Metamorphosis: form programming at the molecular level

In the world, everything is subject to certain laws. Many things that surround us, we can not imagine otherwise. For us, the water is always wet, the fire is hot, the ball is spherical, and the cube is cubic, no matter how childish it sounds. But is it always? By the way, the shape of any object is due to both chemical and physical laws. But man will always strive to adjust the world around him, even if he has to play with the laws of natural sciences. Much attention today is paid to minimizing devices and their individual elements, while maintaining or increasing their performance and reducing power consumption. However, there are those who think a little wider. Today we will get acquainted with the study of the material that can change its shape according to the program laid down in it by scientists. What kind of material it is, what factors influence its metamorphosis and how important it is for the future of technology - we learn about this from the report of the research group. Go.
The basis of the study
')
For a start, scientists point out that liquid crystalline ( LC ) elastomers ( LCE ) already exist that allow you to change the shape of a polymeric material. This process is reversible, which is also a big plus. However, this technology works only with large objects and requires intensive and irreversible programming in order to get full control over the process.
The researchers based their experiment on dynamic covalent chemistry * ( DCC ). The sample changed shape only when and where photo-induced DCC elements were activated.
Dynamic covalent chemistry * - a set of techniques and techniques for the synthetic creation of complex supramolecular structures of discrete molecular elements.Thus, the use of light as an incentive to program the sample activates dynamic link exchange, which is orthogonal * with respect to the phase behavior of the LC. This allows the LCE to adapt to any LC phase or even to an isotropic phase * .
Orthogonality * is a property of linkers (fragments of molecules responsible for attaching a chemical compound to a solid or liquid substrate), allowing them to be removed, removed or modified without affecting other fragments of the molecule.
The isotropic phase * - consists of spherical micelles ** , which are the basis of a liquid crystal and are located on a body-centered cubic package inside an aqueous solution.
Micelles ** - a set of elements of surface-active substances in a colloidal solution, consisting of many amphiphilic (both hydrophilic and hydrophobic) molecules.The above theoretical foundations allowed the researchers to create an LCE whose form changes reversibly according to an established program. To achieve such a result, the sample must have a preliminary effect (thermal, mechanical, chemical, light, etc.).
Video demonstration of the formation of micelles on the example of simple soap.But this video is very funny, nevertheless quite informative (I could not resist, therefore I added it)
The experiment and its results
The base of the sample was liquid crystal oligomers, which differ from polymers in that the number of constituent units of these molecules is limited. Some of the features of polymerization with reversible chain transfer by the addition-fragmentation mechanism ( AFT ) were applied to oligomers.

Image number 1a
Thanks to the thiol-Michael addition reaction, it was possible to provide a fairly trouble-free installation of the necessary functionality by introducing allyl dithiols into oligomers.
Allyl * is a hydrocarbon radical that has a hydrogen atom removed from the third carbon atom.
Thiols * - sulfur analogue of alcohols.This method of attachment allows you to create, say, “controlled” oligomers.
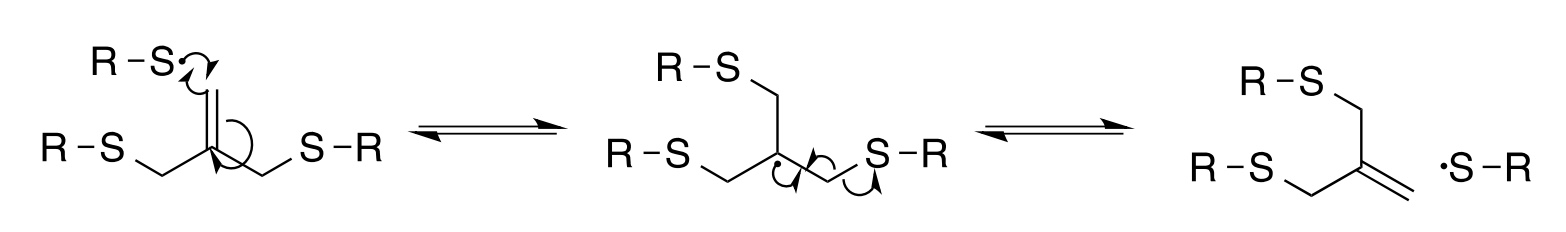
As a monomer * thiol, allyl dithiol reacts with mesogenic diacrylate (RM82) and glycol diacrylate (NPGDA), which leads to the formation of oligomers containing allyl sulfite with AFT function. Next is the photopolymerization into a network of connected polymer chains.
