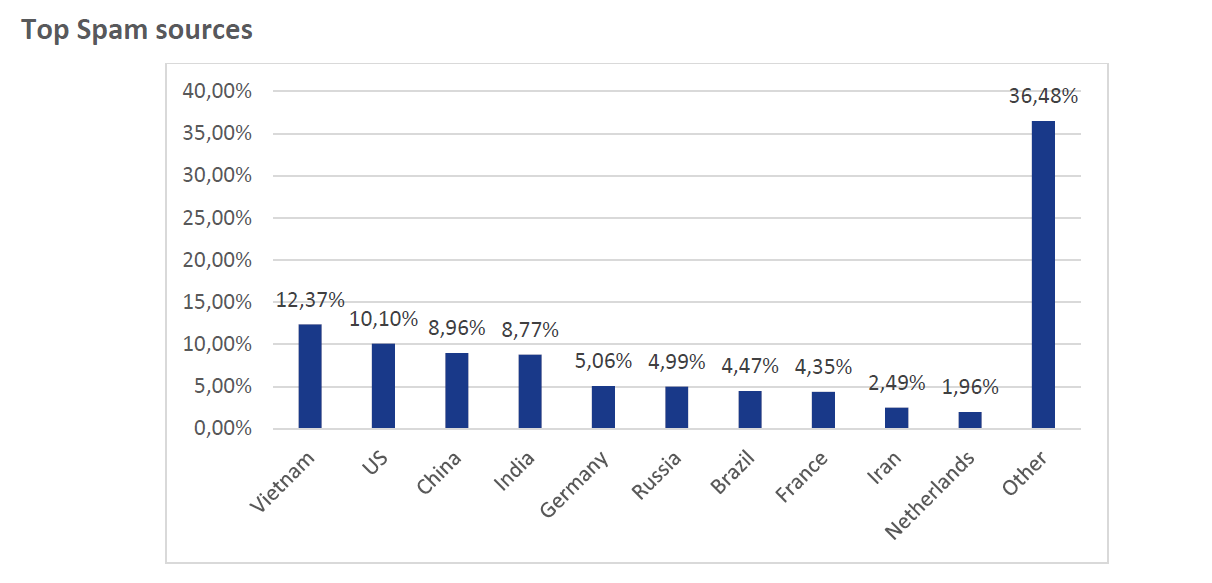
"Top Ten" countries - the source of spam (according to the report " ENISA Threat Landscape Report 2017 "). China is ahead of Russia, ranking third in the world. According to other data, China, India, and Russia are leading in the distribution of botnets.
Whose hackers cause the most damage to US companies? Experts still give the palm to cyber criminals from China. If by “damage” we understand the frequency of attacks and the severity of their consequences, then they occupy the first place. Experts believe that tens of thousands of Chinese hackers, funded by the government of China, can overcome the protection of any company and suggest that they have stolen more secrets and intellectual property than the cybercriminals of any other country.
Each such case can cause considerable damage. For example, when a Chinese company releases a new product faster than a US manufacturer that developed it. Thus, the "specialization" of Chinese hackers is the theft of information at the state and corporate levels.
“Russian hackers”, in addition to sabotage on a national scale, are credited with financial crimes. Moreover, if you leave politics aside, the main goal of Russian hackers is not the theft of someone else's intellectual property, but just a direct financial gain. Vladimir Levin, Vasily Gorshkov, Peter Levashov and Alexey Ivanov - these famous Russian hackers of the last decade pursued purely financial, and by no means political goals. They are credited with damage in the hundreds of millions of dollars - and this is only in the United States.
Actually, Russian hackers gained prestige at the international level after they robbed Bank of America in 1998, for a total of $ 30 million. Now the scale has become smaller: some do trade in personal user data . They are far from the Chinese in this regard, because intellectual property is very expensive.
As for the political benefits due to Russia's notorious influence on the American elections, even some American experts view this scenario as very doubtful .
"Top Ten" countries - sources of cyber attacks (according to the report " ENISA Threat Landscape Report 2017 ", II quarter 2017 ). China - in second place, Russia - only in the seventh.
In the case of the PRC, the US government has formulated its opinion on an important cyber norm: no commercial espionage should be allowed. Governments need to protect equal trade conditions, even if espionage is used tacitly for national security purposes. The United States has stated a firm position in negotiations with the Chinese. China and the United States eventually agreed that neither side would "consciously support or engage in the theft of intellectual property."
After Chinese hackers allegedly stole 21.5 million US citizens in 2015, Beijing offered to sign an agreement on joint struggle with hackers, which was signed by Barack Obama and Xi Jinping.
In the case of Russian hackers all the more difficult. Firstly, the problem of interference in the US presidential election in 2016 is socially more significant than the embezzlement of intellectual property by Chinese hackers. Russia's alleged intervention involves a number of vital national security interests, which implies a tough response from the United States.
Who is "cooler"? It is hardly possible to give a clear answer to this question. The best hackers are those that we do not see or know. They remain in the shadows. In addition, to hack the majority of organizations do not require sophisticated methods. “Elite” hacker groups usually do not use their best arsenal if they really don’t need it. Why hack "wisely" and reveal their tricks, if sometimes a simple amateur script is enough?
For example, no need to go far. In June, hackers who, according to media reports, worked for the government of the People's Republic of China, broke into the computer network of the US Navy contractor and stole classified information of more than 614 GB, which was stored by the contractor on an unprotected server.
In 2014, the British company MWR InfoSecurity interviewed participants of the international conference on cyber security: 34% named the most powerful hackers of Russians, 18% - Chinese. 14% of respondents noted the best technical education of Russians, 17% named political motivation, and 31% - a combination of three factors: good education, political motivation and financial support.
The basis for spreading rumors about “Russian hackers” was laid by the successes of Russian programmers, who have been in demand in the West since the late 1990s.
Modern cyber war often controlled by governments, and many countries, according to experts, resort to the services of hacker groups. Perhaps the most famous was the “pro-Kremlin” hacker group Fancy Bear, which is credited with hacking into the servers of the World Anti-Doping Committee, the US Democratic Party and the OSCE. Fancy Bear appeared in 2007. It was then that they began to talk about the connections of Russian hackers with the special services. It is believed that behind it stands the Central Intelligence Agency of the Russian Federation.
In China, there are about two dozen high-class hacker groups. And some of them represent the interests of the army and the government of the PRC. One of the hacker groups sponsored by the government of China, called the organization Axiom. She specializes in corporate espionage and exposure of political dissidents.
Here are just some well-known hacker groups in Russia and the PRC:
Loud investigations and detentions of the so-called “Russian hackers” do not always concern the scammers from Russia. Residents of the countries of the former USSR and even socialist camps can play this role.
It is difficult to say who is more afraid of the US - Russian (“Russian”) hackers or Chinese. There are no less stories with Chinese hackers, they just rarely write about them in the media. One example: according to the American magazine Foreign Policy, the US attorney’s office uncovered a group of hackers associated with the Chinese state and charged the suspect. In the United States, “emanating a cyber threat from Russia and China” is rated at 8 points out of 10. “Russia, China, Iran and North Korea will represent the greatest cyber threat to the United States during 2018,” according to US intelligence reports.
However, the situations with China and with Russia are fundamentally different: if the PRC is the largest trading partner of the United States, then with Russia, this country has much weaker business ties. Therefore, the hype around the "Russian hackers" is much more, but with the Chinese everything is much more complicated. Sometimes making noise is simply not profitable. And this is one of the reasons why, according to one of the latest public opinion polls, Americans consider Russia to be the main threat to US security . In this, she bypassed China, Iran, the DPRK and even Islamic terrorists.
In May 2018, the US Armed Forces cyber command was even transferred to combat status : the US military could carry out hacker attacks on the computer networks of other countries on a daily basis in order to “disable cyber weapon before it is used”. At the same time, the largest British companies and state institutions received recommendations from the special services to take measures for enhanced protection against possible cyber attacks from Russia.
Since the last elections, government services and US companies have taken measures that complicate the work of hackers. For example, Microsoft has created a program to protect democracy, in which it trains election campaign workers to expose and repel the attacks of “Russian hackers”.
However, the “Chinese threat” from the USA is not forgotten. Thus, according to the leadership of the National Intelligence Agency, representatives of the PRC should be restricted to access to the American infrastructure: "We will not allow our technologies to be stolen."
As can be seen from the table below, where are collected the most famous incidents related to Russian hackers of the last couple of years, the information of which was published in the Western media, news about the “Russian hackers” is published in the Western media almost monthly. Of course, not all of them are true, but such attention to the topic is very significant.
Cyber criminals in both countries sometimes use similar methods. Thus, according to British experts, Russia and China use a cognitive approach based on an understanding of mass psychology and methods of influencing individuals.