Monomer * is a low molecular weight substance that forms a polymer in a polymerization reaction.The liquid crystal elastomer is an elastic compound, however, by applying the methods described above, it begins to behave like a viscoelastic fluid * .
Viscoelastic fluid * is a substance with elasticity, like solid bodies, and irreversible flow, like a liquid.
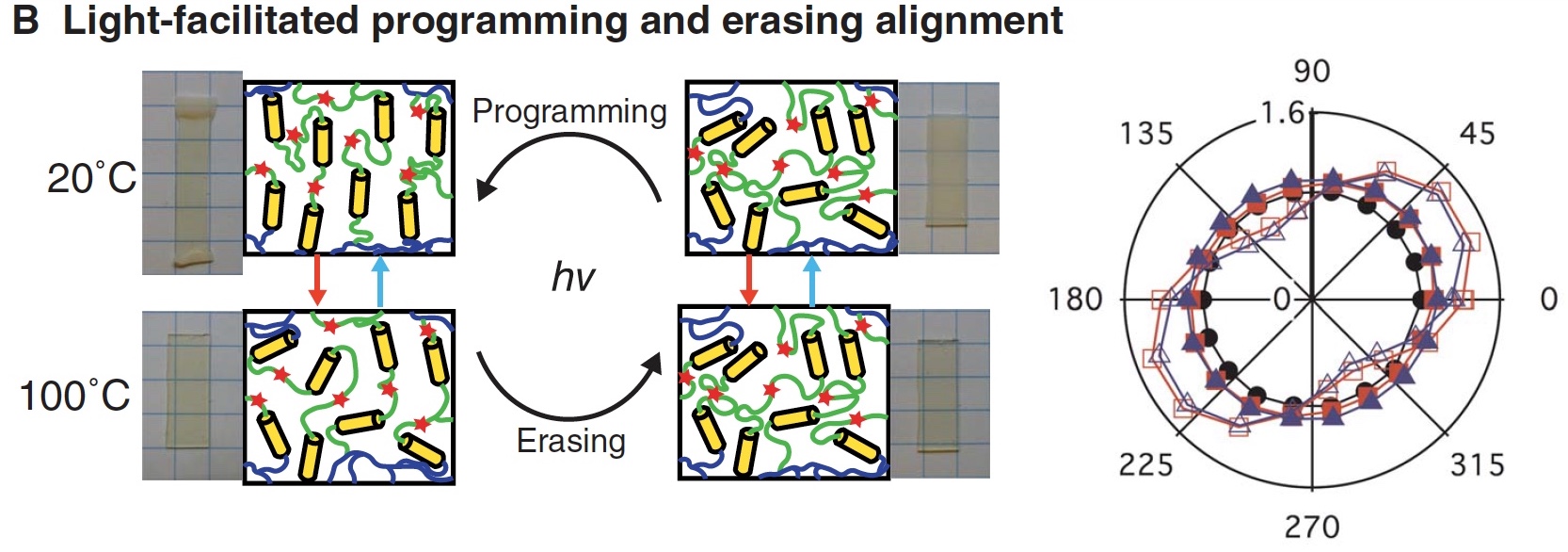
Image №1b
In the image above, we see how the LCE elements undergo alignment and “erase” alignment through mechanical displacement (programming) and thermal destruction (erasure). These processes were naturally accompanied by light exposure (hv, 30 mW / cm 2 , wavelength from 320 to 500 nm).