Information about Chinese hackers appears less frequently, but this does not mean a smaller number of incidents:
Beijing, like Moscow, is regularly accused of organizing hacker attacks on Western countries. Hackers from Russia and the PRC are among the “ordinary suspects” who are blamed by the US authorities for penetrating the computer networks of government agencies and private firms. But some believe that "the Chinese are more productive ." “They wake up in the morning, put on their uniforms and go to work in the office. Russian hackers are more connected with organized crime. ”
According to Kaspersky Lab , the number of professional hacker groups has increased dramatically in the world. If two or three years ago there were only a few such organizations, today there are more than 100 of them. At the same time, the hackers of China have become more active. They are credited with up to 25% of active hacker companies. And if earlier they attacked mainly the USA, then after the meeting of the American president with the head of China they switched to other countries, including organizations from Russia. The most frequently attacked by international hackers are the United States, Germany, Russia. Hackers hack into the system of financial institutions, ministries, departments, government organizations.
The flip side of the coin is a stream of fake news about alleged hacker attacks. Many of them are related to the accusations of China in cyber espionage, the leakage of US industrial secrets. Similar accusations are being made against Russia. And here Russia and China have work to do.


Many countries are actively attracting highly qualified specialists in the field of information security, and a lot of news is also devoted to this every day: from the operations of the “hacker army” of China to the attacks of the “Russian cyber-saboteurs” on the power system of Ukraine. What is it: fake or new reality? Hackers of which country - Russia or China - are more dangerous, more numerous, use the most sophisticated attack methods?
Cyber warfare: politics and economics
In the Western press, it is often possible to find references to the activities of Russian pro-government hacker groups, which are said to lead large-scale economic and political espionage. The activities of such groups, according to Western experts, are planned as a single center, but Russian hackers, unlike their Chinese counterparts, work very carefully.
')
After Russia's alleged attempts to influence the US presidential election in 2016, hacker activity at the state level became a particularly “hot” topic, although in this particular case of email leakage, it seemed to be based on simple password phishing. According to the CIA, hackers from Russia (Fancy Bears group) were involved in hacking into the systems of the US Democratic Party, as a result of which correspondence by the head of the election headquarters Hillary Clinton got into the network.
Interestingly, this story continues. So, recently in the Microsoft company declared that hackers tried to attack three candidates in congressmen. The cybercriminals allegedly wanted to take possession of their personal data using a fake webpage that looked like a copy of the Microsoft website. The company stressed that a similar method was used when intervening in the US presidential election in 2016.
Chinese hackers pursue more than political, but purely economic goals. According to foreign media reports , they have been engaged in hacking security systems of American (and other) companies for more than a dozen years. A number of computer security experts believe that China today can thus obtain any intellectual property it needs. They also believe that the tight control of the Chinese government over the Chinese segment of the Internet gives reason to believe that Chinese hackers are breaking into networks in the United States either by direct order or by tacit consent of the authorities. However, there has been a decline in China’s hacker activity against the United States after President Obama and the Chinese leaders signed an agreement to combat hacking . Observers record a decrease in the number of “Chinese invasions”, in particular, APT (advanced persistent threat) attacks.

"Top Ten" countries - the source of spam (according to the report " ENISA Threat Landscape Report 2017 "). China is ahead of Russia, ranking third in the world. According to other data, China, India, and Russia are leading in the distribution of botnets.
Whose hackers cause the most damage to US companies? Experts still give the palm to cyber criminals from China. If by “damage” we understand the frequency of attacks and the severity of their consequences, then they occupy the first place. Experts believe that tens of thousands of Chinese hackers, funded by the government of China, can overcome the protection of any company and suggest that they have stolen more secrets and intellectual property than the cybercriminals of any other country.
Each such case can cause considerable damage. For example, when a Chinese company releases a new product faster than a US manufacturer that developed it. Thus, the "specialization" of Chinese hackers is the theft of information at the state and corporate levels.
“Russian hackers”, in addition to sabotage on a national scale, are credited with financial crimes. Moreover, if you leave politics aside, the main goal of Russian hackers is not the theft of someone else's intellectual property, but just a direct financial gain. Vladimir Levin, Vasily Gorshkov, Peter Levashov and Alexey Ivanov - these famous Russian hackers of the last decade pursued purely financial, and by no means political goals. They are credited with damage in the hundreds of millions of dollars - and this is only in the United States.
Actually, Russian hackers gained prestige at the international level after they robbed Bank of America in 1998, for a total of $ 30 million. Now the scale has become smaller: some do trade in personal user data . They are far from the Chinese in this regard, because intellectual property is very expensive.
As for the political benefits due to Russia's notorious influence on the American elections, even some American experts view this scenario as very doubtful .

"Top Ten" countries - sources of cyber attacks (according to the report " ENISA Threat Landscape Report 2017 ", II quarter 2017 ). China - in second place, Russia - only in the seventh.
In the case of the PRC, the US government has formulated its opinion on an important cyber norm: no commercial espionage should be allowed. Governments need to protect equal trade conditions, even if espionage is used tacitly for national security purposes. The United States has stated a firm position in negotiations with the Chinese. China and the United States eventually agreed that neither side would "consciously support or engage in the theft of intellectual property."
After Chinese hackers allegedly stole 21.5 million US citizens in 2015, Beijing offered to sign an agreement on joint struggle with hackers, which was signed by Barack Obama and Xi Jinping.
In the case of Russian hackers all the more difficult. Firstly, the problem of interference in the US presidential election in 2016 is socially more significant than the embezzlement of intellectual property by Chinese hackers. Russia's alleged intervention involves a number of vital national security interests, which implies a tough response from the United States.
Who is stronger?
Who is "cooler"? It is hardly possible to give a clear answer to this question. The best hackers are those that we do not see or know. They remain in the shadows. In addition, to hack the majority of organizations do not require sophisticated methods. “Elite” hacker groups usually do not use their best arsenal if they really don’t need it. Why hack "wisely" and reveal their tricks, if sometimes a simple amateur script is enough?
For example, no need to go far. In June, hackers who, according to media reports, worked for the government of the People's Republic of China, broke into the computer network of the US Navy contractor and stole classified information of more than 614 GB, which was stored by the contractor on an unprotected server.
In 2014, the British company MWR InfoSecurity interviewed participants of the international conference on cyber security: 34% named the most powerful hackers of Russians, 18% - Chinese. 14% of respondents noted the best technical education of Russians, 17% named political motivation, and 31% - a combination of three factors: good education, political motivation and financial support.
The basis for spreading rumors about “Russian hackers” was laid by the successes of Russian programmers, who have been in demand in the West since the late 1990s.
Hacker groups in Russia and China
Modern cyber war often controlled by governments, and many countries, according to experts, resort to the services of hacker groups. Perhaps the most famous was the “pro-Kremlin” hacker group Fancy Bear, which is credited with hacking into the servers of the World Anti-Doping Committee, the US Democratic Party and the OSCE. Fancy Bear appeared in 2007. It was then that they began to talk about the connections of Russian hackers with the special services. It is believed that behind it stands the Central Intelligence Agency of the Russian Federation.
In China, there are about two dozen high-class hacker groups. And some of them represent the interests of the army and the government of the PRC. One of the hacker groups sponsored by the government of China, called the organization Axiom. She specializes in corporate espionage and exposure of political dissidents.
Here are just some well-known hacker groups in Russia and the PRC:
| APT28387 (also known as Fancy Bear, Pawn Storm, Sofacy Group, Sednit and Strontium) | The hacker group, according to foreign media, is probably sponsored by the Russian government. |
| APT29388 | Is a Russian group of hackers, which is believed to be associated with Russian intelligence. In 2017, this group was found to target several government agencies from Norway and the Netherlands. |
| APT17389 | A group of hackers from China, which conducted network attacks against US government, defense industry, law firms, IT companies, mining companies and non-governmental organizations. The researchers attributed to her also an attack using the application CCCleaner. |
| Hacker CyberCaliphate and CyberBerkut Communities | According to the Pentagon, they are associated with the Russian military. |
| Russian hacker group "Humpty Dumpty" | Specialized in the interception of correspondence and hacking accounts of Russian officials and businessmen, and then selling their data via the Internet. |
| Group Thrip (PRC) | Formed in 2013. Attacked satellite companies, as well as a number of US telecommunications enterprises and defense contractors. |
| Apt3 | Active since 2010. The group is often mentioned in reports of various cybersecurity companies, such as UPS, Gothic Panda and TG-011, and is associated with the theft of private business intellectual property and cyber espionage. Published data that link the "contractor" of the Chinese intelligence Boyusec with cyber attacks, which were committed by the group APT3. According to the Intrusion Truth and Recorded Future , Boyusec is just one of many cybersecurity contractors that the Chinese government uses to support its cyber-intelligence operations. Sources claim that Boyusec reports to the Information Technology Security Assessment Center in Guangdong (or ITSEC in Guangdong Province), which is the local office of the China Information Technology Assessment Center (CNITSEC), an organization operated by the Ministry of State Security of China (MSS). |
Loud investigations and detentions of the so-called “Russian hackers” do not always concern the scammers from Russia. Residents of the countries of the former USSR and even socialist camps can play this role.