The polar graph (right) presents Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy results that correspond to the C – H aromatic * core (3350 - 3300 cm –1 ) at different angles of polarization of light.
Aromatic compounds * are cyclic compounds in which the conjugated unsaturated bond rings have anomalous stability.
Miura-ori
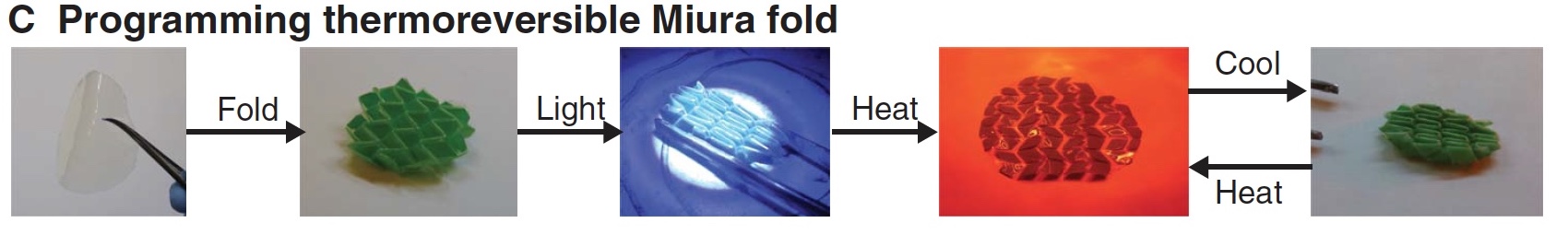
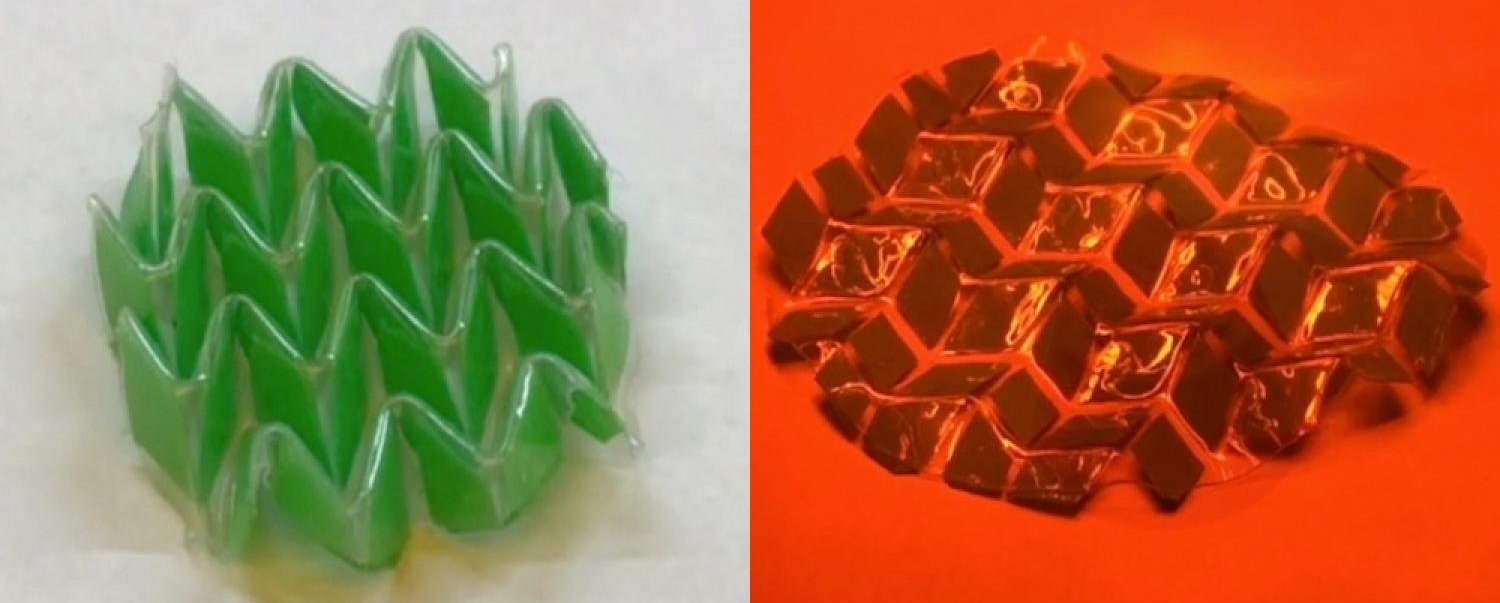
Image number 1c
1c shows the process of programming a thermo-reversible film. A 250-micron polydomain polymer film was folded manually according to the Miura-Ori scheme, after which it was exposed to light (320–500 nm, 100 mW / cm 2 ) and a slight thermal (30 ° – 40 ° C). As a result, when exposed to high temperature, the film was unfolded, and in the process of cooling it was folded back.