Who is worse?
It is difficult to say who is more afraid of the US - Russian (“Russian”) hackers or Chinese. There are no less stories with Chinese hackers, they just rarely write about them in the media. One example: according to the American magazine Foreign Policy, the US attorney’s office uncovered a group of hackers associated with the Chinese state and charged the suspect. In the United States, “emanating a cyber threat from Russia and China” is rated at 8 points out of 10. “Russia, China, Iran and North Korea will represent the greatest cyber threat to the United States during 2018,” according to US intelligence reports.
However, the situations with China and with Russia are fundamentally different: if the PRC is the largest trading partner of the United States, then with Russia, this country has much weaker business ties. Therefore, the hype around the "Russian hackers" is much more, but with the Chinese everything is much more complicated. Sometimes making noise is simply not profitable. And this is one of the reasons why, according to one of the latest public opinion polls, Americans consider Russia to be the main threat to US security . In this, she bypassed China, Iran, the DPRK and even Islamic terrorists.
In May 2018, the US Armed Forces cyber command was even transferred to combat status : the US military could carry out hacker attacks on the computer networks of other countries on a daily basis in order to “disable cyber weapon before it is used”. At the same time, the largest British companies and state institutions received recommendations from the special services to take measures for enhanced protection against possible cyber attacks from Russia.
Since the last elections, government services and US companies have taken measures that complicate the work of hackers. For example, Microsoft has created a program to protect democracy, in which it trains election campaign workers to expose and repel the attacks of “Russian hackers”.
However, the “Chinese threat” from the USA is not forgotten. Thus, according to the leadership of the National Intelligence Agency, representatives of the PRC should be restricted to access to the American infrastructure: "We will not allow our technologies to be stolen."
Who is more famous?
As can be seen from the table below, where are collected the most famous incidents related to Russian hackers of the last couple of years, the information of which was published in the Western media, news about the “Russian hackers” is published in the Western media almost monthly. Of course, not all of them are true, but such attention to the topic is very significant.
| date | The essence of the attack |
|---|---|
| July 2018 | The hacker grouping Dragonfly (or Energetic Bear) has managed to crack the networks of electric companies in the United States that were considered to be secure, according to the Department of Homeland Security. According to the department, it is associated with the Russian authorities. |
| June 2018 | Created by Fancy Bear hackers, the virus has infected routers and network devices around the world. Malicious software can block Internet traffic and collect information passing through routers. In addition, the program can completely disable infected devices. |
| June 2018 | Russian and Chinese hackers attacked a number of South Korean facilities on the eve of the US-DPRK summit. The attacks are attributed to Chinese hackers from the TempTick group, which a month earlier introduced malicious code in Microsoft Word, and the Russian group Turla, which attacked a number of governments in April of this year using JavaScript. |
| December 2017 | The hacker group APT28, also known as Fancy Bear, attacked the German Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Ministry of Defense. Hackers stole valuable data. |
| February 2017 | By the opening of the Games, more than 300 computers at the Olympics in Pyeongchang were under the control of “Russian military hackers,” according to US intelligence agencies. The attack was organized with the aim of revenge for the decision of the IOC. |
| August 2017 | The APT28 hacker group attempted to steal data from Western officials and businessmen as they traveled around Europe. |
| November 2017 | The Spanish government announced the intervention of "Russian hackers" in the Catalan crisis. |
| November 2017 | Former Yahoo CEO Marissa Mayer accused Russian hackers of stealing 3 billion user accounts in 2013. |
| October 2017 | A group of hackers known as Dragonfly, Energetic Bear or Berserk Bear gained access to the systems of US energy companies. Hackers used viral websites and virus-infected letters, with which they managed to obtain some credentials of computer networks in enterprises. |
| October 2017 | Russian hackers allegedly stole data from the US National Security Agency (NSA) using Kaspersky Lab antivirus. |
| July 2017 | The hackers, who are believed to be supported by the Russian government, attacked the energy networks of Ireland and the UK in order to penetrate their control systems. |
| July 2017 | The United States suspected Russia in a cyber attack on "dozens of power plants" in Kansas, including nuclear installations. According to media reports, the attack was carried out with the aim of “disrupting the country's energy supply”, as well as penetrating the control systems of equipment used in the power industry. |
| July 2017 | The media reported that the responsibility for hacking Qatar news agency lies with the "Russian hackers." |
| April 2017 | Thousands of Pentagon employees were attacked by Russian hackers who sought to gain access to their Twitter accounts. |
| March 2017 | Berlin announced attacks by Russian hackers on Merkel’s party servers. |
| February 2017 | A group of hackers APT29, which is considered to be Russian, has committed a cyber attack on an email to nine state officials in Norway. |
| January 2017 | The German Federal Conservation Agency suspected Russian hackers (Fancy Bear) to attack the OSCE in December 2016. |
| Autumn 2016 | According to the US Department of the Interior, the attack of the “Russian hackers” in the summer and autumn of 2016 affected the electoral systems in 21 US states. At the same time, Moscow has repeatedly denied allegations of attempts to influence the results of elections in the United States. |
Cyber criminals in both countries sometimes use similar methods. Thus, according to British experts, Russia and China use a cognitive approach based on an understanding of mass psychology and methods of influencing individuals.
Information about Chinese hackers appears less frequently, but this does not mean a smaller number of incidents:
| June 2018 | Symantec has identified cyber attacks from China on companies in the US and Southeast Asia, behind which there are hackers from the Thrip group. They attacked satellite companies, as well as a number of US telecommunications enterprises and defense contractors. The purpose of the cyber attack was espionage and interception of data from civilian and military communication channels. At the same time, hackers were able to infect viruses with computers that control satellites, having the opportunity to change their geolocation in orbit and prevent transmission of information. |
| June 2018 | Hackers associated with the Chinese authorities broke into the US Navy contractor’s systems, gaining more than 600 GB of submarine weapons development data, as well as data on the American submarines themselves. |
| May 2018 | The article about the “Great Gun” is a weapon of attack, an excellent attack tool that intercepts foreign Internet traffic coming to Chinese Internet sites, “complements” it with malicious code and redirects it at its discretion. |
| April 2018 | Experts have discovered a new hacker group attacking defense and industrial enterprises for the purpose of espionage. Among the objects of attack is the Russian military-industrial complex. The main task of SongXY was espionage, and the malicious software used, after entering the victim’s corporate system, allowed attackers to not only secretly monitor users, but also remotely control the infected system. Attacks SongXY associated with Chinese hackers. |
| November 2017 | From July to September, Chinese-speaking hackers organized 10 targeted attacks and cyber-espionage campaigns against Russian companies related to the implementation of state projects in Russia, Kaspersky Lab reports. |
| September 2017 | Chinese-speaking hackers have launched attacks on anti-virus software developers Netsarang and CCleaner. The introduction of malicious code in legitimate products would allow hackers to penetrate the corporate networks of organizations. |
| May 2017 | The large-scale hacker attack using the extortion virus WannaCry affected from 200 to 300 thousand computers in at least 150 countries. In Russia, servers of telecommunications companies and security agencies were attacked. Experts point out that the creators of WannaCry speak the southern dialect of Chinese. |
Beijing, like Moscow, is regularly accused of organizing hacker attacks on Western countries. Hackers from Russia and the PRC are among the “ordinary suspects” who are blamed by the US authorities for penetrating the computer networks of government agencies and private firms. But some believe that "the Chinese are more productive ." “They wake up in the morning, put on their uniforms and go to work in the office. Russian hackers are more connected with organized crime. ”
According to Kaspersky Lab , the number of professional hacker groups has increased dramatically in the world. If two or three years ago there were only a few such organizations, today there are more than 100 of them. At the same time, the hackers of China have become more active. They are credited with up to 25% of active hacker companies. And if earlier they attacked mainly the USA, then after the meeting of the American president with the head of China they switched to other countries, including organizations from Russia. The most frequently attacked by international hackers are the United States, Germany, Russia. Hackers hack into the system of financial institutions, ministries, departments, government organizations.
The flip side of the coin is a stream of fake news about alleged hacker attacks. Many of them are related to the accusations of China in cyber espionage, the leakage of US industrial secrets. Similar accusations are being made against Russia. And here Russia and China have work to do.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/422323/
All Articles