Demonstration of changing the shape of a flat film into a folded and square into a circle (from 02:05)
Similar results suggest that the use of AFT-elements allows to combine thermosetting and thermoplastic properties in one material.
This sample form (Miura-ori) was not chosen by chance. This option is much more complicated than simple stretching and compression, and makes it possible to understand how effectively the programming of a substance works.

The image above shows a simplified version of changing the shape of a sample by programming its elements. The flat film ( A ) was twisted into a spiral ( B ) by hand and worked on it for 10 seconds with light of 50-100 mW / cm 2 with a wavelength of 320-500 nm. Heating the spiral sample to 100 ° C and another 10 seconds of exposure to light returned its former flat shape ( C ).
As a result, the isotropic form, which the object assumes when the temperature rises, can be specified in the process of primary photopolymerization. And the LC-form, which the object takes at room temperature (without additional light and heat exposure), is programmed by exchanging AFT elements.
Square → Circle → Square
The above method was also used to change a square-shaped sample into a round one (exaggerated, because the sample’s volume for the sake of simplicity is not taken into account in the scientists ’report).
As can be seen from the above roller, a square bar has a stable shape when it is not affected by additional heat and light radiation. When the temperature rises to 100 ° C, the sample changes shape in accordance with the hole into which it could not pass with the original shape.
Using different temperatures, the researchers found a different reaction to this effect. So while programming a sample at a temperature of 120 ° C, the polymer assimilates the monodomain in the LC phase and almost completely corresponds to the deformation applied in the isotropic phase. And the sample programmed in the LC phase at temperatures of 25 and 67 ° C practically showed no programmed deformation in the isotropic phase. In other words, at such temperatures the sample did not take the desired shape. If the programming temperature is above the phase transition temperature (80 ° C), then a very evenly distributed voltage is observed throughout the sample network, as a result, uniform relaxation also occurs throughout the sample area. Thus, by trial and error, the optimum (at this stage of the research) temperature was established for programming the substance form.
The researchers provided a report for all who wish to familiarize themselves with their work.
As well as additional materials to it.
Epilogue
According to scientists, their work allows for a deeper understanding of some processes that take place within various substances. The use of light as an external factor gives spatial and temporal control over the programming process of the sample shape.
Scientists have succeeded in creating a photopolymerizable, thermo-reversible material that can be programmed multiple times using mechanical, light and thermal effects. The change in the molecular structure of the sample made it possible to make it universal — the sample can take on virtually any shape specified by man.
In the future, scientists will continue their research, as they have yet to improve the programming process itself, as well as continue the search for new, possibly more effective, ways to influence the sample during the programming process.
The ability to change the shape of the sample, more precisely to manipulate it, opens up new possibilities in creating devices for various spheres of human life: from medicine and the army to computer and space technology.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
3 months for free if you pay for new Dell R630 for half a year - 2 x Intel Deca-Core Xeon E5-2630 v4 / 128GB DDR4 / 4x1TB HDD or 2x240GB SSD / 1Gbps 10 TB - from $ 99.33 a month , only until the end of August, order can be here .
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/421589/
All Articles